Kidneys: Basic Renal Processes- Glomerular Filtration
1/14
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Glomerular Filtration
Nondiscriminant filtration of a protein-free plasma from the glomerulus into Bowman’s capsule
The glomerular membrane is…
Considerably more permeable than capillaries elsewhere
The glomerular capillary wall consists of a single layer of flattened endothelial cells (with added holes to make it leaky)
What is the major force that causes glomerular filtration?
Glomerular capillary blood pressure
Blood pressure pushes filtrate, forces involved in glomerular filtration, glomerular filtration rate
Increase in blood pressure = increase in filtration
To be filtered, a substance must pass through..
The pores between and the fenestrations (capillary pore) within the endothelial cells of the glomerular capillary (100 times more permeable to H2O and solutes than regular capillaries)
An acellular basement membrane (collagen for structural strength, negative charged glycoproteins to repel proteins, particularly smaller proteins like albumin)
The filtration slits between the foot processes of the podocytes in the inner layer of Bowman’s capsule
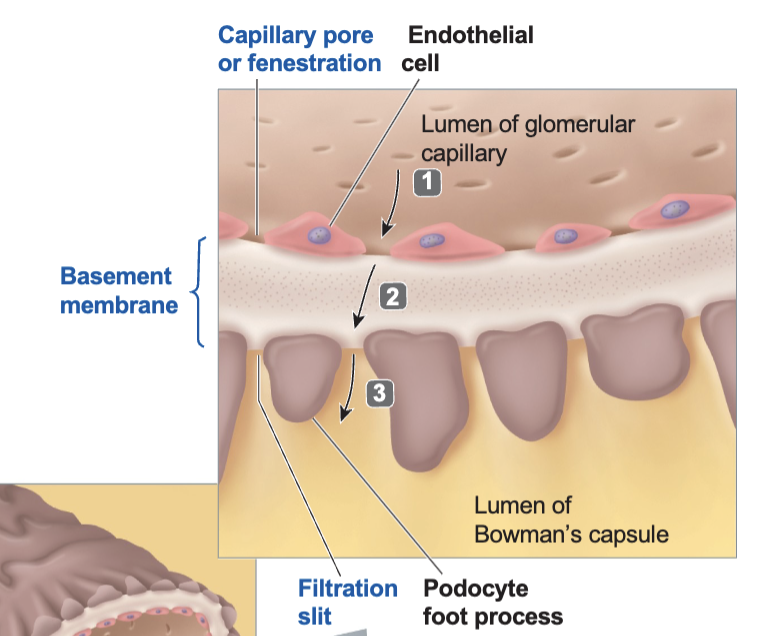
What is filtration?
Act of the kidneys pushing plasma of the blood out of the capillaries of the glomerulus and into Bowman’s capsule
What are three forces that contribute to glomerular filtration rate (GFR)?
Glomerular capillary blood pressure
Plasma-colloid osmotic pressure
Bowman’s capsule hydrostatic pressure
Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure
The fluid pressure within the glomerular capillaries
Favors filtration
Variable
About 55 mmHg
Plasma-Colloid Osmotic Pressure
Caused by unequal distribution of protein between plasma (contains protein) and glomerular filtrate (no protein)
Water wants to move down the osmotic gradient into glomerulus/ back into plasma
Opposes filtration
Constant
About 30 mmHg
Bowman’s Capsule Hydrostatic Pressure
The fluid pressure by the filtrate in Bowman’s capsule
For more fluid/ filtrate to enter, the existing needs to be pushed out, which requires pressure
Opposes filtation
Constant
About 15 mmHg
What is net filtration pressure?
The sum of glomerular capillary blood pressure, plasma-colloid osmotic pressure, and Bowman’s capsule hydrostatic pressure
Favors filtration
Controlled by glomerular pressure
Glomerular Filtration Rate
Depends on
net filtration pressure (major)
glomerular surface area available for penetration (minor)
permeability of the glomerular membrane (minor)
What are the controlled adjustments of the GFR?
