human bio
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
nephrons, excretory system, endocrine system, nervous system and homeostasis
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
what is homeostasis
homeostasis is the body’s ability to keep the internal environment stable through changes in the external environment
what are some examples of homeostasis within the body
examples of homeostasis include; shivering when you are cold, sweating when you are hot, peeing yellow when you are dehydrated and increased heart rate during exercise.
what are the components of the negative feedback loop and describe them
stimulus: the change in the external environment
receptor: the receptor that detects the stimulus, be it in the skin or the eyes
modulator: the organ, usually the brain or the spinal chord, that receives the information passed through the PNS and decides what should be done to counter the stimulus
the effector: the muscle that receives the decision that the modulator made and carries it out
the response: what actually happened to counter the stimulus
example: you accidentally touch a boiling kettle and your hand pulls back from it
the stimulus is the boiling kettle coming in contact with your hand
the receptor is the receptors in your fingertips
the modulator is the brain, making the decision to pull away
the effector are the muscles in your arm
the response is the act of the hand pulling away from the hot kettle
what is it meant by ‘negative feedback’
the term ‘negative feedback’ refers to the action to counter a change in the external environment to keep the body’s internal environment stable
explain the process of temperature regulation in cold and hot conditions
when we are cold, our body starts shivering to generate kinetic energy, we get goosebumps and out hair stands up to try create a thin layer of warm air and the arteries near our skin constrict so to allow less heat to escape
when we are hot, our body stars sweating to allow some heat to leave with it when it evaporates and vasodialation occurs where the arteries near our skin dialate to allow more heat to escape
explain the process of temperature regulation during fever
when you have a fever, it means that there is a virus in you. your hypothalamus responds to this by setting the body’s ‘normal temperature’ much higher than it usually is
explain negative feedback loops for blood glucose regulation
if the blood sugar is too low, the pancrease detects the change and releases glucogon into the bloodstream to break down glycogen into glucose
on the other hand, if the blood sugar is too high, the pancrease senses this and releases insulin instead to store glucose as glycogen
explain why homeostasis is necessary for survival of an organism
homeostasis is necessary for the survival of an organism as it needs to be able to adapt and change to different environments
describe the difference between excretion and elimination
excretion is the removal of metabolic wastes such as urea or carbon dioxide while elimination is the removal of undigested wastes such as feces
list the major substances excreted from the body and their path of excretion. (carbon dioxide, water, salts & urea)
the major substances excreted from the body include urea, carbon dioxide, salts and water.
urea, salts and water are filtered in the kidneys, then travel through the ureters, bladder and exit through the urethra
carbon dioxide leaves through the lungs
salts and water can also be excretes through the skin in the form of sweat
explain the need for regulation of each major substance excreted
urea needs to be removed simply because it is toxic
salts and water are excreted as they affect blood pressure and hydration
carbon dioxide needs to be excreted because it affects the pH level of the blood
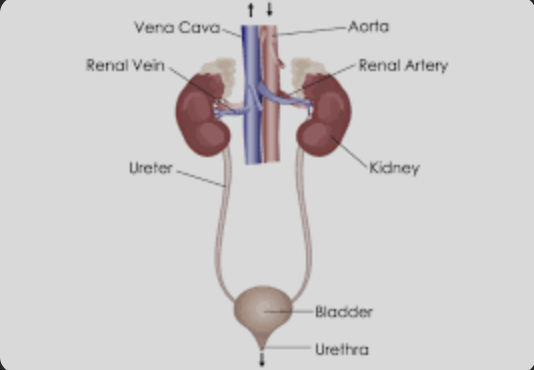
label and describe connection between major parts of the human excretory system (kidney, ureters, urinary, bladder, urethra, urinary opening)
the kidneys filter blood to remove any poisons or extra water, salts which leads to the ureter which transports the urea into the bladder where it is kept until it can be released through the urethra
draw and label a diagram of a nephron (including glomerulus, proximal convoluted tubule, loop of henle, distal, distal convoluted tubule, collecting duct.
