Entomology Midterm Practice
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
Hexapoda (insects)
2-30 million
monophyletic (origin of shared, derived trait
cambrian explosion
phylum arthropoda
main extant groups of arthropods: insects, crustaceans, myriapods, chelicerates
body segmented with jointed paired appendages, repeated tagma segments
5 main groups (subphylum) of phylum arthropoda
trilobitomorpha (extinct)
crustacea
hexapoda (mostly Insecta)
myriapoda
chelicerata - arachnids and allies
subphylum chelicerata
1st pair of appendages: chelicerae
developmentally different mouthparts
2 tagma: cephalothorax and abdomen
subphylum crustacea
1st 2 pairs of appendages modified into sensory organs like antennae
7 pairs of walking legs
2-3 body regions
subphylum myriapoda
class chilopoda and diplopoda (centipedes and millipedes)
1st pair of segments = antennae
mouthparts are mandibles instead of chelicerae
subphylum hexapoda
3 body regions: head, thorax, abdomen
3 pairs of walking legs
1st pair of appendages are antennae
evolutionary success of Hexapoda
Long evolutionary history - among earliest land colonists
High rates of evolution - large populations, short gen. times
Small body size - many ecological niches
Flight - escape and migration
Diapause - resting stages which endure unfavorable conditions
Complete metamorphosis - separate feeding lifestyles for larvae and adults
Exoskeleton - great adaptability
Hexapod groups 4 significant develpment events
position of mouthparts (entognatha vs extognatha
presence of wings (apterygota vs pterygota
wing folding (paleoptera vs neoptera
development of complete metamorphosis (exopterygota vs endopterygota
3 basic types of metamorphosis
ametabolous - no metamorphosis. entognatha, apterygota
hemimetabolous - incomplete metamorphosis. paleoptera, exopterygota
holometabolous - complete matamorphosis. endopterygota
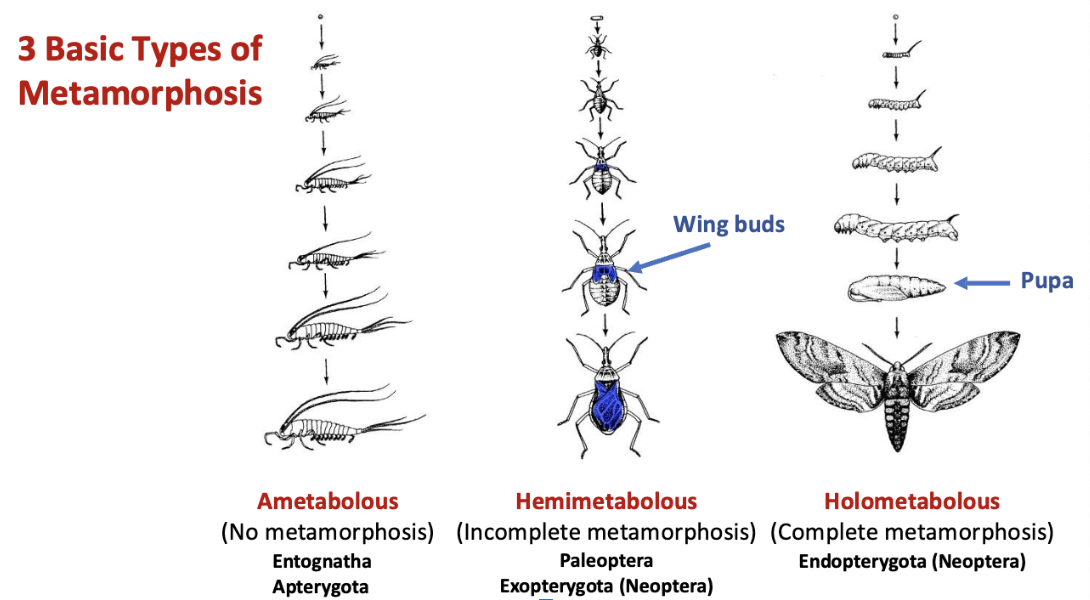
Endopterygota (holometabola)
complete matamorphosis
egg > larva > pupa > adult
larva looks different from adult
wings develop internally during pupal stage
beetles, butterflies, flies, bees
exopterygota
incomplete metamorphosis
egg > nymph > adult
nymph resmbles adult but lacks wings and sexually immature
wings develop externally as wing pads
