Functions and Composition of Blood
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Transport
Movement of nutrients, gases, hormones, and wastes.
Regulation
Maintaining homeostasis of pH, ions, water, and temperature.
Defence
Protection against fluid loss, pathogens, and toxins.
Haem
UK prefix meaning 'blood'; equivalent to Heme in US.
Blood
Specialized connective tissue with plasma, cells, and platelets.
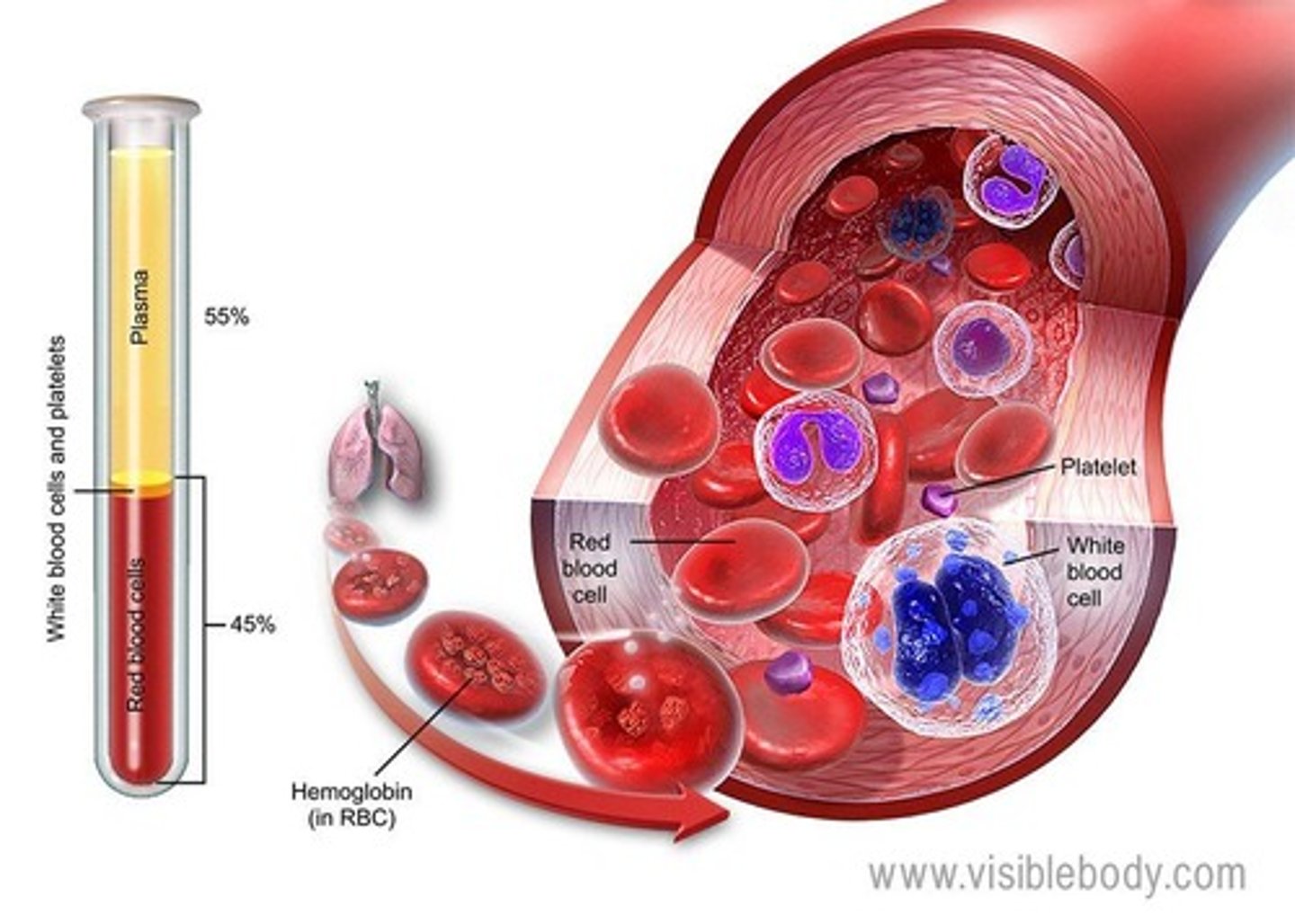
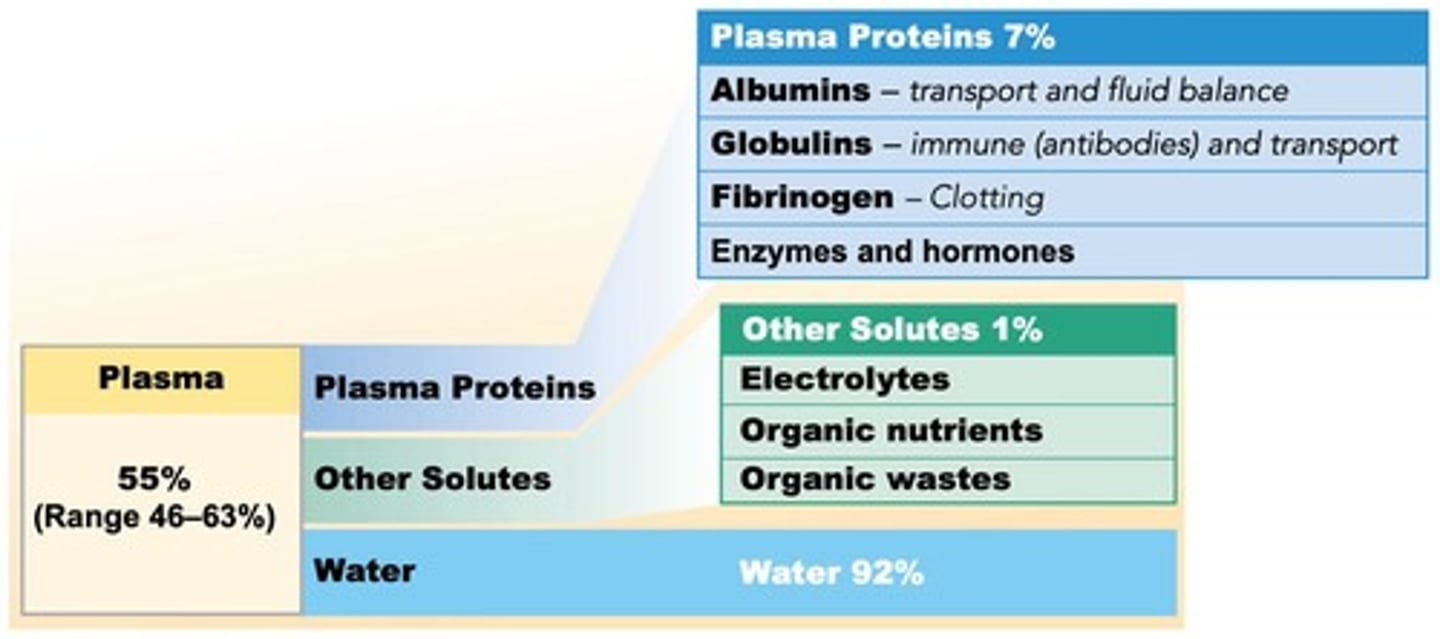
Plasma
