Stage 2 - Cells as the Basis of Life
1/76
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
What does cell theory state? (5 points)
Cells are the units of structure and function in all organisms.
New cells arise from existing cells.
Cells require and use energy.
Cells contain DNA which is passed onto daughter cells.
Some cells are unicellular and multicellular.
What is the role of a cell membrane?
The cell membrane controls what materials comes in or out of the cell and are involved in cell communication, cell adhesion, and binding of hormones.
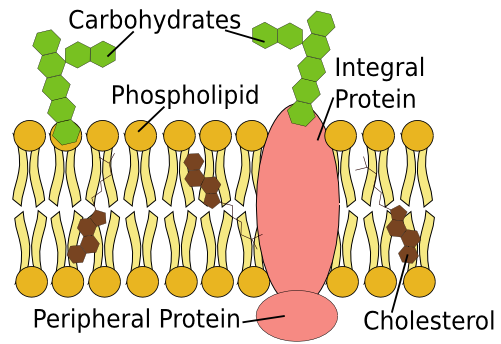
Why is the cell membrane semi-permeable?
Some substances can pass through the membrane while some can’t.
What makes up the two layers of the cell membrane?
Phospholipids
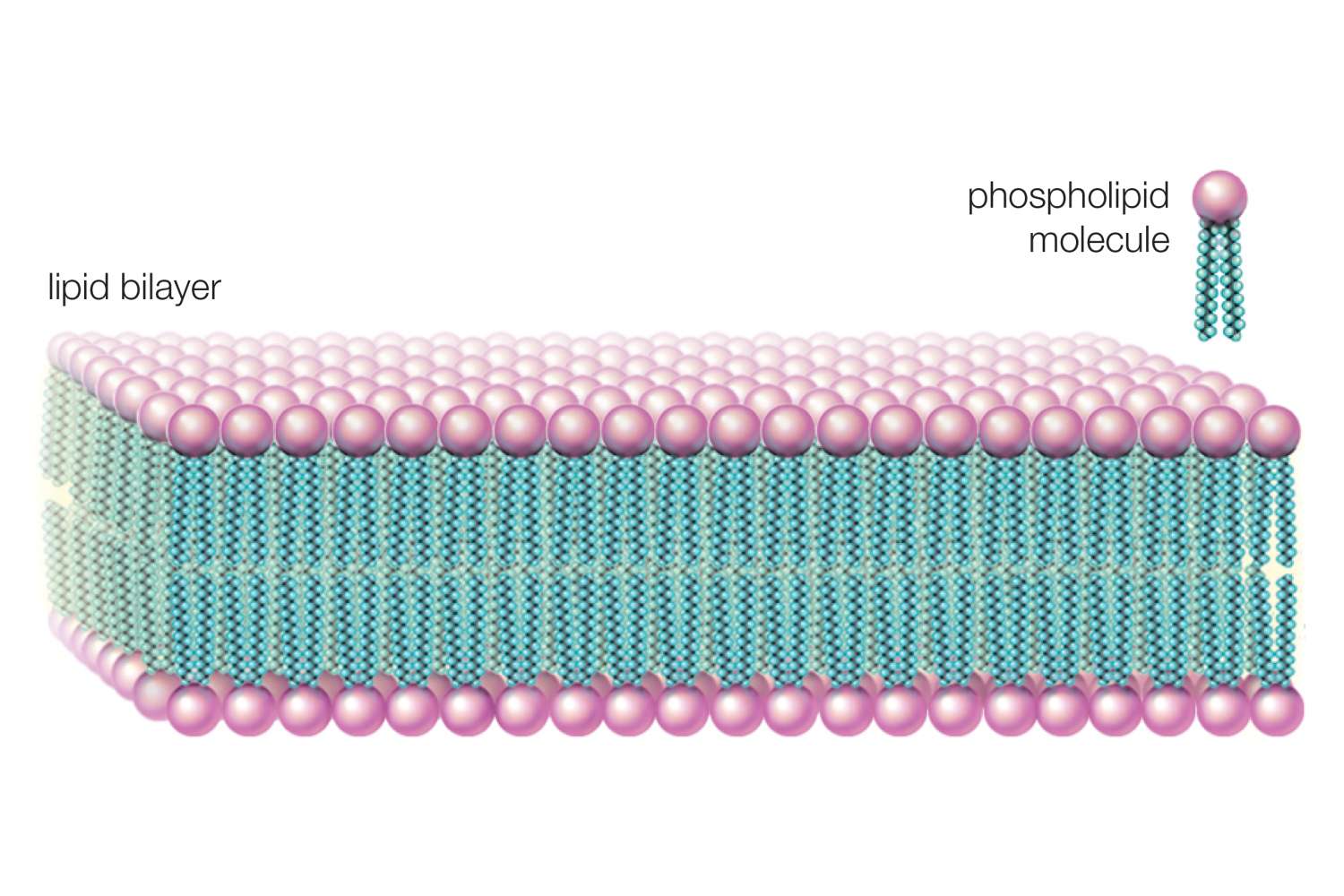
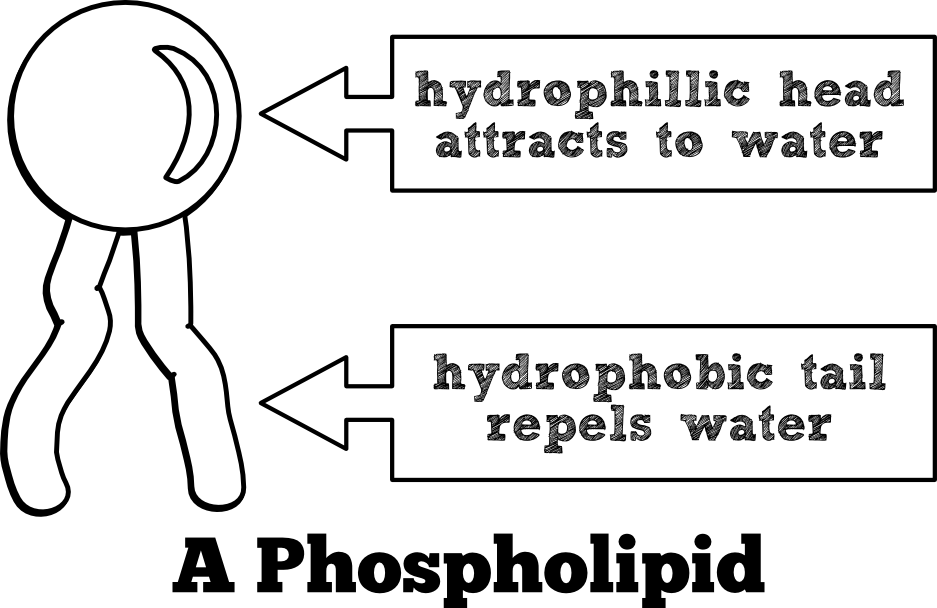
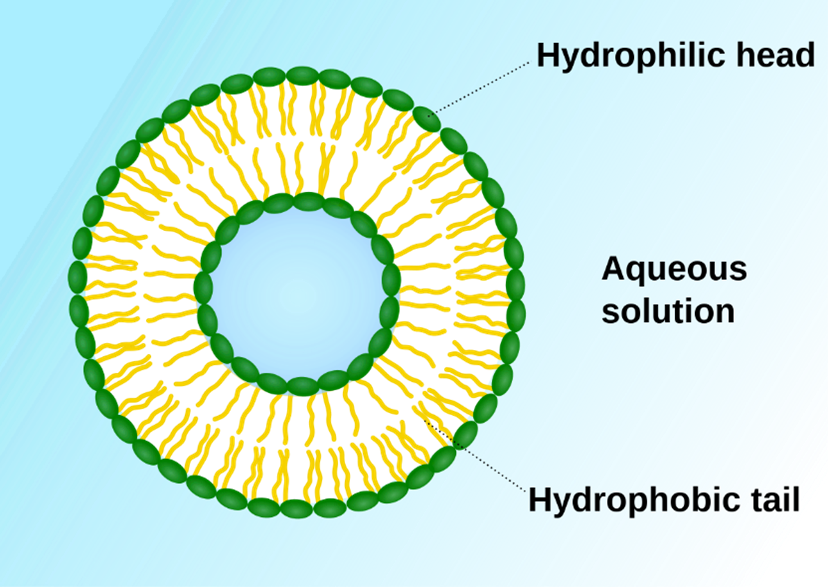
In a phospholipid bilayer, which part is hydrophilic and which is hydrophobic?