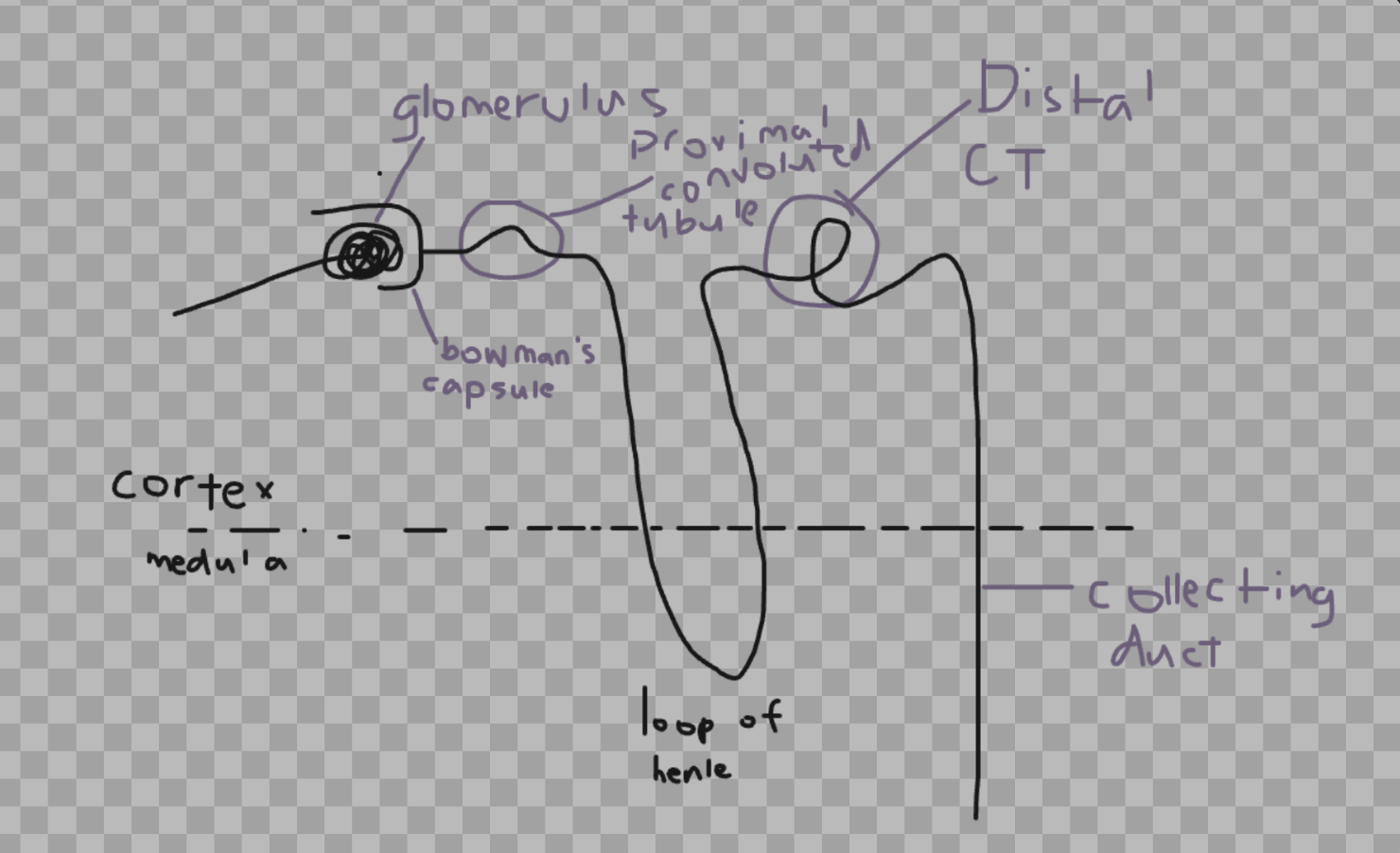
describe the role the kidney tubules play in filtration, reabsorption and secretion, and relate this to types of cell transport
filtration
they filter out excess things out of the blood such as extra water and salts to control hydration and blood pressure respectively
passive diffusion
reabsorption
after the water, salts, amino acids, urea, glucose and proteins are filtered out of the blood, they go through several stages of reabsorption to take back the substances that are necessary
stages of reabsorption are at the proximal convoluted tubule, the loop of henle and the distal convoluted tubule
glucose and amino acids are reabsorbed through active transport
water is taken back by osmosis, mainly in the loop of henle and collecting duct
passive and active transport
secretion
the active transport of waste and excess ions from the blood into the kidney tubules as they are too large to pass through the first filtration stage in the glomerulus
they also actively transport harmful substances such as drugs or poisons as they are also too large to pass through the first stage
this helps control the blood pH and keep us safe
passive and active transport
explain why an excretory system is necessary for survival of an organism
the excretory system is necessary as it removes harmful substances and helps maintain stable hydration, blood pressure and blood pH levels which helps our organs work properly
list and show diagrammatic relationships between the divisions of the nervous system – Central (brain & spinal cord); and Peripheral (sensory and motor); then Autonomic and Somatic divisions of Peripheral NS.
