DRR All Lesson Prelim G12
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Hazard
___________ is a process, phenomenon, or human activity that may cause loss. of life, injury or other health impacts, property damage, social and economic disruption or environmental degregation.
Disasters
__________ are serious disruptions of the community or a society involving widespread human, material, economic, and environmental losses and impacts which exceeds the ability of the community or society to cope using its own resources
Disaster Risk
_____________ is the potential loss of lives, health status, livelihood, and various assets which are often challenging to quantify.
World Risk Index
"provides an analysis of disaster risks worldwide and indicates which countries are in the greatest need to strengthen measures for coping with and adapting to extreme natural events."
Risk Assessment
________ ___________ is based on the general notion that the intensity of the extreme weather event is not the only factor of relevance to the disaster risk, but that the SOCIETY'S LEVEL OF DEVELOPMENT is equally important. If it is less developed, a society will be more vulnerable to natural events than if it is better prepared in regard to susceptibility, coping capacities and adaptive capacities.
Exposure
Exposure to earthquake, cyclone, flood, drought, and sea level rise.
Susceptibility
Sanitation and water supply, percentage of undernourished, dependency ratio, population below poverty line, gross domestic product per capita (measure of a country's economic output), GINI index (is a measurement of the income distribution of a country's residents).
Coping Capacity
Corruption perception index, failed states index, number of physicians per 10,000 people, number of hospital beds per 10,000 people, and insurance coverage.
Adaptive Capacity
(AC) - adult literacy rate, combined gross, enrollment ratio, gender parity in educ., women in national, parliament, water quantity, life expectancy at birth, agriculture etc.
Vulnerability
Susceptibility to damage and capacity to cope and/or to adapt
Exposure
Population and infrastructures situated in low-lying coastal areas.
1 RESCUE
Within 72 hours but can be longer.
2 ASSESSMENT
Within 0-5 days
(RDANA) Rapid Damage Assessment and Needs Analysis
3 RELIEF
Within 7-90 days
4 RECOVERY AND RECONSTRUCTION
Within 30 days to 2 years
5 REHABILITATION AND DEVELOPMENT
Can be an ongoing process
Vulnerability
We must control on ___________________
Department of Disaster Resiliency Act of 2017
What is the short title of House Bill 6075
The Valley Fault System Atlas
Released by the Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology (PHILVOLCS), showcases areas in Metro Manila, Rizal, Bulacan, Cavite, and Laguna that lie along fault lines. These maps are crucial for identifying cities, municipalities, and barangays that could be impacted by the Big One - an earthquake with a potential magnitude of 7 or higher that could occur at any moment.
Philippine Institute of Volcanology and Seismology
PHILVOLCS - It is a Philippine national institution that provides information on volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, and tsunamis. It also offers specialized information and services to protect life and property and support sustainable development.

Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration
PAGASA - It is the national meteorological and hydrological service, responsible for providing weather forecasts, flood warnings, and other related services

National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Council
NDRRMC - It is the primary government body in the Philippines responsible for coordinating disaster preparedness, response, and recovery efforts.

Department of Science and Technology
DOST - provides direction, leadership, and coordination of all scientific and technological efforts/activities in the Philippines and ensures that the results therefrom are geared and utilized in areas of maximum economic and social benefits for the people.

Department of the Interior and Local Government
DILG - t is a government agency in the Philippines responsible for promoting peace and order, ensuring public safety, and strengthening the capacity of local government units (LGUs).
Department of Social Welfare and Development
DSWD - It is a Philippine government agency mandated to develop, implement, and coordinate social welfare and development programs and services. The focus is on improving the living conditions and empowering vulnerable and disadvantaged sectors of Philippine society.