Aqueous component of blood, contains proteins and solutes.
Formed elements
Cells or fragments in blood for various functions.
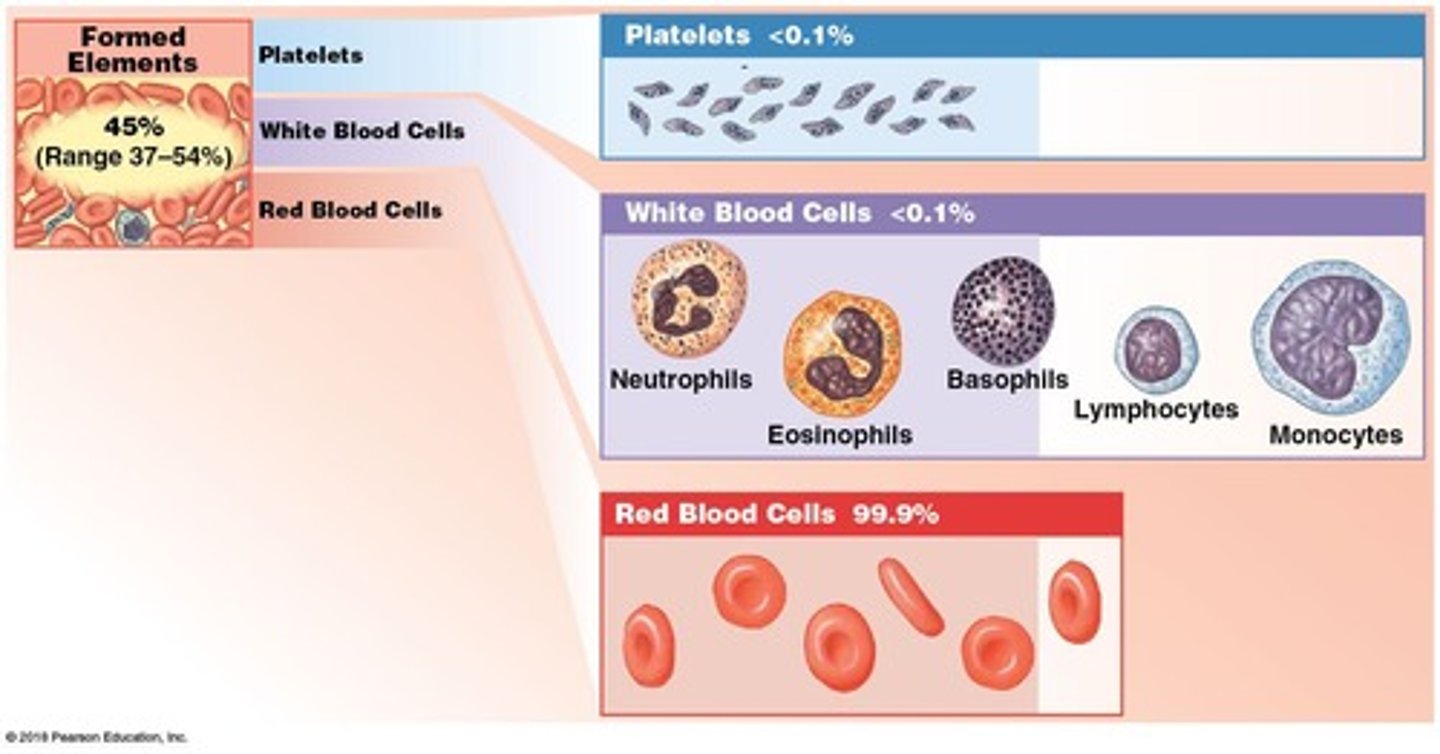
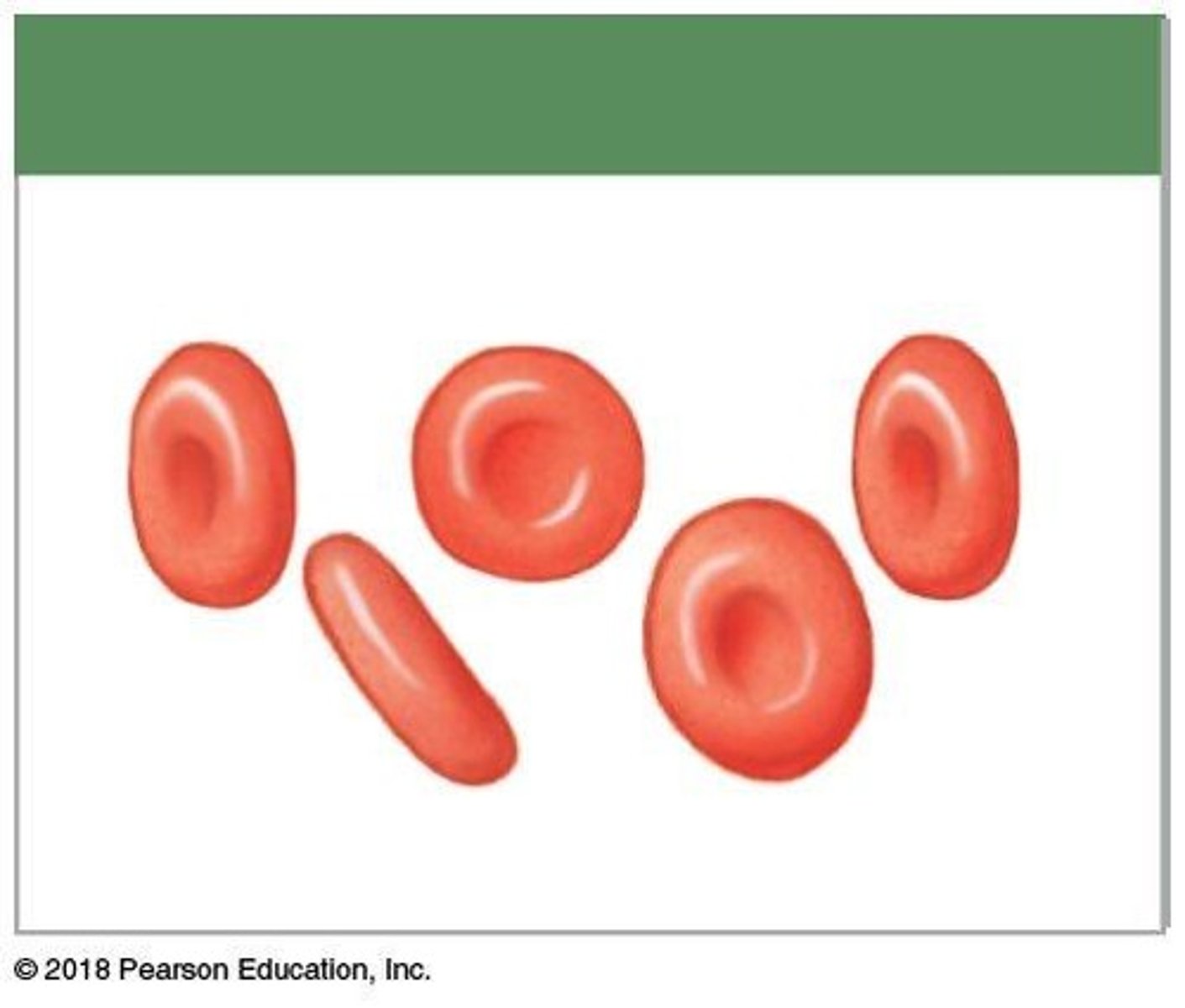
Red Blood Cells (RBCs)
Erythrocytes responsible for oxygen transport.