central nervous system
made up of the brain and the spinal chord
peripheral nervous system - the nerves that transmit the information
sensory - carries information from receptors to cns
motor - carries information from the cns to the effectors
somatic - voluntary movements like moving arms to catch a ball
automatic - involuntary movements like heart rate and digestion
sympathetic - controls the fight or flight response
parasympathetic - helps the body relax during sleep or rest
Describe the role of each division of the nervous system.
central nervous system
makes decisions based on information gathered from the sensory receptors
is made up of the brain and the spinal chord
peripheral nervous system
transmits information between sensory receptors, the cns and effector muscles
made up of the other nerves running through the body excluding the spinal chord
sensory
a division of the peripheral system which specifically transmit information from the sensory receptors to the cns
motor
a division of the peripheral system which specifically transmit information from the cns to the effector muscles
somatic
a division of motor nerves which control voluntary movements such as moving to catch a ball or writing an essay
automatic
a division of motor nerves which control involuntary movements such as heart rate, breathing and digestion
sympathetic
a division of automatic which controls the ‘fight or flight’ reaction in stressful situations, increasing heart rate, thus the amount of oxygen being pumped to the muscles allowing us to move faster
parasympathetic
a division of the automatic which helps the body relax during rest. during this time the body digests its food and rests
Describe and explain the interaction between the central and peripheral nervous systems, and parts of the peripheral nervous system.
the pns transfers information from the sensory receptors to the cns through sensory nerves, which make the decision on what to do to counter the change, then sends the information through the pns again to the effectors through motor nerves
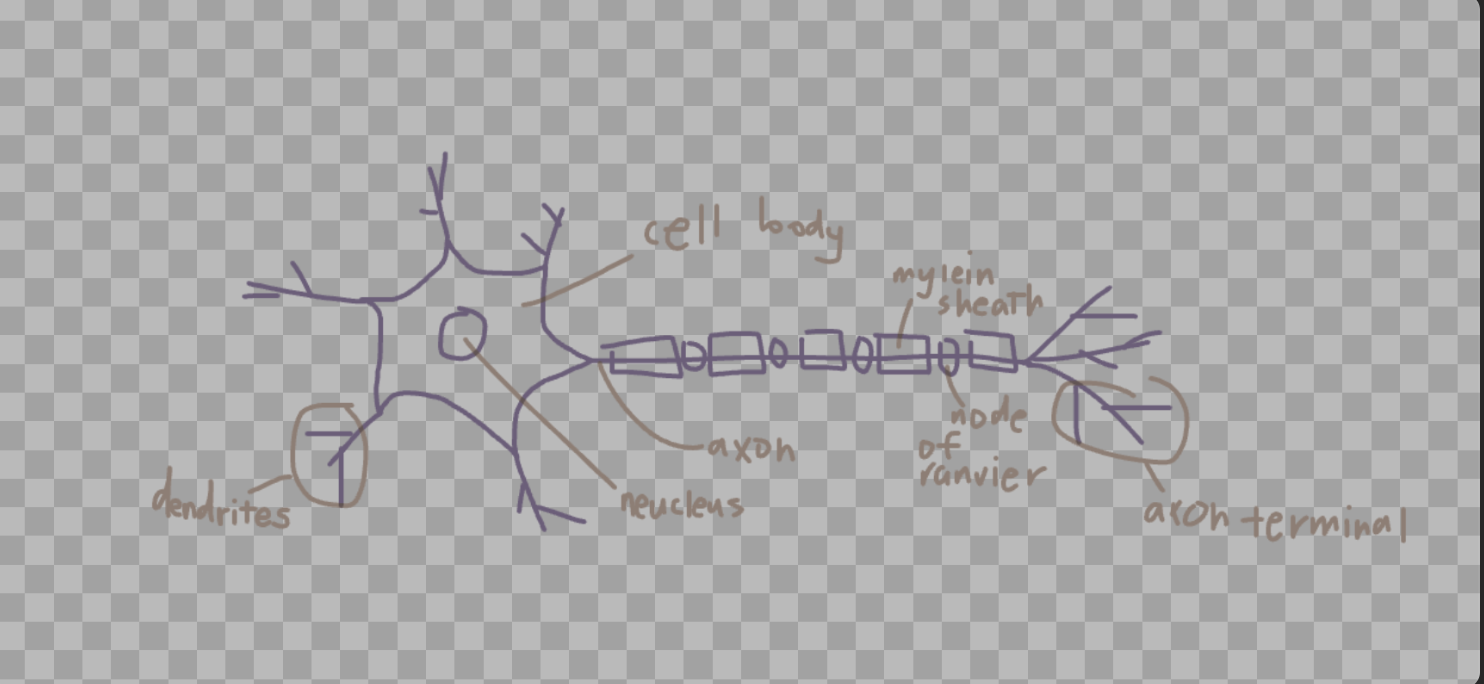
Draw and label the basic parts of a motor neuron (cell body, dendrites, axon, axon terminal, myelin sheath).
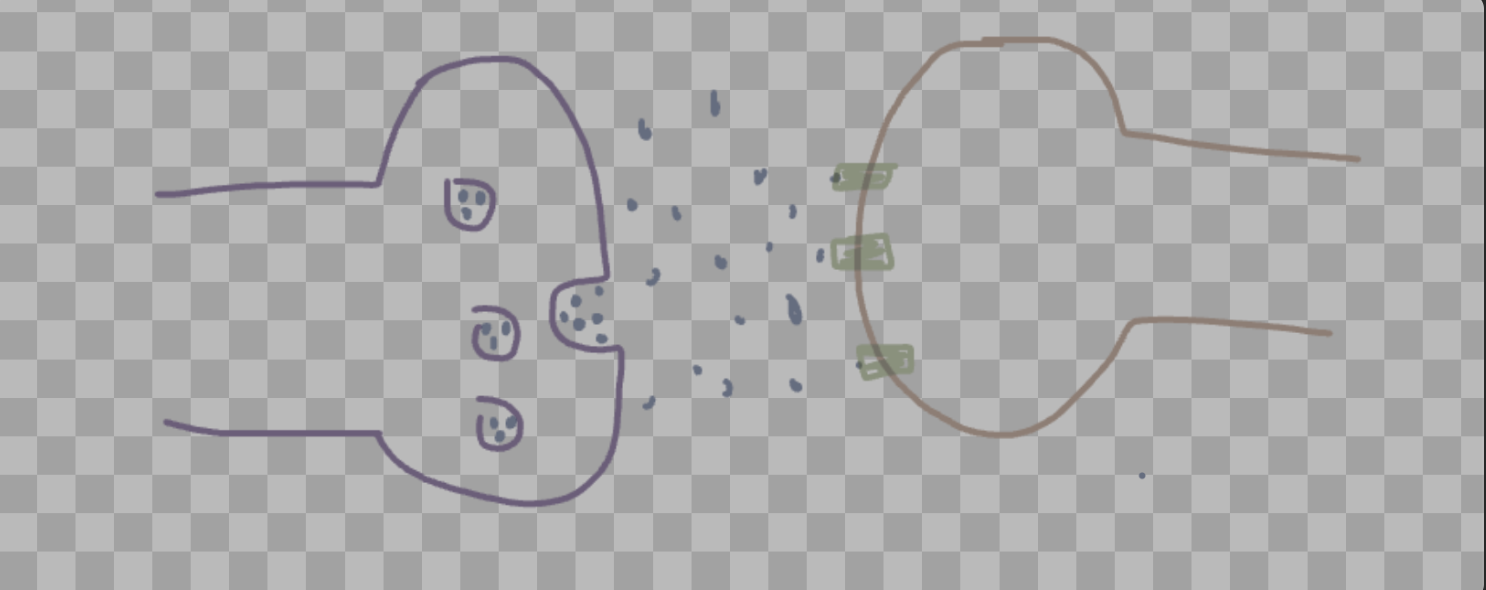
Describe and draw a synapse and describe the process of the transmission of a message across a synapse to another neuron.
the axon terminals (purple) receive the electrical impulses passed down the axon and transmit them to the dendrites of the next neuron in the form of neurotransmitters which latch onto the receptors of the dendrites of the next neuron, causing the action to occur multiple times until it reaches its target
Explain the role of the nervous system in the survival of an organism.
the nervous system allows us to react quickly in stressful situations, helps us coordinate our movements and keep our internal environment stable even through changes in the external environment
