GEOL 109 - BYU - FINAL REVIEW
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Io has tidal forces that pull on the moon while it orbits Jupiter and it creates friction of the surface that allows for activity of volcanism to continue
Io has an eccentric and elliptical orbit
it is pulled into different shapes based on its proximity and position to Jupiter
causes tidal heating through friction
Few geologic processes driven by internal energy are still active on the small inner planets (like the Moon and Mercury), whereas Io, another small "planet," has a very young surface and active volcanoes. Why?
If there is a heavily cratered surface its older, if its younger its smoother.
Impact cratering is a fundamental geologic process. Describe a generalized cratering history for a planet. Make sure you explain how the number of impact craters on a planet's surface is related to its age.
It accreats and while it heats up it has differentiation, the iron moves to the core the silicates move to the mantle and as it goes outward the materials become lighter in density
Describe a typical thermal history of a silicate planet. If there are significant deviations from this scenario describe them
No atmosphere's change. for example earth had a lot of carbon dioxide and as life and certain rocks came about it added more oxygen to the atmosphere
Once an atmosphere is outgassed, does its composition or mass stay constant? Give examples of some changes in planetary atmospheres
It has to do with heat and where it comes from. Earth has a lot of internal heat which is why it still has a lot of tectonic activity today.
Why are some planetary bodies tectonically active today and others are not?
Because of their closeness to sun the less dense materials dissipate faster than the outer planets
solar thermal gradient
Why are the inner planets dense and rocky when compared to the outer planets?
Old/young surface
There is volcanisms/not
Liquid/not
Density shows if its closer to sun/not and type of materials probably present
Is atmosphere thick/not
Color of atmosphere
it has a density of 5.3. Suppose that you had no other information about this planet. What can you infer about its present state and past geologic history from this photo?

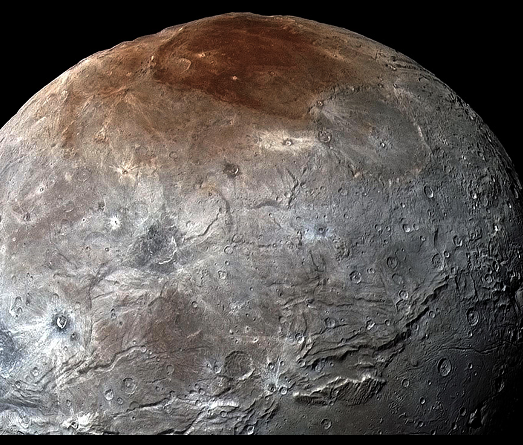
condensed atmosphere of Pluto as it was blown off from Pluto
probably methane from Pluto
How did the red terrain on Charon form? It lies at the moon’s north pole.

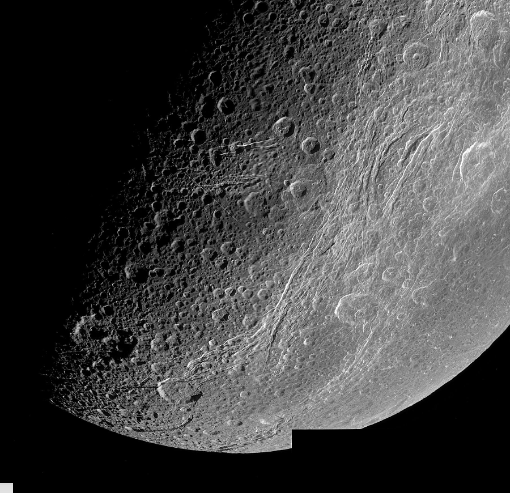
Older surface
Lots of impact craters
tectonic extension seen through the lines
fractures as opposed to mountains
no active flow features so not very tectonically active
low density may suggest that it is icy rather than rocky
low density means farther from the sun
Imagine that this photograph is our first close-up picture of an extrasolar planet called Incognita in the Alpha Beta system.
Incognita has a density of about 1.3 g/cm3.
We think that this solar system formed 5.6 billion years ago.
Suppose that you had no other information about Incognita. What can you infer about Incognita’s present state and past geologic history from this photo?

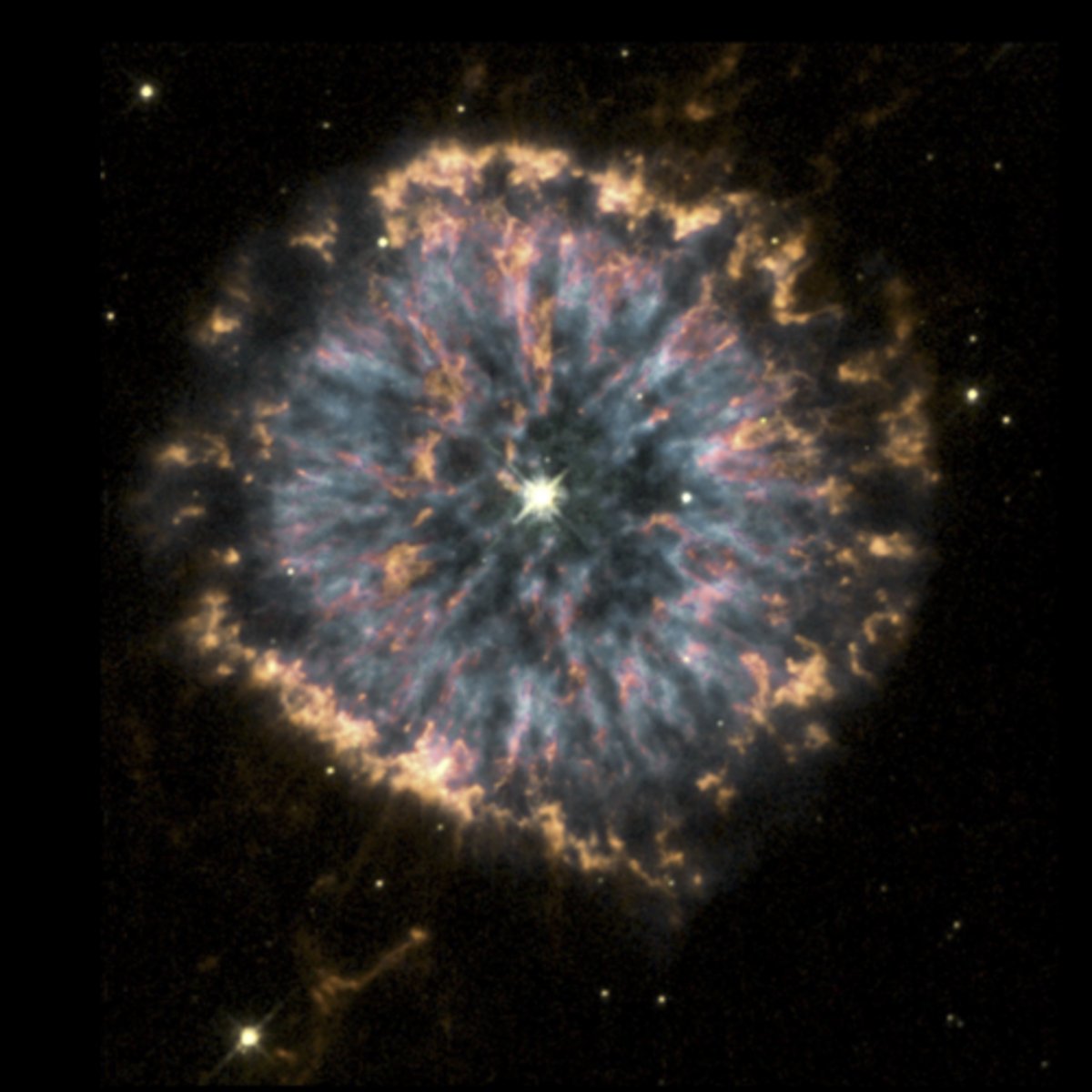
Planetary nebula - when medium sized star can’t hold onto their materials anymore and basically explodes
occurs when medium sized star dies, like the sun
it creates a cool cloud of dust and gas
How did this image form?
as basaltic lava cools and then contracts
contraction creates ridge
How do these wrinkle ridges form?

T-Tari stage
sucks in material and shoots out of the poles
What is this?

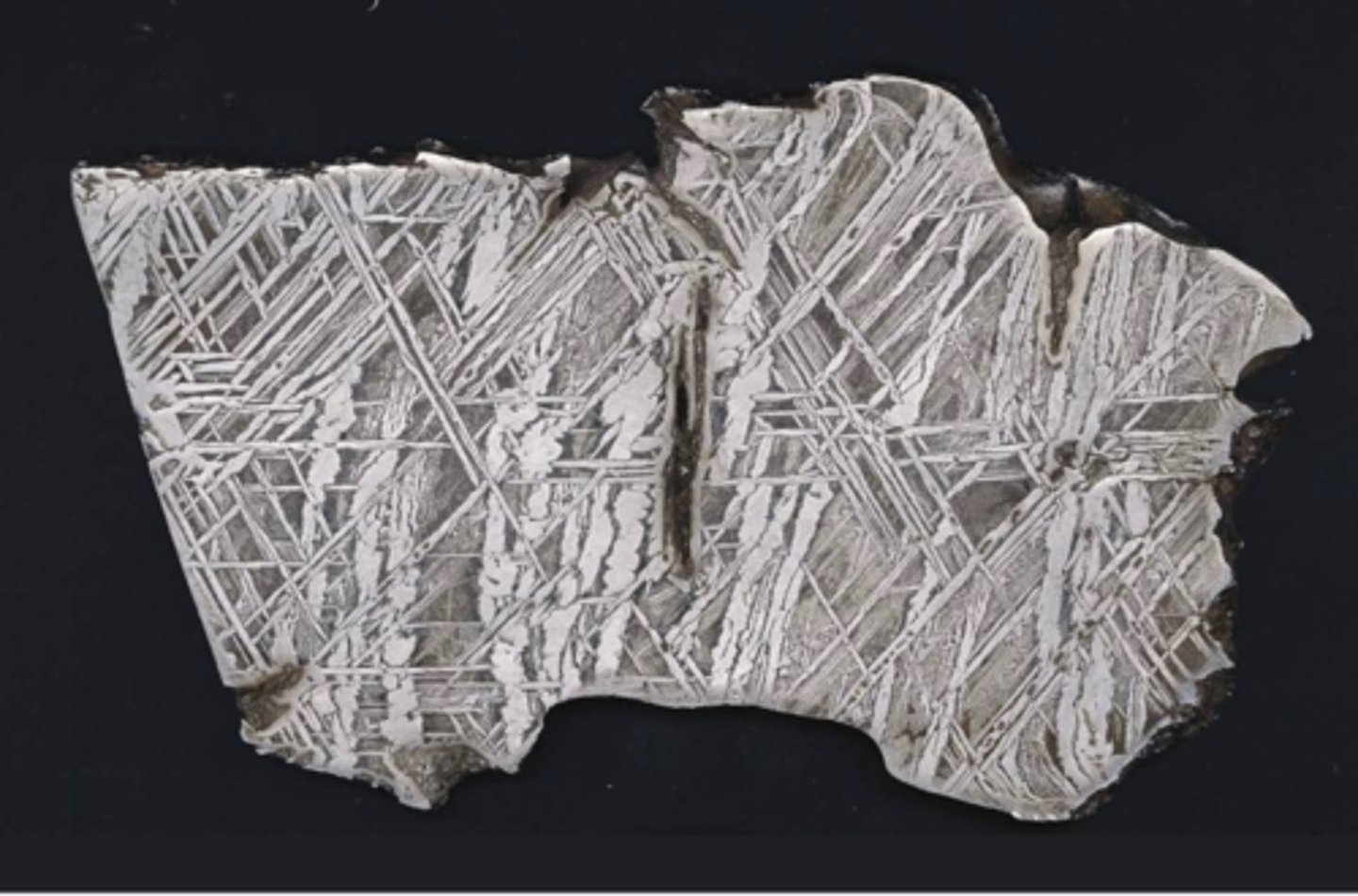
Iron meteorite
no stony evidence
What type of meteorite is this?

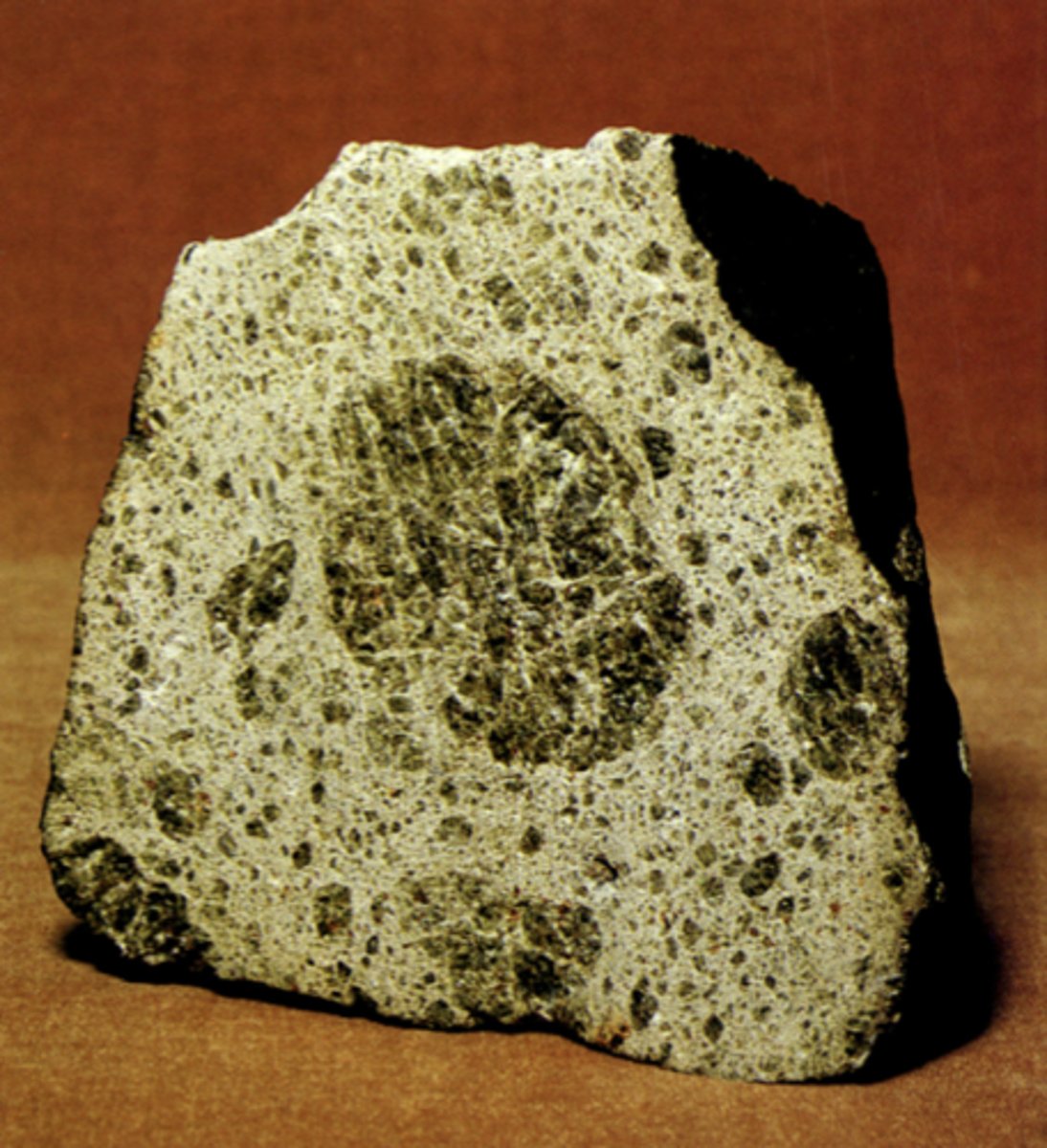
Stony - Chondrite meteorite
chondorite= nodules that contain different materials (like olivine)
What is this?

