lifespan- human development 2
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
theory
et of logically related concepts
what do theorys seek to do
Organize, explain, & predict data, the information gathered by research.
what do theoretical concepts help see
connections between isolated pieces of data
Hypotheses
possible explanations for phenomena, used to predict the outcome of research.
what did locke say that a young child is
a blank slate
what did rousseau believe child were
he believed children are born noble savages
Mechanistic model
model that views human development as a series of predictable responses to stimuli.
what do Mechanistic researchers want to identify
the factors that make people behave as they do
Organismic model
model that views human development as internally initiated by an active organism and as occurring in a sequence of qualitatively different stages.
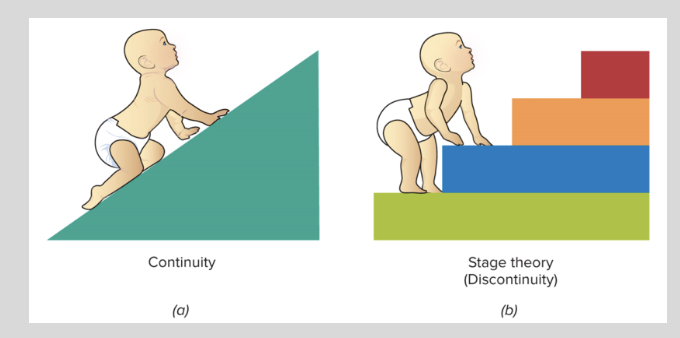
what do Mechanist theories see development as
continuous: as occurring in small incremental stages
Organismic theorists are…
proponents of stage theories in which development is seen as occurring in a series of distinct stages, like stair steps
Quantitative change
changes in number or amount, such as in height, weight, size of vocabulary, or frequency of communication
Qualitative change
discontinuous changes in kind, structure, or organization.
A major difference among developmental theories is:
a) whether it proceeds continuously, as learning theorists and information-processing theorists propose,
or
(b) whether development occurs in distinct stages, as Freud, Erikson, and Piaget maintained.
what are the 5 major perspectives that underlie much influential theories and research on human development
◦ Psychoanalytic
◦ Learning
◦ Cognitive
◦ Contextual
◦ Evolutionary /Sociobiological
who was the originator of the psychoanalytic perspective
sigmund freud
psychoanalytic perspective
a view of human development as shaped by unconscious forces that motivate human behavior
psychoanalytic perspective parts
◦ Much of development involves learning how to satisfy urges in socially acceptable ways.
◦ Early experiences shape later functioning.
◦ Childhood is the precursor to adult behavior.
Sigmund Freud: Psychosexual Development- oral stage
age- birth to about 15 Months
unconscious conflict- sucking and feeding
Sigmund Freud: Psychosexual Development- anal stage
age 12-18 Months to 3 year
unconscious conflict- potty training
Sigmund Freud: Psychosexual Development- phallic stage
age 3-6 years
unconscious conflict- attachment to parents
Sigmund Freud: Psychosexual Development- latency stage
age- 6 to puberty
unconscious conflcit- socialization
Sigmund Freud: Psychosexual Development- genital stage
age- puberty to adult
unconscious conflict- mature adult sexuality
how many hypothetical parts of the personality did Freud proposed
3
id part of personality
The id governs newborn behavior and operates on the pleasure principle.
ego part of personality
The ego, which represents reason, develops gradually in early life and operates under the reality principle.
superego part of personality
The superego develops later in childhood and includes the conscience
Psychosexual development
in Freudian theory, an unvarying sequence of stages of childhood personality development in which gratification shifts from the mouth to the anus and then to the genitals.
what did erik erikson do
modified and extended Freudian theory by emphasizing the influence of society
Psychosocial development
in Erikson’s eight-stage theory, the socially and culturally influenced process of
development of the ego, or self.
what does each stage of erik thing involove
a major psychological challenge or issue that must be satisfactorily resolved for healthy development.
Learning perspective
view of human development that holds that changes in behavior result from experience or from adaptation to the environment.
Behavior is the focus because it is observable/countable.
Behaviorism
learning theory that emphasizes the predictable role of environment in causing
observable behavior. Focuses on associative learning between two events:
• Classical conditioning
• Operant conditioning
Classical conditioning
learning based on associating a stimulus that does notordinarily elicit a response with another stimulus that does elicit the response.
classical conditioning examples
ivan pavlovs experiement with dogs
stimulus and response
Operant conditioning
learning based on association of behavior with its consequences
involoves volubtary behavior
who is a important person for operant conditioning
B.F skinner
reinforcement
The process by which a behavior is strengthened, increasing the likelihood that the behavior will be repeated
punishment
the process by which a behavior is weakened, decreasing the likelihood of repetition
Social learning theory
theory that behaviors are learned by observing and imitating models.