Local Government Unit
LGU - It refers to a political and administrative division within the country, such as a province, city, municipality, or barangay, that is responsible for local governance.
Poverty and vulnerability
The poor often face limited access to quality housing, public amenities, and job prospects, leaving them susceptible to disasters.
The Disaster Risk-Poverty Nexus
It is the correlation between poverty and disaster risk. Factors at both local and global levels expose individuals and communities to higher risks, exacerbated by poverty. Disasters not only affect vulnerable groups but also harm their economic and social well-being, further deteriorating their circumstances. Additionally, their situation is worsened by the unequal allocation and distribution of resources.
Global Drivers
Uneven economic and urban development, Climate change, Weak governance and limited endogenous capacities
Underlying risk driver
Poor urban and local governance, Vulnerable rural livelihood, Ecosystem decline, Lack of access to risk transfer and social protection
Intensive Risk
Major concentration of vulnerable population and economic assets exposed to extreme hazards
Extensive Risk
Geographically dispersed exposure of vulnerable people and economic assets to low or moderate intensity hazards
Everyday Risk
Households and communities are exposed to food insecurity, disease, crime, accidents, pollution, lack of sanitation, and clean water
Poverty
Short and long term impacts on income, consumption, welfare, equality, and other factors such as powerlessness, exclusion, illiteracy, and discrimination.
Limited opportunities to access and mobilize assets.
Disaster impact
Major mortality and economic loss. Damage to housing, local infrastructure, livestock, and crops
Hazard Analysis
Is the "identification, study, and monitoring of any hazard to determine its potential, origin, characteristics, and behavior."
Natural Hazards
A. Hydro-meteorological and climatological hazards
B. Geologic hazards
C. Biological hazards
D. Astronomical hazards
Anthropogenic Hazards
A. Fire
B. Industrial and technological hazards
C. Hazards related to high-risk recreation activities such as mountain climbing
D. Other hazardous human activities
Human-Induced Hazards
A. Arson
B. Terrorism
C. Wars
Community hazards and disaster history constructions
In this method, the existing hazards and the disasters that the community experienced are identified.
Hazard and vulnerability mapping
Areas in the community that are vulnerable to a specific hazard are identified and then located on the map.
Frequency
How often does the hazard occur
Duration
How long does it occur?
Speed of Onset
How fast does it occur upon initial detection?
Intensity
What is the strength or magnitude?
Forewarning
Adequate time to prepare upon detection. Are there signals before the occurrence?
Manageability
How manageable are the effects of the hazard?
Survival Kit
In some other cases, called GO BAGS or GRAB BAGS, A survival kit enables a person to get nourishment in times of disasters. That bag should enable a person to survive prior to any assistance or help, such as rescue or relief efforts.
72 hours or 3 days
A survival kit should have enough supplies and tools that could last at least ___________
Emergency Management
Disaster = Hazard:
Disaster Preparedness
Improves the concept of emergency management by going one step backward before a disaster or crisis happens. This time, people mitigate and possibly prevent the effects of a disaster. Disaster preparedness is geared to safeguard the lives and assets of at-risk people and communities from an imminent threat or disaster. Disaster = Hazard + Unpreparedness:
Disaster
= Hazard x Vulnerability / Capacity
Disaster Risk
= Hazard x Vulnerability x Exposure / Capacity
Disaster Management Cycle
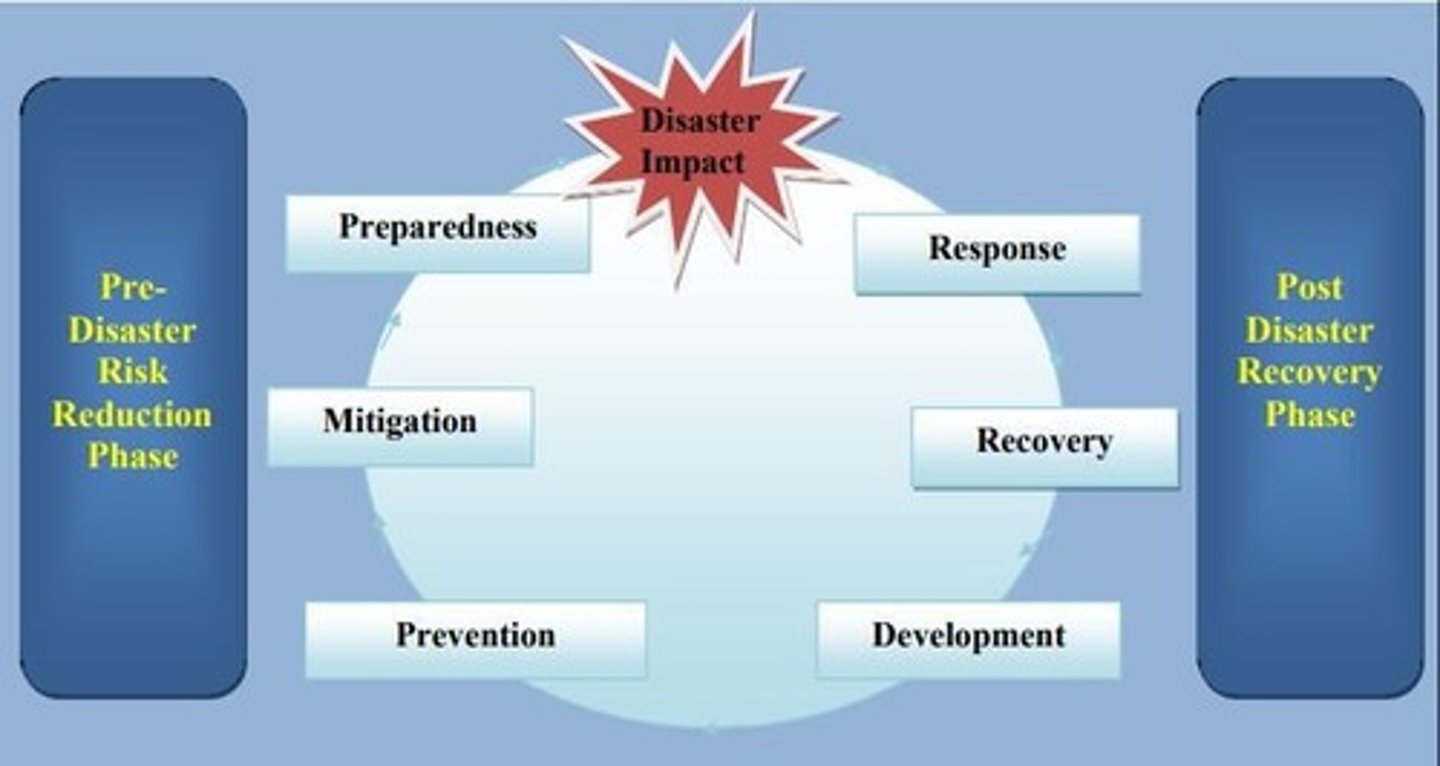
Disaster Risk Management
It is the systematic process of using administrative decisions, organizational skills, and available capacities to implement policies, strategies, and coping mechanisms within society and communities to reduce the impact of natural hazards, as well as environmental and technological disasters. This approach includes all types of activities, both structural and non-structural, aimed at preventing or mitigating the adverse effects of hazards.
Disaster risk reduction
It is defined as "the conceptual framework encompassing elements designed to minimize vulnerabilities and disaster risks across a society, aiming to avoid (prevention) or limit (mitigation and preparedness) the negative impacts of hazards within the broader context of sustainable development" (ISDR, 2007). The disaster risk reduction model illustrates how each component of disaster risk management must work towards reducing risks.
Prevention
This involves actions to completely avoid or minimize the impact of hazards and related disasters. Investing in such measures is justified in high-risk areas based on feasibility and cost-benefit analysis. Public awareness and education play a key role in fostering a"culture of prevention "by changing attitudes and behaviors.
Mitigation
This includes structural measures, like engineering works and hazard-resistant construction, and non-structural measures, such as awareness-raising, knowledge development, and policy creation for land use and resource management.
Preparedness
This involves pre-disaster activities based on risk analysis, including developing or improving preparedness strategies, policies, structures, warning systems, and plans to help at-risk communities protect lives and assets by responding effectively to hazards and imminent threats.
Relief / Response
This refers to providing assistance during or immediately after a disaster to preserve life and meet basic needs. Relief and response operations can be immediate, short-term, or extended.
Recovery
This includes structural measures, like engineering works and hazard-resistant construction, and non-structural measures, such as awareness-raising, knowledge development, and policy creation for land use and resource management.
Development Planning Process
This involves proactive actions that allow national, sectoral, regional, or local government and its partners to support and engage the intellectual, physical, and economic resources to chart a course toward a desired future of development related to each level.
THE HYOGO FRAMEWORK FOR ACTION 2005 to 2015
At the World Conference in Kobe, Japan, Disaster Risk Reduction (January 18-22,2005), 168 countries, including the Philippines, adopted the Hyogo Framework for Action (HFA) 2005-2015. The HFA addresses disaster impacts and highlights disaster risk reduction as crucial for development and various fields.
SENDAI FRAMEWORK FOR DISASTER RISK REDUCTION 2015-2030
Following the end of the HFA in 2015, the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction 2015-2030 (Sendai Framework)was endorsed by the UN General Assembly during the 2015 Third UN World Conference on Disaster Risk Reduction (WCDRR). It has seven targets and four priorities for action.