Autoregulation
Myogenic
Tubularglomerular Feedback
Extrinsic Sympathetic Control
Baroreceptor Reflex
Vasoconstriction: decrease in glomerular capillary blood pressure → decrease in net filtration → decrease in GFR
Vasodilation: increase in glomerular capillary blood pressure → increase in net filtration → increase in GFR
Myogenic (autoregulation)
Local response within arteriolar smooth muscle wall to stretch
Increase in blood pressure → vasodilation → decrease in blood pressure
Tubularglomerular Feedback (autoregulation)
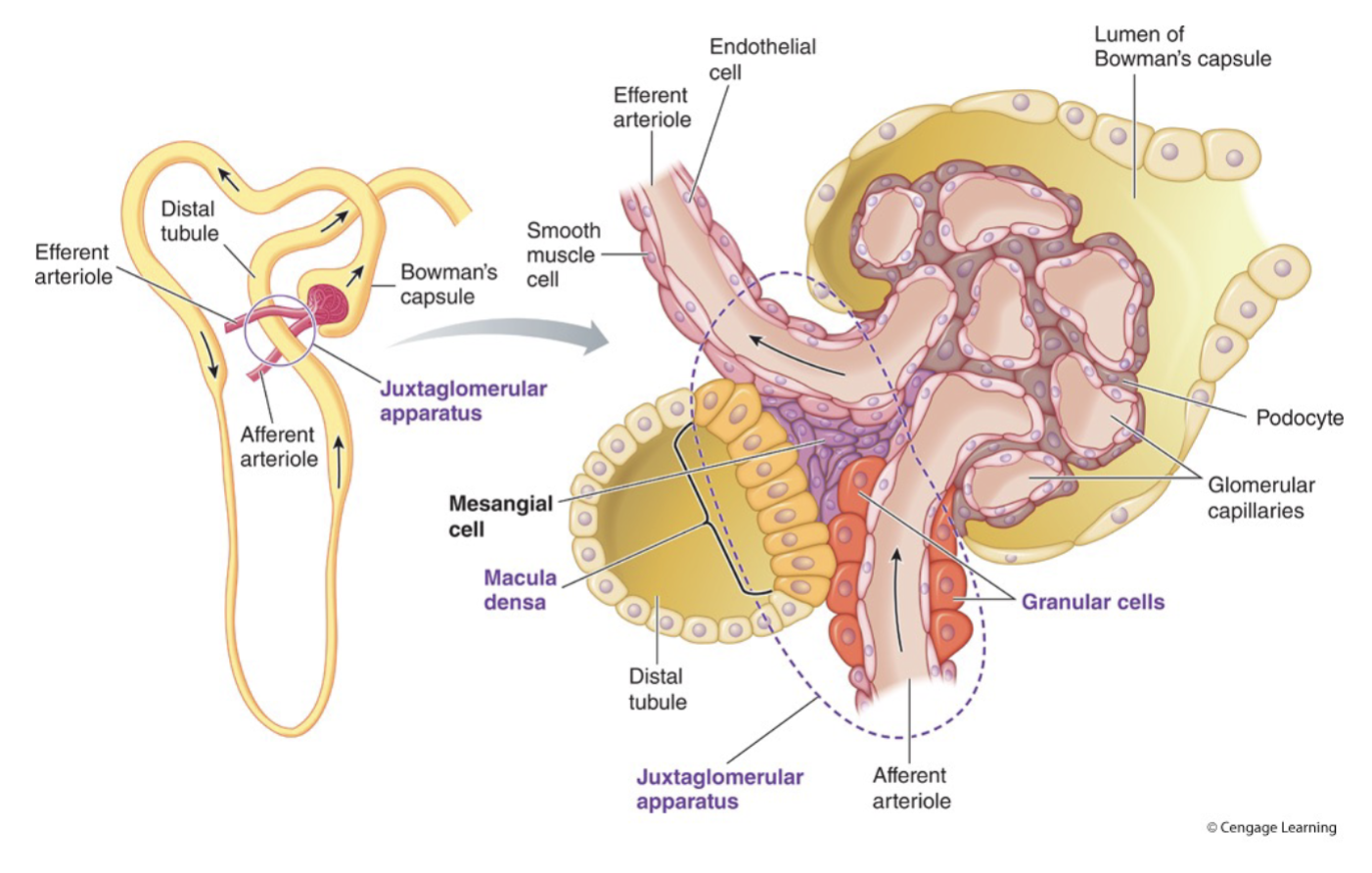
Adjsutments to afferent arteriolar pressure in response to salt concentration in the loop of Henle at the juxtaglomerular apparatus
Maintains constant GFR across a large blood pressure range, allows glomerular capillary blood pressure to stay constant even when upstream efferent arteriole blood pressure increases
Increased blood pressure leads to increased GFR and increases the salt delivery to the distal tubules
Macula densa cells (specialized tubule cells in the juxtaglomerular apparatus) detect this increase in salt delivery and release paracrine factors that constrict the adjacent afferent arteriole
Glomerular capillary pressure and GFR decrease, and salt is pushed out
Baroreceptor Reflex in Extrinsic Control (GFR)
A sudden drop in blood pressure causes the body to respond with general vasoconstriction to help increase the blood pressure
At the same time, constriction of afferent arterioles reduces GFR and volume of filtrate and urine produced