grasshoppers, cockroaches, true bugs, dragonflies
entognatha
mouthparts surrounded by head capsule
collembola
diplura
protura
Ectognatha (Insecta)
great majority of hexapods
apterygota (primarily wingless)
pterygota (ancestor with wings)
Order Collembola - sprintails
3 tagmata
3 pairs of legs
Furcula, tenaculum, collophore
Encapsulate mouthparts
No tracheal respiratory system
Indirect copulation
Order zygentoma - silverfish, apterygota
Wingless, flattened
Long antennae
3 equally long filaments
Small or absent eyes
Scavengers
Under bark
Urban settings
Order ephemeroptera - mayflies (paleoptera infraclass)
Large fore wings, small hing wings
Very short antennae
Adults have 2 or 3 cerci
Larvae: gills
Order odonata - damselflies, paleoptera
Large eyes
Predatory
Arvae: external gills at the end of abdomen
Slender abdomen
Wing folded at rest
Order odonata - dragonflies, paleoptera
Large eyes
Predatory
Larvae: internal gills at the end of abdomen
Wide abdomen
Wing held open at rest
Order grylloblattodea - orthopteroids, icebugs/ice crawlers - exopterygota
Incomplete metamorphosis
Wingless
Cold adapted
Snow pack, glavier, ice cave
3 places on earth: pacific northwest, east asia, rocky mountains in northern us and canada. Canadian national insect
Order phasmatodea - the orthopteroids, walking sticks, exopterygota
Masters of camouflage
Order orthoptera - the orthopteroids, grasshoppers, crickets, katydids
1st pair of wings robust and leathery (tegmen)
2nd pair of wings membranous
Stridulation
Saltatorial hind legs
Order mantodea - orthopteroids, praying mantids
Exopterygota
Enlarged for legs
Movable head
Voracious female
2 spp introduced, 1 sp native
Order blattodea - cockroaches
Round bodies
Round pronotum
Long antennae
Around 30 spp associated with human habitats
Order blattodea infraorder isoptera (termites)
Eusocial insects
Parental care
Division of labor (caste) - workers, soldiers, queens
Digest wood-fiber (symbiont protists)
Exopterygota
chelicerata appendages
no antennae
chelicerae (mouthparts)
pedipalps (small limbs used in sex and or feeding)
8 walking legs
mandibulata
basic mouthparts: mandibles, maxillae
tagma / tagmata
specialised grouping of multiple segments
head, thorax and abdomen
prognathous
mouth parts positioned forward

