microbio 2460 chapter 3
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
spontaneous generation
ancient belief: life can arise from nonliving matter
Key scientists of spontaneous generation
Francesco Redi, John Needham, Lazzaro Spallanzani
Francesco Redi
This scientist disproved spontaneous generation by showing that maggots do not spontaneously arise from decaying meat.
John Needham
Believed there was a life force that caused spontaneous generation
Lazzaro Spallanzani
replicated redi and needham's experiments, disproved of spontaneous generation
Louis Pasteur
Disproved of spontaneous generation, swan neck experiment (won Alhumbert prize)
Modern Cell Theory
All living organisms are composed of one or more cells
2 Basic Tenents of Modern Cell Theory
1. Cell is a basic unit of structure
2. All cells come from existing cells (recall spontaneous generation)
People of Cell Theory: Tenet 1
1. Robert Hooke- cork tissue
2. Matthias Schleiden- plant tissue
3. Theodor Schwann- compared plant and animal cells
People of Cell Theory: Tenet 2
1. Robert Remak- cells come from other cells (i.e. cell division)
2. Rudolf Virchow -published Cellular Pathology
(all cells arise from cells)
Endosymbiotic Theory
Origin theory about cellular structures (how Mitochondria and chloroplasts were originally prokaryotic cells)
Famous scientist: Konstantin Mereschkowski, Ivan Wallin, Lynn Margulis
Konstantin Mereschkowski (1905)
Proposed that chloroplasts could reproduce independently and must have lived outside plant cell
(said DNA could be found in organelles)
Ivan Wallin (1926)
showed mitochondria outside of cell (but likely contamination)
also said DNA could be found in organelles
Lynn Margulis (1967)
mitochondria and chloroplasts are of prokaryotic origin
-
DNA, ribosomes, binary fission
Germ Theory of Disease
Diseases may result from microbial infection
Famous scientist: Girolamo Fracastoro, Ignaz Semmelweis, John Snow, Louis Pasteur, Joseph Lister, Robert Koch
Girolamo Fracastoro (1546)
"spores" can be carried on clothing and transferred between individuals
Ignaz Semmelweis (1847)
"Contaminated" physicians transferred causative agent to patients
-promoted handwashing as a solution
John Snow (1848)
cholera outbreaks in London traced to sewage in drinking water
Louis Pasteur (1856)
Organisms could spoil food and therefore people
Joseph Lister (1867)
Handwashing + carbolic acid in surgery for disinfection
Robert Koch (1884)
a specific microbe can cause a specific disease
-koch's postulates
Common elements of the general cell
cytoplasm, plasma membrane, chromosome(s), ribosomes
Prokaryotes
No nucleus
domains: bacteria & archaea
eukaryotes
nucleus
domain: eukarya
Unique elements of the prokaryotic cell
1. nucleoid
2. Inclusion bodies
3. plasmids
4. Pili
5. Fimbriae
6. .Endospore
common prokaryotic cell arrangments
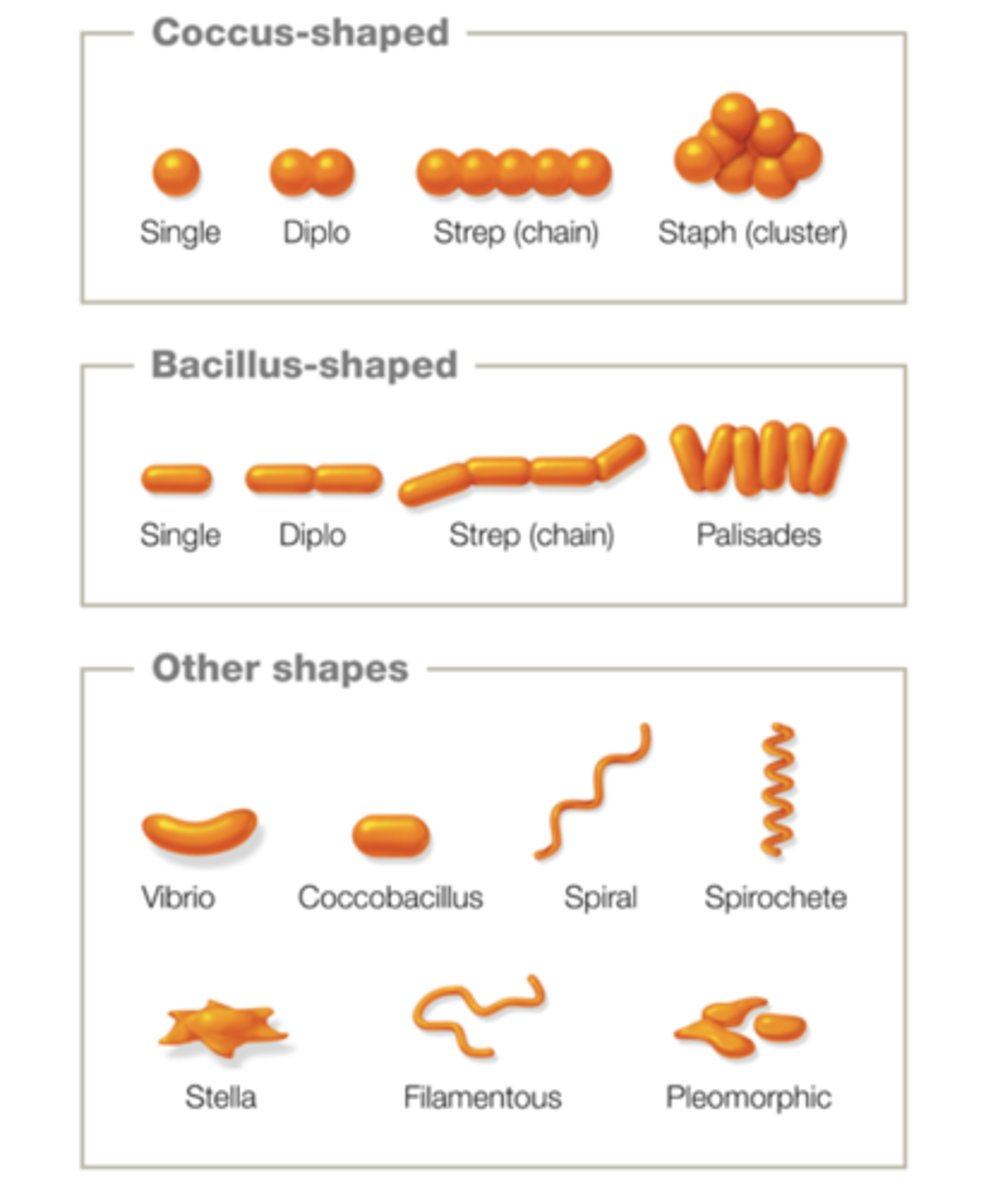
cell wall