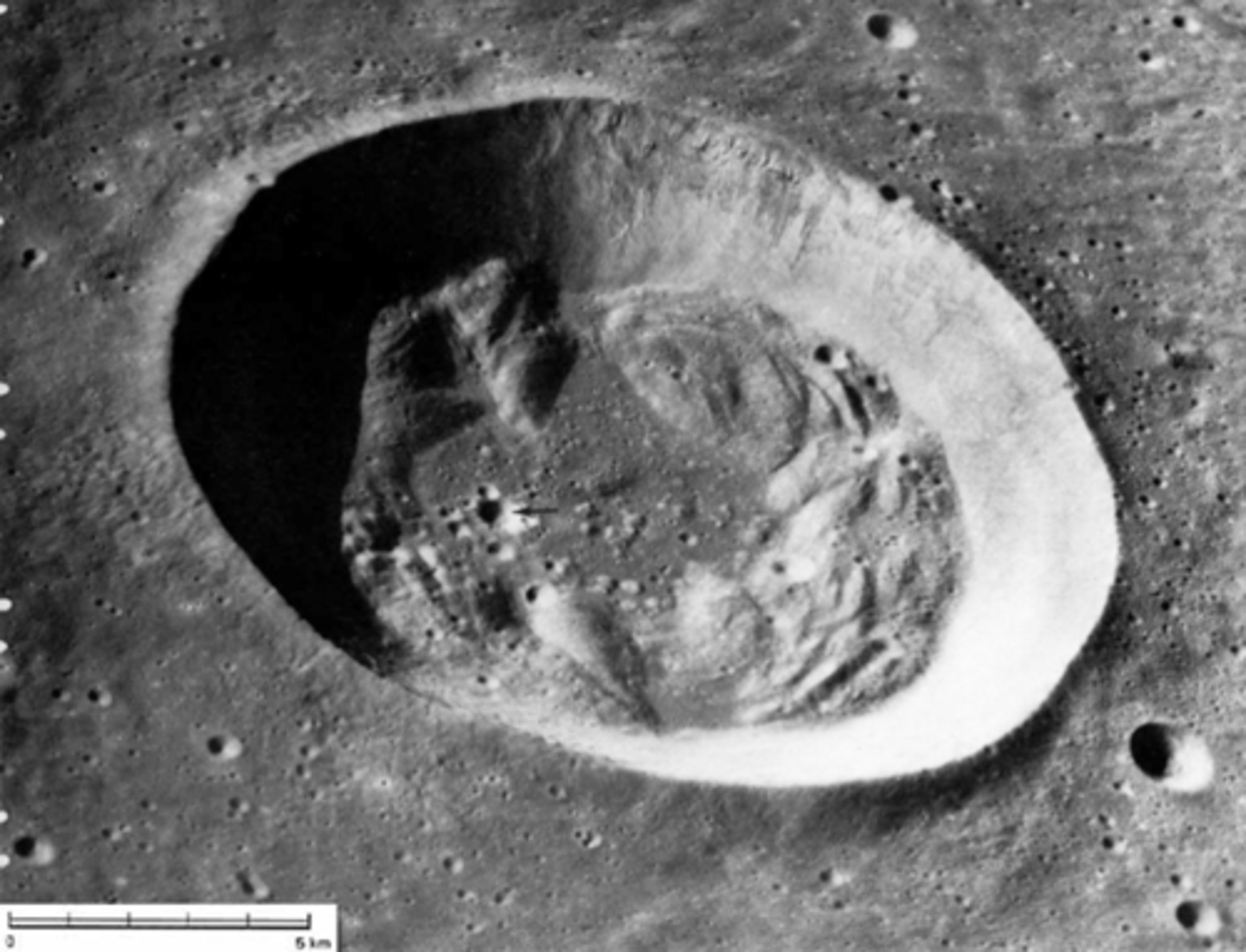
Medium - no multiple rings so a bit bigger than 30 km
not big enough to have rings
Older but more middle aged than ancient
no ejecta blanket
smaller impact craters around it
steep walls
flat floor
material in the center
How large is this crater (on a relative scale)?
How old is the crater (on a relative scale?
Highlands (older, protrude against level of mare)
smooth area= Mare/lava plains (erases the older features)
impact carters
huge multi ring impact basin in the back
The highlands are older bc more craters
What terrains are in this image?
Which is older?

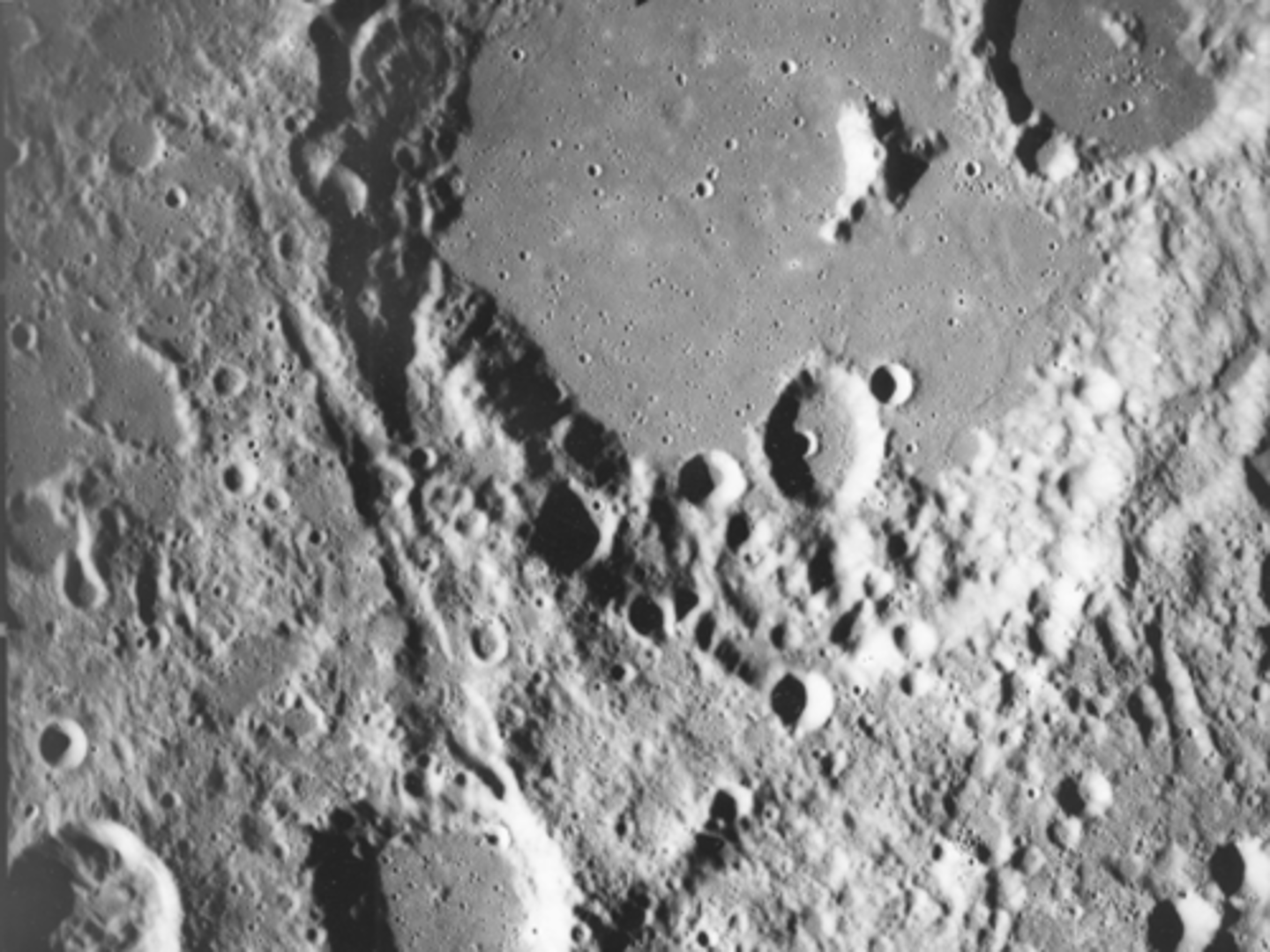
a: Crater rim/edge
b: small impact crater:
c: Flood plains/ mare
d: Sinuous rille
e: Wrinkle ridge
oldest : a (part of it is worn out)
c: wears out other features
e
b
d:cuts across the wrinkle ridge
What features are present in this image?
What are their relative ages from oldest to youngest?

Its older bc they are craters
extensional
What is the age of crater marked by yellow arrows compared to the others in the image?
What is the feature indicated by the red arrow?
Venus- does not have any signs of hydrologic system, but does have lots of volcanics
Lava flow & extensional tectonic features
What planet is this?
What created the sinuous channel and the bright straight lines?
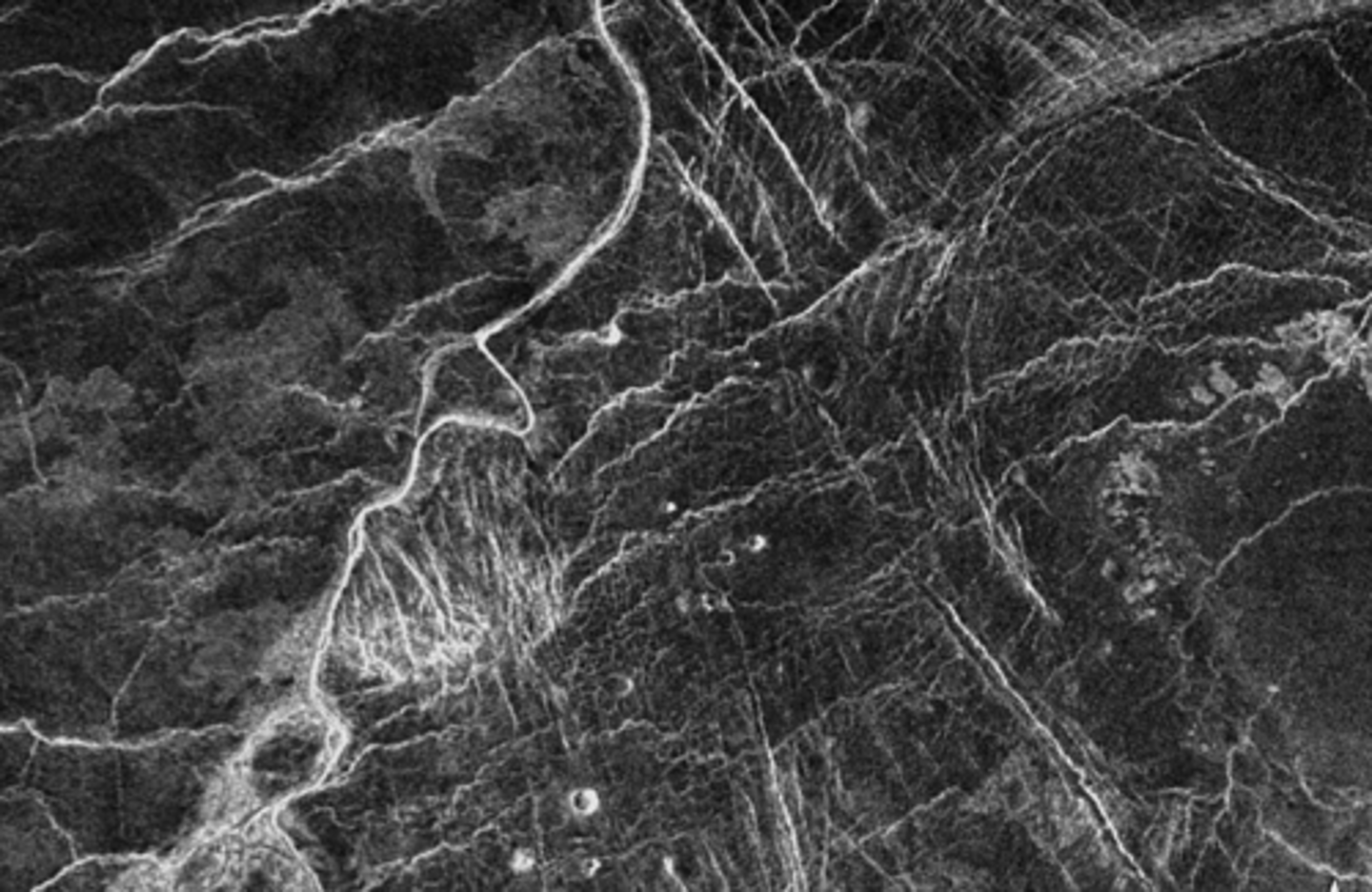

Older than the surrounding stuff
you can barely see it because it is covered by other craters
Palimpsest as the meteor hits it, the ice will go back into the planet which makes it more flat
How old is this light colored area?
How did it form?
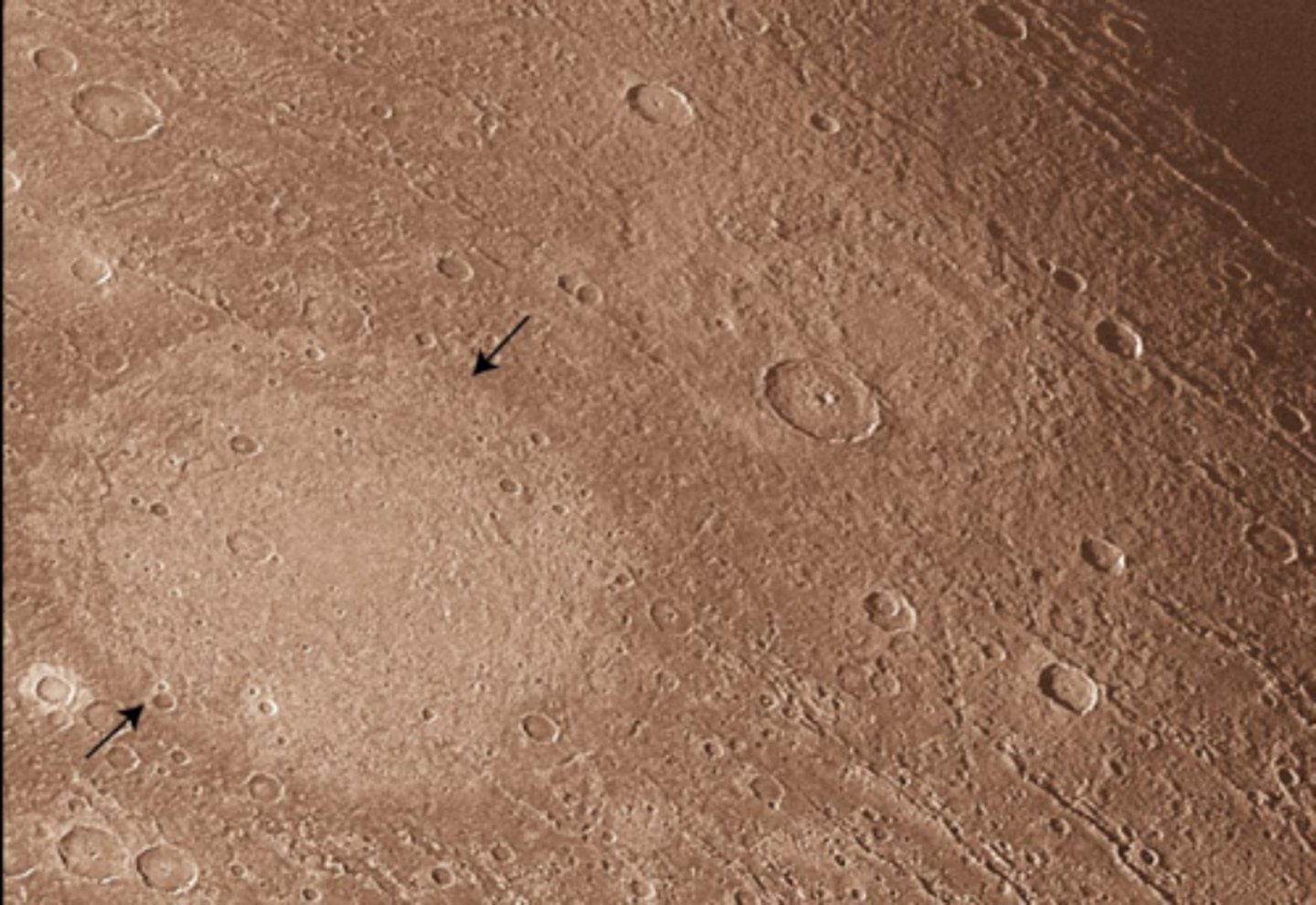