hypognathous
mouthparts positioned downward
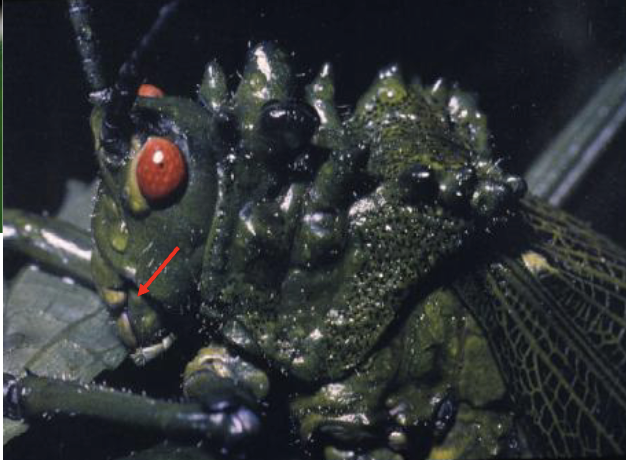

ophistognathous
mouthparts positioned backward

tentorium / endoskeleton
internal cutivular structure for muscle attachments and strength
filiform antennae
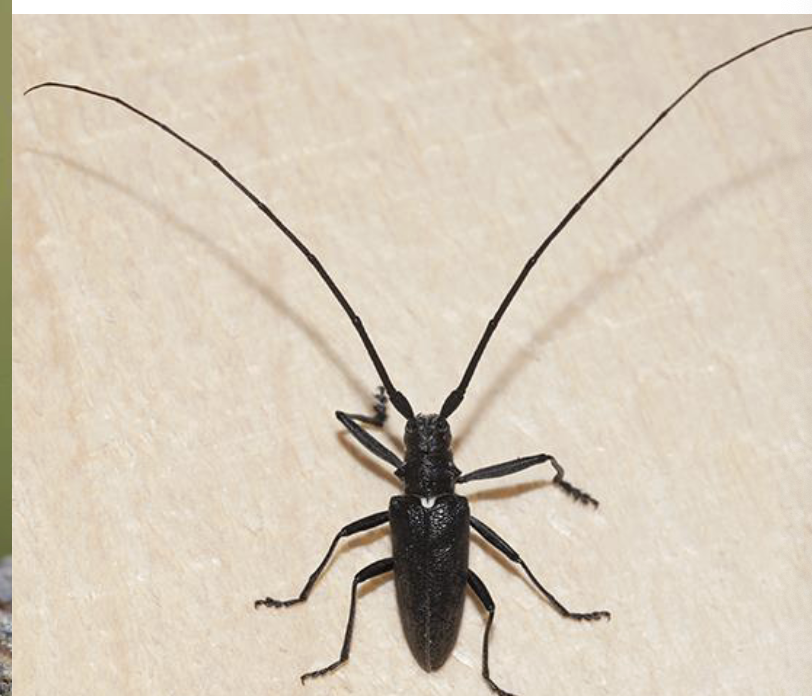

