Week 2 Torque
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What is torque?
Angular force or ‘twist’ applied to an object
What are the important parts of force?
Magnitude
Point of application
Line of application/line of action
Direction
As a muscle pulls, what occurs at the axis (the joint)?
Torque
What are the important parts of torque?
Axis of rotation
Magnitude of force applied
Distance from axis to applied force (moment arm)
Angle (direction) of force
What is the hard way to calculate torque?
Cross product
What is the easy way to calculate torque?
Moment arm; T = F perpendicular * moment arm
What is the moment arm?
The straight-line distance to the point of application of the perpendicular force component
What is the angle of insertion?
The angle that is formed by the bone axis and tendon insertion
How can we find the length of the moment arm?
Identify F perpendicular (the rotational force component) and draw a line from the axis to that point
Draw a line from the axis to the point it makes a right angle with the line of action, and that distance is the moment arm
Small moment arm = less _______ to create the same amount of torque
Force
Large moment arm = more force to create the ______ amount of torque
Same
The greater the force….
The greater the torque (specifically the tangential force)
The _______ the moment arm, the greater the torque
Longer
When something is in equilibrium, it means that all torques applied are…
Equal
What is effort force?
The force that is causing the rotation of the lever (the force of the prime mover)
What is resistance force?
The force that is opposing the rotation of the lever
What is the effort arm?
Moment arm of effort force
What is the resistance arm?
Moment arm of resistance force
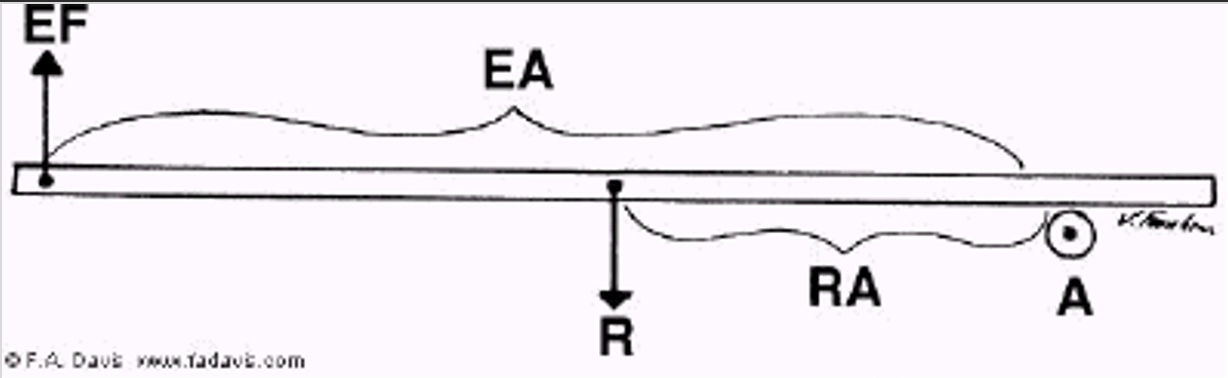
What are first class levers?
2 parallel forces are applied on either side of an axis at some distance from that axis, creating rotation of the lever in opposite directions (teeter-totter)
In a first class lever the effort arm may be…
Greater than, smaller than, or equal to the resistance arm
What is an example of a first class lever in the body?
Head flexion and extension
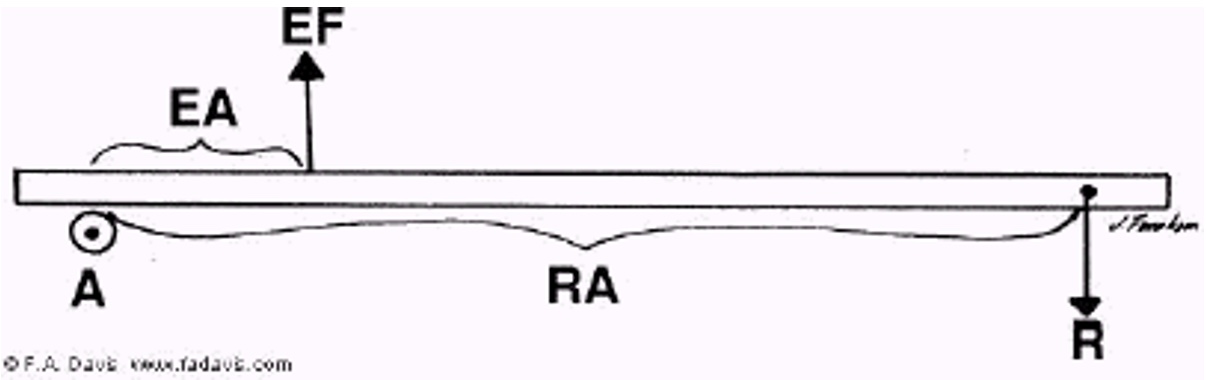
What is a second class lever?
2 parallel forces are applied at some distance from the axis
In second class levers the _________ force is applied closer to the axis than the ______ force
Resistance, effort
In a second class lever, which is always greater?
