Module 3 Digital Imaging Pre-Processing and X-Ray Spectrum & Exposure
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts from the lecture notes on digital imaging pre-processing and x-ray spectrum and exposure, including definitions, correction methods for artifacts, and the factors influencing x-ray exposure and their proportional relationships.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What is pre-processing in digital imaging?
Computerized corrections applied to raw image data before display.
How does pre-processing differ from post-processing?
Pre-processing corrects flaws; post-processing refines images.
What happens to dead pixels during pre-processing?
They are corrected by interpolation from neighboring pixels.
Why can’t dead pixels be physically repaired easily?
Detector elements are extremely small, making servicing impractical.
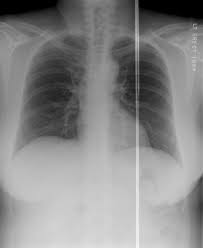
What is row or column drop-out?
A whole row/column of pixels fails, appearing as straight lines.
How is row/column drop-out corrected?
Interpolation assigns average values of adjacent rows/columns.
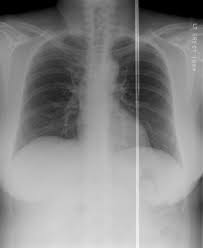
What is a detector seam?
Variations at panel junctions of the detector.
Can detector seams always be corrected?
Minor seams can be interpolated; severe seams may be uncorrectable.
When does interpolation occur?
During pre-processing, before the image is displayed.
Why is pre-processing critical in clinical imaging?
Prevents detector flaws from mimicking pathology.
Name two proprietary pre-processing features.
Pixel calibration and interpolation.
What issue do small dust particles or scratches cause?
Minor flaws corrected automatically during pre-processing.
What type of noise is reduced during pre-processing?
Detector system noise.
What’s the primary software role in pre-processing?
Automatic correction of system imperfections.
Are pre-processing corrections visible to the MRT?
No, they occur behind the scenes.
Give an example of equipment-caused artifact eliminated by pre-processing.
Dead pixels.
What term describes assigning values to missing pixel data?
Interpolation.
Why are digital detectors built in multiple parts?
To allow large imaging areas.
What happens if detector seam damage is too severe?
Artifact may remain uncorrectable.
What is the overall purpose of pre-processing?
Ensure raw image data is diagnostically reliable.
What factors determine x-ray exposure?
Target Z, mAs, kVp², and 1/d².
Exposure is directly proportional to what tube setting?
mAs.
Exposure is proportional to the square of which factor?
Tube voltage (kVp).
What does the inverse square law state?
Exposure decreases as 1/d² with increasing distance.
If mAs increases by 15%, how much does exposure change?
15% increase.
If kVp increases by 15%, how much does exposure change?
~32% increase.
If SID increases by 35%, how much does exposure change?
~45% decrease.
How must mAs change if SID increases by 15% but exposure must remain constant?
Increase mAs ~32%.
What is the effect of target atomic number (Z) on x-ray exposure?
Higher Z leads to more efficient x-ray production.
What happens to exposure if mAs is doubled?
It doubles.
What does 'Exposure is proportional to V squared (V²)' mean in practice?
Small increases in kVp cause large increases in exposure.
What happens to image brightness if exposure decreases too much?
The image appears noisy/underexposed.
What exposure results from increasing kVp from 65 to 75 kV, given an initial exposure of 33 mR?
~44 mR.
If kVp increases, what can be done to reduce patient dose but keep exposure constant?
Reduce mAs.
If 22 mAs at 65 kV gives correct exposure, what mAs is needed at 75 kV?
~17 mAs.
What is the relationship between exposure and SID?
Inversely proportional to distance squared.
What happens to exposure if SID doubles?
Exposure decreases by a factor of 4.
Why is kVp more powerful than mAs in affecting exposure?
kVp affects both quantity and quality, and exposure is proportional to V².
What is the clinical importance of understanding exposure relationships?
Balancing image quality and patient dose.
How do pre-processing and exposure settings work together?
Pre-processing corrects detector flaws, while exposure settings control the radiation reaching the detector.