found in eukaryotes & prokaryotes, Found outside the cell membrane, Aids in protection against osmotic pressure changes
Osmosis
diffusion of water in response to different solute concentrations
isotonic solution
same solute concentration, no movement
hypertonic solution
higher water concentration, water moves out (plasmolysis)
crenation
cell shrivels due to lack of water
hypotonic solution
less water concentration, water moves in
Nucleoid
Central region of cell with DNA and RNA associated proteins, circular/haploid chromosomes
plasmids- circular, non essential DNA
Prokaryotic ribosomes
-Sites of protein synthesis
-70S (50S + 30S)
inclusions
Structures used for storage of glycogens, starches, etc.
Polyhydroxybutrate (PHB)
inclusion with monolayer that can be harvested for biodegradable plastics
Volutin granules
polymerized inorganic phosphates for biofilm formation
Magnetosomes
magnetic iron oxide or iron sulfide allow cell to align along a magnetic field
Gas Vacuole
a prokaryotic inclusion, protein-lined vesicle of gas that alters buoyancy
Carboxysome
a prokaryotic inclusion containing RuBisCO and carbonic anhydrase for carbon metabolism
endospores
Structure formed in dormant state to protect genome
Resistant to extreme temperatures and radiation
Do not absorb Gram stain, only special endospore stains,
Dehydrated (no metabolic activity)
Dormant (no growth or metabolic activity)
sporulation process
1. DNA replicates
2. membranes form around DNA
3. forespore forms additional membranes
4. protective cortex forms around spore
5. protein coat forms around cortex
6. spore is released
vegetative cells
present in normal favorable conditions, Sensitive to extreme temperatures and radiation, Gram-positive, Normal water content and enzymatic activity, Capable of active growth and metabolism
clinically important endospore formers
-B. anthracis - causative agent of anthrax
-C. difficile - causes pseudomembranous colitis
-C. perfringens - causes gas gangrene
-C. botulinum - causes botulism
-C. tetani - causes tetanus
cell (plasma) membrane
-Present in all organisms
-phospholipid bilayer that protects and encloses the cell
-Has selective permeability to move molecules in & out (most important function)
archaea cell membrane
-Ether linkages, not ester
-Many are monolayer, not bilayer
Membrane Transport Mechanisms (4)
1. Passive transport - diffusion of molecules (ex. CO2)
2. Facilitated diffusion - carrier proteins that ferry larger molecules across w/o ATP
3. Active transport - membrane proteins that move molecules with ATP
4. Group translocation - molecule chemically modified as it enters a cell against unfavorable concentration gradient.
Photosynthetic Membrane Structures
-Cyanobacteria and photosynthetic bacteria have specialized structures to perform photosynthesis
- Infoldings of the plasma membrane encloses photosynthetic pigments (e.g. chlorophyll)
Cyanobacteria
Photosynthetic, oxygen-producing bacteria (formerly known as blue-green algae).