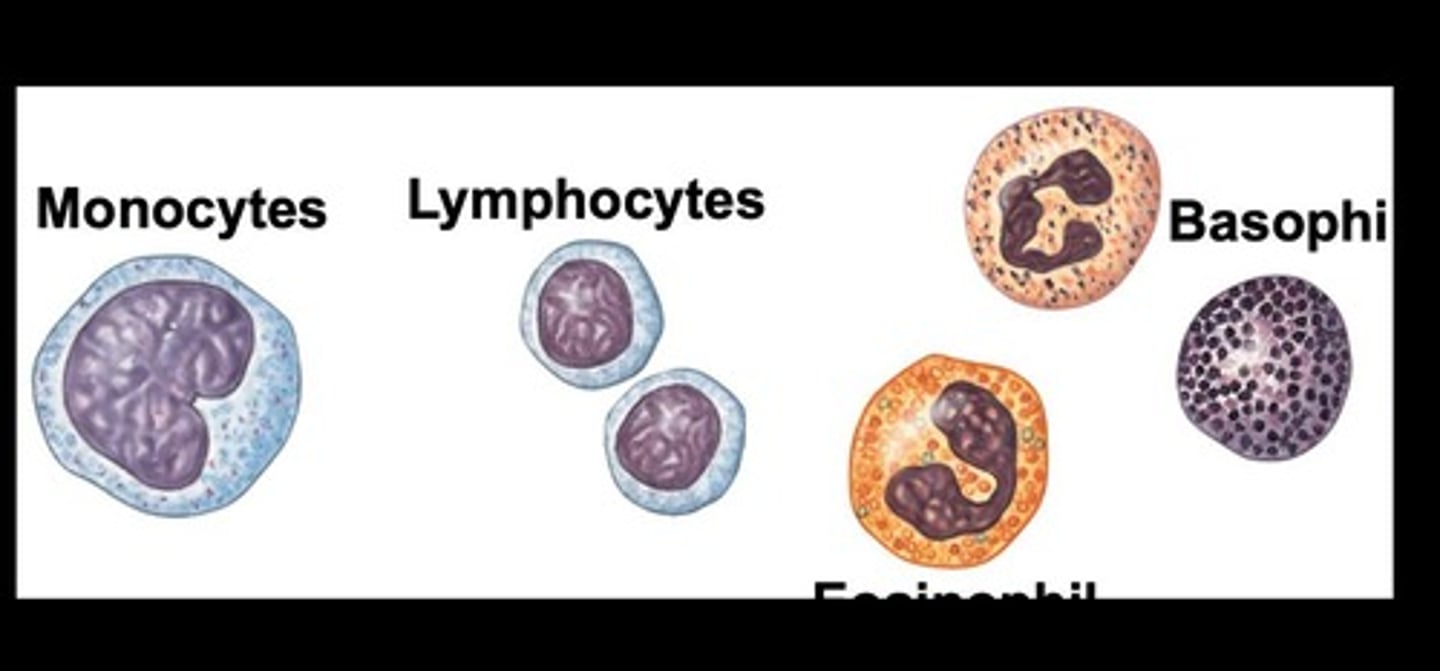
White Blood Cells (WBCs)
Leukocytes involved in immune response.
Platelets
Cell fragments aiding in blood clotting.
Total blood volume (male)
5-6 liters in adult males.