EOLIAN DUNES, wind or eolian process
No
How do these landforms form?
Is this from the Moon?
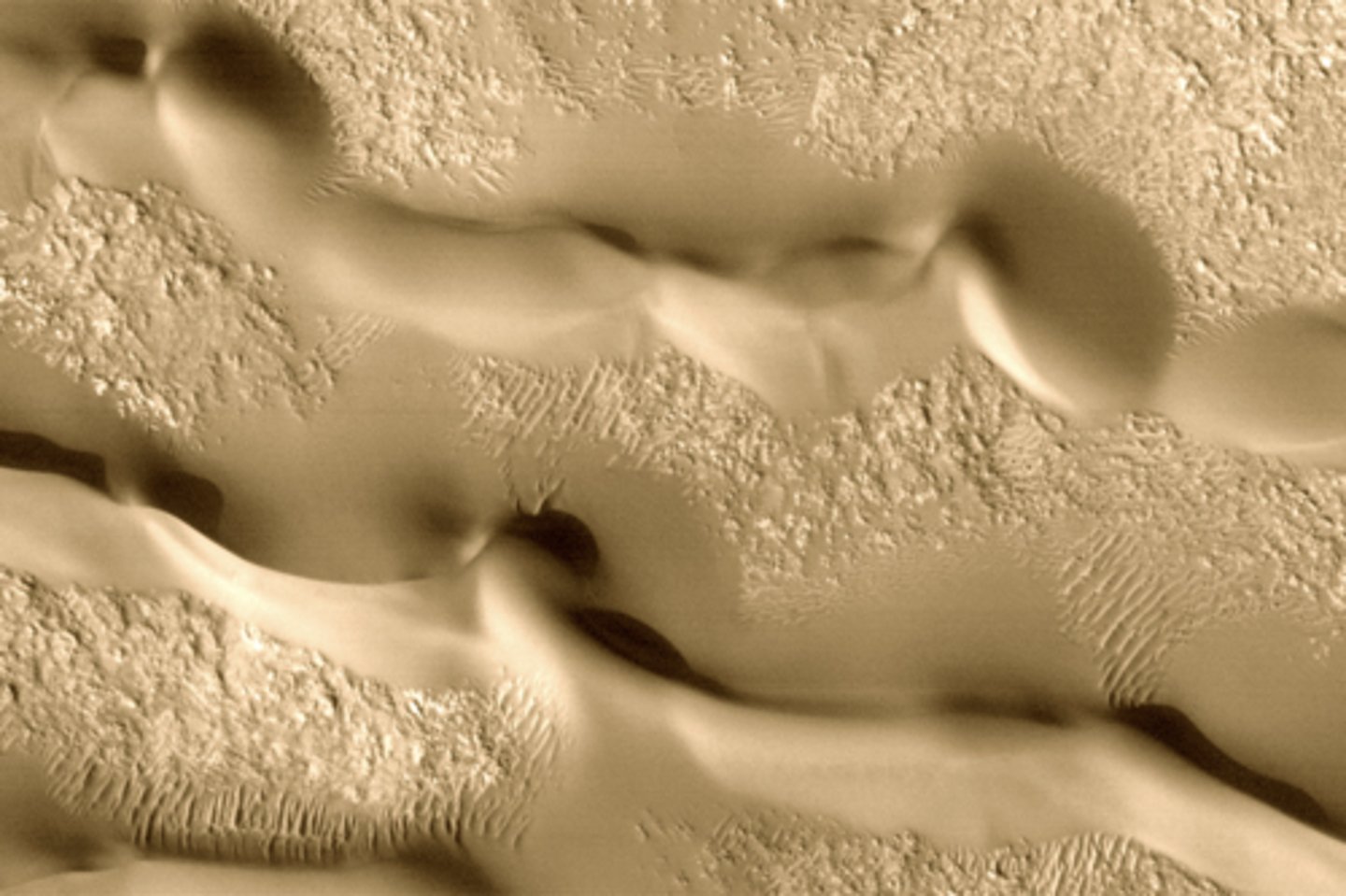

Mars
mud like ejecta planet
impact may have melted some ice and caused a splatter pattern surrounding impact crater
What planet do rampart craters form on?
from dust and gas as the Sun heats up the comets interior and they evaporate
how do the bright streaks form?

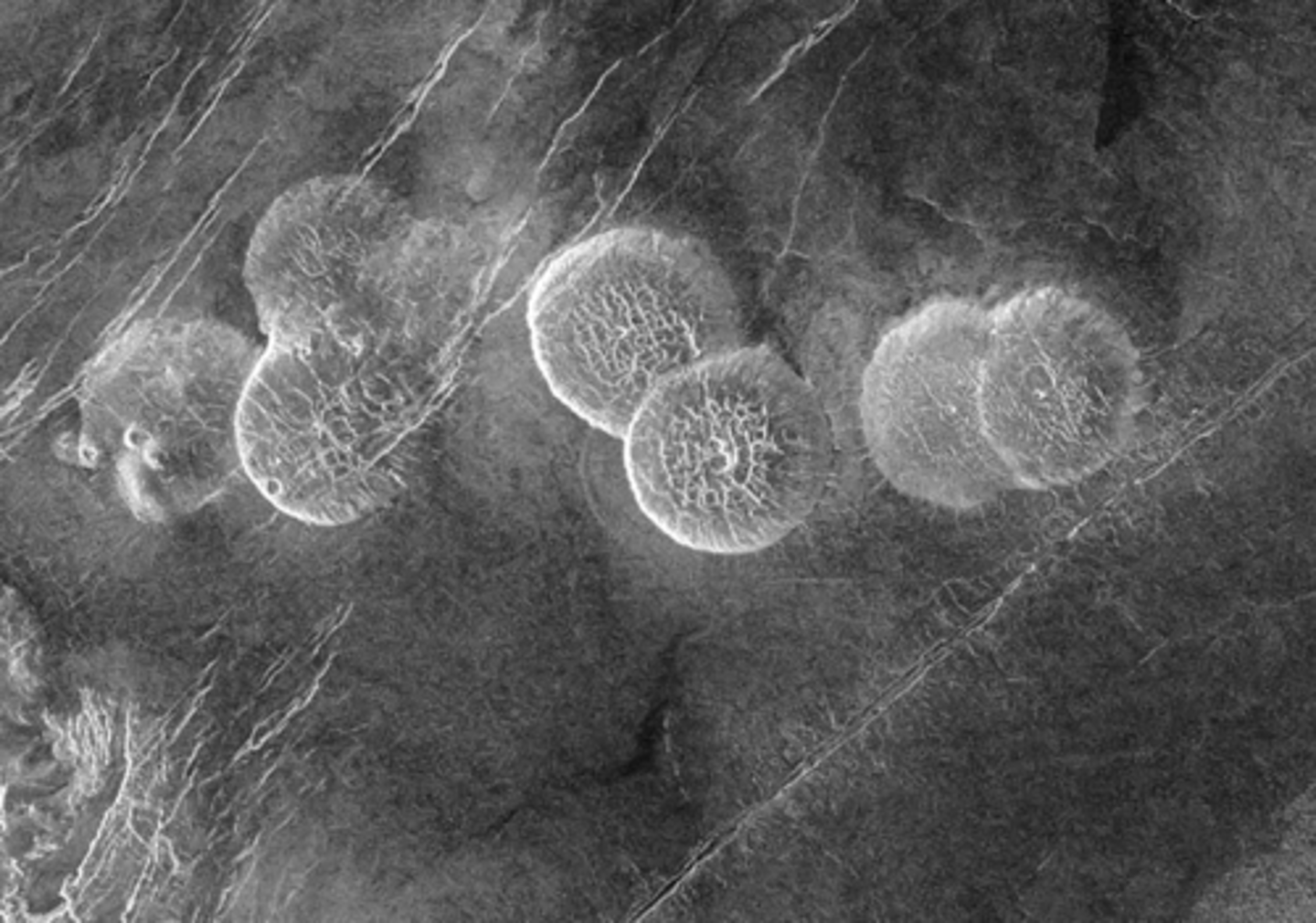
Venus - they are pancake domes
What are these circular features?
extensional features because they are long lines aka rilles
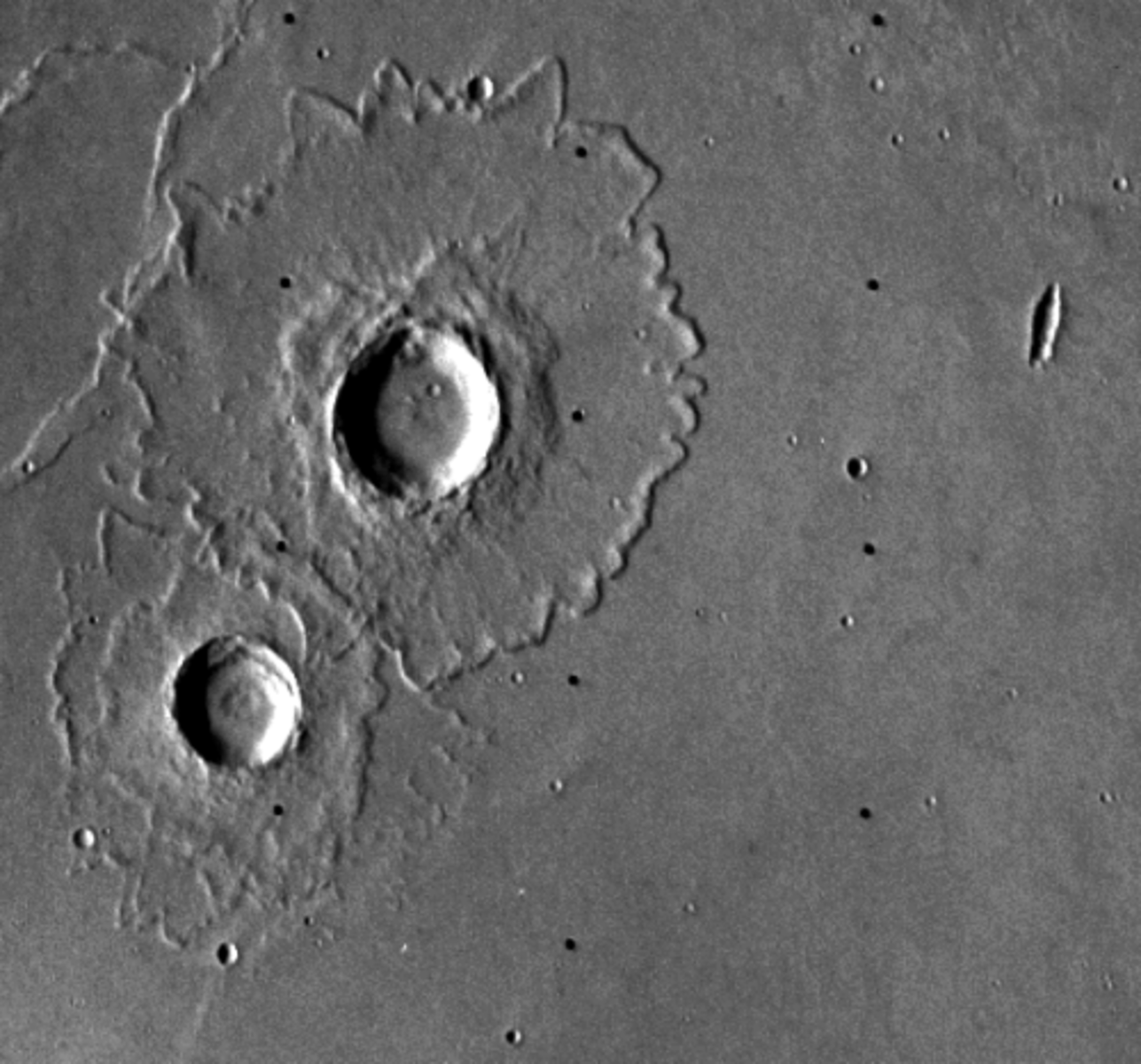
older becasue impact craters appear on top of them
Explain the origins of the lineated terrain? Is it older or younger?
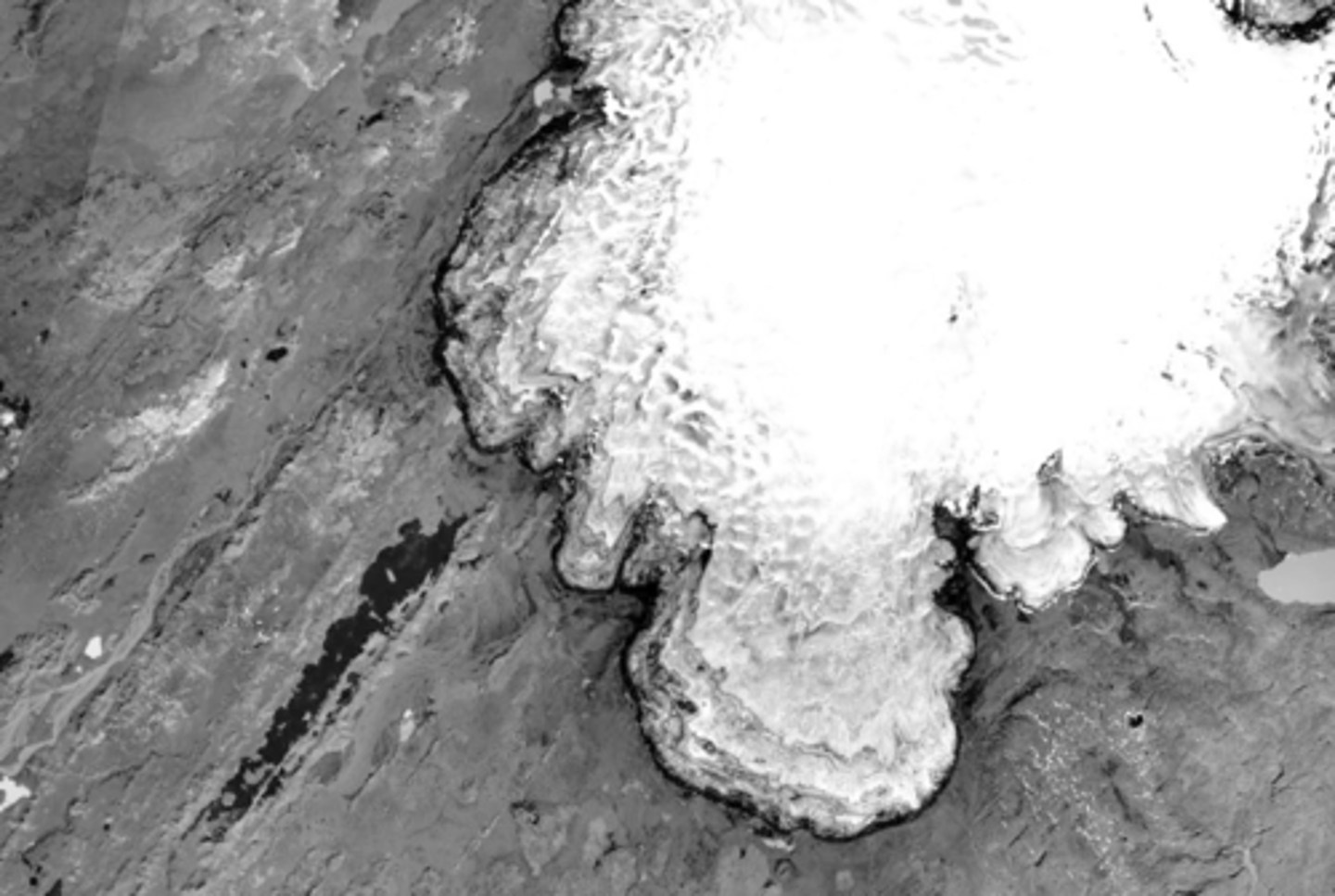
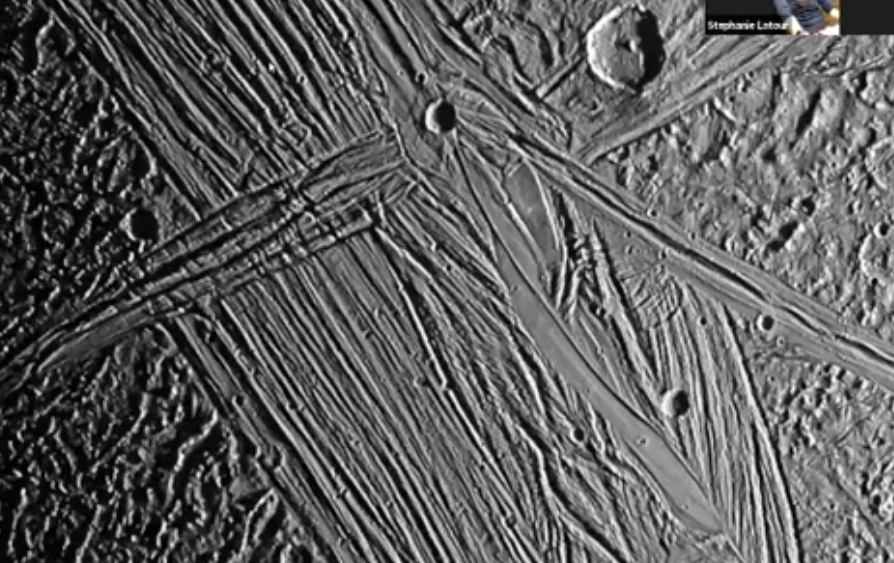