The phosphate head is hydrophilic, and the lipid tail is hydrophobic.
What is the difference between carrier and receptor proteins?
Carrier proteins can facilitate the movement of molecules by acting as channels whereas receptor proteins can bind to complementary molecules to signal a response.
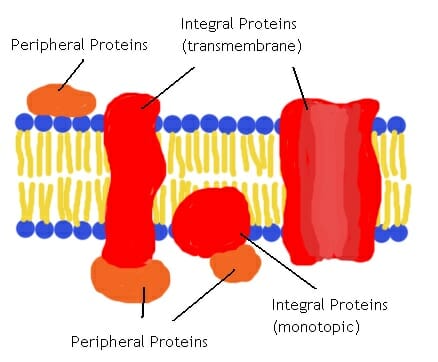
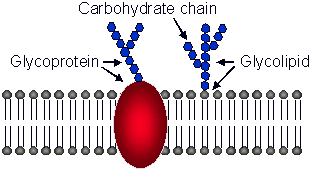
What is common between glycoproteins and glyocolipids?
They both have a carbohydrate chain attached.
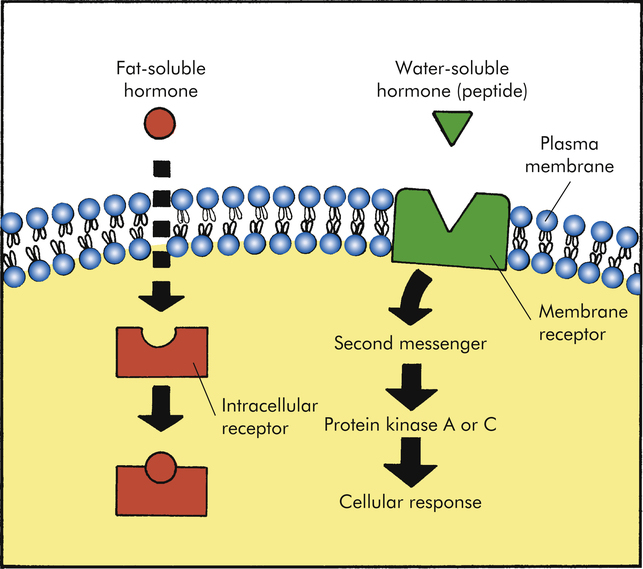
How is the cell membrane involved in the binding of hormones?
Some proteins on the cell membrane are complementary to specific hormones from the blood, which initiates cellular changes and gene activity.
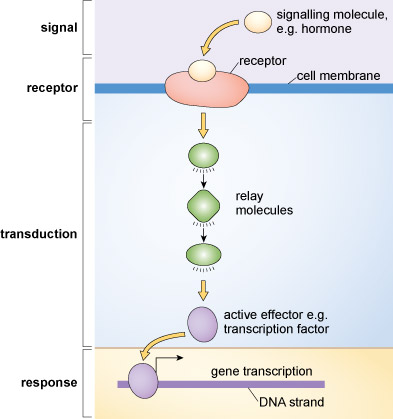
How is the cell membrane involved in cell communication?
In the cell membrane, direct communication can occur between proteins of adjacent cells or via hormones or via neurotransmitters.
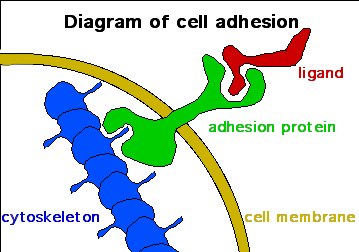
How is the cell membrane involved in cell adhesion?
Integral proteins can stick out and bind to specific protein molecules on adjacent cells or attach to the cytoskeleton.
Where would you find prokaryotic cells?
In bacteria and archaea.
Where would you find eukaryotic cells?
In animals, plants, fungi, and protists.
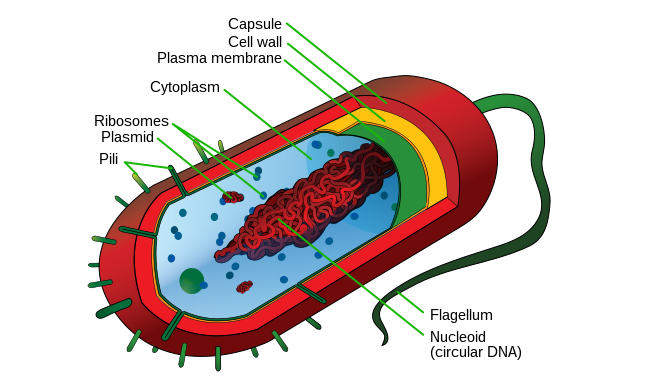
What are some characteristics of prokaryotes? (4 points)
Unicellular and have a cell wall to retain shape of the cell.
No membrane bound nucleus or organelles.
Have pili, flagella, or cilia to help with movement.
Typically, capsule shape.
What are some characteristics of eukaryotes? (3 points)
Multicellular and highly specialised that is more complex than prokaryotes.
Has membrane bound organelles and nucleus.
Typically, circular or rod-shaped.