Total blood volume (female)
4-5 liters in adult non-pregnant females.
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
Measures formed elements and RBC health.
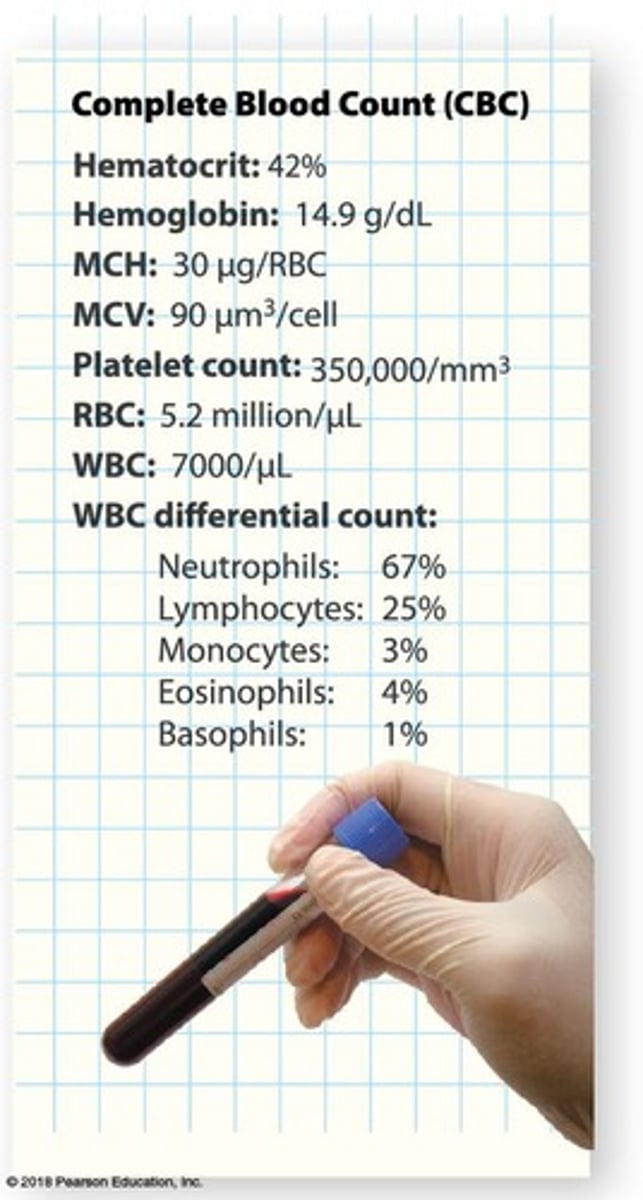
Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (MCH)