Earth, ice feature/polar cap
What is this feature and where is this
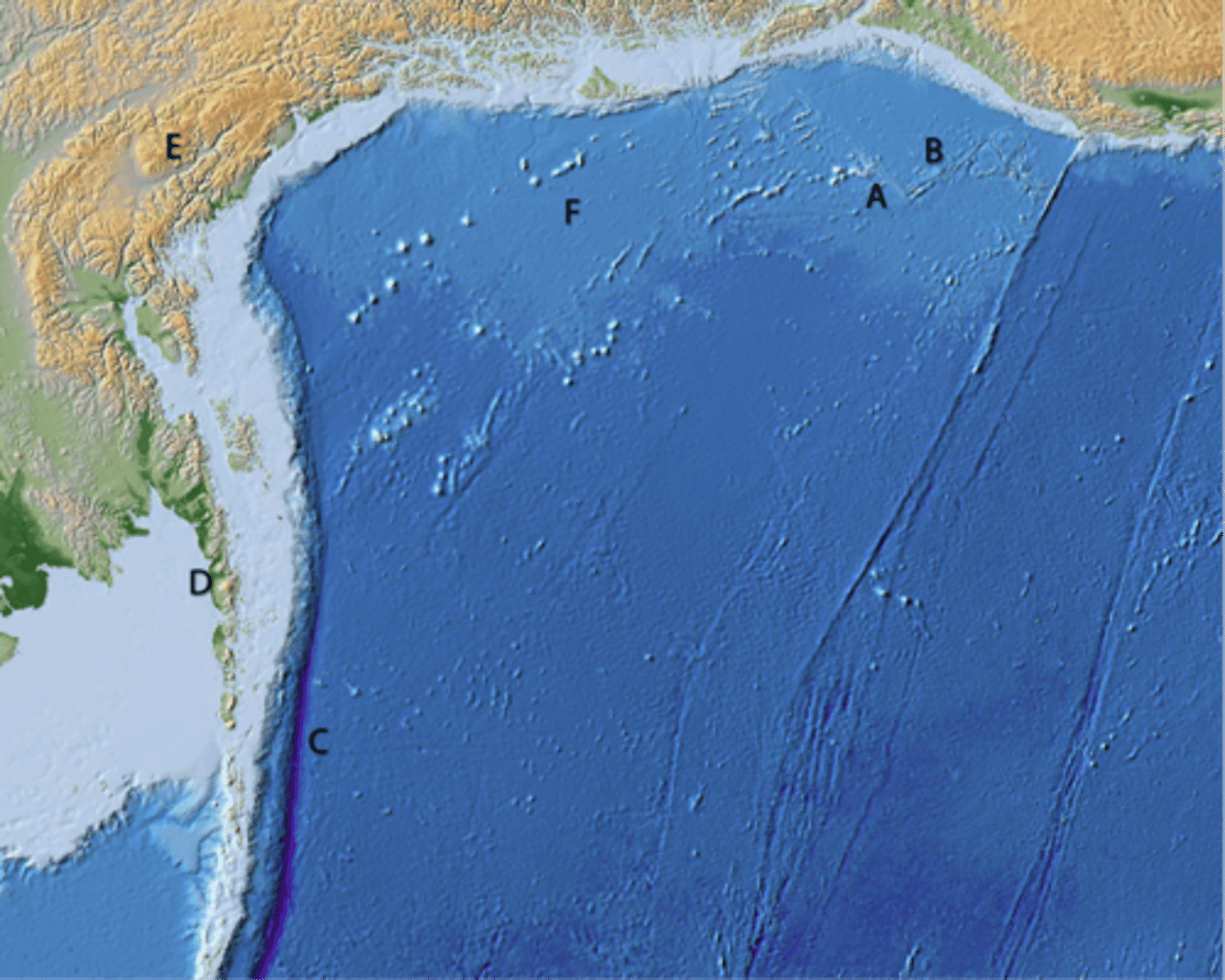
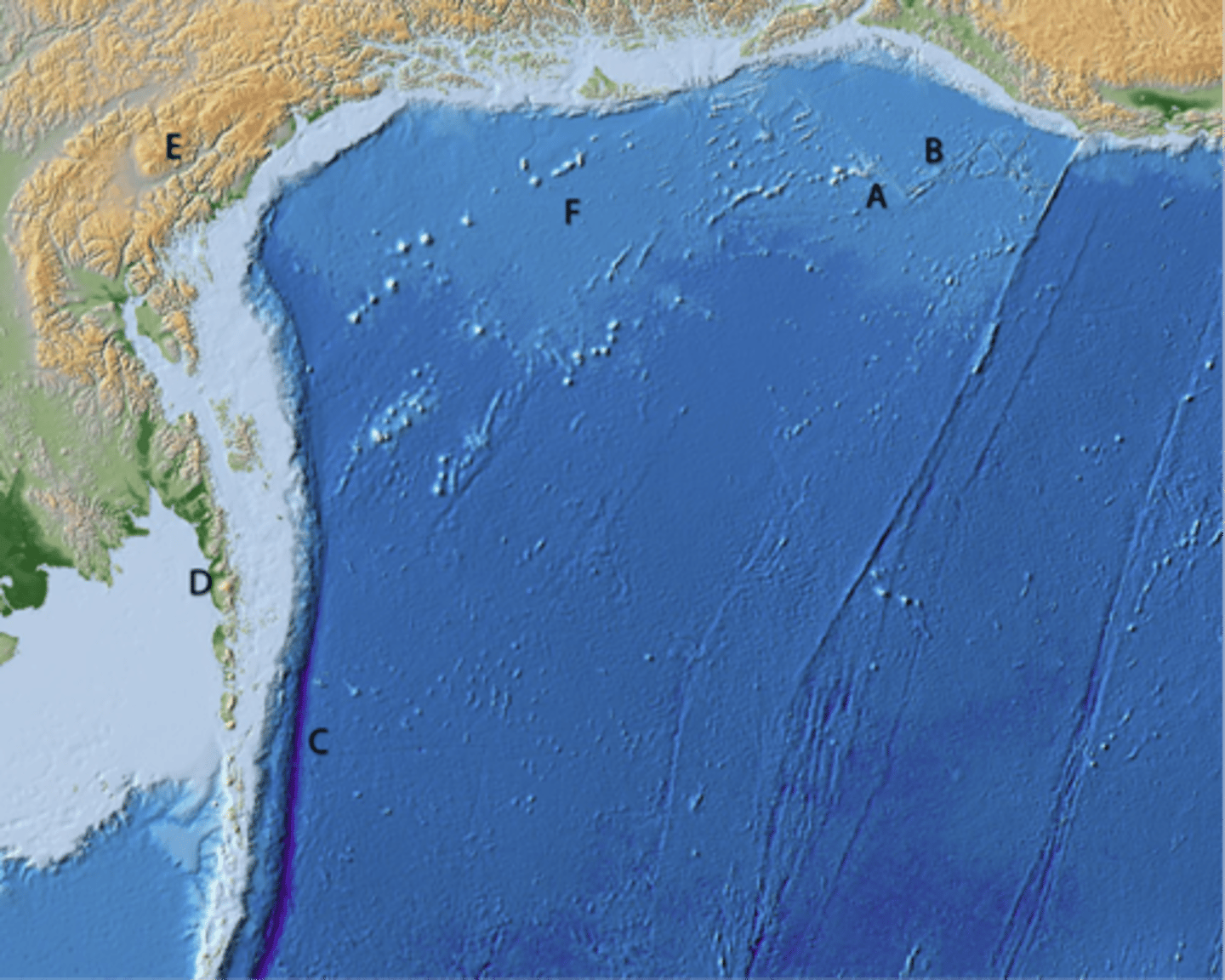
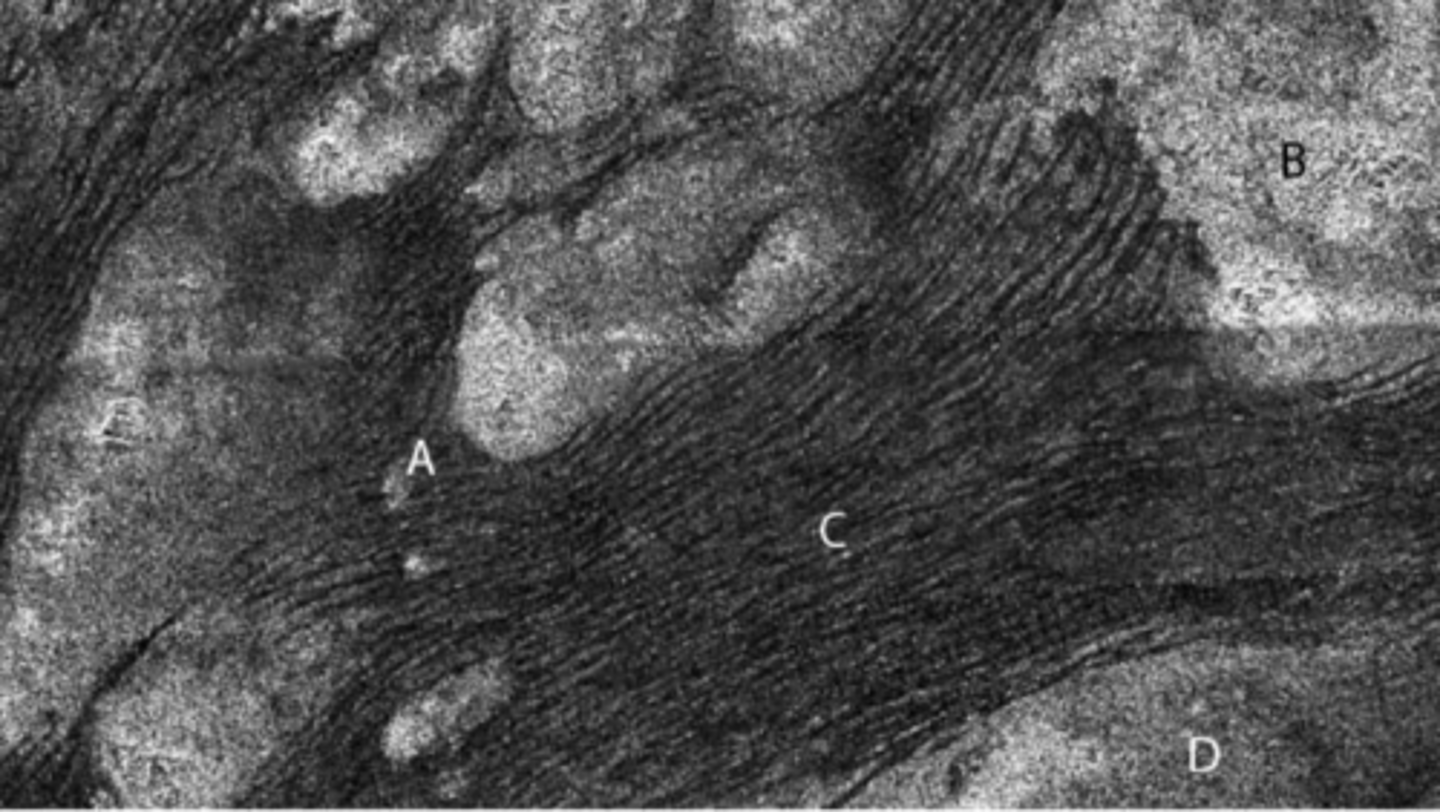
A and E are not
B, C, and D are
What types of tectonic features do the different letters mark?
Are they all plate boundaries?
Io Volcanoes
What are the dark features?
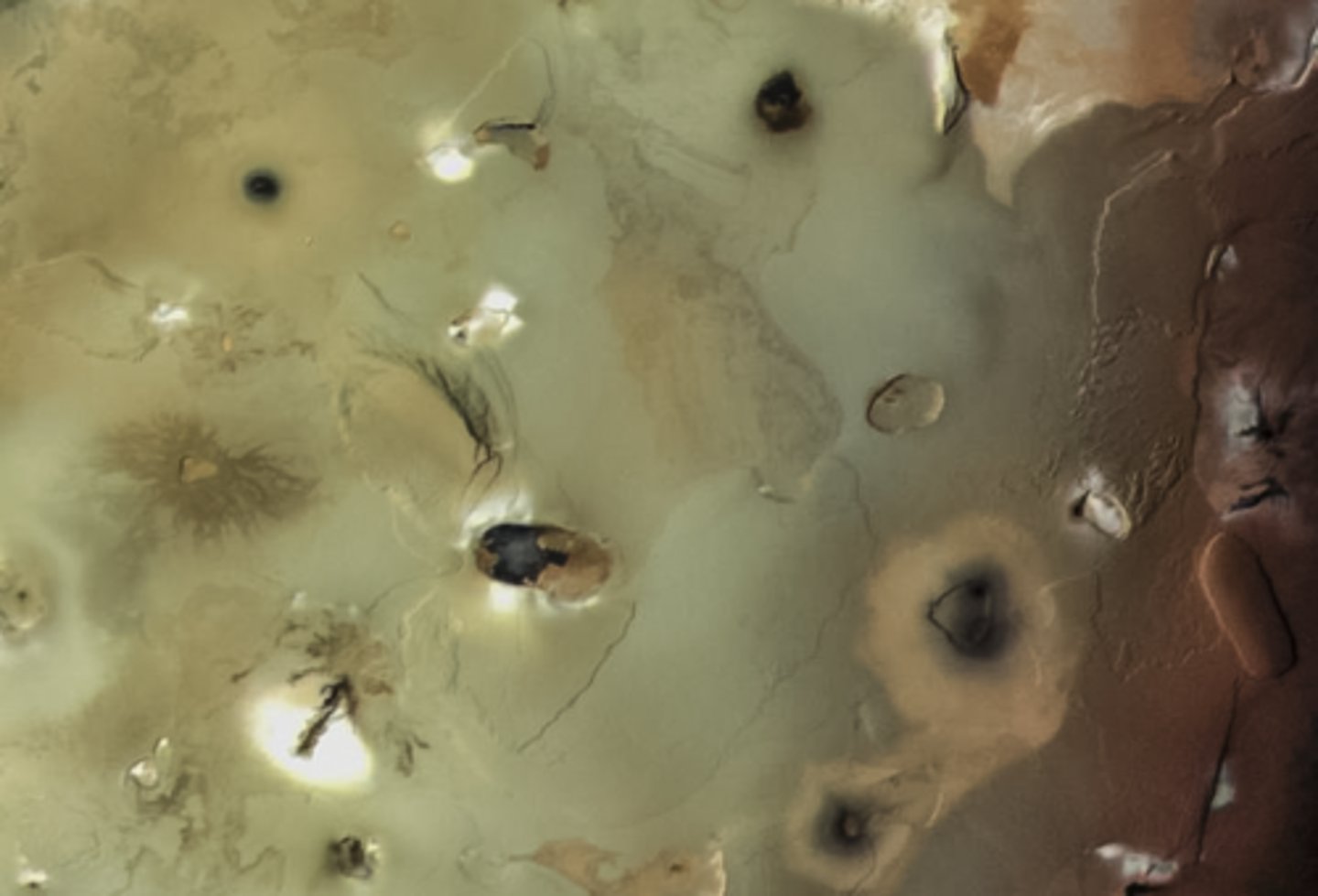
Europa - it broken up ice
What could make the chaotic area to the left of the center?
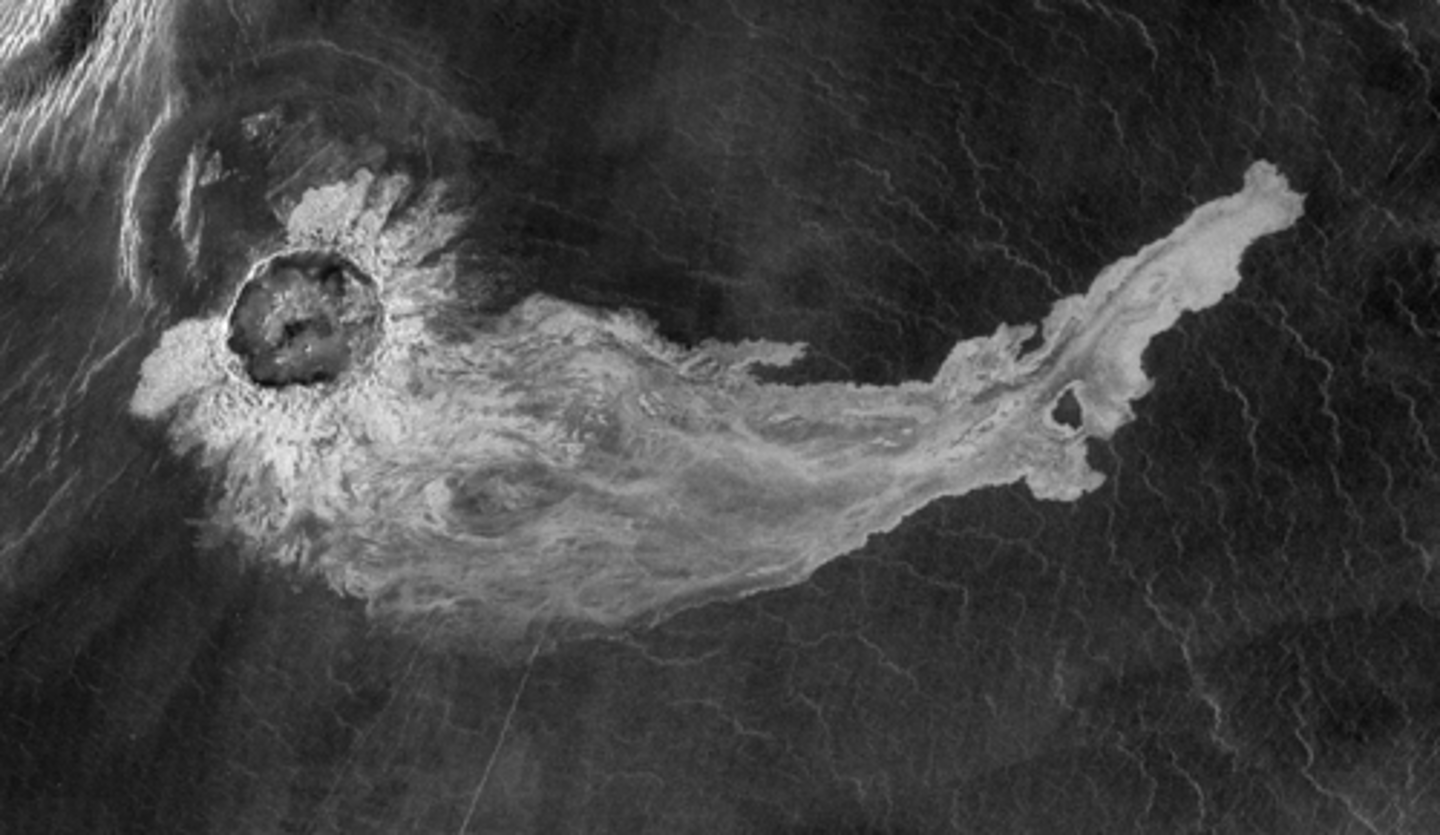
found on Venus
formed from interaction between Venus’s atmosphere and the impact crater
Venus has lots of wind, so material spreads out
Molten material from the impact
What planet are craters like this found? Why does this impact crater have long "bright" deposits extending downhill away from its right edge?
Sand dunes
It has eolian processes so wind and it has an atmosphere
What are the black linear features?
What do they tell us about the differentiation of the planet?
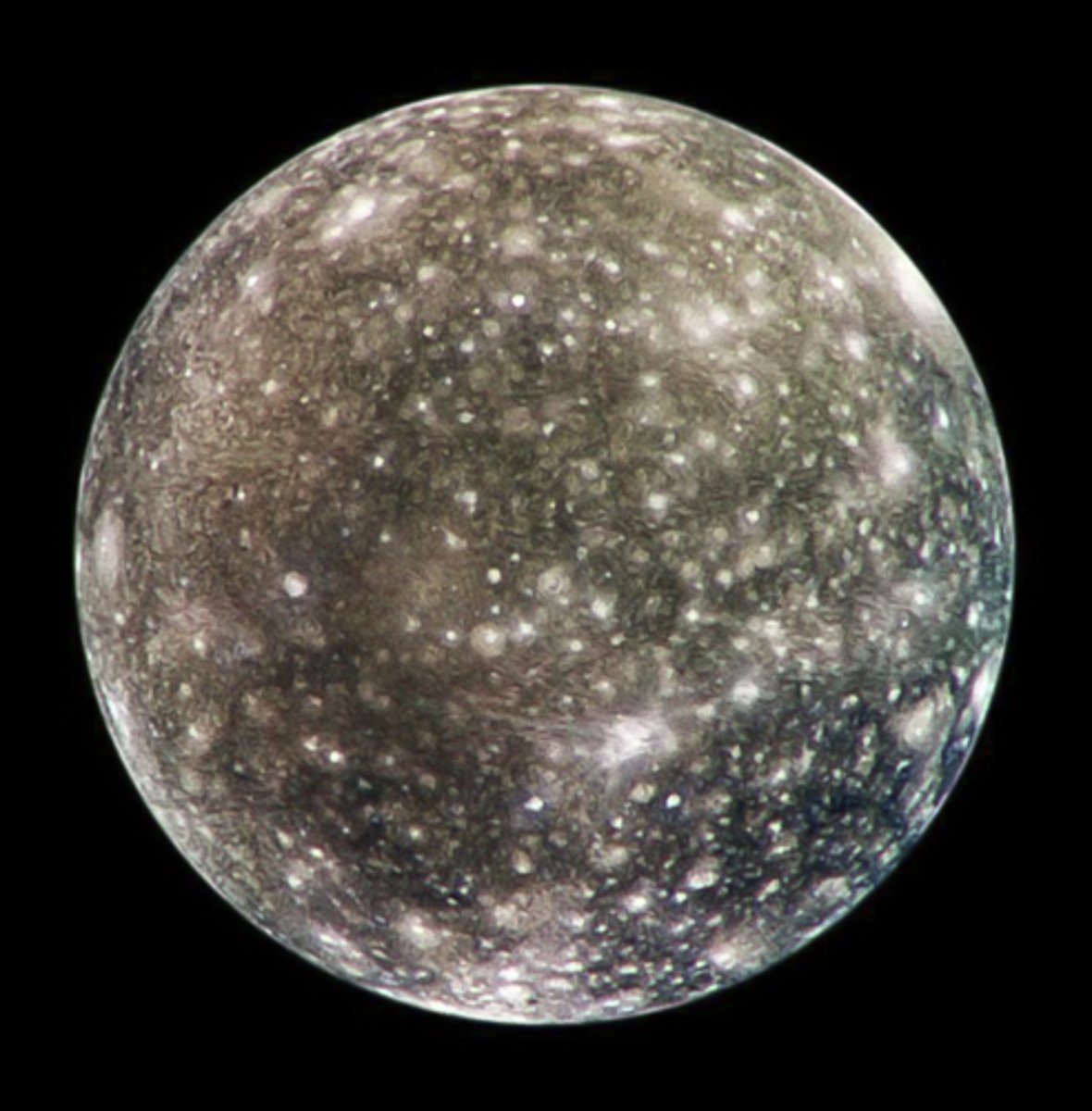
Callisto
heavily cratered so very old
4.5 million years old
Which planet’s moon is this? What is the surface age of this moon?