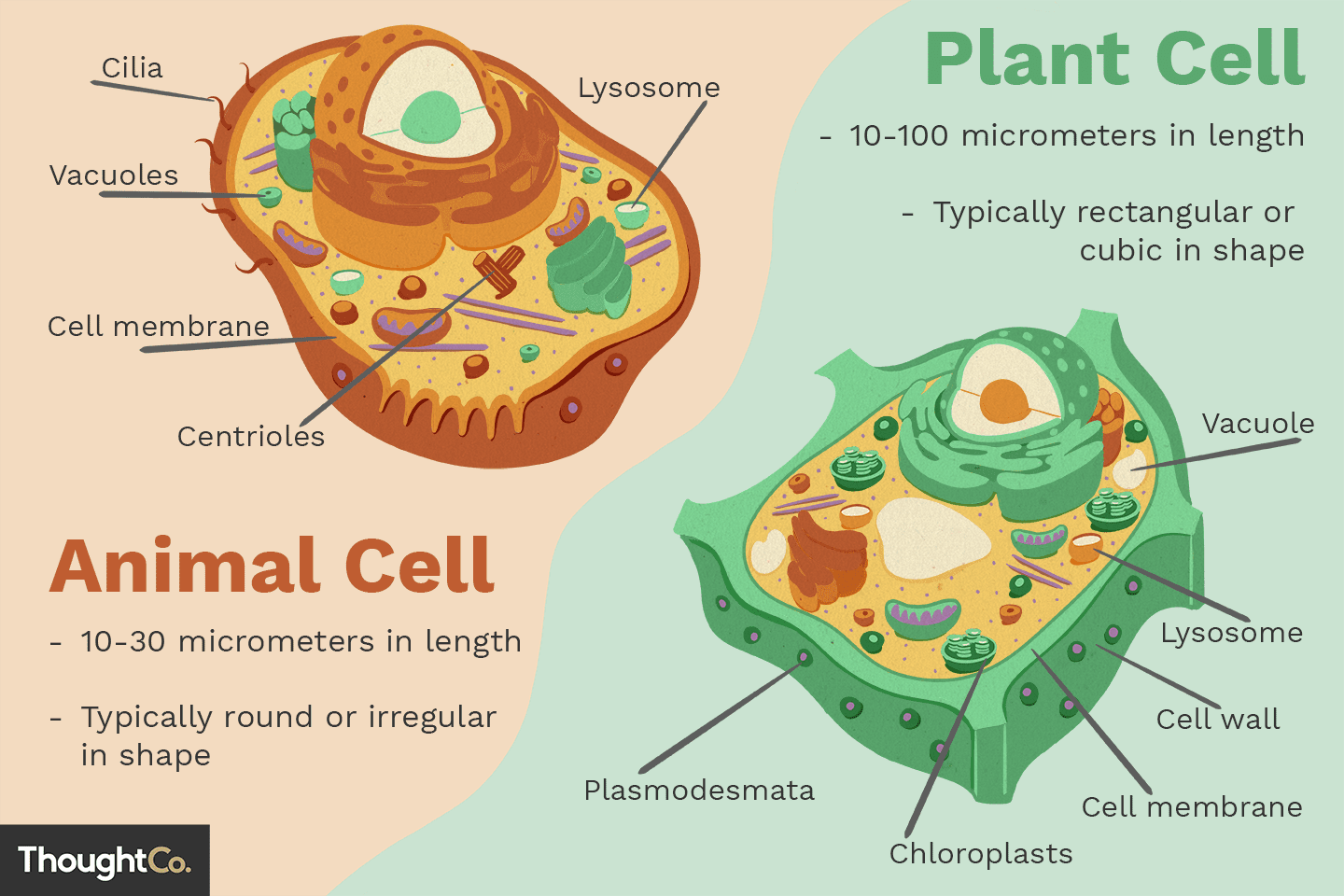
Organelles
Organelles are small structures within a cell that possess a specific function.
What do prokaryotes and eukaryotes share in common? (3 points)
Cell membranes.
Presence of DNA as a nuclear material.
Presence of ribosomes for protein synthesis, however they’re made from different proteins/RNA.
What are some structural differences between plant and animal cells? (3 points)
Plants cells have cell walls.
Plant cells may contain chloroplasts.
Plant cells have a large central vacuole. whereas animals have smaller ones.
What is the role of the nucleus?
It directs and controls cellular activity like growth and division as it contains genetic material.
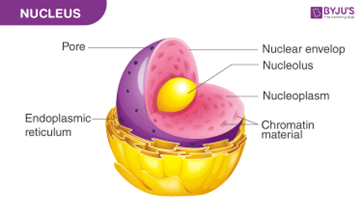
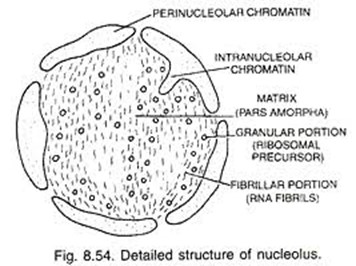
What is the role of the nucleolus?
It contains proteins and RNA to make ribosome sub-units.
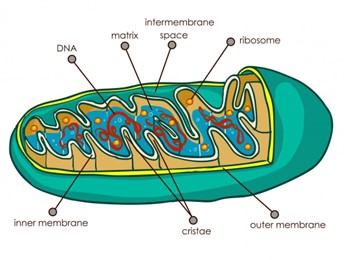
What is the role of the mitochondria?
Mitochondria is involved in energy transformations like cellular respiration.
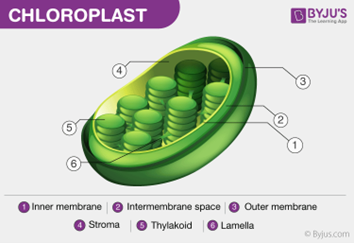
What is the role of chloroplasts?
Found in plant cells, it can perform photosynthesis.
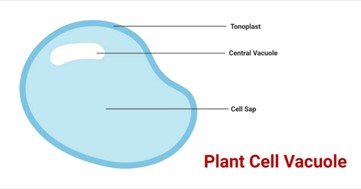
What is the role of vacuoles?
A large storage for plant cells (or small for animals) to store solutes and/or food.
What is the role of a vesicle?
It can help transport materials across the membrane that is stored in the aquaeous solution.
What is the difference between secretory vesicle and membrane-renewal vesicle?
Secretory fuses to the membrane and empty its contents into the extracellular space whereas membrane-renewal inserts its contents (typically proteins and lipids) into the membrane.
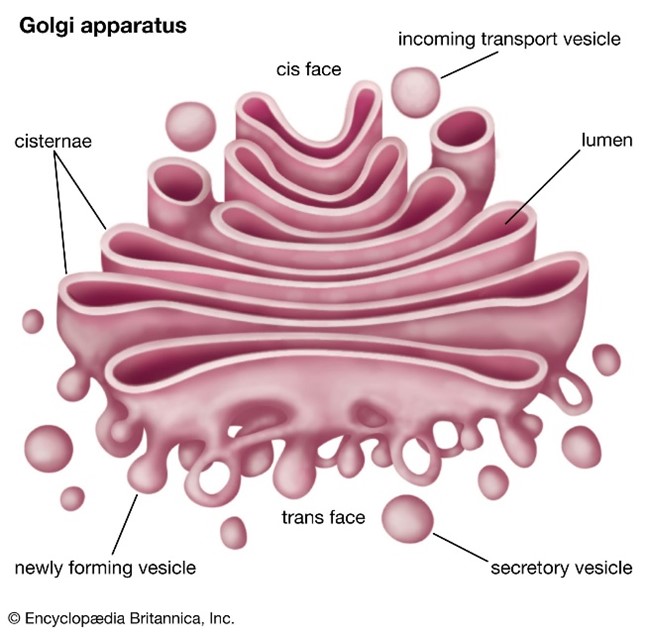
What is the role of the golgi apparatus/body?
It can accept vesicles from ER to modify the membrane and further process products before it’s distributed throughout the cell.
What is the difference between rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)?
Although both are a network of membranes, RER modifies proteins made in ribosomes whereas SER is involved in the synthesis and metabolism of lipids.