Measure of average hemoglobin per RBC.
Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV)
Measure of average RBC size.
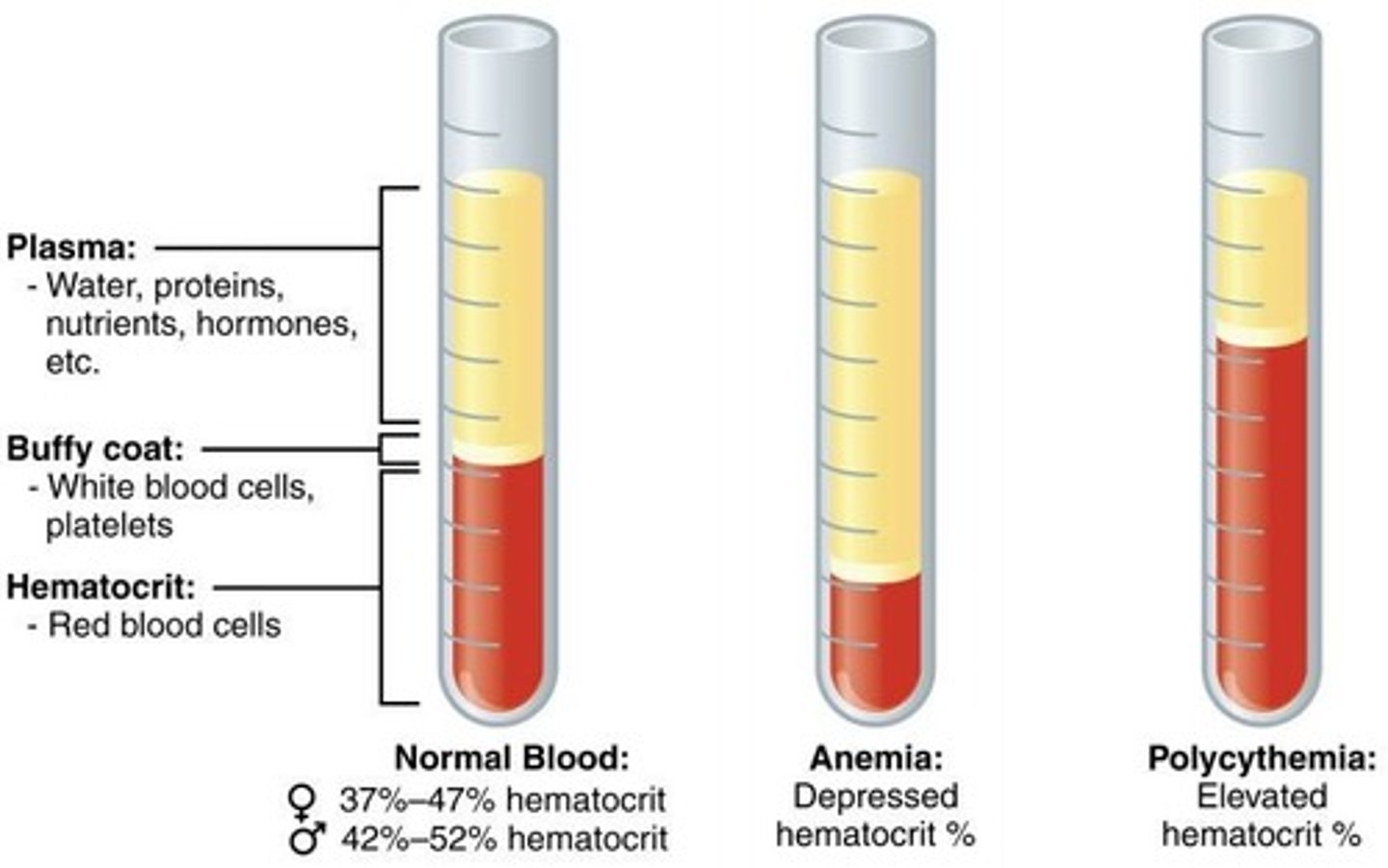
Haematocrit
Percentage of RBCs in whole blood.
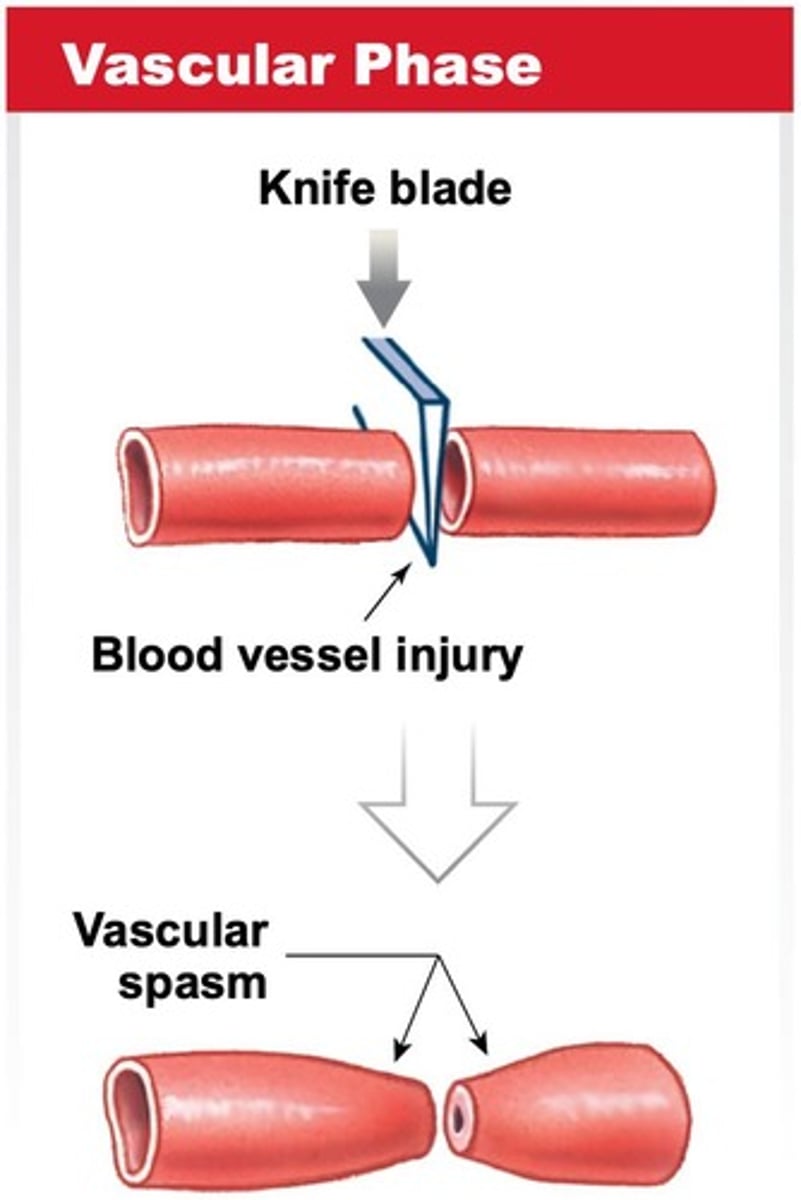
Haemostasis
Processes to limit or halt blood loss.
