Motor Pathways 1: Corticospinal Tract, Upper and Lower Motor Neurons
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
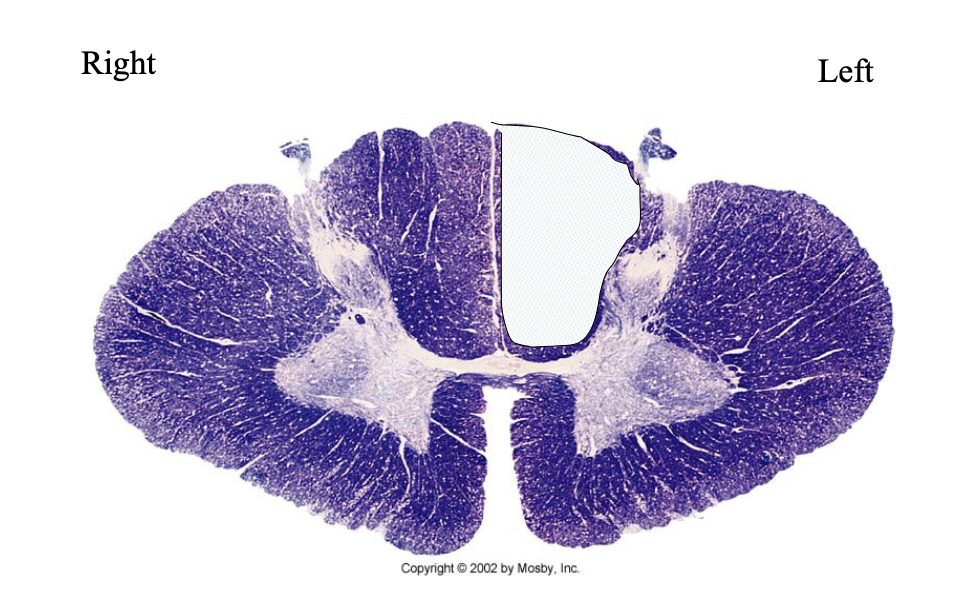
What clinical findings would you expect with each of these lesions?
loss of dorsal column modalatities (ipsilateral)
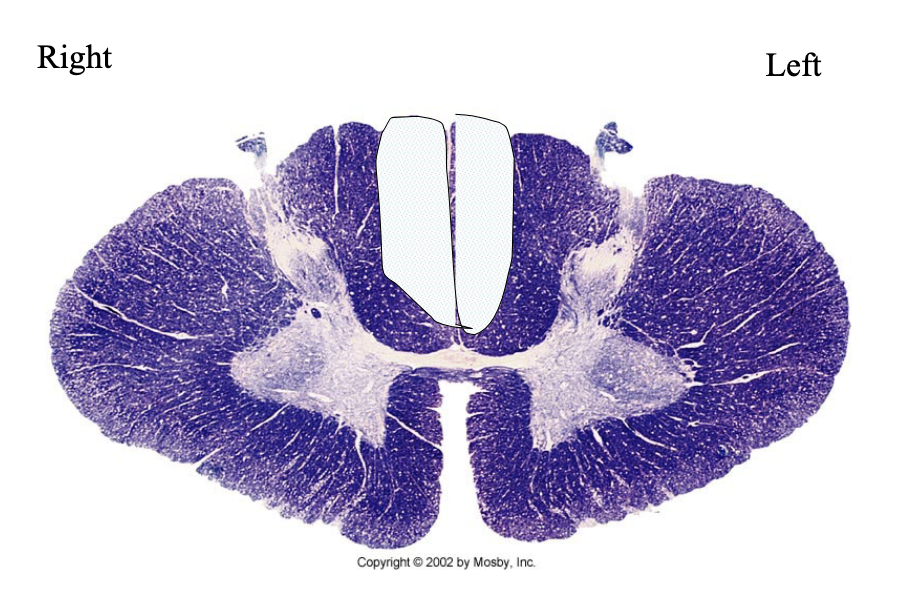
What clinical findings would you expect with each of these lesions?