plumose antennae

thorax segments
prothorax
mesothorax
metathorax
exoskeleton (integument)
protects internal organs and tissues
protective and preventative barrier
needs to be molted to allow growth
ectodermal tissue (foregut)
cuticular lining
ingests, processes food
endodermal
secretion, absorption
midgut
ectodermal tissue (hindgut)
cuticular lining
absorption, excretion
peritrophic membrane
very efficient high flux sieve
selectively transports substances through the membrane
insect guts
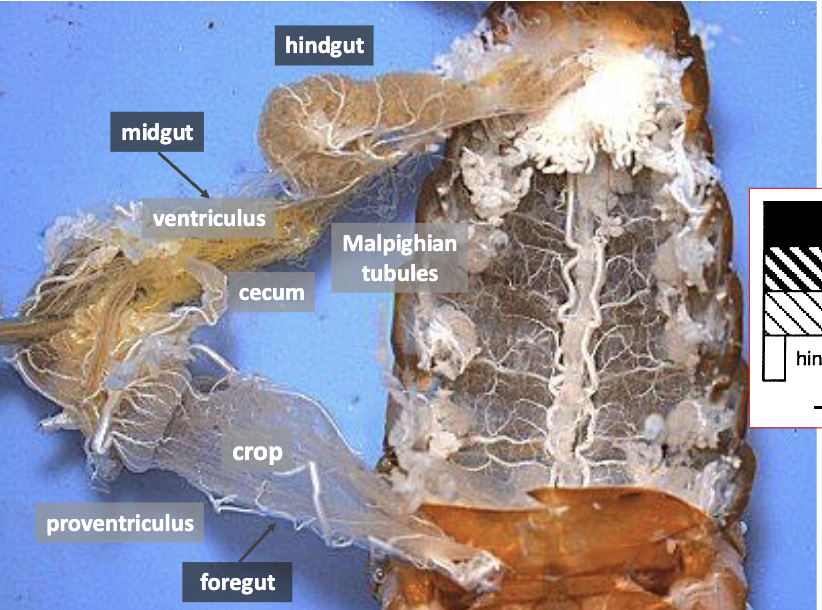
foregut
store ingested food
fermentation chamber in scarab larvae
midgut
columnar and secretory cells
mycetomes house bacterial symbionts, help with digestion
filter chamber: midgut modified for liquid diets, honey dew
hindgut
malpighian tubules primary organ for excretion
fat bodies
center of metabolism
analogous to vertebrate liver
storage, synthesis, breakdown, release nutrients
hemocytes
insect blood cells, no O2, protection, transfer hormonal products
tracheal system
carries oxygen in and C02 out
reproduction methods
swarming - mayflies, scarabs
hilltopping - butterflies
nuptial gifts, short range courtship
sex pheromones
females produce, males detect plume
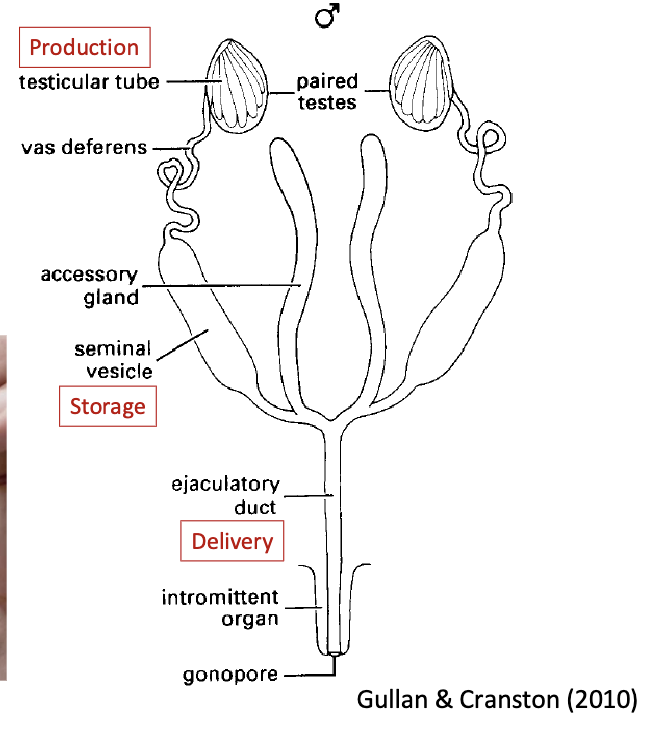
male reproduction systems
production, storage and delivery of sperm
supply female with nutrients
regulate female fecundity
spermatophore
protein envelop that contains sperm
spermatophylax
a non sperm portion of spermatophore eaten by female
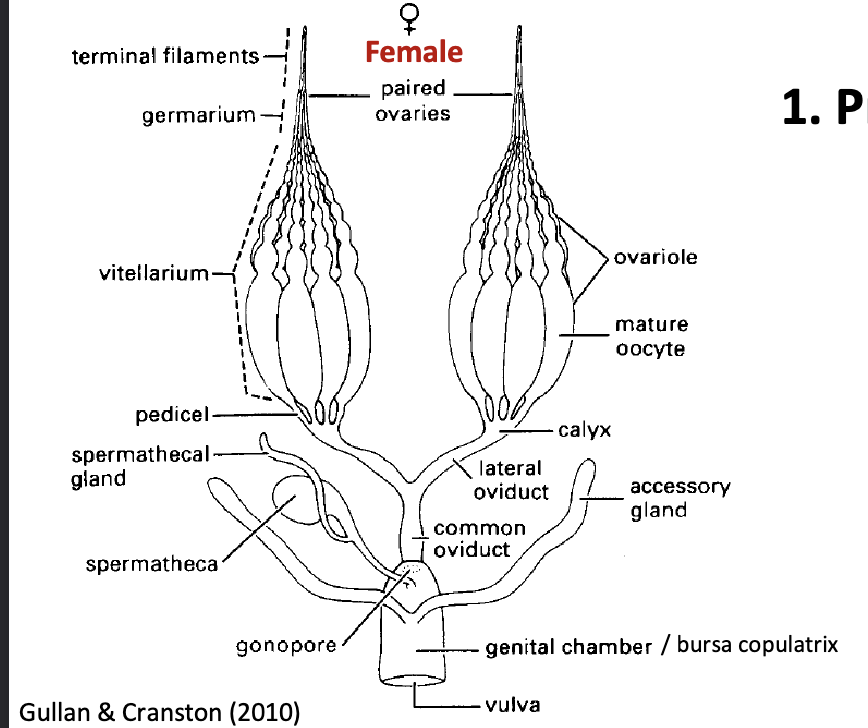
female reproduction systems
production of eggs
sperm reception/storage
fertilization
oviposition
vitellogenesis
development of egg cells
oogenisis
nutrient moved into the eggs
oosorption
eggs are resorbed
neuron
cell type that transmits information
action potential
occurs when a neuron sends information down an axon
dendrite
where nerve impulses start, an energy transducer. converts light, chemical, or physical kinetic energy to electricity
3 types of neurons
monopolar
bipolar
multipolar
central nervous system (CNS)
brain + subesophageal ganglion + ventral nerve cord