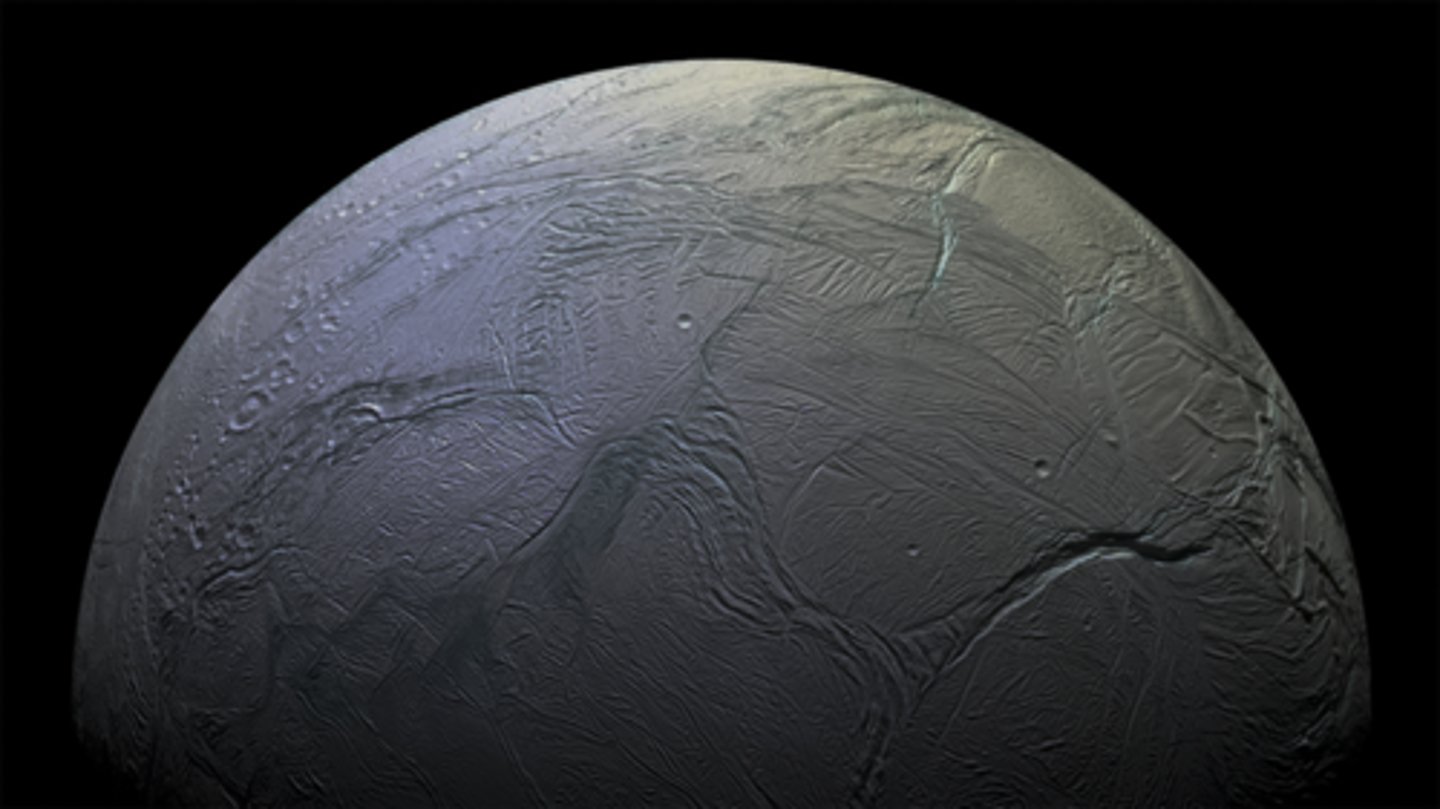
Saturn’s moon Enceladus
It has lots of smooth plains not a lot of craters meaning its young
white and bright
lots of cracks likely due to ice
surface is young
ice causes expansion, which leads to cracks
colder because it reflects the light back and does not absorb it
What is the surface composition of this moon?
What is unusual about the surface of this small moon?