loss of spinothalamic modalaties on left side
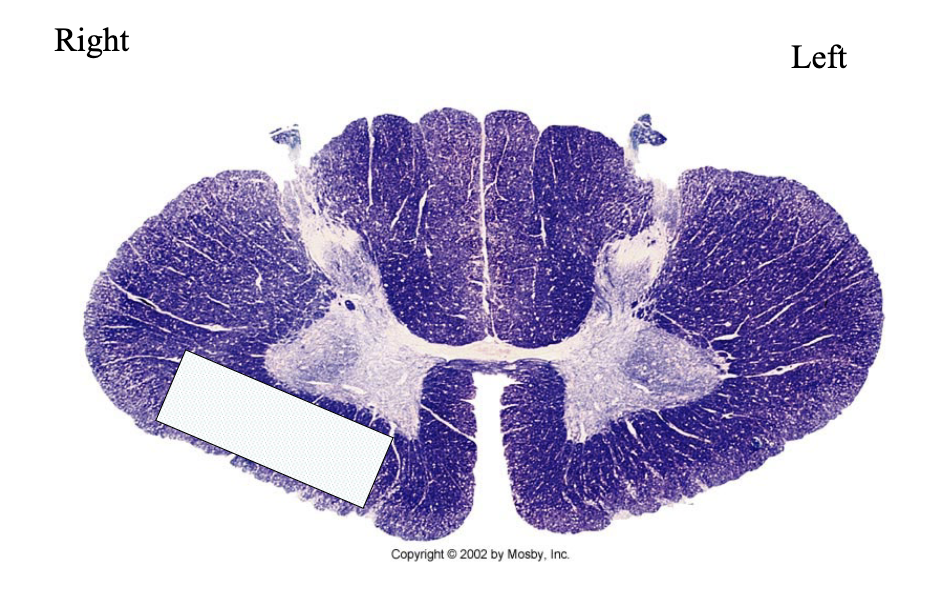
What clinical findings would you expect with each of these lesions?
loss of sensation in lower extremeties
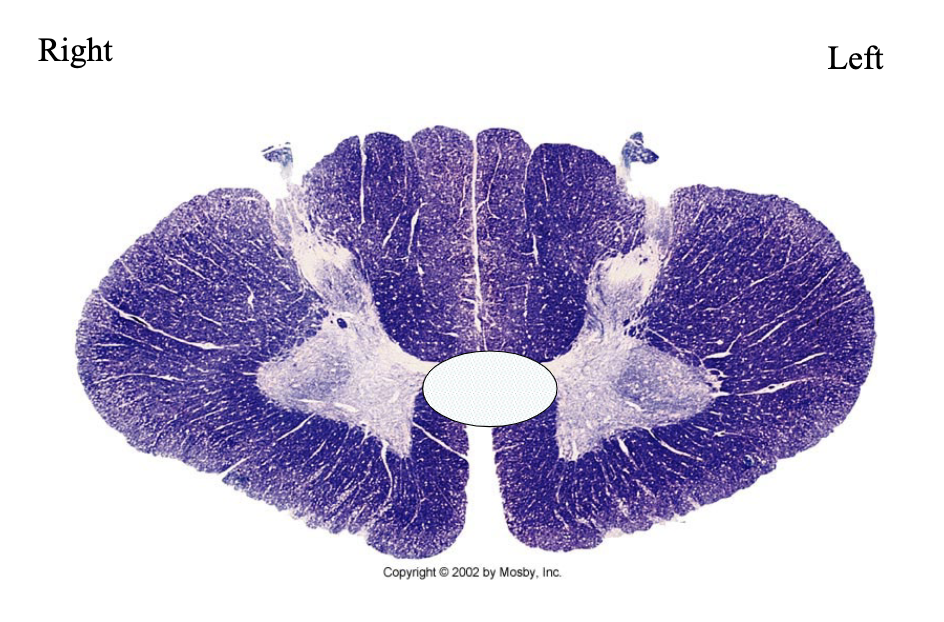
What clinical findings would you expect with each of these lesions?
