theatre final vocab 2025
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Theatre
1: a place especially a building, where plays, opera, musicals, and film is presented
2: the dramatic art
Arena theatre
A theatre having a central stage surrounded by an audience. Ex. The arena stage in Washington D.C
Proscenium stage
The frame that defines the physical stage, the opening through which the audience views the stage
Thrust stage
A theatre where the audience is surrounding 3 sides of the stage
Call board
Where an actor would go to look for audition sign ups, call backs, role assignments, and information about the production
Lobby
Where the audience waits prior to the opening of the house before a show
House
Where the audience sits
Apron
The part in the front of the proscenium arch
Wings
The left or right of the stage
Aisle
The entrance and exit row for the audience from the house to the lobby
Backstage
Behind and off the stage, where the audience can not see the performers
Antagonists
Adversary, opponent, villain
Protagonist
Main character- hero
Genre
Type of play- comedy, drama, musicals, farce,melodrama
Objective
Direct or indirect object of verb or a goal to attain
Obstacle
Where characters, prop, or set pieces gets in the way of the other characters objective
Given circumstances
The environment at the opening of the play “ the special world” of the play. Who ,what ,when ,where, and why
Levels
Not playing at the same action/choice/verb continuously but changing to a different degree of energy
Stage directions
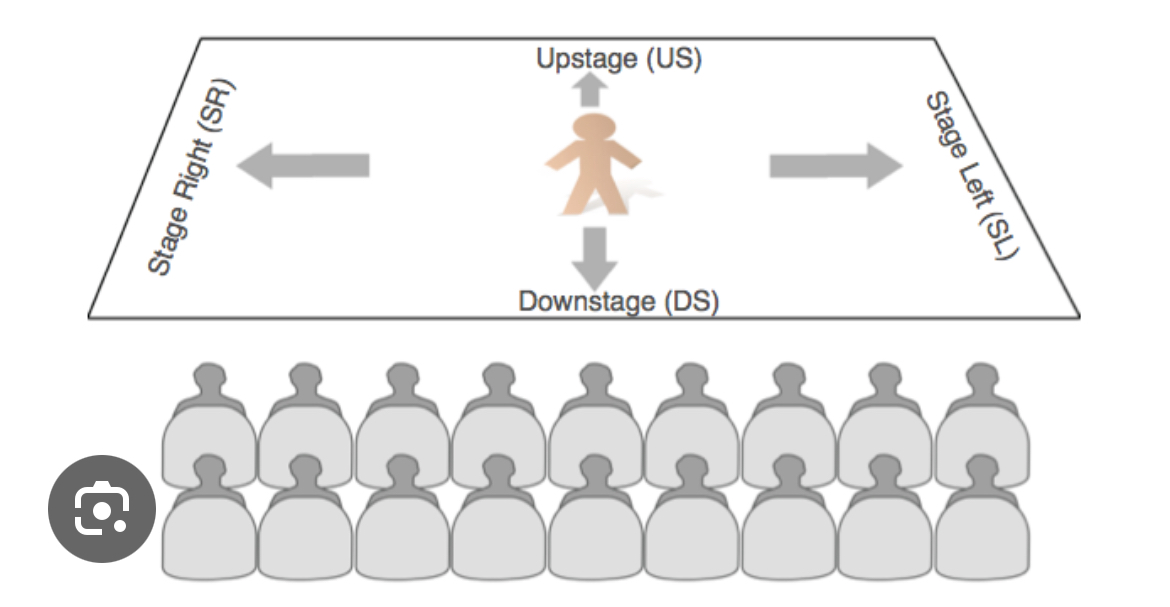
Denouement
The solution to the conflict in a play; the wrapping up of events
Intention
The actors real reason for performing and action
Emotional life
The characters emotion development that leads to their ultimate transformation. This allows the audience to connect on a personal level with the choice of the characters making.
Super objective
Can direct and connect an actors choice of objectives from the scene to scene. Serves as the final goal that the character wishes to achieve within the script.
Dramatists
The person who writes the play
Central dramatic question
The line that drives the play
Pacing
Rate of performance. Speed is not the only fact of pacing equally important or intensity, precision,clarity, and frequency of new impressions.
6 elements of drama by Aristotle
Plot, dictation/language, melody/music, character, thoughts and spectacles
Aside
An observation or remark made by a character to the audience that is not being heard by other actors
Slate
And introduction of the actor typically for auditions, including name of actor, name of character, portraying, title of play/musical and playwright
Commedia Del’ Arte
Comedy skills. An improvisational style of theater, which began in the 16th century. Uses stock characters Sasha Pantalone, Il Dottore, Il capitano, Arecibo,Brighella, and columbina
Improvise
1: to compose and perform or deliver without previous preparation extemporize
2: to compose play, recite, or sing on the spur of the moment
Tilt
Interesting twitch to advance a scene or cause status exchange. Example wife at breakfast announces out of the blue she’s pregnant.
Viola spolin
a recognized originator of improvisational theater
Mugging
Making silly faces instead of acting truthfully. Usually found upon.
Short form
Style of improvise theater in which short and typically unrelated scenes are played. Short form improv is often more grammatically and more based on silly games or handles