Clotting
Major part of haemostasis involving fibrin formation.
Vascular phase
Fastest phase of haemostasis with vascular spasm.
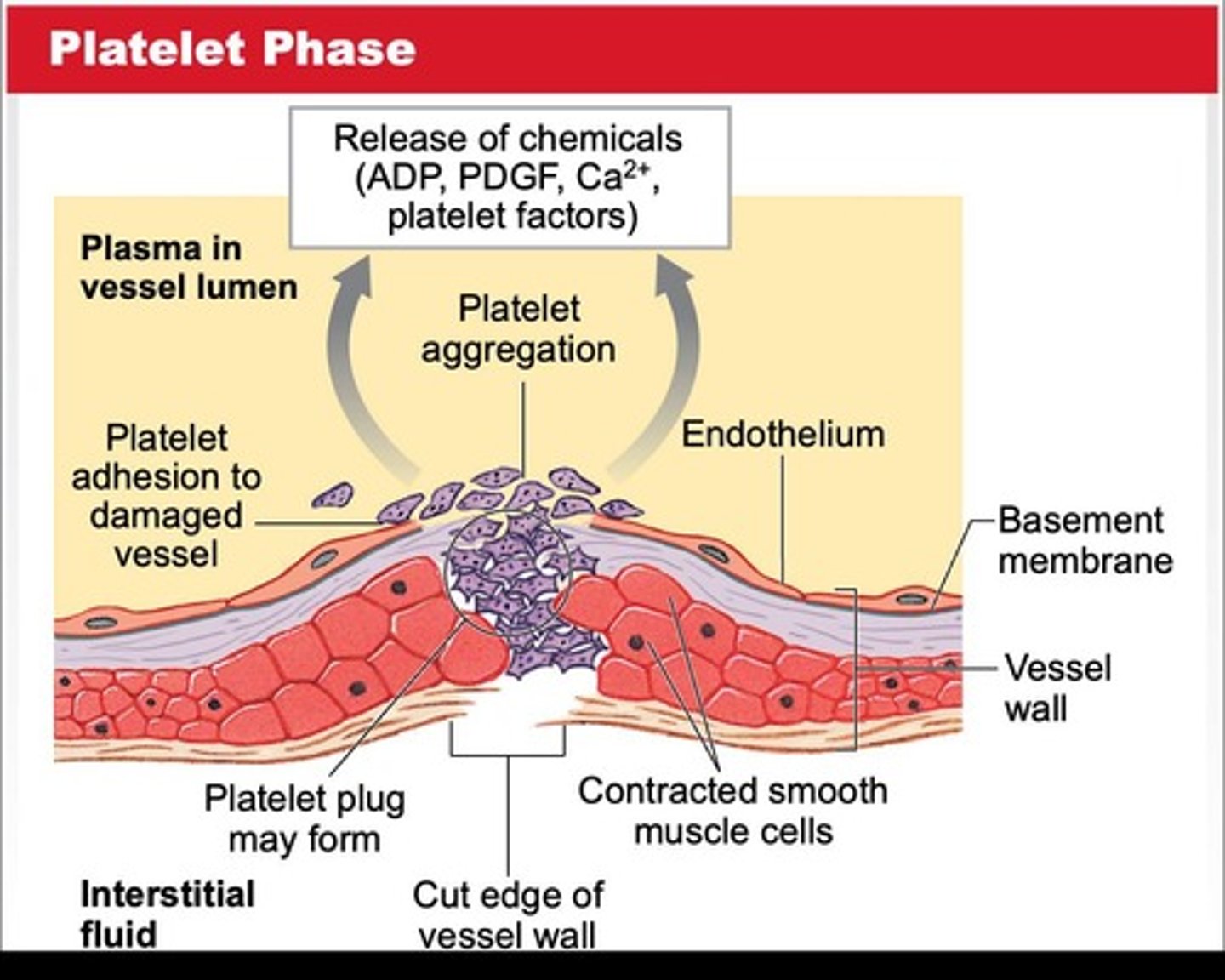
Platelet phase
Platelets aggregate to plug broken vessels.
