IB Economics SL - Quarter 1
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Production Possibility Fronteir (PPF)
A type of model that illustrates the trade-offs facing a business that produces only 2 goods.
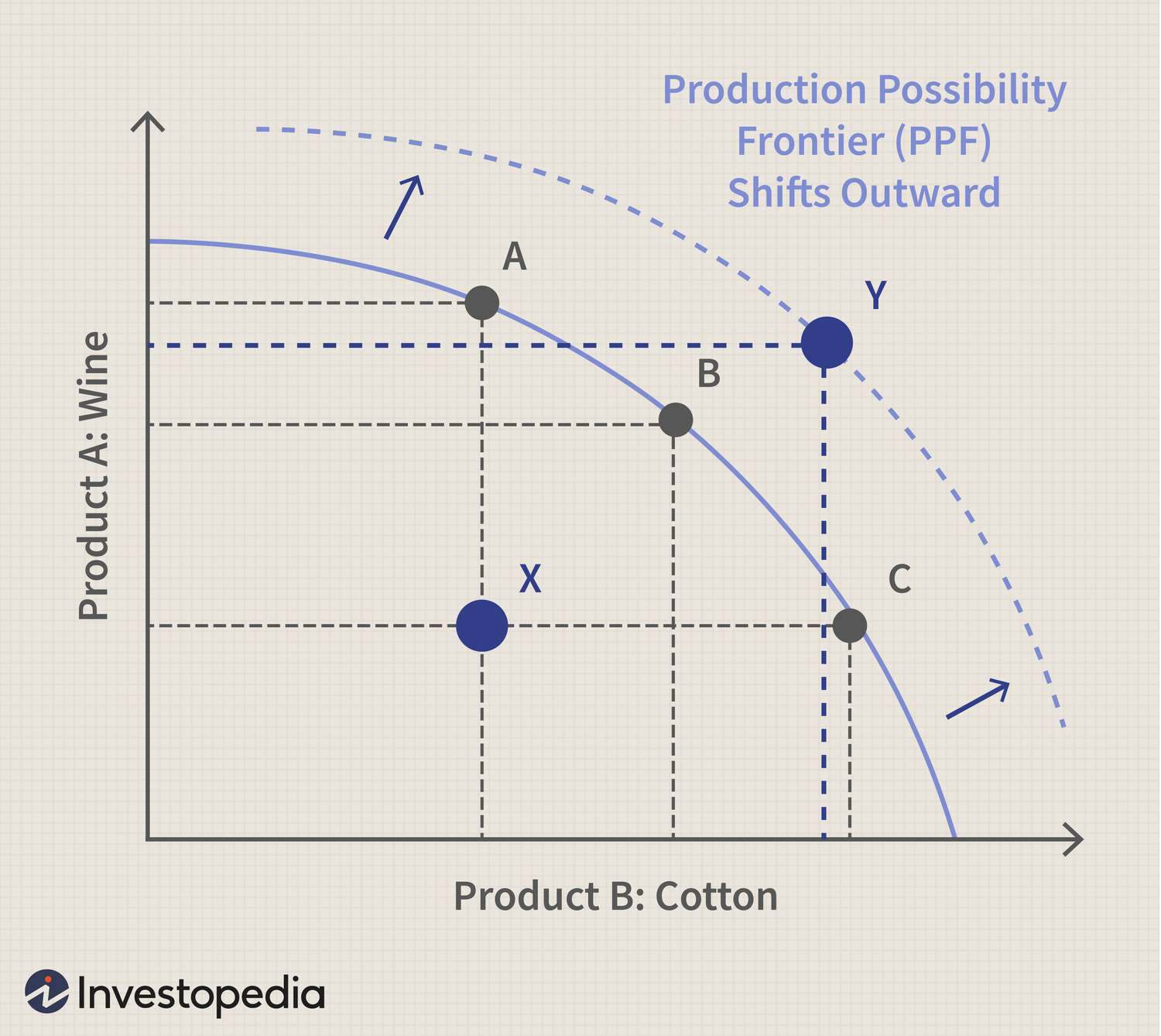
Production Possiblity Curve (PPC)
A graphical representation that shows scarcity and opportunity cost
Market
where buyers and sellers come together to carry out an economic transaction
Demand
the quanity of a good/service that consumers are willing and able to purchase at a given price in a given able
law of demand
as the price of a product falls, the quanity demanded of the product will usually increase (ceteris paribus)
determinants of demand
Factors that cause the demand curve to shift (change in price)
income effect
when a price of a good falls, people will have an increase in their real income, which will cause people to buy more goods
real income
amount their incomes will buy
substitute effect
when the price of a good falls, then the good will be relatively more attractive to people over goods whose prices have not changed
normal goods
as income increases, the demand for this good increases (the demand curve shifts right)
inferior goods
as income increases, the demand for these goods will fall because the consumer will begin to buy higher priced substitutions
demand curve
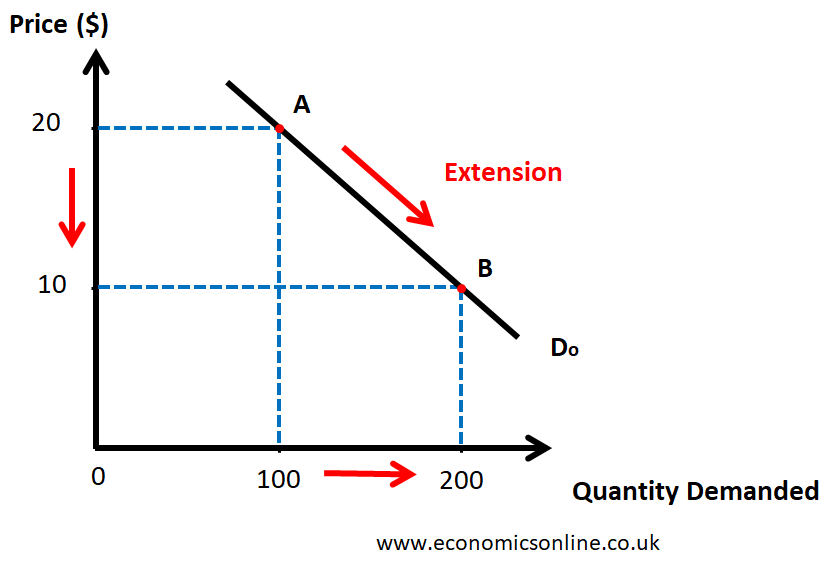
complements
products that are often purchased together, a change in price of one product will lead to change in demand for the other
unrelated goods
a change in the price of one good will have no effect on the demand for the other goods
law of diminishing marginal unity
as a consumer consumes more units of a good, the additional satisfaction (utility) they get from consuming an additional unit falls.
supply
the willingless and ability of producers to produce a quanity of a good/service at a given price in a given time period.
law of supply
as the price of a good/service increases, the quanity supplied of the good/service will increase
cost of production
if there is an increase in the cost of a factor of production (wages), then this will increase the cost and will supply less.
the price of other products
which the producer could produce instead of the existing product
state of technology
improvements in technology in a firm or industry should lead to an increase in supply, shifting the supply curve to the right.
expectations
producers make decisions about what to supply based on their expectation of future prices
equilibrium price
when a price has moved to a level at which the quanity of the good/service demanded equals the quanity of that good/service supplied.
market shortage
when the price decreases (pe to p1), quantity supply will decrease (qe to q1), but quantity demand will increase
price mechanism
forces of supply and demand that moves prices towards equilibrium
consumer surplus
the extra satisfaction (utility) gained by consumers from paying a price that is lower than that which they are prepared to pay.