Label a diagram of the endocrine system with key glands, i.e. hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, adrenal gland, ovary/testes. (plus which hormones they secrete)
hypothalamus
TRH
CRH
GnRH
pineal gland
melatonin
pitutary gland
growth hormone
ADH
thyroid/parathyroid
thyroxine
parathyroid releases parathyroid hormone
thymus
thymosin
pancreas
insulin
glucogon
ovary
estrogen
adrenal glands
adrenaline
cotisol
testes
testosterone
placenta
estrogen
relaxin
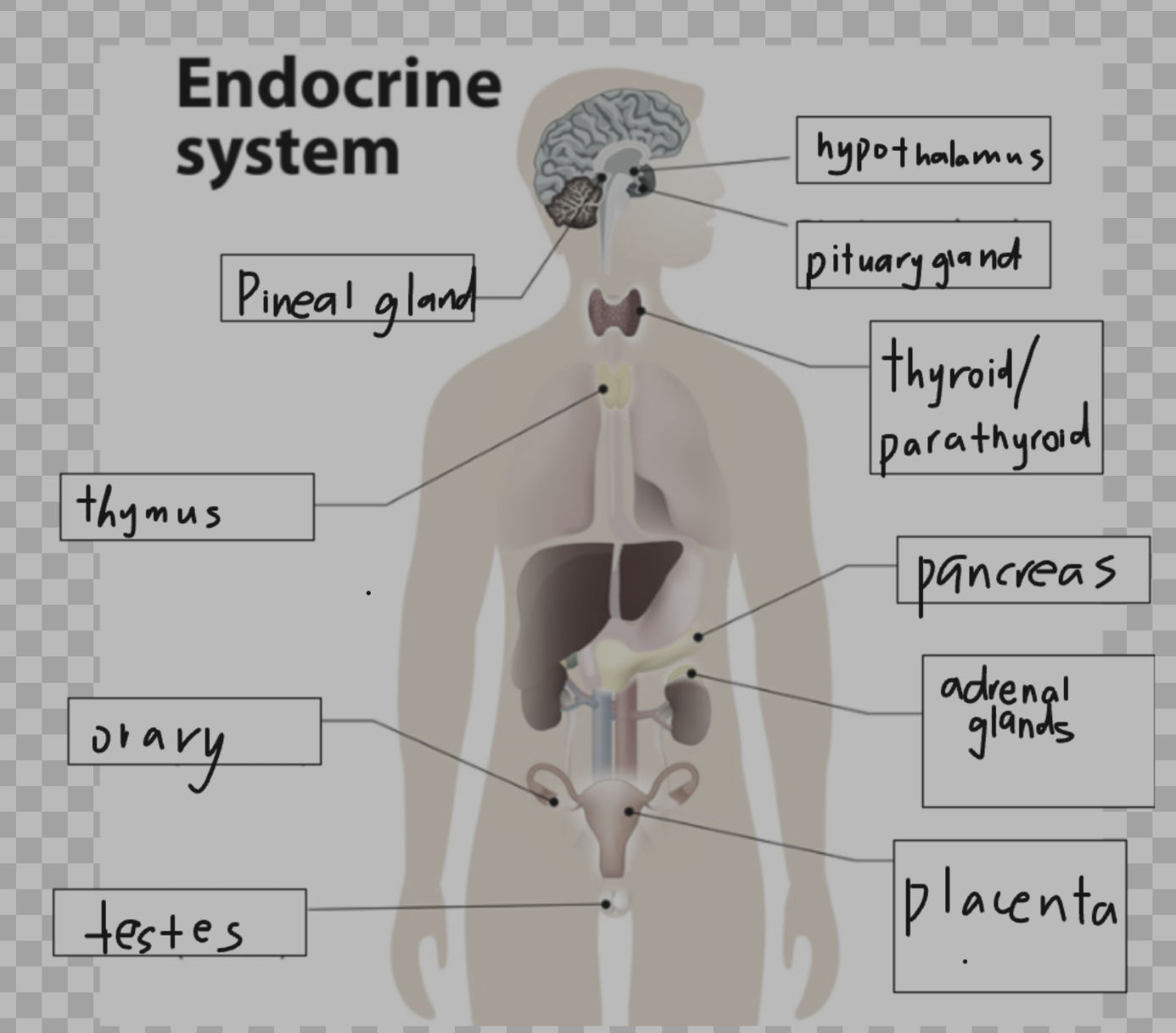
Explain the purpose of the endocrine system, especially hypothalamus, in coordinating and regulating functions throughout the body.
the endocrine system’s purpose is to control long term processes such as growth and metabolism
Give two or more examples of hormones secreted by endocrine glands e.g. antidiuretic hormone, adrenaline, testosterone, oestrogen.
examples of hormones secreted by endocrine glands include ADH, which control the amount of water reabsorbed by the kidneys, melatonin, which helps us relax, and insulin which decreases blood sugar levels by storing excess glucose as glycogen
Describe and explain how the endocrine system responds to exercise.
the endocrine system may:
release adrenaline from the adrenal glands to speed up heart rate
release ADH to conserve more water
release glucogon to increase blood sugar levels as they are used
Explain action of antidiuretic hormone on kidney function in balancing salt & water levels.
the antidiuretic hormone, or ADH, controls the kidney functions in balancing salt and water levels by controlling the permeability of the nephron’s tubules allowing more or less water or salt back into the bloodstream
Compare the endocrine system and nervous system in control of body functions, speed, specificity and extent of effects.
these two systems cooperate to maintain homeostasis but have different ways of doing so
control of body functions
the endocrine system uses the bloodstream to transmit their messages while the nervous system uses the pns to
endocrine system uses hormones while the nervous uses electrical signals
speed
the endocrine system is significantly slower than the nervous system as the hormones have to travel with the bloodstream to their intended location but the nervous system uses the pns and instantly transmits messages through the neurons
specificity
the nervous system is very specific with which glands or muscles the message is transmitted to while the endocrine system is more broad, affecting any cell with the right receptors
extent of effects
while the nervous system is very quick to act, the effects are very short lived and stop after a few minutes, on the other hand, the effects of the endocrine system last much longer as long as weeks
an example of this is the ‘fight to flight’ response, the nervous system controls the reflexes, heart rate instantly, but the endocrine system controls the adrenaline release, causing the body to be in alert mode for longer