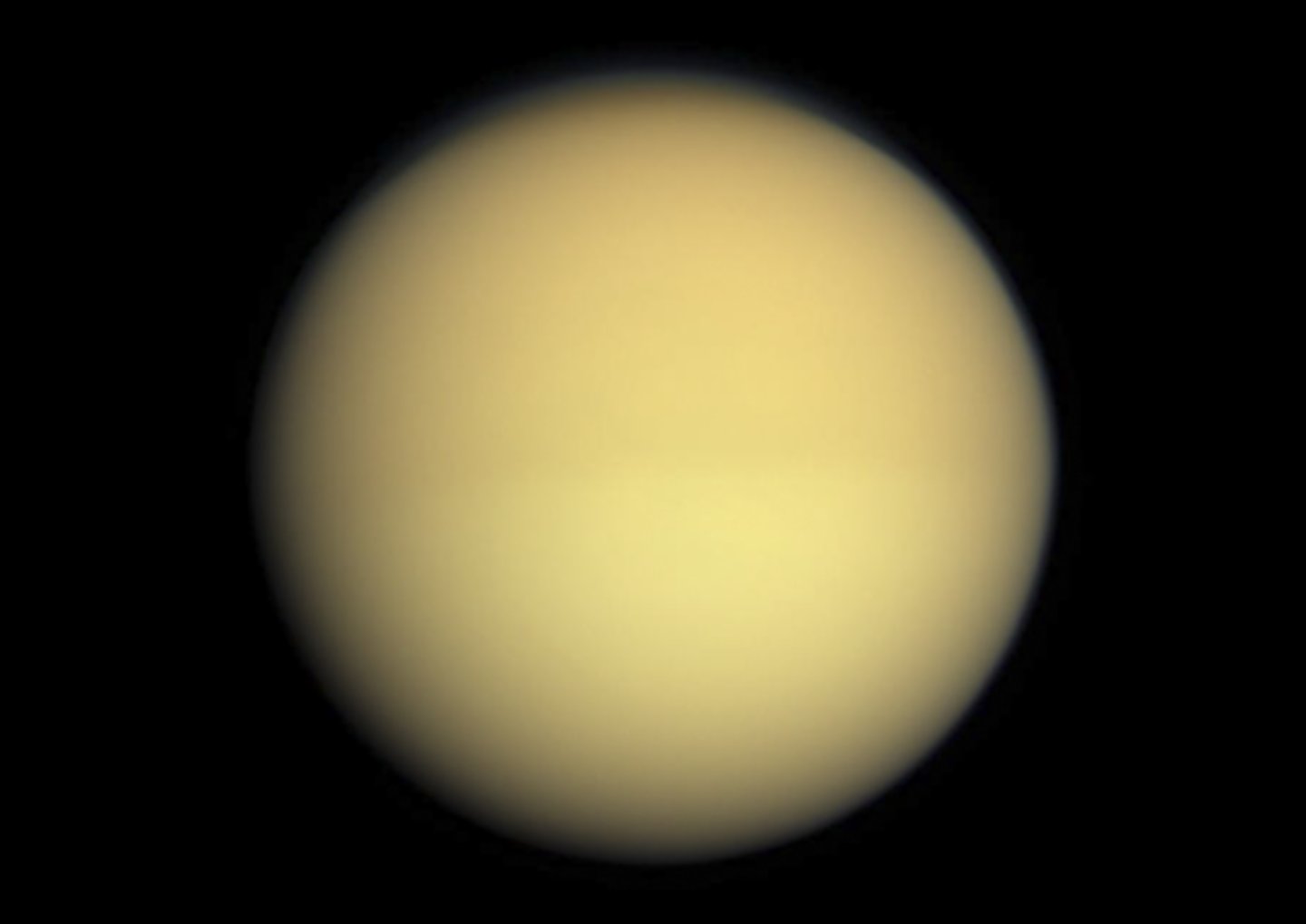
It is Saturn’s moon, Titan
largest moon of Saturn
outer solar system its made of nitrogen
thick nitrogen atmosphere
hydrologic system of methane
What is the composition of this atmosphere?
Where is it in the Solar System?
a moon of Neptune
Atmosphere freezes and it forms these nitrogen poles while in winter
it is frozen nitrogen ice, and hase water ice and carbon dioxide ice
frozen version of Earth’s atmosphere
How does the bright material on the bottom half of Triton form?
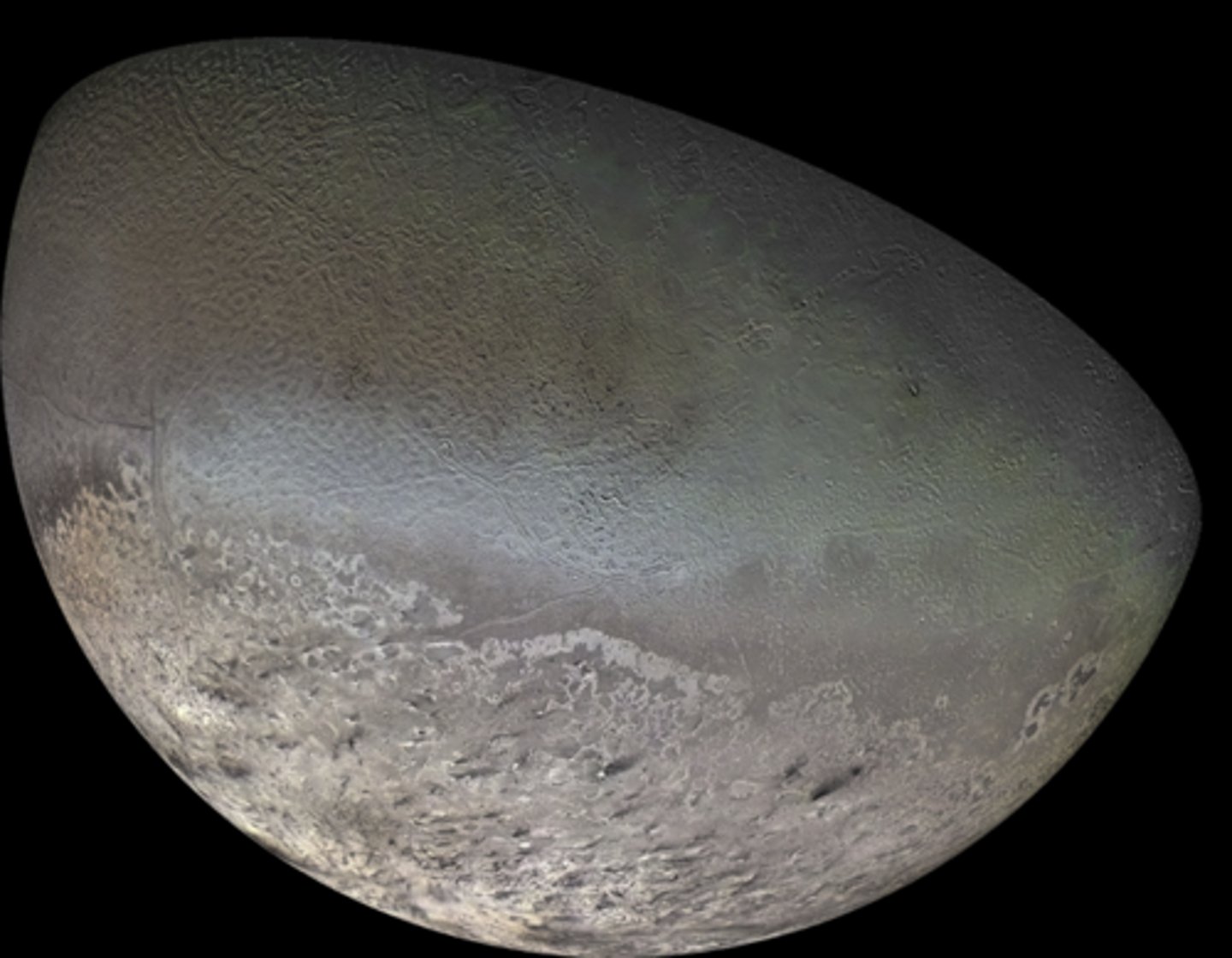
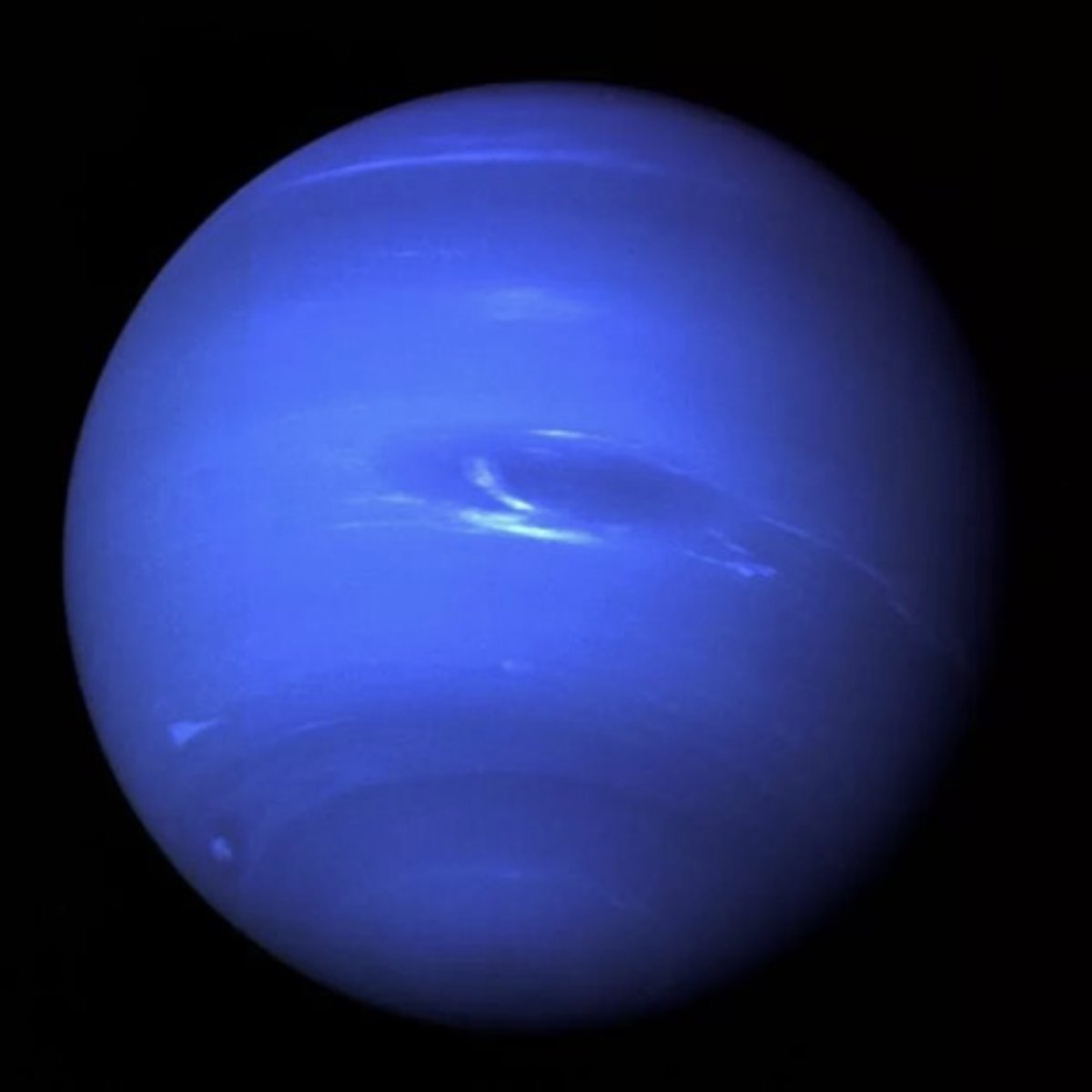
it is neptune!
Methane
takes in light
absorbs spectrum from red and refelcts blue
Why is this planet blue?

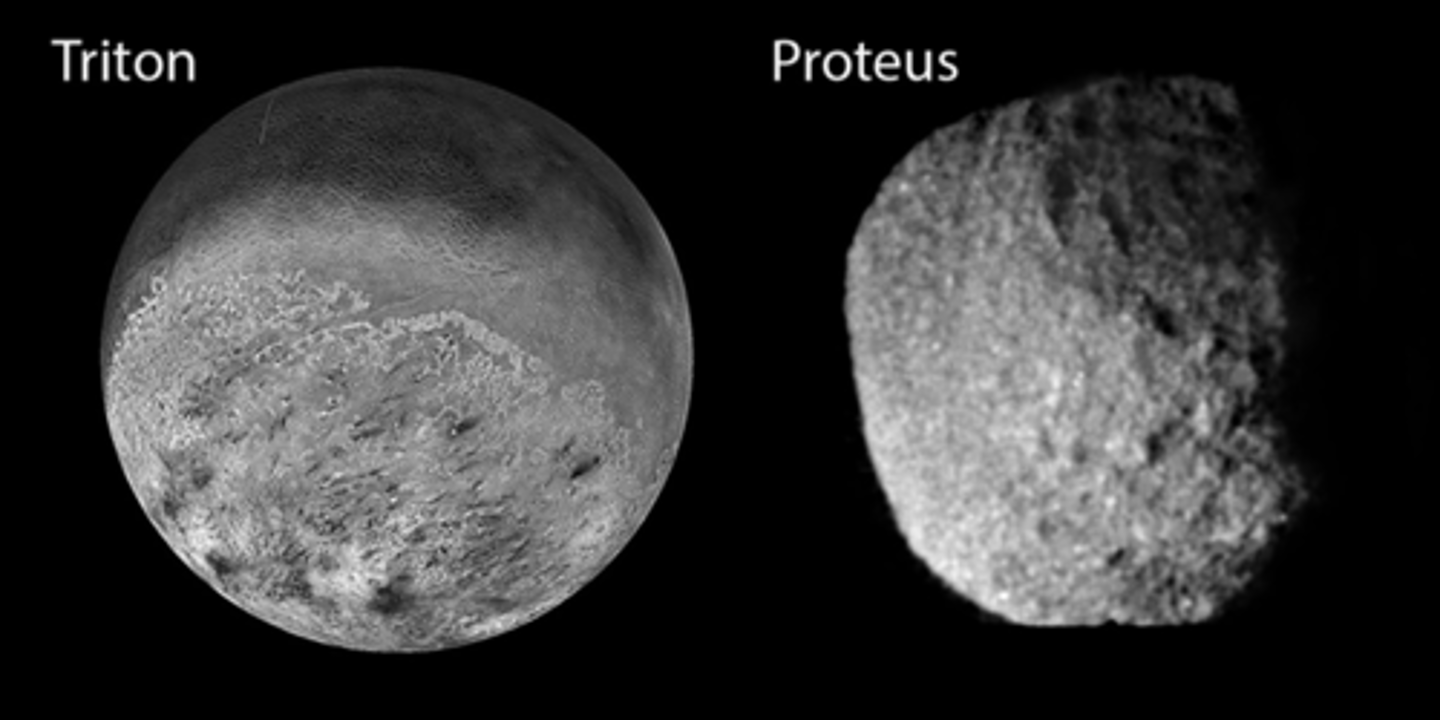
Triton is larger b/c
it has sufficient gravity, is round, thought to be a captured dwarf planet, has a retrograde orbit (opposite rotation)
composition similar to pluto
Proteus is …
an icy body
was acquired later on
does not have much gravity because it is not round
What are the important differences between these two bodies? Which one is actually larger?
liquid flowing
liquid methane
What process forms the dendritic pattern on Titan?

Extensions, as the ice cools it freezes it expands
happens with lots of water planets
ice is less dense than water
ice takes up more space then liquid
as it freezes, it expands
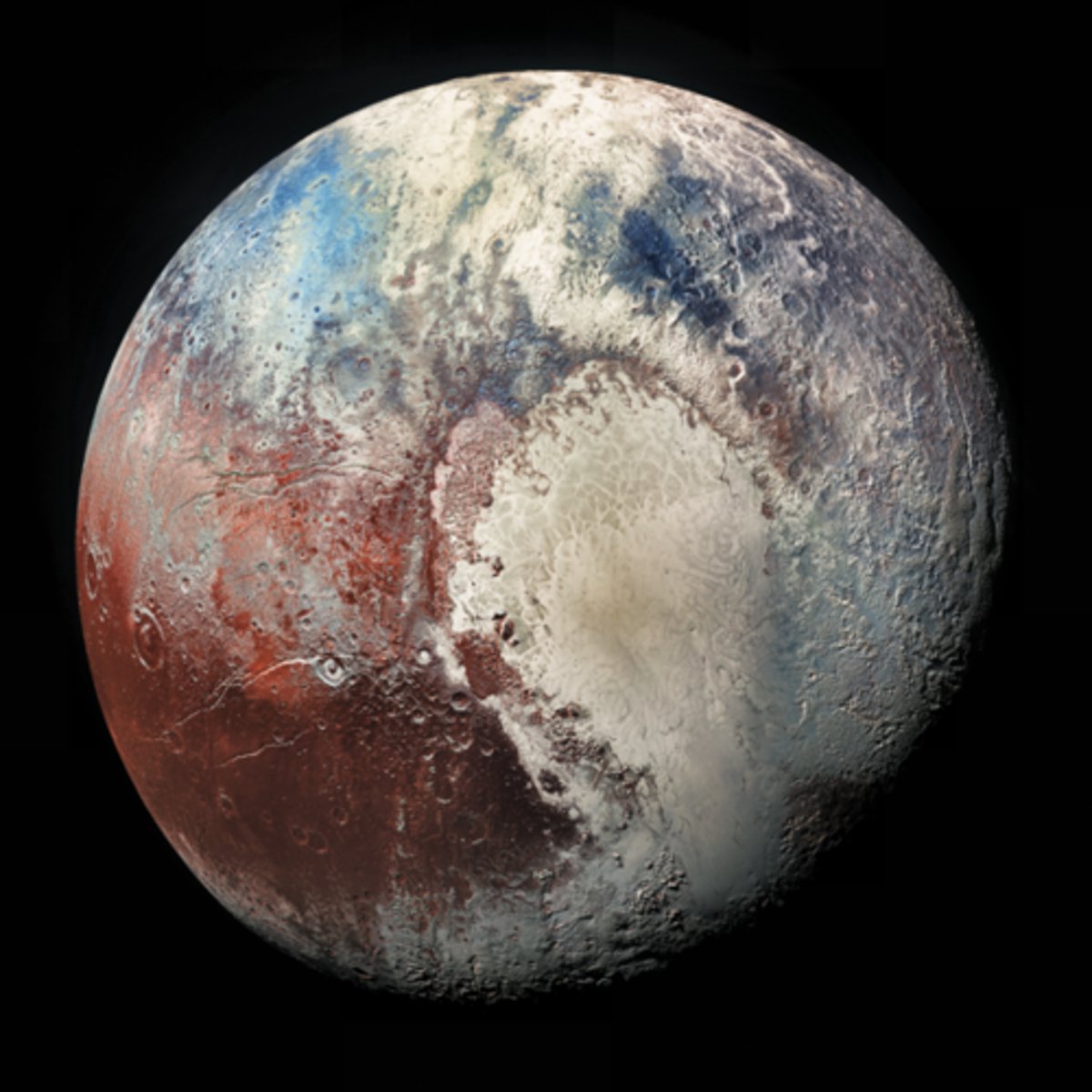
How did the tectonic fractures form on Pluto?

