Chapter 14 NMR
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
NMR purpose
structure determination
Nuclear spin
odd number of protons or neutrons
spin = rotating sphere of charge that generates a magnetic moment
alpha spin state
protons aligned with magnetic field
lower energy
beta spin state
proton against magnetic field
higher energy
nucleus in resonance
Absorption of electromagnetic radiation causes nucleus to flip to beta spin state (higher in energy)
do all nuclei absorb same frequency of rf
no bc nucleus surrounded by electrons
diamagnetism
In presence of an external magnetic field, e- density circulates, which produces a local (induced) magnetic field that opposes the external magnetic field
all materials have this property
deshielded electrons
electron deficient areas
higher in energy
downfield
experience a net magnetic field strength greater than external magnetic field
shielded electrons
surrounded by electrons
lower in energy
upfield
experiences a net magnetic field strength smaller than external magnetic field
magnitude of energy gap between spin states depends on…
strength of external magnetic field
energy gap increases with …
increases magnetic field strength
strength of magnetic field (in tesla) determines …
range of frequencies (in MHz) that must be used
Solvents Used in NMR
can’t have protons
use deuterated substances
three protons of a CH3 group are ….
always chemically equivalent
two protons of a CH2 group are ….
generally equivalent if compound has no chiral centers
chiral center
bonded to four different atoms
Chemical Shift (δ)
location of signal
indicates electronic environment of protons giving rise to signal
δ = observed shift from TMS in hertz / operating frequency of the instrument in hertz
constant regardless operating frequenct
in ppm
left is downfield = deshielded
right is upfield = shielded
inductive effects
Electronegative atoms like halogens can withdraw electron density from neighboring atoms making protons deshielded and pushed downfield
additive effect
more electronegative atom = stronger effect
where are inductive effects most significant?
position closest to electronegative atom
alpha positions
positions 2 away from electronegative atom are beta positions and are only slightly affected
feel 1/5 of effect alpha protons feel
Anisotropic effects
protons outside of ring (aromatic positions) experience a deshielding effect and protons shifted downfield
protons inside of ring are shielded
protons vinylic to pi bond (attached to pi system) are more deshielded
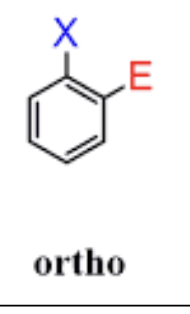
ortho positions
next to each other
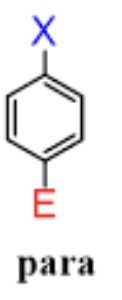
para positions
across
meta
separated by one group
integration
area under each signal
number of protons giving rise to signal
gives relative number or ratio of protons
how to calculate integration value
divide by all integration values by smallest number
once ratio of who numbers obtained, check molecular formula to determine actual amounts
multiplicity
number of peaks in signal
shape
indicates number of neighboring protons
if two H atoms are not equivalent and within 3 sigma bonds apart, will split one another = spin-spin coupling
can be singlet, doublet, triplet, etc
spin-spin coupling or coupling (multiplicity)
if two H atoms are not equivalent and within 3 sigma bonds apart, will split one another
n+1 gives multiplicity
n = number of neighboring protons
neighboring protons must be chemically equivalent
do equivalent protons split each other
no
coupling constant
J value
distance between individual peaks
neighboring protons always split each other with equivalent J values
value is independent of operating frequency
Complex splitting
proton split by two different neighbors
shape will depend on J values
whichever has greater J value will give primary multiplicity
ex: If Jab is greater than Jbc and Ha is a doublet and Hc is a triplet, signal will appear as a doublet of triplets
no complex splitting
if structure lacks rigid double bonds, J values will be generall similar
13C NMR spectrum
only chemical shift is reported
usually no splitting between neighboring C bc low abundancde of 13C
13C-1H splitting occurs causing an unreadable spectra
splitting suppressed through broadband decoupling