bilateral spinothalamic suspended sensory loss
t/f: the spinothalamic tract deals with localized pain but collaterals of the pathway in the brainstem are part of multisynaptic spinal reticular pathways that deal with the affect of pain (emotion, chronic pain, etc.)
true
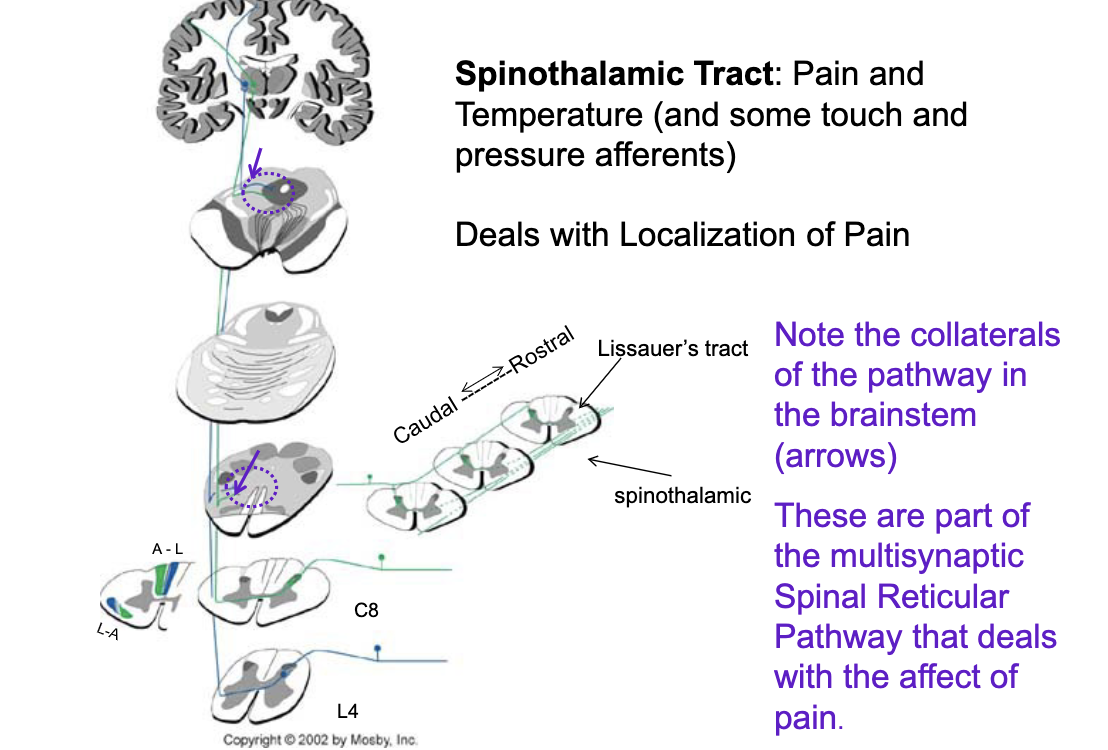
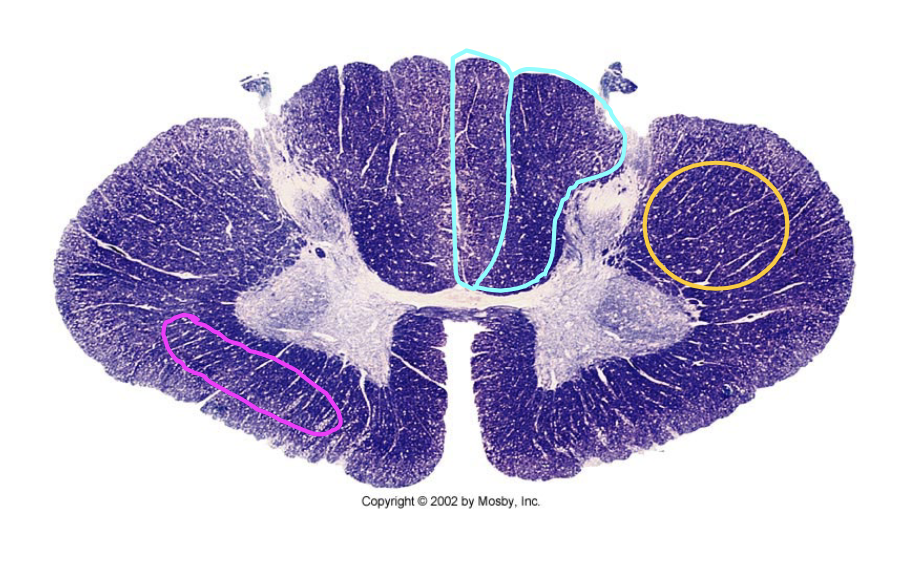
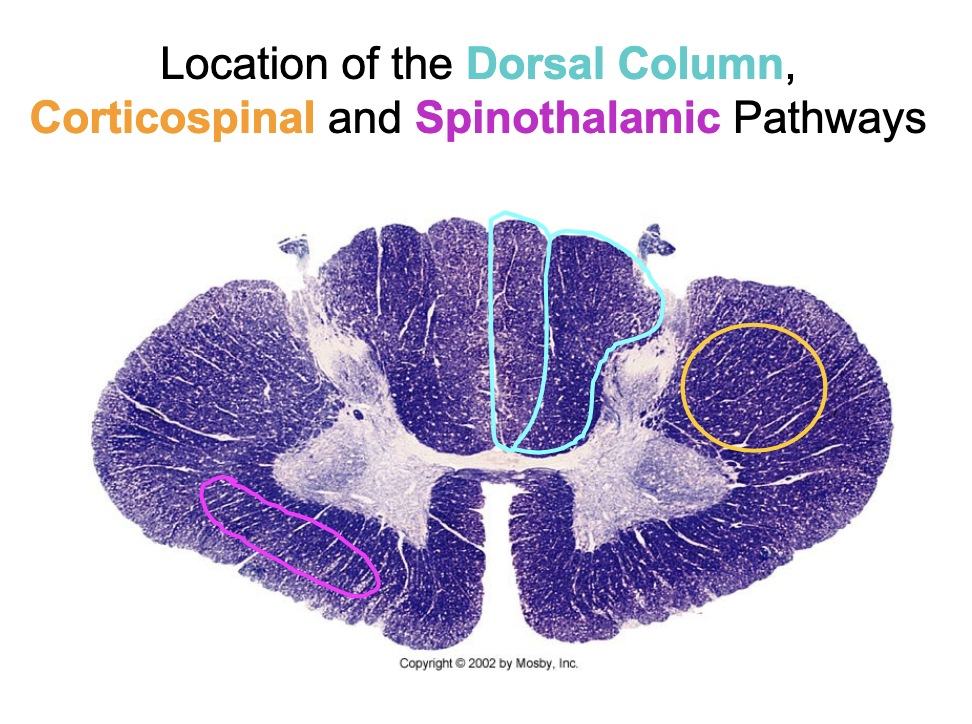
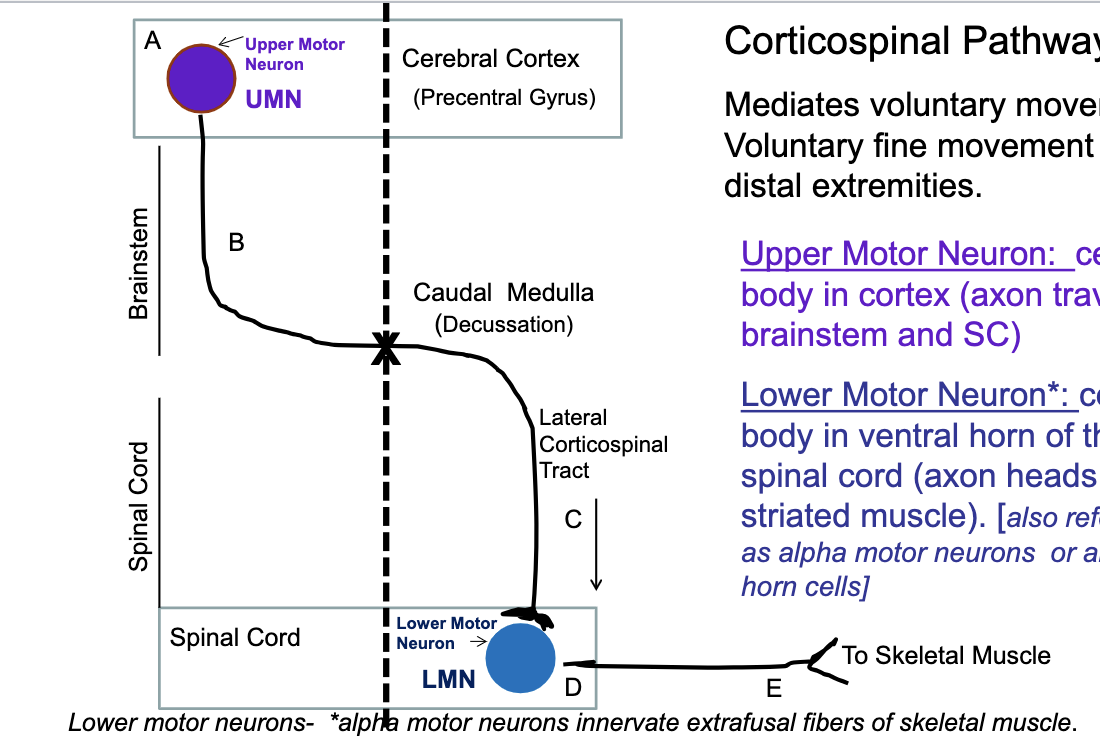
what does the corticospinal pathway control?