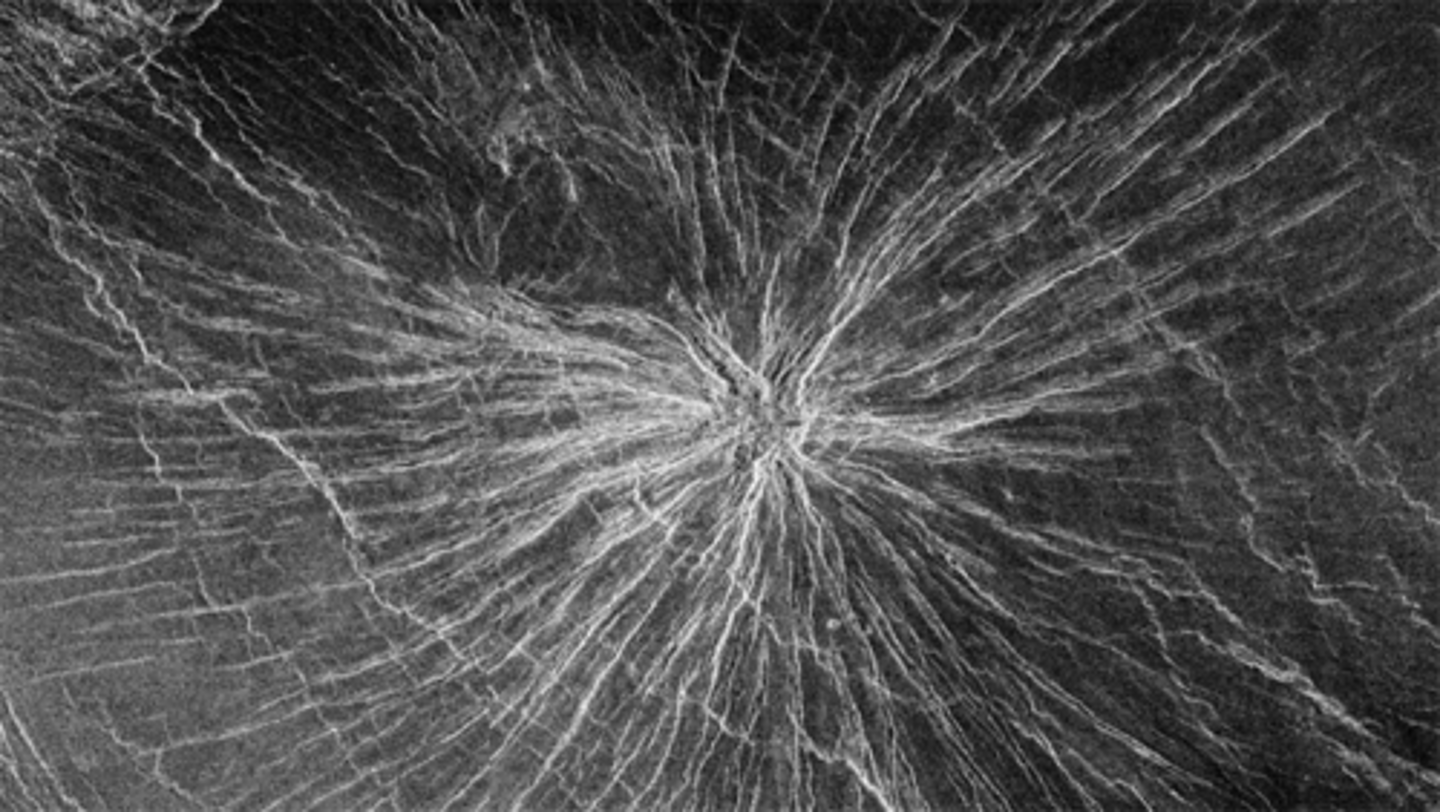
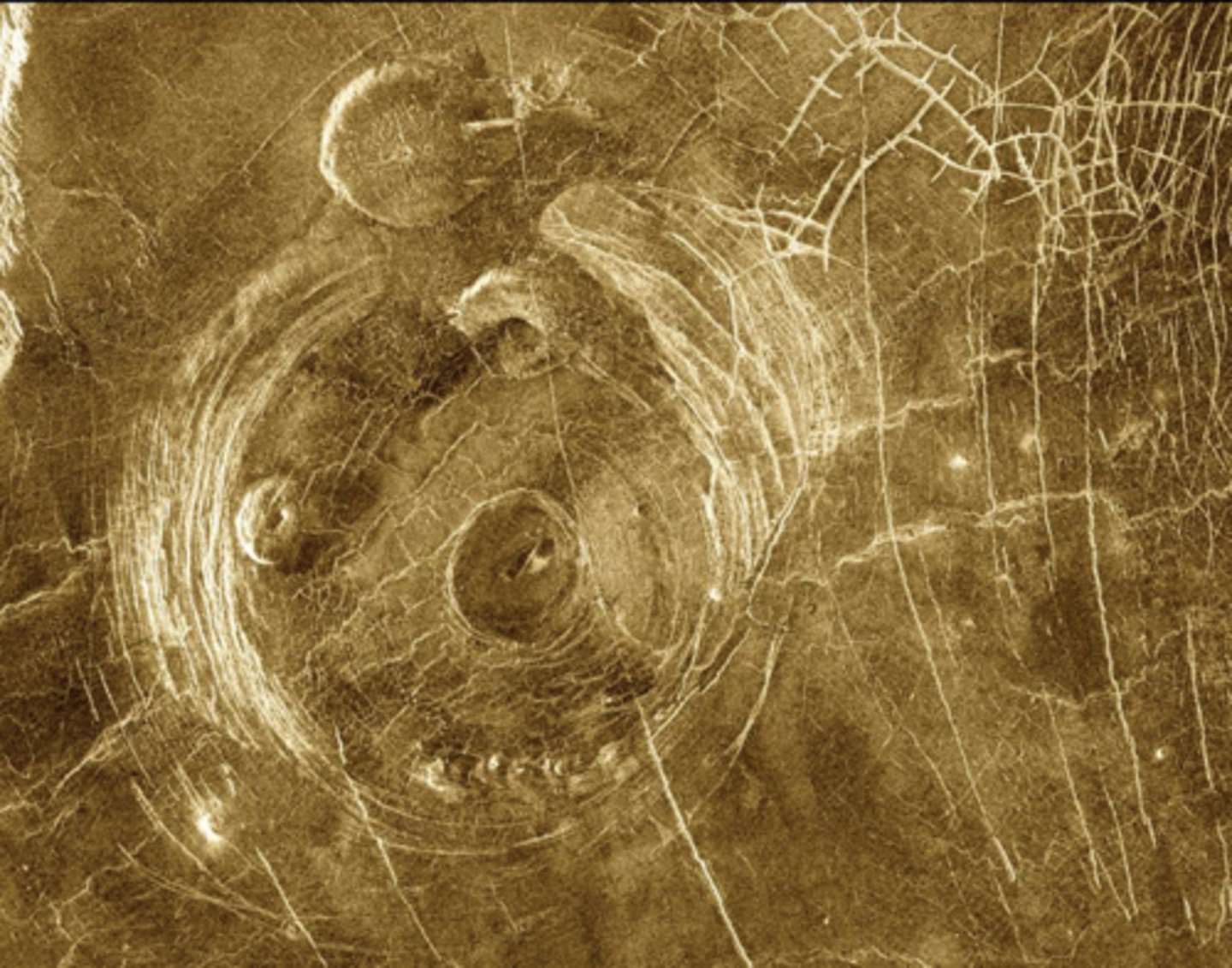
on venus!
has things that are coronas- circular plains surrounded by belts
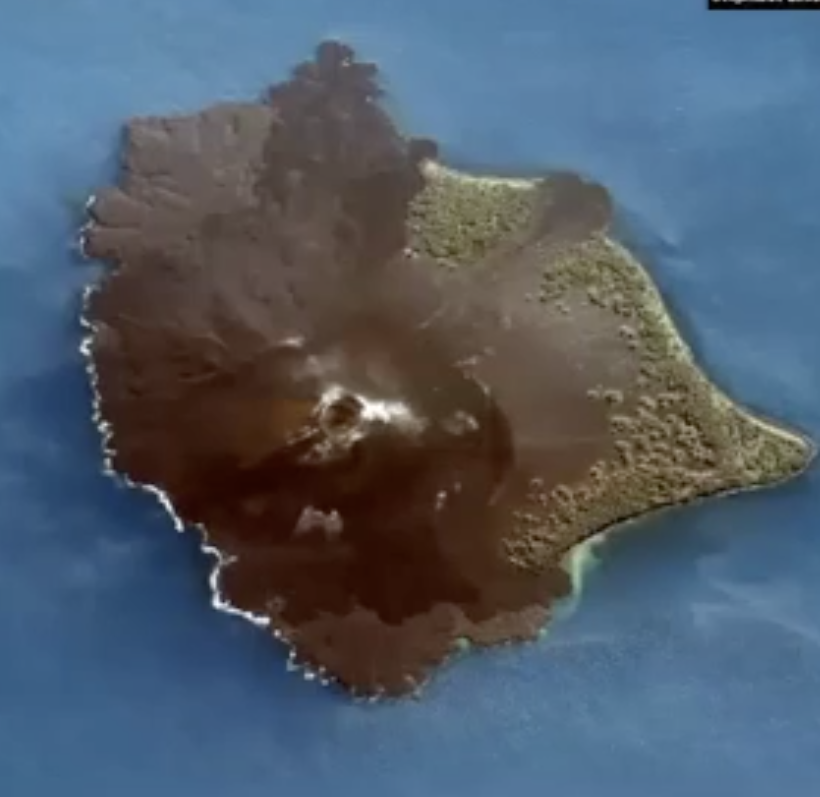
Volcano.
As it lifts up it extends everything around it
How did this radial pattern form?

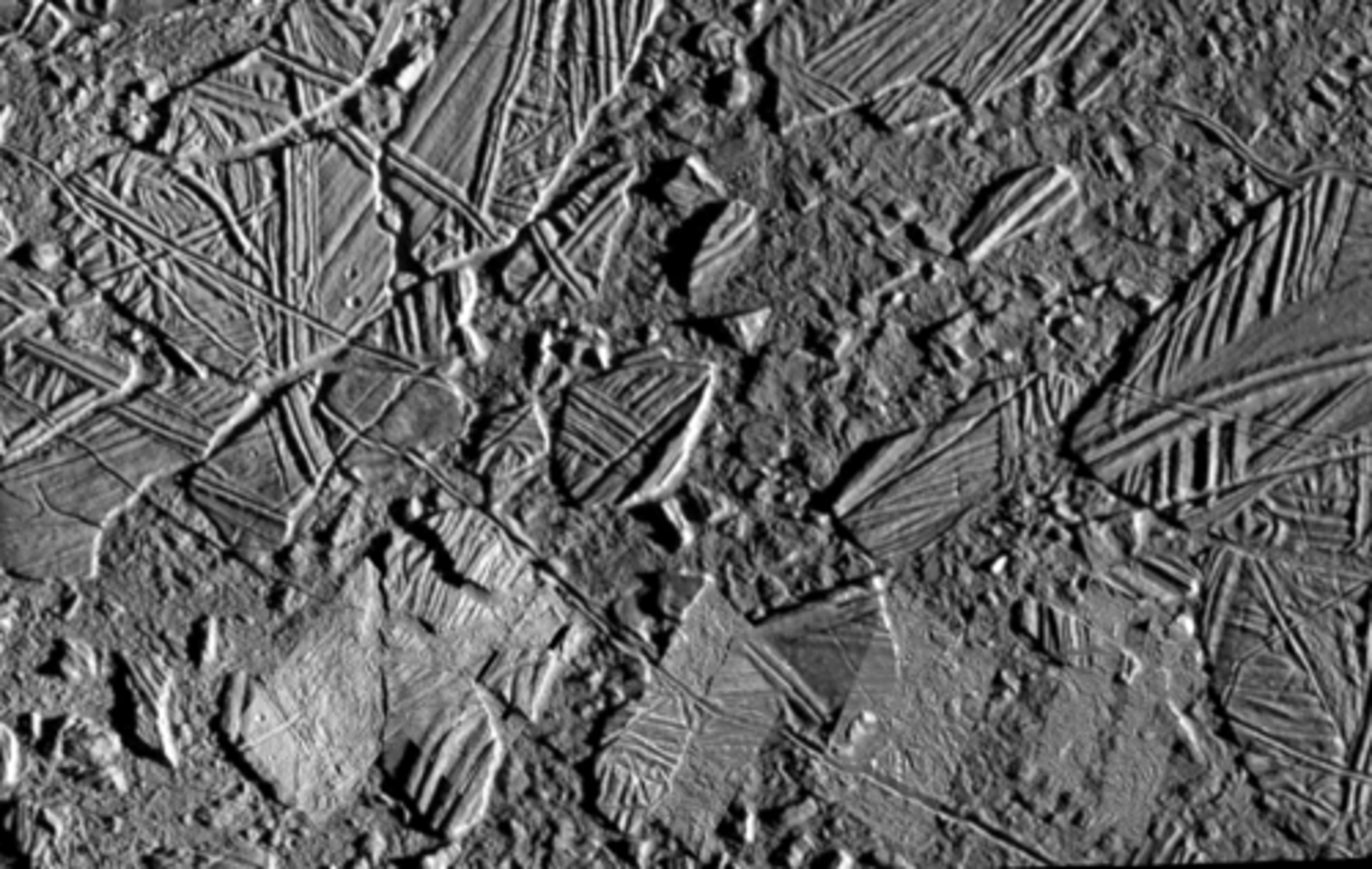
Related to coronas form as mantle plume comes up through crust and as it cools it gets more dense and drains out of the center and sinks
What process is this feature related to?
Ice
What is the most likely composition of this surface?