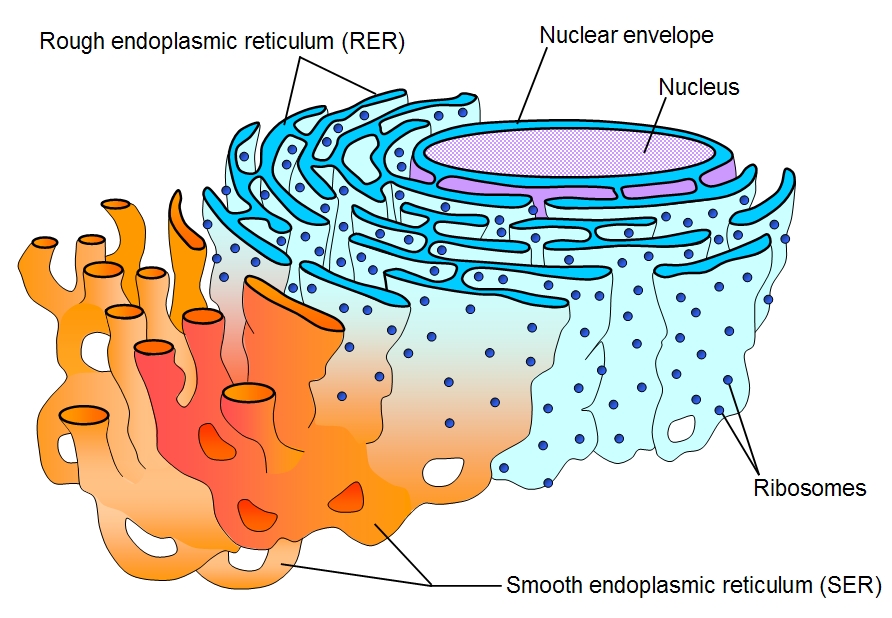
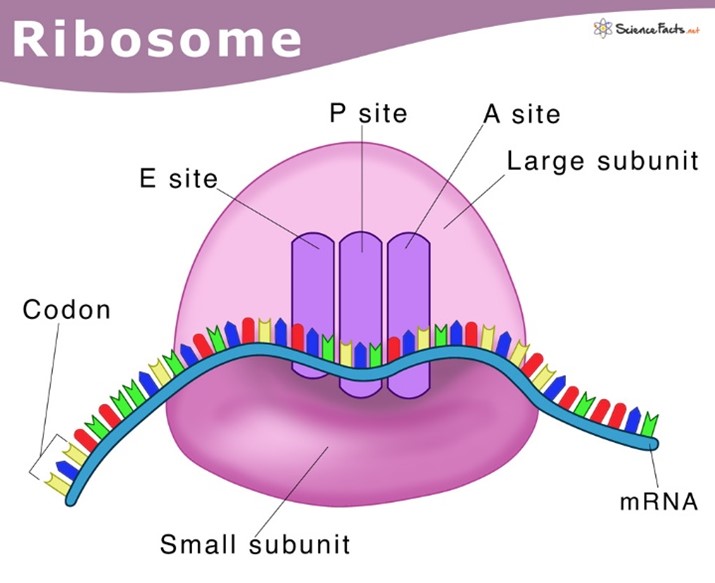
What is the role of ribosomes?
Ribosomes are involved in protein synthesis, specifically translation.
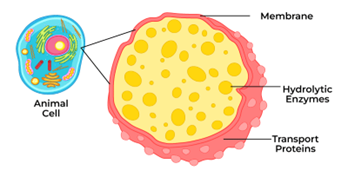
What is the role of lysosomes?
Lysosomes contain digestive enzymes to break down and recycle foreign materials in the cell.
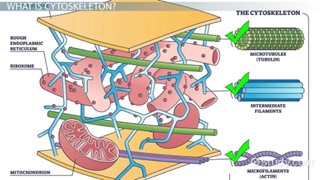
What is the role of the cytoskeleton?
Cytoskeleton acts as a framework for the cell that are involved in cell division, movement and shape of cells, and movement and anchorage.
What does the law of conservation of energy state?
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only changed from one form to another.
What is the difference between autotrophs and heterotrophs?
Although both are organisms, autotrophs can convert inorganic molecules into organic molecules that can be stored whereas heterotrophs consume autotrophs for energy.
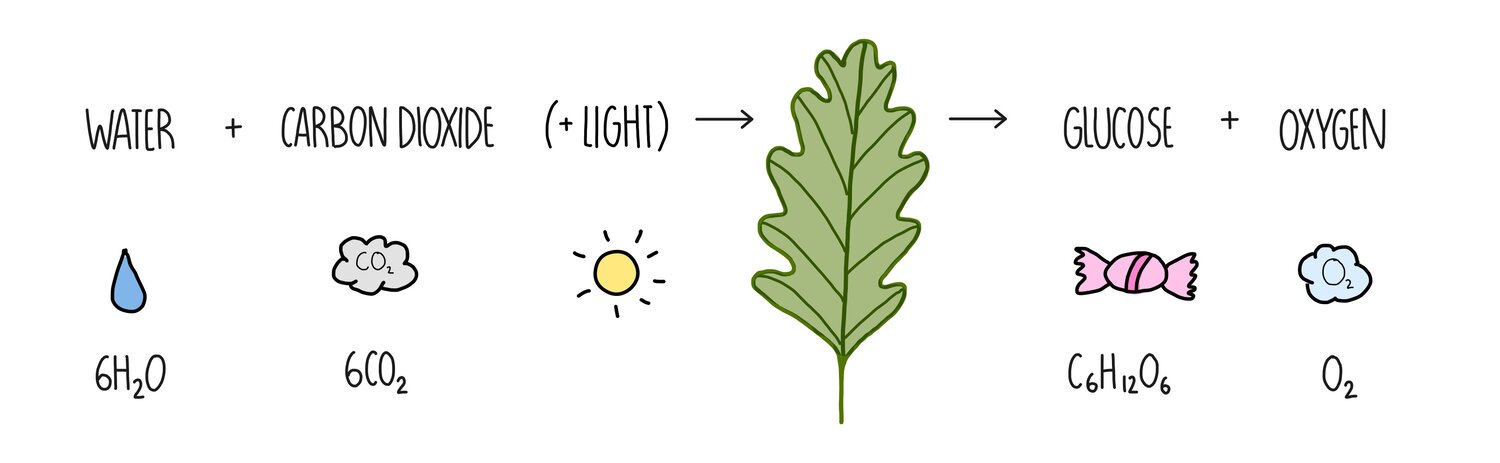
Photosynthesis
A cellular process that occurs in the chloroplast of plant cells that converts light energy into chemical energy in the form of oxygen and glucose.
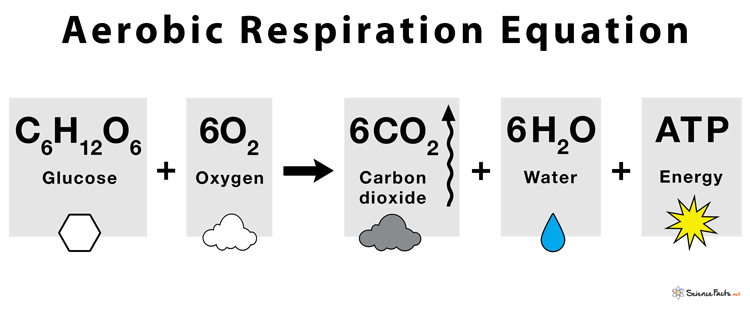
Aerobic (Cellular) Respiration
A cellular process that occurs in the mitochondria of eukaryotes which uses oxygen and glucose to produce energy (ATP).