mediates voluntary movement
voluntary fine movement of distal extremeties
describe the corticospinal pathway?
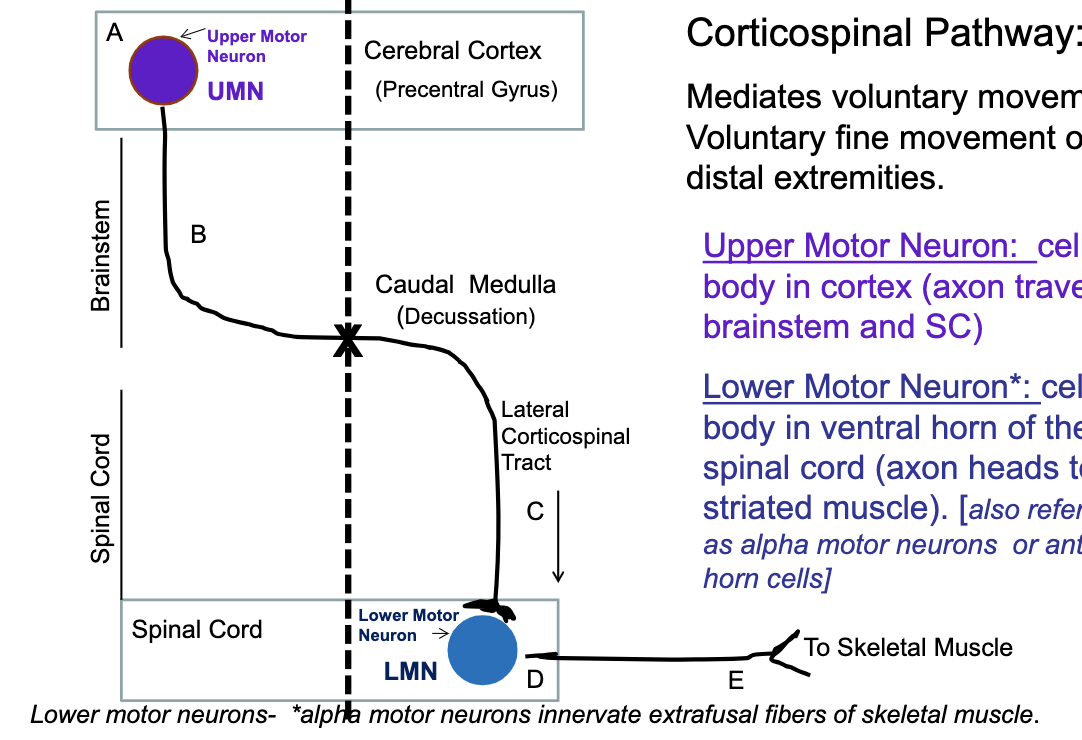
where is the upper motor neuron in the corticospinal pathway (body and axon)? lower motor neuron?
