Eye Anatomy: Difficult Topics
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Superior Rectus
elevation with adduction and medial rotation
-looking up
-CN III
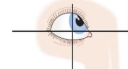
Inferior Rectus
depression with adduction and lateral rotation
-looking down
-CN III
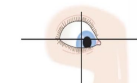
Lateral Rectus
abduction
-engages one eye at a time
-CN VI
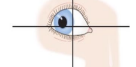
Medial Rectus
adduction
-engages one eye at a time
-CN III
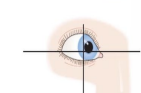
Superior Oblique
depression and abduction with medial rotation
-looks down and out, opposite of where it’s located
-CN IV
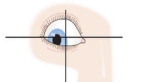
Inferior Oblique
elevation and abduction with lateral rotation
-looks up and out; opposite of where it’s located
-CN III
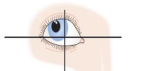
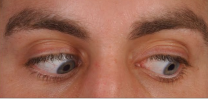
inferior oblique (right eye, CN III) and superior rectus (left eye, CN III)
What muscles are being engaged here?
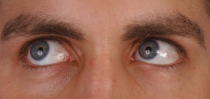
lateral rectus (right, CN VI) and medial rectus (left, CN III)
What muscles are being engaged here?
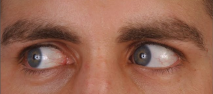
Superior oblique (right, CN IV) and inferior rectus (CN III)
What muscles are engaged here?
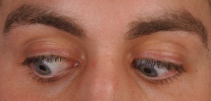
Superior rectus and inferior oblique
What muscles are being engaged here?
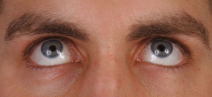
Superior oblique and inferior rectus
What muscles are being engaged here?
Superior rectus (right, CN III) and inferior oblique (left, CN III)
What muscles are engaged here?
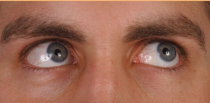
Medial rectus (right, CN III) and lateral rectus (left, CN VI)
What muscles are being engaged here?
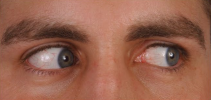
Inferior rectus (right, CN III) and superior oblique (CN IV)
What muscles are being engaged here?
Optic Nerve
special sensory innervation from the retina to brain (vision)
Oculomotor Nerve
innervates the levator palpebrae superioris, sphincter/dilator pupillae, ciliary body, and 4/6 EO muscles
CN V-I
sensory to the upper/lateral eyelid; sensory innervation to the lacrimal gland, conjunctiva, cornea (corneal light reflex)
CN V-II
supplies sensory to the infra-orbital (lower eyelid) region
CN VII
visceral motor: parasympathetic innervation to the lacrimal gland (makes you cry)
motor: orbicularis oculi muscle
Uveal Tract
choroid, ciliary body, iris
Loosens, near
Accommodation of the lens: ciliary body contracts, _______ zonular fibers, shortens lens for _____ vision
Tighten, far
The ciliary body can also relax and _________ the zonular fibers, therefore flattening the lens and allowing for ___ vision
afferent, efferent, optic, oculomotor
Pupillary Light Reflex:
-Mediated by the optic (________) and oculomotor (________) nerves
-Incoming light > _____ nerve > pretectal area of midbrain > efferent impulses sent back to the eye through ____________ nerve > pupil constriction
Pigmented layer
single layer of melanocytes in the retina that helps absorb light rays, covers back side of iris and choroid too
Optic chiasm
If the patient had this visual defect, where would you expect a lesion to be?

Optic tract/radiation
If a patient presented with this focal deficit, where would you expect to find a lesion?

Optic nerve
If a patient presented with monocular blindness, where would you expect to find a lesion?

Left homonymous hemaniopia
If there is a lesion in the right optic track, what deficit would you expect the patient to display?
Right homonymous hemianopia
If there is a lesion found in the left optic tract, what deficit would you expect the patient to display?
Contralateral, ipsilateral
Information gathered from the nasal fields is processed on the _________ side of the brain, while information gathered from the temporal fields is processed on the _______ side of the brain
Blindness
Complete lesion of the optic nerve will cause _______
Bitemporal heteronymous hemianopia
A lesion in the optic chiasm will cause _______ __________ ________
Homonymous hemianopia
Destruction of one optic tract causes _________ _______, which is the complete loss of vision in the inner half of one eye and the outer half of the other
homonymous defect
Destruction of the optic radiation causes a __________ _____
Optic Nerve
-blindness in the affected eye
-monocular blindness
Optic chiasm
-loss of fibers crossing the midline from the nasal half of each retina causes loss of temporal visual field on both sides
-bitemporal heteronymous hemianopia
Optic tract
-loss of fibers for the visual field on the opposite side of the lesion
-homonymous hemianopia
Optic radiation
-loss of fibers for the visual field on the opposite side to the lesion
-homonymous hemianopia
Visual cortex (one side)
-loss of visual processing for the visual field on the opposite side to the lesion
-homonymous hemianopia with macular sparing
Accommodation
allows for focusing on nearby objects, lens shortens
Convergence
active process of turning the eyes inward to maintain alignment of the visual axes with an object
Strabismus
one of the extraocular eye muscles are not working, therefore affecting convergence
Myopia
globe is too long
near is clear, distant blurry = nearsightedness
corrected by concave lens
Hyperopia
globe too short
near blurry, distant clear = farsightedness
corrected by convex lens
Presbyopia
lens is unable to increase its refractive power, becomes more rigid
-can’t accommodate on near objects
-vision changes due to age
20/200, 20
Legal Blindness:
Best corrected acuity of __/___ or less in the better eye
Binocular visual field of __ degrees or less