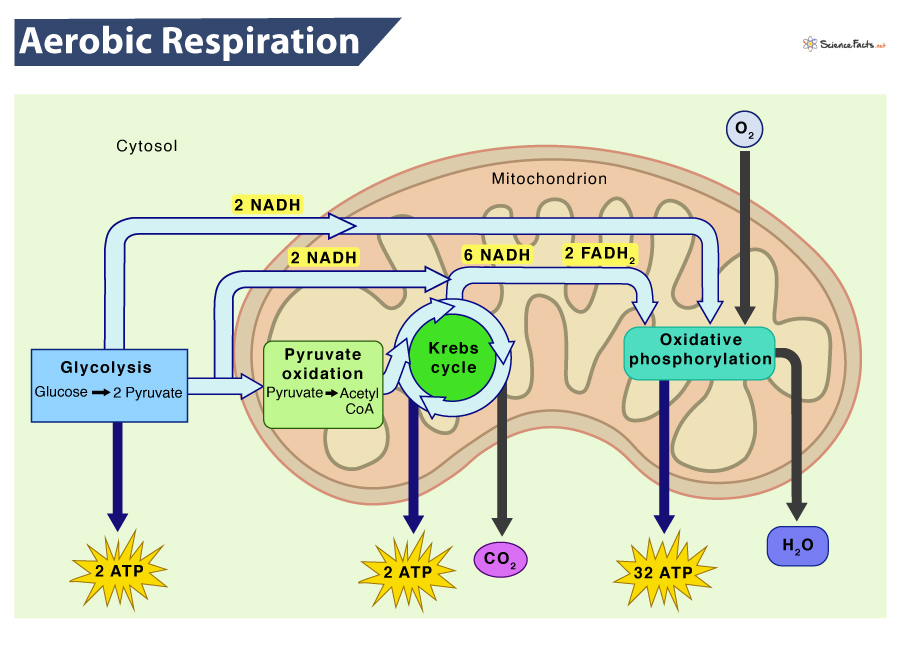
What are the three processes within aerobic respiration?
Glycolysis
Krebs Cycle
Electron Transport Chain
Metabolism
All bio-chemical reactions occurring in the cells of organisms.
What are four characteristics of metabolic pathways?
There are many regulated steps
Each step loses some energy as heat
Some steps produce intermediate compounds
Specific enzymes are required for each step
What environmental factors can influence metabolic pathways (4 points)?
Temperature
pH
Coenzymes and Cofactors
Inhibitors
What chemicals can interfere with cell metabolism (4 points)?
Poisons
Herbicides
Medicine
Insecticides
Why is ATP important?
It is the main source of energy used in almost every energy-requiring reaction processes.
What are the two anaerobic (fermentation) processes?
Alcohol Fermentation
Lactic Acid Fermentation
What is alcohol fermentation used for?
To make alcoholic drinks and in baking processes
What is lactic acid used for?
Humans use lactic acid during strenuous exercise to provide some energy when there is a low supply of oxygen.
What is the difference between active and passive transport?
Although both processes move substances across the membrane, active is from low concentration to high concentration whereas passive is from high concentration to low concentration.
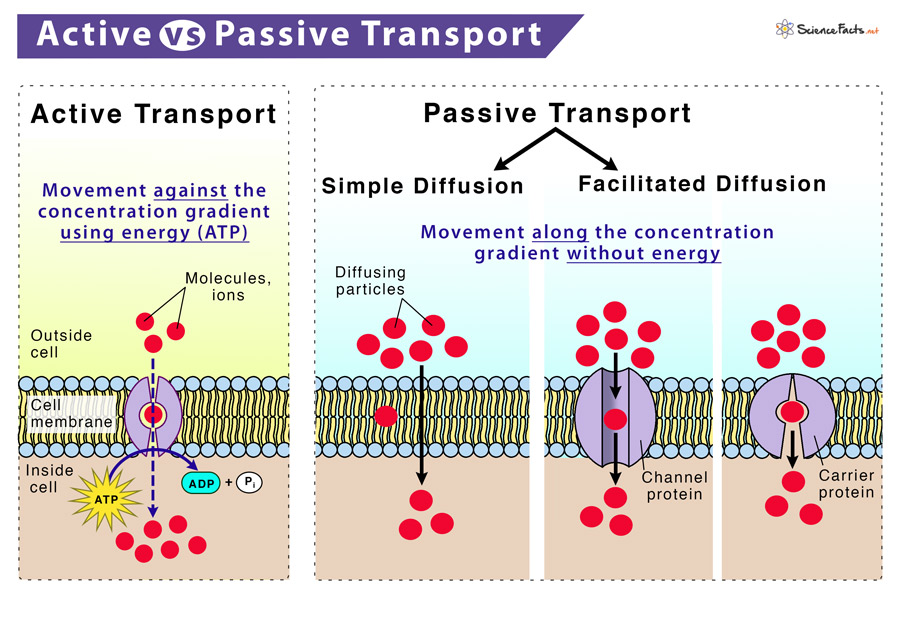
When molecules are small, neutrally charged, and insoluble; they can…
Diffuse through the bilayer.
When molecules are big, soluble, and charged; they can…
Move through a protein channel or pump protein.
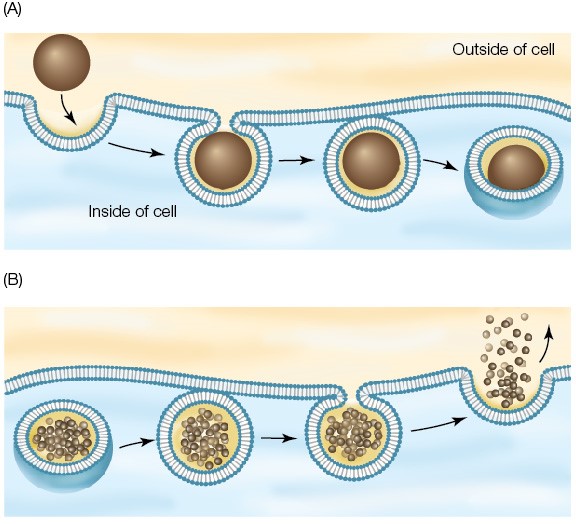
What is the difference between endocytosis and exocytosis?
Endocytosis is where substances are ingested whereas exocytosis is where substances are removed.
What are some factors that can affect exchange of materials across membrane (3 points)?
Surface Area to Volume Ratio
Concentration Gradient
Nature of substances being exchanged
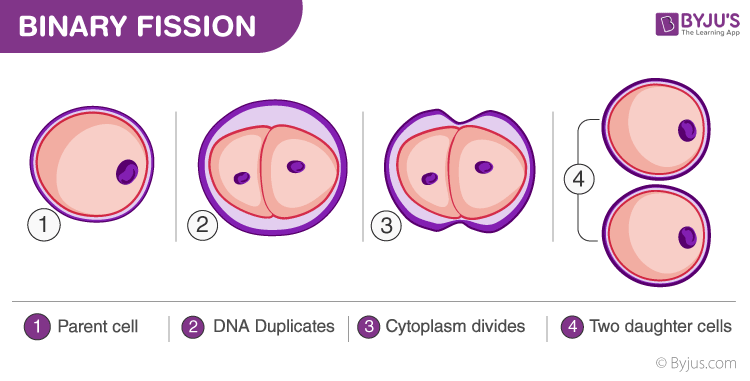
Binary Fission
A type of cell division process where prokaryotic organisms divide and asexually reproduce two genetically identical daughter cells.