upper motor neuron → body in cerebral cortex, axon traverses brainstem/spinal cord
lower motor neuron → body in ventral horn of spinal cord, axon heads to striated muscle
85% (majority) of fibers cross in the _________ and form the ______ corticospinal pathway
caudal medulla
lateral
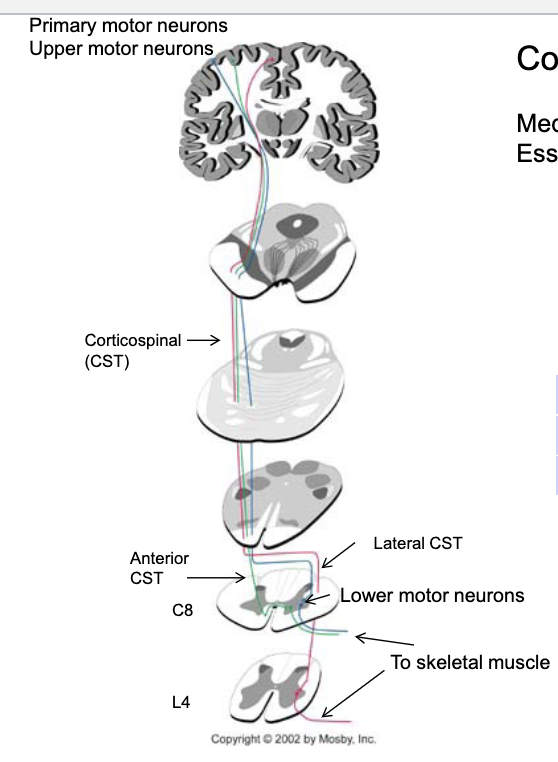
15% (minority) of fibers cross in the _________ and form the ______ corticospinal pathway
midline at the level of the lower motor neurons they will contact
anterior coticospinal pathway
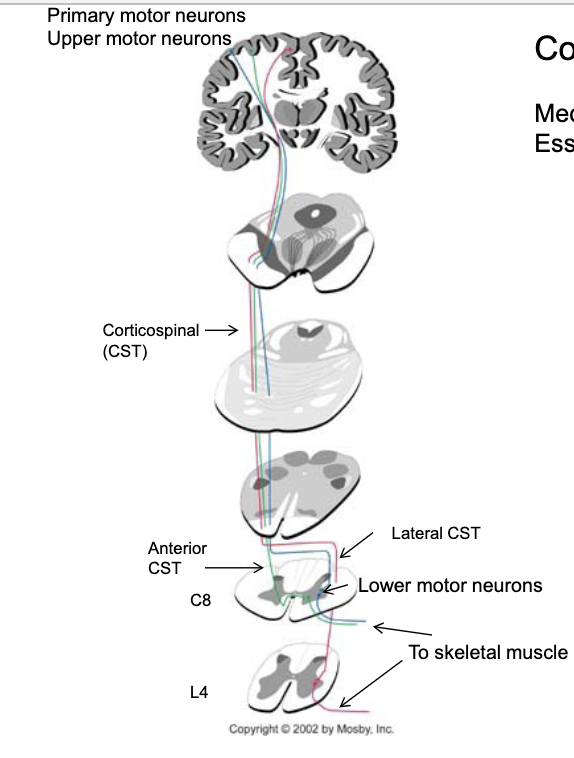
corticospinal pathway
if there is a lesion in the upper motor neuron or brainstem, will there be a contralateral or ipsilateral deficit?