Effort arm is always greater than the resistance arm
What kind of lever is depicted?
First class lever
What kind of lever is depicted?
Second class lever
What is an example of a second class lever?
A wheelbarrow
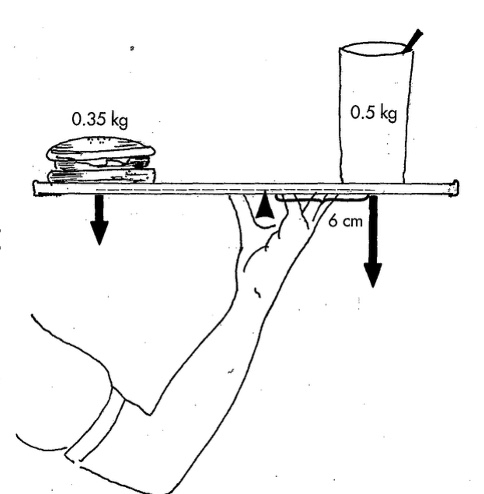
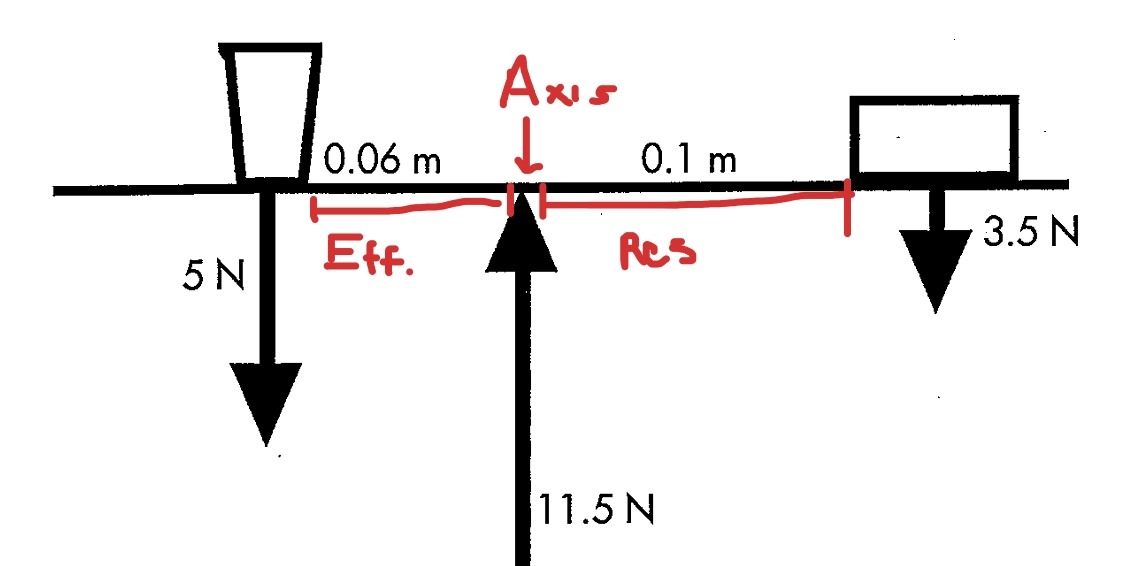
What is a third class lever?
2 parallel forces are applied at some distance from the axis
In a third class lever the ________ force is applied closer to the axis than the _________ force
Effort, resistance
In a third class lever, what is always greater?
Resistance arm is alway greater than effort arm
What kind of lever is depicted?
Third class lever
Third class levers are the most…
Common type in the human body
What is mechanical advantage?
Describes efficiency of a lever system; the more efficient the lever system, the less force needed to overcome a large resistance
When something has mechanical advantage, the longer the __________ the more efficient
Effort arm
What do anatomical pulleys do?
Change direction of the muscle force; deflects the line of pull of the muscle from the joint axis to increase the moment arm so the muscle can produce greater torque
What is stress?
Force on an object that might cause it to deform
What is strain?
Change in shape of an object due to stress; new length relative to original length
What are the principle stresses?
Compression
Distraction
Shear
What are axial loads?
Stress (or force) applied along axis of object (tension/distraction and compression)
What are bending loads?
Stress (or force) applied in the same plane but along a different line
What are torsional loads?
Stress (or force) applied around long axis of object (twisting)
Where can we see all principle stresses?
The spine
What is elasticity?
Material is able to immediately return to its original size and shape when stress is removed (unchanged by stress)
What is plasticity?
Material retains some of its stressed size and shape when stress is removed (material is changed by stress)
What is viscoelasticity?
Material does not deform instantaneously when loaded, but does change over time (stress makes changes over time)
What is Wolff’s Law?
Bones in the human body will adapt to loads under which they are placed over time; bone density changes due to increased or decreased stress
What is Davis’ Law?
Tissues in the human body will be shaped by mechanical stresses placed upon them; tissues change in length due to stress put upon them