When cells rapidly grow, it is known as an….
Exponential growth
What is the difference between mitosis and meiosis?
Although both follow similar steps and are a type of cell division, mitosis produces two genetically identical daughter diploid cells whereas meiosis produces four gamete haploid cells.
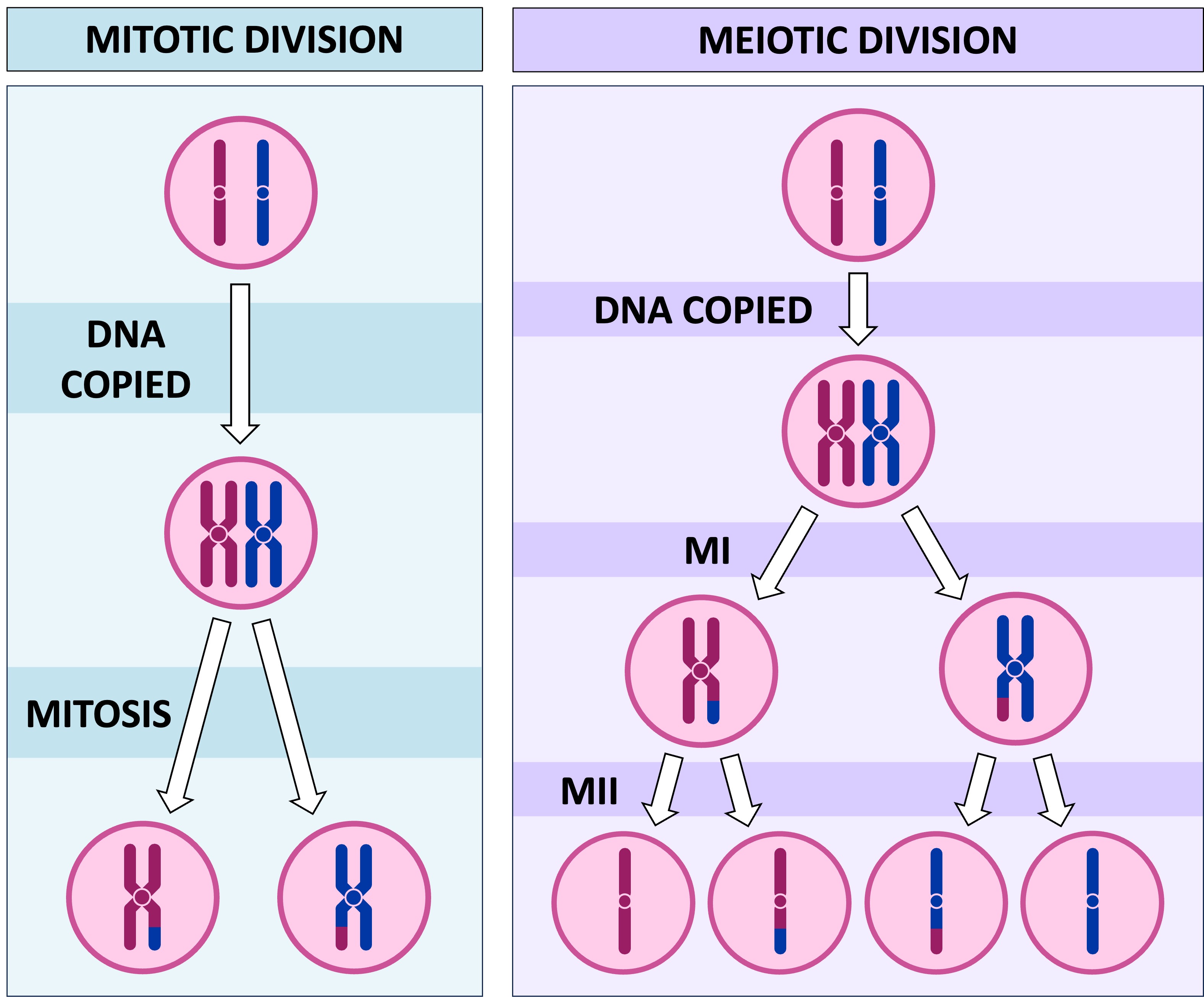
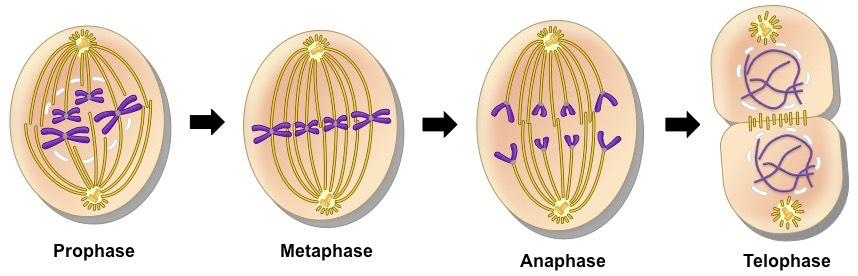
What are the four stages of mitosis?
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
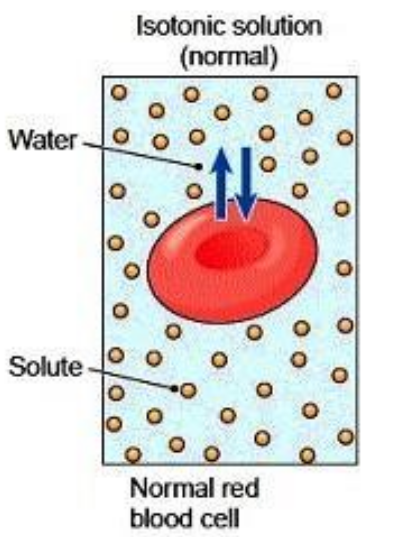
Isotonic
Refers to when a cell has the same concentration of solute and water, in and outside of the cell.
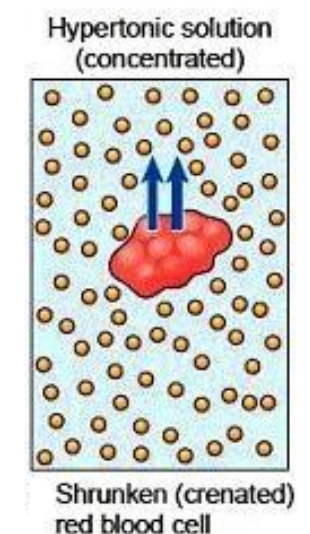
Hypertonic
Refers to when a cell has a higher concentration of solute than water.
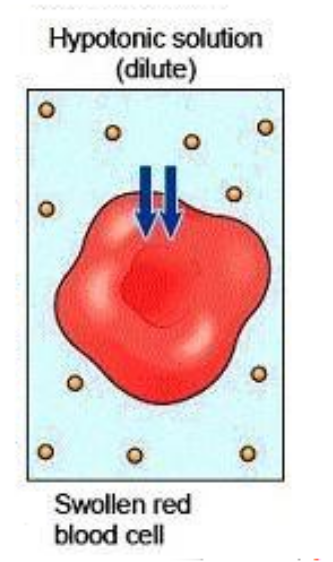
Hypotonic
Refers to when a cell has a higher concentration of water than solute.