Coagulation phase
Fibrin mesh forms around platelets to create clot.
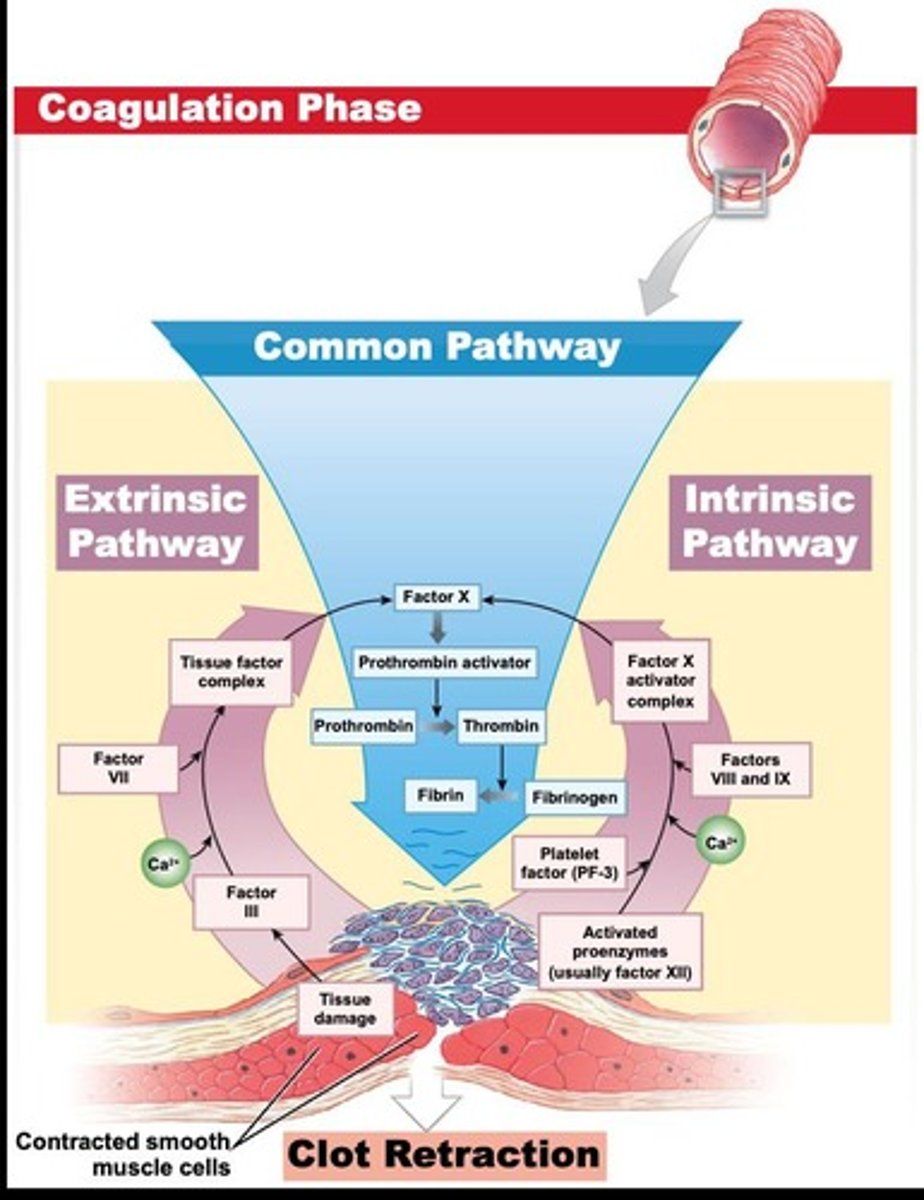
Fibrin
Insoluble protein forming the structure of clots.
Fibrinolysis
Process of dissolving clots after vessel repair.
Erythropoietin (EPO)
Hormone stimulating RBC production in response to hypoxia.
Megakaryocytes
Cells producing platelets in the bone marrow.
RBC lifespan
Approximately 4 months before recycling.
Iron recycling
Recycling of Fe2+ from degraded RBCs.
Intracellular fluid (ICF)
Fluid within cells, comprising 18% of body fluid.
Interstitial fluid (ISF)
Fluid between cells, facilitating nutrient exchange.
Extracellular fluid (ECF)
Fluid outside cells, including plasma and ISF.