visceral system (VS)
corpus cardiacum + corpus allatum (controls guts, endocrine organs, reproductive and treacheal systems)
insect sensory systems
photosensilla (vision, UV, photoperiod)
mechanosensilla (hearing, touch)
chemosensilla (smell, taste)
thermosensilla (IR infrared detection)
hygrosensilla (humidity)
photosensilla - sight
specialized structures sensitive to light
stemmata, ocelli, compound eyes
mechanosensilla - hearing
exocuticular, endocuticular
trichogen, tormogen, sense cells
scolopale
actual transducer that converts mechanical energy to nerve impulse
sounds percieved by mechanosensilla
mate attraction, species recognition (differences in stridulation songs), antipredator adaptations
chemosensilla
smell, taste
odor receptor: generally located in insect antennae, setae with many pores
taste receptor: uniporous, fewer nerve endings. mostly located in maxillary and labial palps
role of pheromones
sex
aggregation
alarm
trail
host marking
pheromones
chemicals that induce behavioural or developmental responses between individuals of the same species
thermosensilla
pyrophilic insects have infrered receptors
hygrosensilla
detect changes in air moisture
impacts of severe defoliation
reduction in photosynthesis
interference of transpiration
interference of food translocation
root mortality because of disruption of nutrient movement
defoliators
lepidoptera (larval butterflies and moths)
hymenoptera (larval sawflies, leaf cutting ants)
diptera (larval flies with leaf and bud mining habits)
coleoptera (adults and larvae esp leaf beetles and weevils)
phasmatodea (walking sticks and leaf insects)
orthoptera (katydids)
lepidoptera
scales are modified and flattened setae
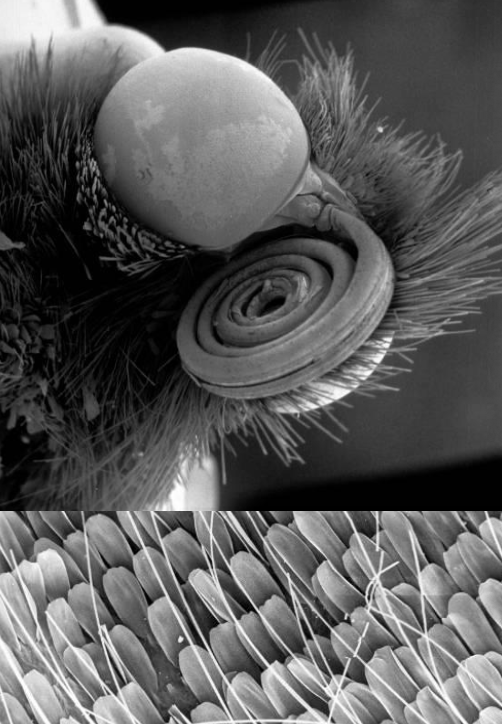
lepidoptera vs hymenoptera
lepidoptera: 5 or less prolegs
hymenoptera (sawfly): more than 5 pairs prolegs
family gracillaridae (defoliators) - leaf miners and blotch leaf miners
larvae develop within the leaf
univoltine, not economically important
premature leaf drop
pattern of leaf mine and host plant can be diagnostic