What is the difference between phagocytosis and pinocytosis?
Although both are considered endocytic processes, phagocytosis ingests solids whereas pinocytosis ingests fluids and solutes.
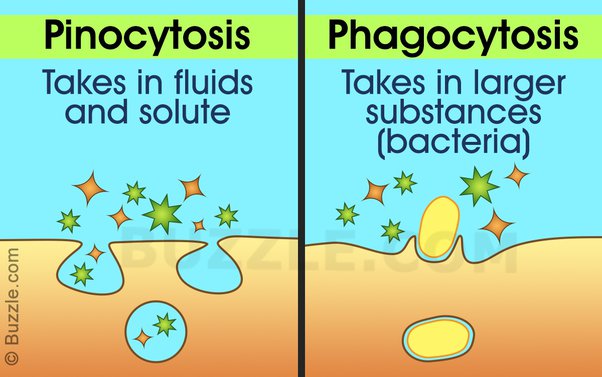
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
A type of endocytic process where cells use specific receptors on their surface to engulf molecules.

What is the difference between haploid and diploid cells?
Haploid cells have one set of chromosomes whereas diploid cells have two sets of chromosomes, one from each parent.

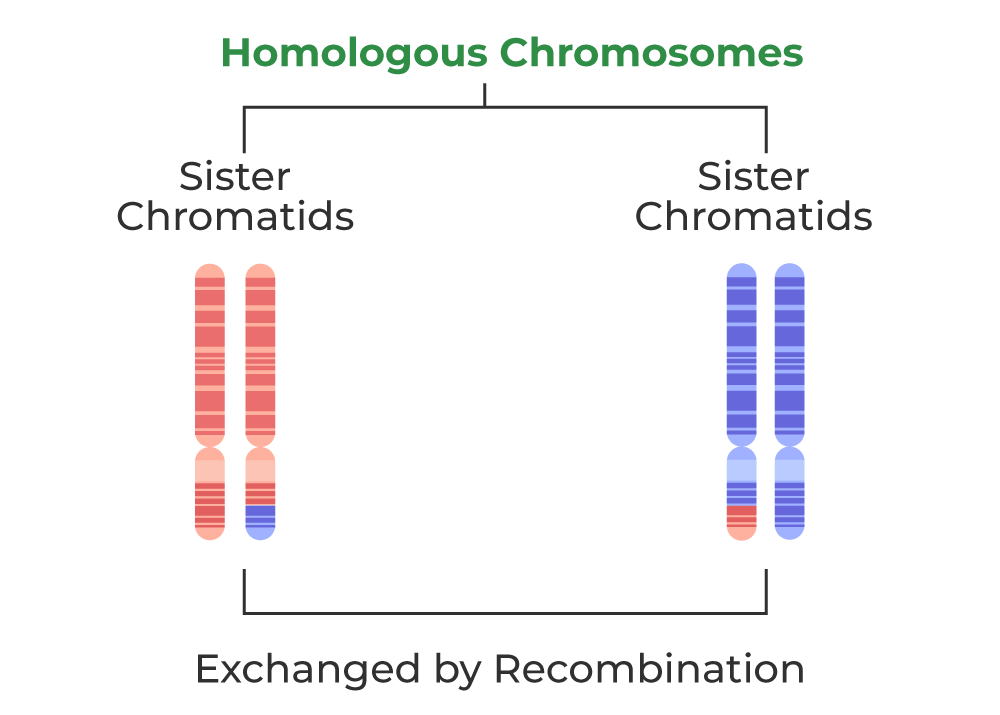
What is the difference between homologous chromosomes and sister chromatids?
Homologous chromosomes are pairs of chromosomes that are similar to each other in terms of size, shape, and gene content whereas sister chromatids are identical copies of a single chromosome.
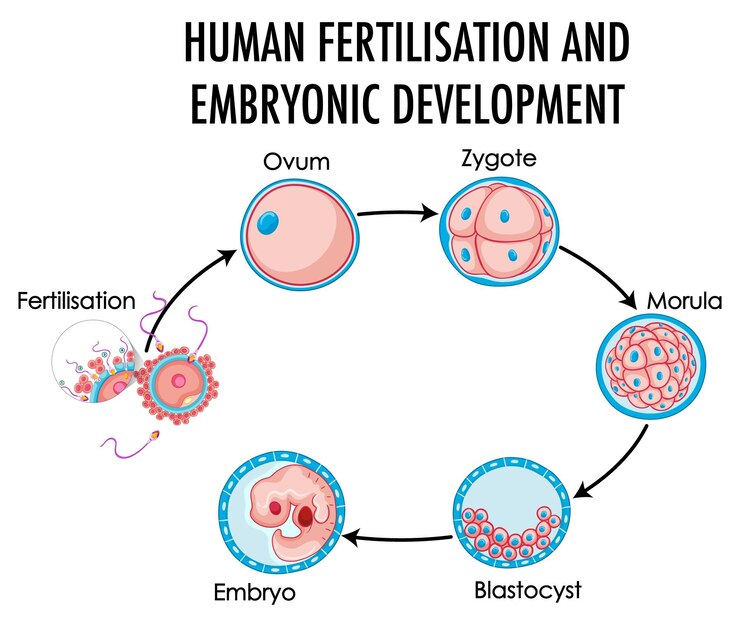
Fertilisation
A complex multi-step process where a sperm and ovum (egg) fuse together, which will eventually become a baby.
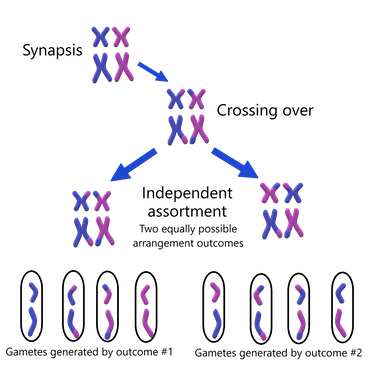
What is the difference between crossing-over and random assortment?
Although both occur during meiosis, crossing-over is the result of swapped DNA between non-sister chromatids and random assortment is where homologous maternal and paternal are randomly lined up on either side of the metaphase plate.
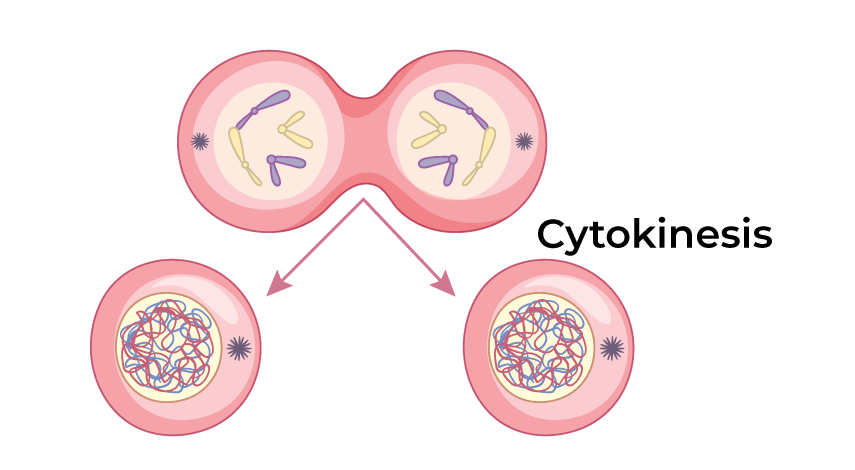
Cytokinesis
A part of cell division where the cytoplasm splits to form genetically identical daughter cells.