Photosynthetic bacteria
chromatophores, lamellae, or chlorosomes
Function of cell wall
-protect cell from adverse environment conditions
-differentiates Gram (+) and Gram (-)
-Peptidoglycan (bacteria) is major component and provides shape
cell wall in myobacteria
have embedded mycolic acid (Recall Acid-fast stain method)
cell wall in gram +
have peptidoglycan in thicker layers than Gram (-) & embedded teichoic acids
cell wall in gram -
-have outer membrane that contains lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
-Contributes to fever, shock, & hemorrhaging
cell wall of archaea
-pseudopeptidoglycan
-a few archaea do not have cells walls
Glycocalyces and S-Layers
1. Glycocalyx - sugar coat outside cell wall that allows cells to adhere to surfaces, protect against desiccation and/or antibiotics and disinfectants
2. S layer - composed of structural proteins and found outside cell wall; thought to help with rigidness and against osmotic pressure changes
2 kinds of glycocalyx
1. capsule- polysaccharides or proteins
2. slime layer- loosely attached and made of polysaccharides, glycoproteins, or glycolipids
Filamentous Appendages (2 Kinds)
1. Fimbriae - short bristly proteins that aid in attachment
2. Pili - longer appendages aid in attachment OR transfer of DNA (sex pilus)
Flagella
-Structures used by cells to move in aqueous environment towards an environmental signal
- Basic structure includes: basal body, hook, & filament
Phototaxis
moving toward light signal
chemotaxis
moving toward chemical signal
magnetotaxis
moving toward magnetic field signal (also uses magnetosomes)
Unique elements of the eukaryotic cell
1.Nucleus
2.Mitochondria
3.Endoplasmic Reticulum
4.Golgi Apparatus
5.Lysosomes
6.Peroxisome
7.Cytoskeleton
8.Cilia*
9.Chloroplasts*
*not all cells contain this structure
nucleus
-DNA material is surrounded by a membrane
-Chromosomes are linear
Nucleolus
-Dense region in nucleus where ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is synthesized
eukaryotic ribosomes
-80S (40S and 60S)
-Chloroplasts & mitochondria have smaller(70S) ribosomes
Endomembrane System function
move materials around & within the cell
Included organelles of Endomembrane System
-Endoplasmic reticulum(smooth & rough)
-Golgi apparatus
-Lysosomes
-Vesicles
Endoplasmic Reticulum
-Group of tubules & flat sacs (cisternae) that function to synthesize various molecules
rough er
ribosomes are present & synthesizes proteins
smooth er
no ribosomes and synthesizes lipids, metabolizes carbs, and detoxifies compounds
Golgi Apparatus
-modifies lipids & proteins that arrive from ER
-Membranous disks (dictyosomes) stacked together
-Vesicles carry modified molecules to other parts of the cell
Lysosomes
-Membrane bound organelles that contain digestive enzymes
-functions to break down food, damaged organelles or cellular debris
Peroxisomes (not part of Endomembrane System)
-Membrane bound organelles that produce hydrogen peroxide
-Function: contribute to lipid synthesis as well as break down molecules
Cytoskeleton
-Filaments inside the cell that provide structure and network for transport
-Main components:
1.Microfilaments
2.Intermediate filaments
3.Microtubules
Microfilaments
allow locomotion
intermediate filaments
-anchor nucleus and other organelles
-form nuclear lamina
microtubules
support the cytoskeleton, largest of the 3, function in flagella and cilia as well as cell division (centrosomes)
mitochondria
-Complex organelles and sites for aerobic respiration
-"power house" of the cell
-Composed of two lipid membranes
2 lipid membranes of mitochondria
1. outer - remnant of ancient cell membrane
2. inner - engulfed by ancestrial organism
chloroplasts
-Present in photosynthesizing eukaryotes(plants and algae)
-Major Components:
1.Outer membrane
2.Inner membrane
3.Thylakoid membrane system
Plasma Membrane
- Similar to prokaryotes but additional embedded molecules (sterols) that add to structure
-help fluidity and shape
Membrane Transport System
Same as prokaryotes: diffusion, facilitated diffusion, & active transport PLUS endocytosis & exocytosis
Eukaryotic Cell Walls of eukaryotic organisms
-Fungi & plants: cellulose
-Protists & algae: silica, agar, or calcium carbonate
-Fungi: chitin
Extracellular Matrix
-no cell wall
- Proteoglycans and fibrous proteins help maintain cell shape and stability
Flagella
-help locomotion
-flexible
-made of microtubules in 9+2 fashion
Cilia
-Unique to eukaryotes but not present in all
-Structure is similar to flagella but are shorter
-Function may be locomotion and also sweeping particles away from or towards cell