family coleophoridae (defoliators) - casebearers
leaf mining > construct a case
exotic invader from europe
outbreaks can last up to 10 yrs

family Psychidae (defoliators) - bagworms
cedar, juniper, white pine
make bags as soon as they hatch
females stay in bag and lay 500-1000 eggs

family Cossidae (defoliators) - carpenterworms
attacks hardwoods, poplar
2-4 years development
200-800 eggs in bark
no defoliators

family Erebidae (defoliators) - subfamily arctiinae
moths

family Notodontidae (defoliators) - prominents
gregarious feeders as early instars
various hardwoods

family Nymphalidae (defoliators)
elms, poplars and willows
gregarious feeding of entire branches
camouflage

family Saturniidae (defoliators) - giant silkmoths
not economially important
distinctive feeding pattern (consumes entire leaf then cuts petiole)

family Sphingidae (defoliators) - hawkmoths and hornworms
aerodynamic, good fliers
larva have horns

family Sesiidae (defoliators) - clearwing moths
transparent wings
transverse yellow/orange bends across abdomen
long narrow forewings

defoliators big 5
leaf rollers
budworms
tent caterpillars
loopers/inchworms
spongy moth
family Tortricidae (defoliators) - leafrollers and budworms
eastern and western spruce budworm
large aspen tortix

family Lasiocampidae (defoliators) - tent caterpillars
communal tent spinning
thermoregulation
mass anti predator displays
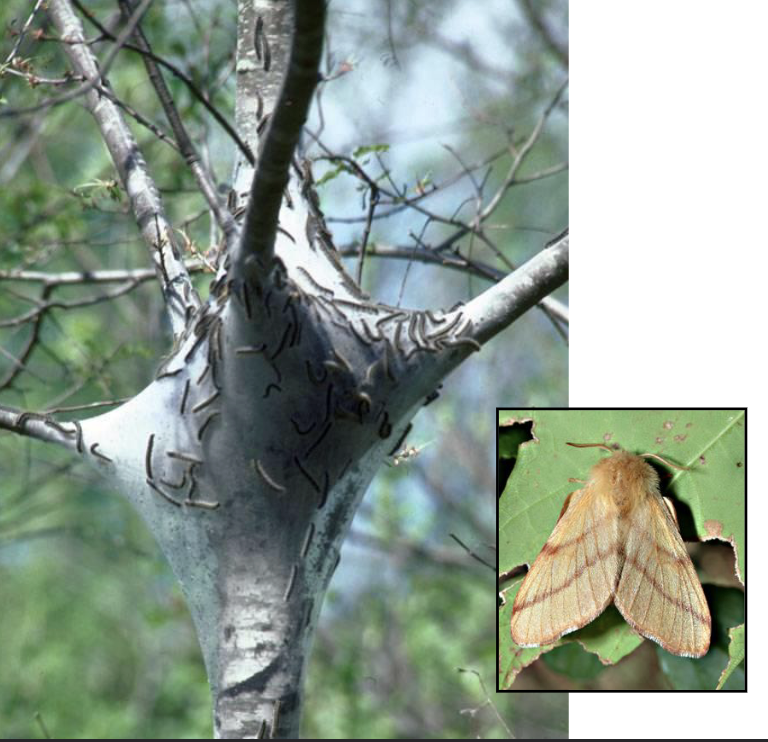

family Geometridae (defoliators) - loopers and inchworms
2-3 pairs of prolegs at end of abdomen, move by looping

family Erebidae (defoliators) - tussock moths
sexual dimorphism
some of most costly forest pests