What are three checkpoints in the cell cycle?
End of G1
End of G2
M during Metaphase
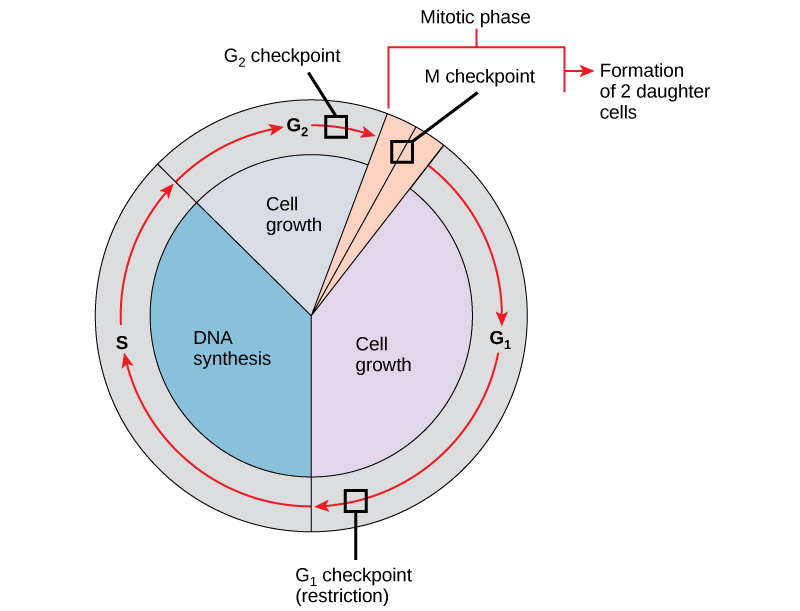
What happens if a cell doesn’t pass a checkpoint?
It is either put on pause until the problem is fixed or can perform apoptosis, which triggers the death of a cell.
What external factors regulate cell division? (3 points)
Nutrient dependence
Anchorage dependence
Density dependence
What internal factors regulate cell division? (3 points)
Hormones (e.g. FSH)
Growth factors (e.g. cytokines)
Carcinogens
What is the difference between mutagens and carcinogens?
Although closely related, mutagens are physical or chemical factors that can cause mutations whereas carcinogens are physical or chemical factors that can increase the likelihood of cancer.
What factors limit photosynthesis? (4 points)
Light availability
Water availability
Temperature
Chlorophyll availability
Cell culture
A process where cells are removed from an organism under controlled conditions, typically in a laboratory setting to be grown.
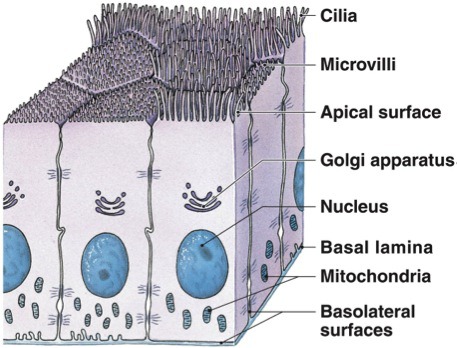
What is the difference between microvilli and cilia?
Although both are extensions of the cell (plasma) membrane, microvilli helps increase surface area of membrane whereas cilia can move materials over the surface.
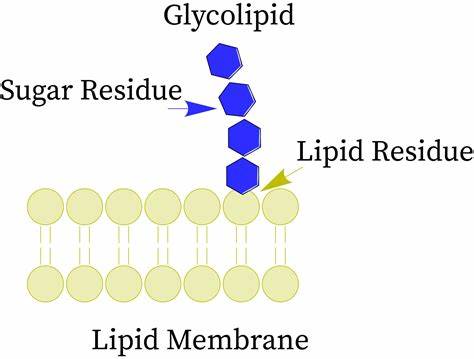
What is the role of glycolipids?
They have multiple roles like protecting and lubricating the cell membrane, anchorage and cell movement, cell specificity and recognition.
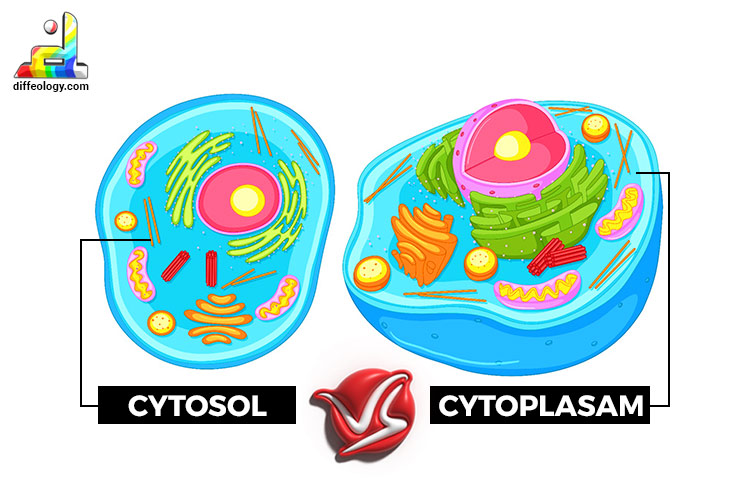
What is the difference between cytoplasm and cytosol?
Cytoplasm contains all the cell contents except the nucleus, which is made up of cytosol that contains dissolved nutrients, ions, proteins, and waste products.
What are the five types of intracellular communication mechanisms?
Endocrine communication
Paracrine communication
Autocrine communication
Synaptic communication
Direct communication
Endocrine communication
A type of intercellular communication mechanism where a cell releases a hormone into the bloodstream to affect the activity of a specific target cell(s) in another part of the body.
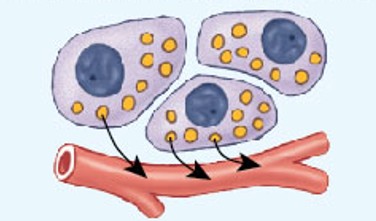
Paracrine communication
A type of intercellular communication mechanism where a cell releases paracrine into the extracellular fluid to transfer information from cell to cell, primarily within a single tissue.
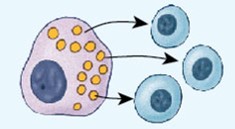
Autocrine communication
A type of intercellular communication mechanism where autocrine hormone/chemicals affect the same cells.
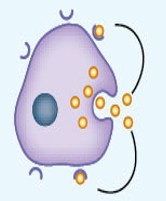
Synaptic communication
A type of intercellular communication mechanism where a neuron releases a neurotransmitter at a chemical synapse with a target cell.
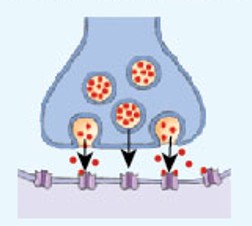
Direct communication
A type of intercellular communication mechanism that occurs between two cells of the same type in physical contact, using gap junctions (protein channel) to exchange ions and molecules.