Reciprocal determinism
Albert Bandura’s term for bidirectional forces that affect development. The person acts on the world as the world acts on the person
observational learning/ modeling
learning through watching the behavior of others.
Children develop self-efficacy and confidence.
Cognitive perspective
view that thought processes are central to development.
◦ The cognitive-stage theory of Jean Piaget;
◦ Vygotsky’s sociocultural theory of cognitive development; and
◦ The information-processing approach.
what deos learning evolove from
sensorimotor activity to logical and then abstract thought.
Cognitive-stage theory
Piaget’s theory that children’s cognitive development advances in a series of four stages involving qualitatively distinct types of mental operations.
Organization
creation of categories or systems of knowledge. Schemes to organize patterns.
Adaptation
adjustment to new information about the environment, achieved through processes of assimilation and accommodation.
assimilation
incorporation of new information into an existing cognitive structure.
accommodation
changes in a cognitive structure to include new information.
Equilibration
the tendency to seek a stable balance between cognitive structures and experiences. A balance between assimilation and accommodation
what does cognitive development begin
with an inborn ability to adapt to the environment
whos created Sociocultural theory
vygotsky
Sociocultural theory
Vygotsky’s theory of how contextual factors affect children’s development.
what do people learn through
social interaction
Zone of proximal development
difference between what a child can do alone and what the child can do with help.
sociocultural theory of development
a person’s cognitive development is largely influenced by their surrounding culture
Scaffolding
temporary support to help a child master a task.
holding the towerwhile the kid builds the base
Evolutionary/sociobiological perspective
view of human development that focuses on evolutionary and biological bases of behavior ( Wilson,1975)
what is the Evolutionary/sociobiological perspective influenced by
darwin’s theory of evolution
darwin’s theory of evolution
survival of the fittest
natural selection
survival of the fittest
o Animals with traits suited to environment survive
o These adaptive traits are passed on to offspring
natural selection
As environments change, traits change in adaptiveness
Researchers in human development work with two methodological traditions what are they
quantitative and qualitative
◦ Each has different goals and different ways of seeing and interpreting reality.
◦ Each emphasizes different means of collecting and analyzing data.
what must research attempt to balance
the possible benefits against the risk of mental, emotional, or physical injury to participants.
what are the ethics of research considerations
◦ Informed consent
◦ Avoidance of deception
◦ Protection from harm and loss of dignity
◦ Privacy and confidentiality
◦ Right to decline or withdraw
◦ Responsibility of investigators to correct undesirable effects
Erik Erikson: Psychosocial Development: Age: birth to 12-18 mon
stage- basic trust versus mistrust
virtue- hope
Erik Erikson: Psychosocial Development: Age: 12-18 mon to 3 yr
stage- autonomy versus shame and doubt
virtue- will
Erik Erikson: Psychosocial Development: Age: 3 -6 yr
stage- initiative vs guilt
virtue purpose
Erik Erikson: Psychosocial Development: Age: 6 yr to puberty
stage- industry vs inferiority
virtue- skill
Erik Erikson: Psychosocial Development: Age: puberty to young adulthood
stage identity vs identity confusion
virtue- fidelity
Erik Erikson: Psychosocial Development: Age: young adulthood
stage- intimacy vs isolation
virtue- love
Erik Erikson: Psychosocial Development: Age: middle adulthood
stage- generativity vs stagnation
virtue- care
Erik Erikson: Psychosocial Development: Age: late adulthood
stage- integrity vs despair
virtue- wisdom
Jean Piaget’s Cognitive-Stage Theory: sensorimotor
age: birth to 2 yr
features: organizing activites in relation to the environment throughsensory and motot activity
Jean Piaget’s Cognitive-Stage Theory: preoperational
age: 2-7yr
features: development of a representational system, use of symbols, language and imaginative play
Jean Piaget’s Cognitive-Stage Theory: concrete operations
age: 7-11 yr
features: logical problem solving when focused on the here and now not able to think abstractly
Jean Piaget’s Cognitive-Stage Theory: formaal operations
age: 11- adulthood
features: thinking abstractly, dealing with hypothetical situations, and thinking about possibilities.