A
line of volcanic cones
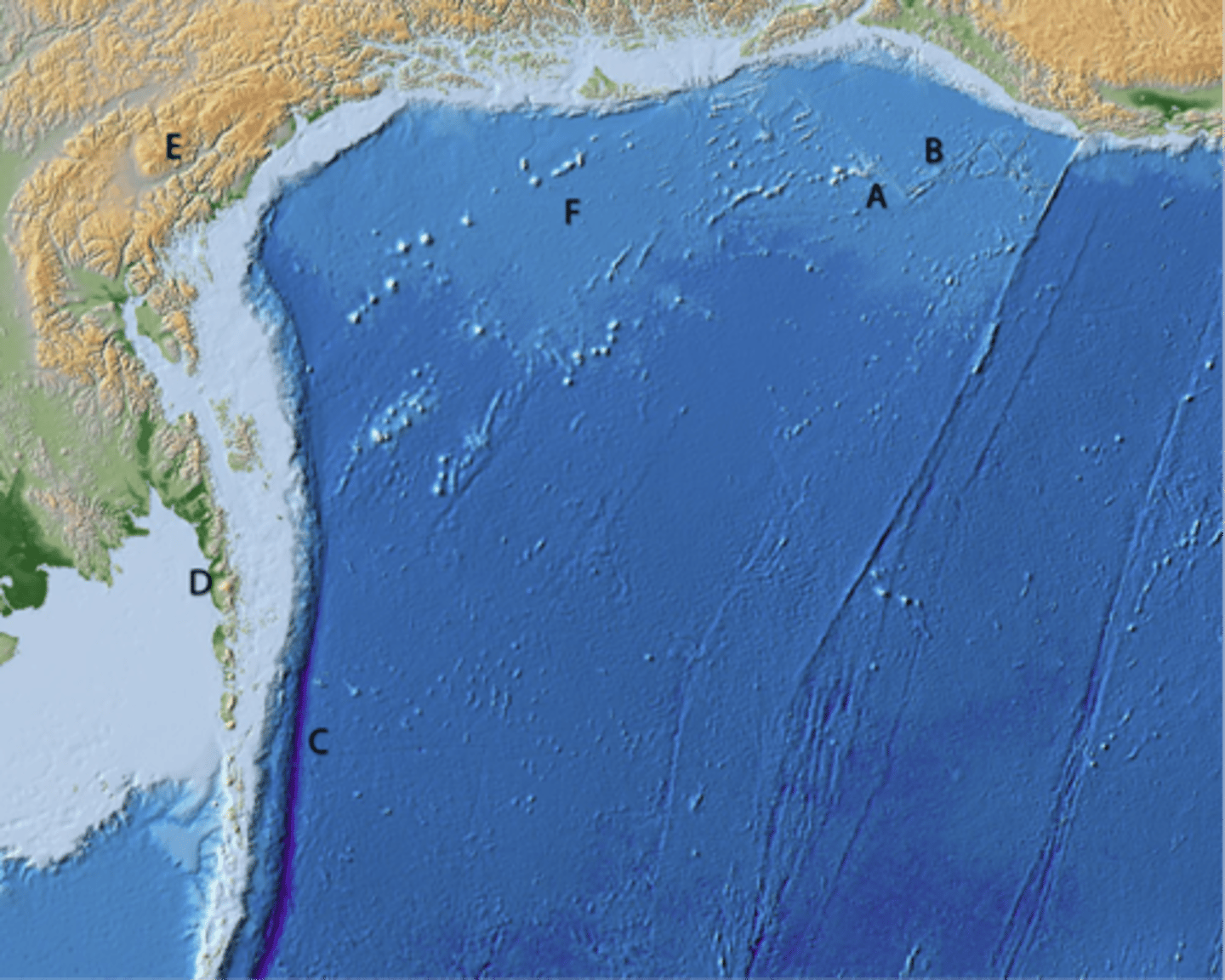
B
transform boundary
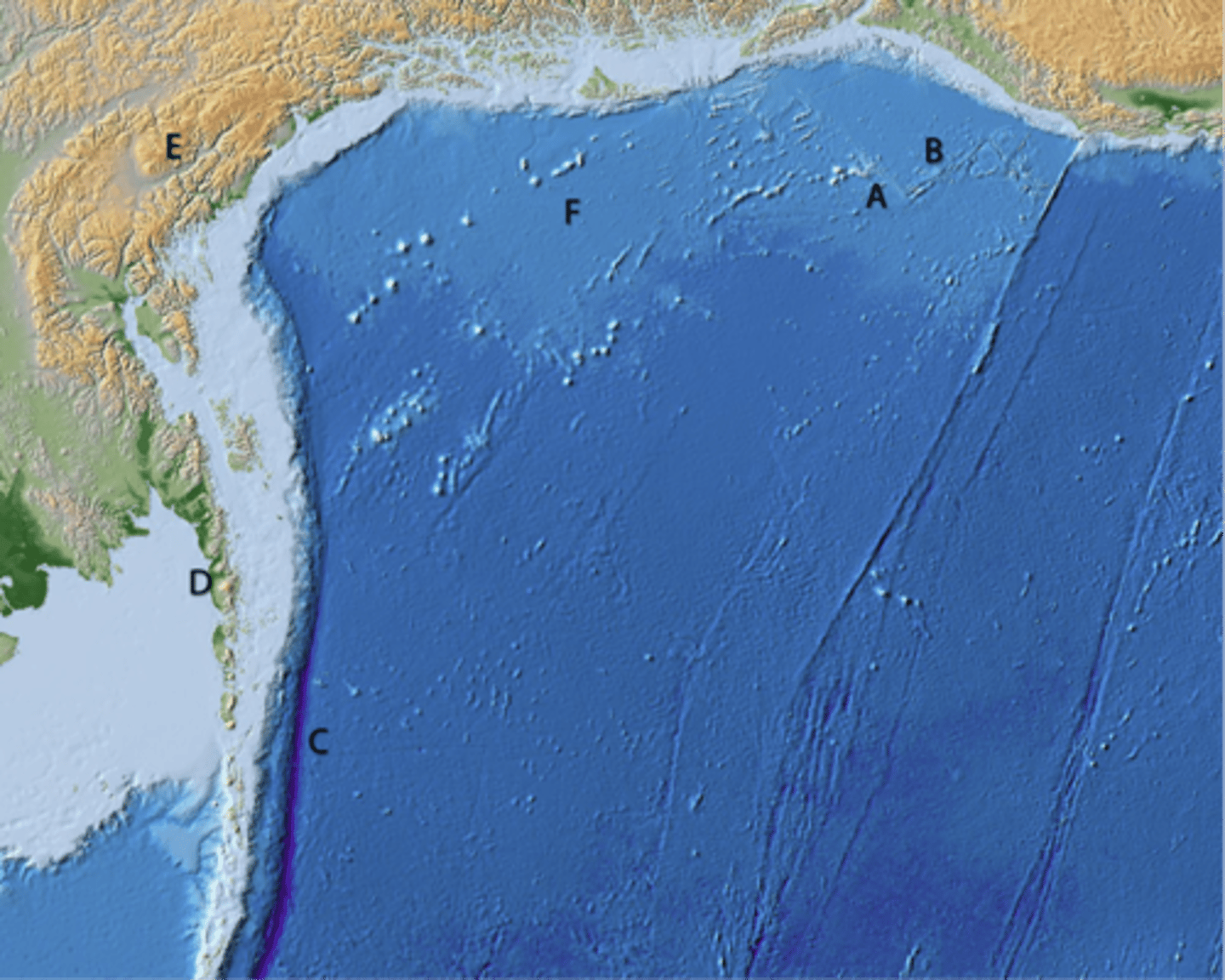
C
divergent boundary
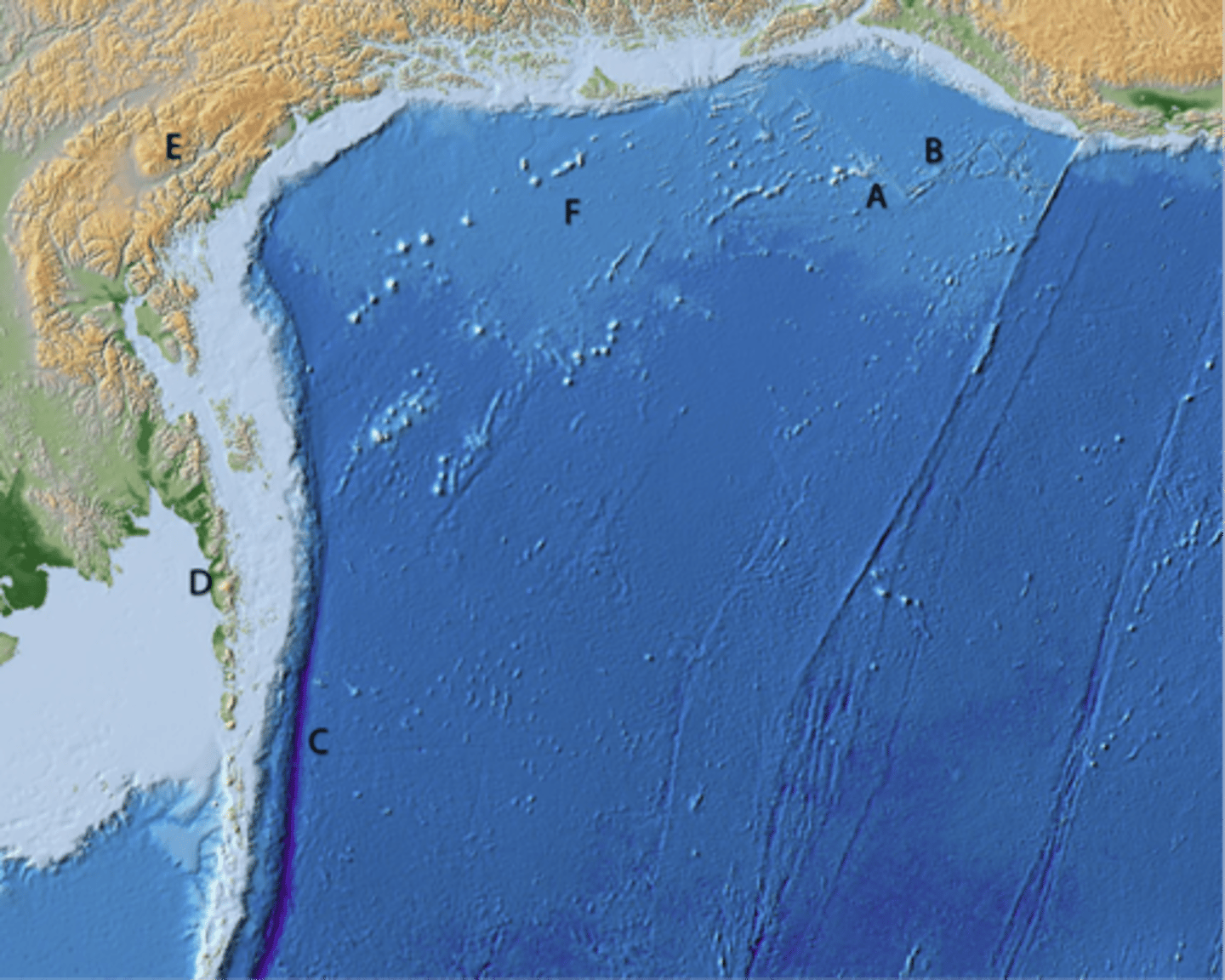
D
convergent boundary
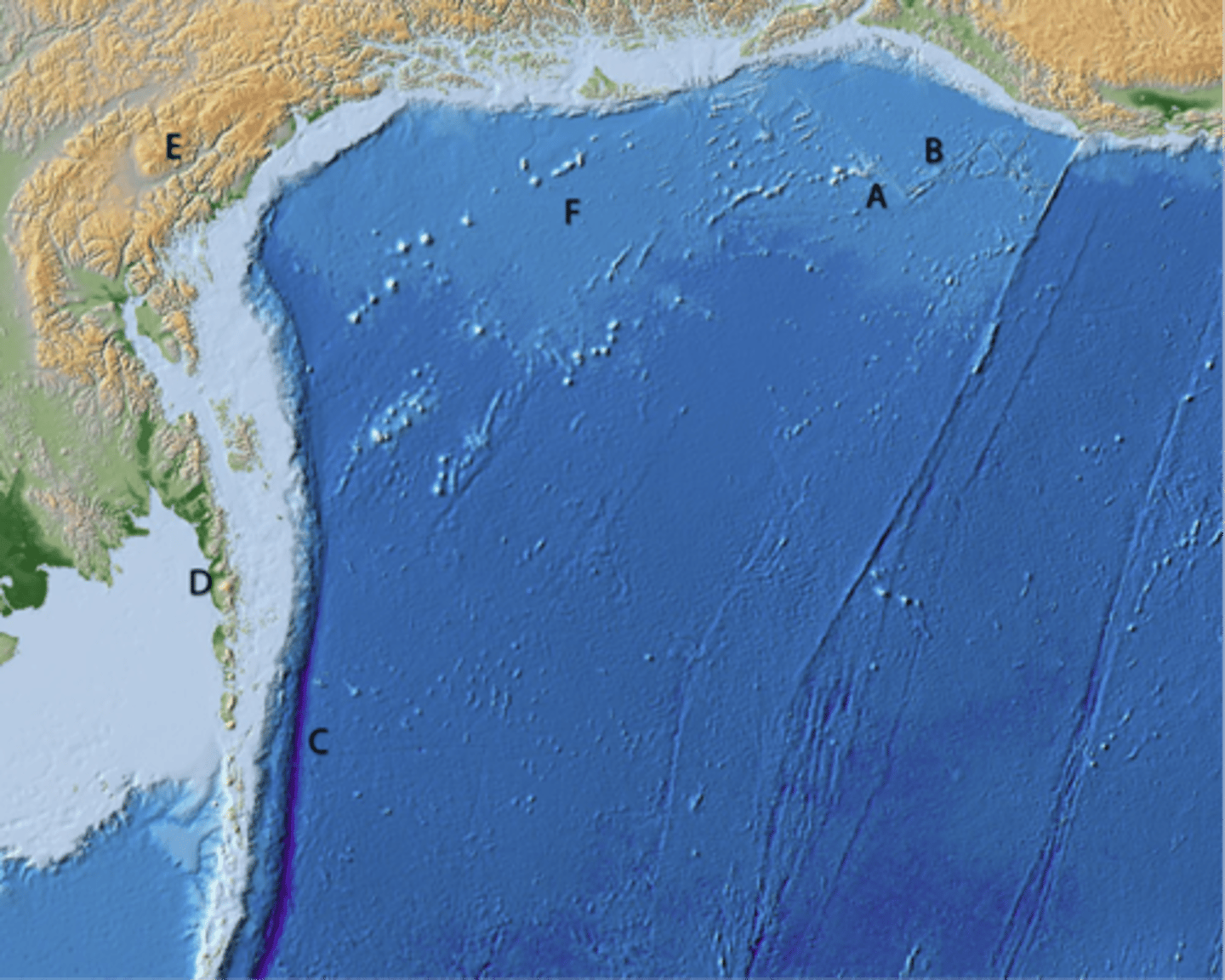
B
oldest becasue it has the most craters
Which area of Enceladus is the oldest?
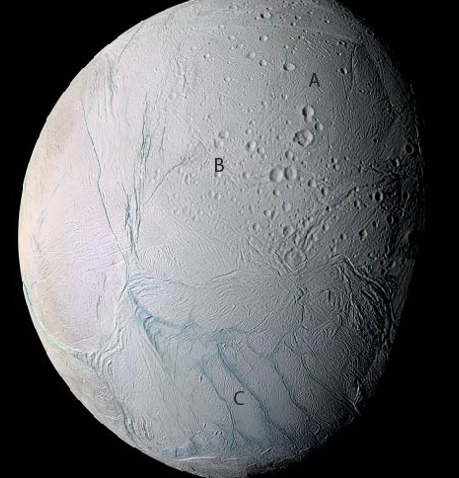

E
continental highlands