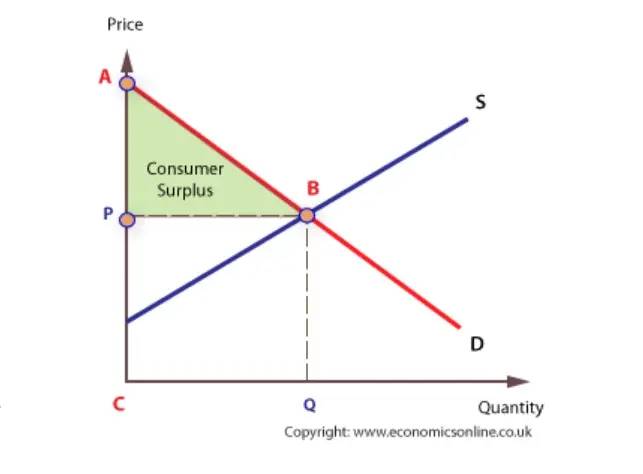
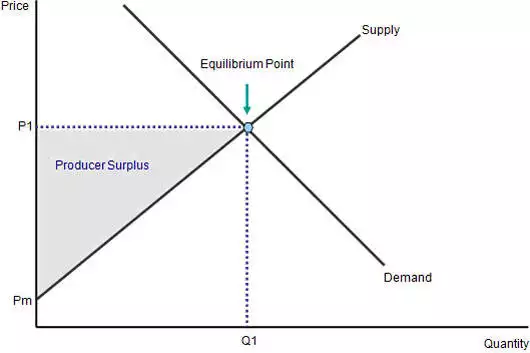
producer surplus
the amount below market price that a producer is willing and able to produce a good for.
price elasticity of demand (PED)
the responsiveness of quanity demanded to changes in the selling price
formula for calculating PED
% change in quanity demand / % change in price
ped elastic good
a good where change in price leads to a greater than proportional change in quanity demanded (PED is > 1)
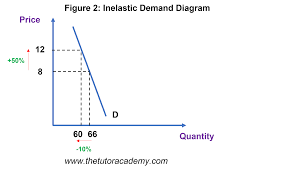
ped inelastic good
where change in price leads to a smaller than proportional change in quanity demanded (ped < 1)
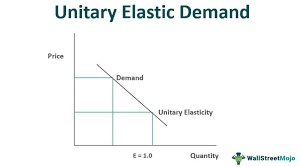
ped unitary good
where change in price leads to a proportional change in quanity demanded. (ped = 1)
determinants of ped
Factors that influence the price elasticity of demand
number and closeness of substitutes
more substitutes for a product, more elastic demand, closer substitutes for a product, more elastic demand
necessity of the product
necessary goods are inelastic
share of income spend on good
inexpensive goods will be less elastic
the time period considered
as the price of a product changes, it often takes time for the consumer to change their habits. PED tends to be more inelastic in the short run, amd more elastic in the long term
income elasticity of demand (YED)
measure of how demand for a product changes when there is a change in consumer’s income
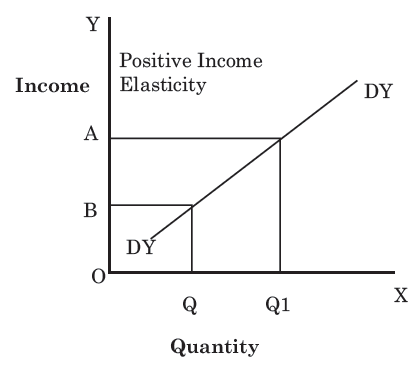
formula for YED
% change in demand / % change in income
sticky goods
goods that’s demand does not likely change
elasticity of supply (PES)
a measure of how much the supply of a product changes when there is a change in the price of a product

formula for calculating pes
% change in quanity supplied / % change in price
cost of production
as cost of production increases supplier will not raise supply
unused capacity
if unused capacity (of good) exists, PES is elastic
mobility of factors of production
if factors of production can be easily changed PES is elastic.
time period considered (PES)
the longer the time period considered, the more elastic the supply will be
ability to store stock
if a firm can store high levels of stock, they’ll be able to react to price with supply, pes will be relatively elastic
commodities
raw materials such as cotton or coffee.
commodities ped
tend to have inelastic demand because they are necessities
commodities supply
tend to have an inelastic supply.