contralateral
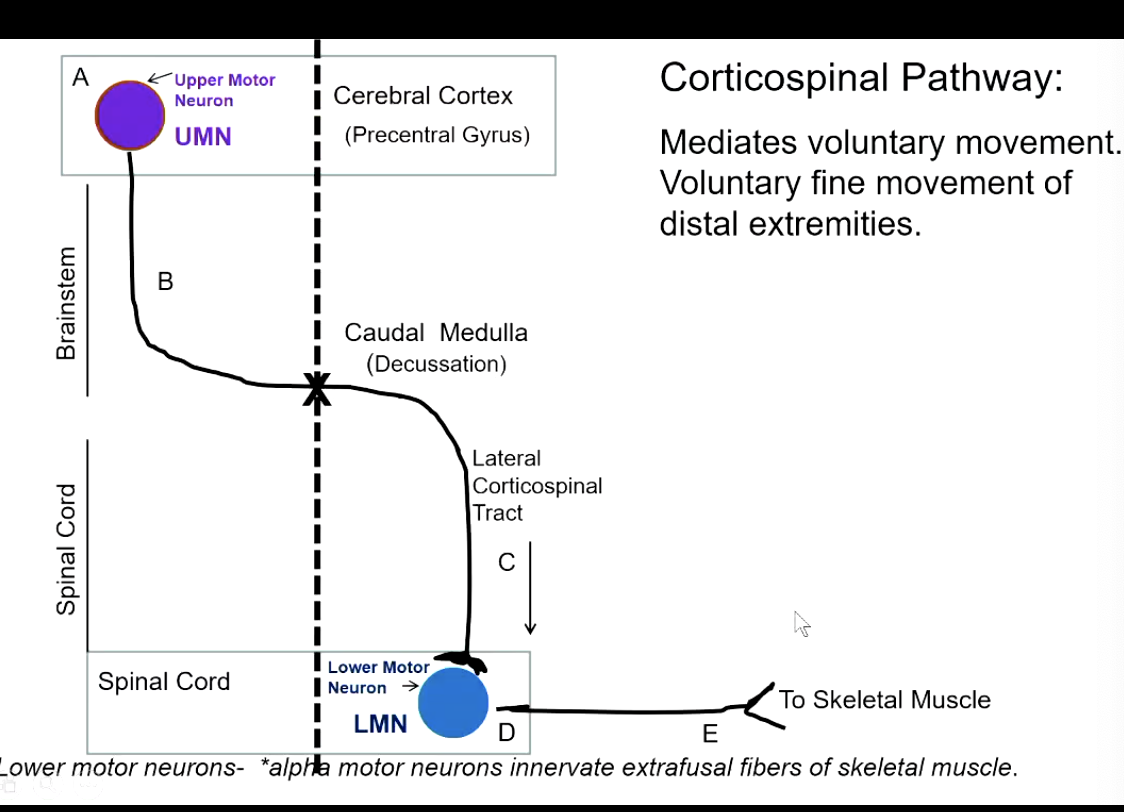
corticospinal pathway
if there is a lesion in the lateral corticospinal tract or lower motor neuron, will there be a contralateral or ipsilateral deficit?
ipsilateral
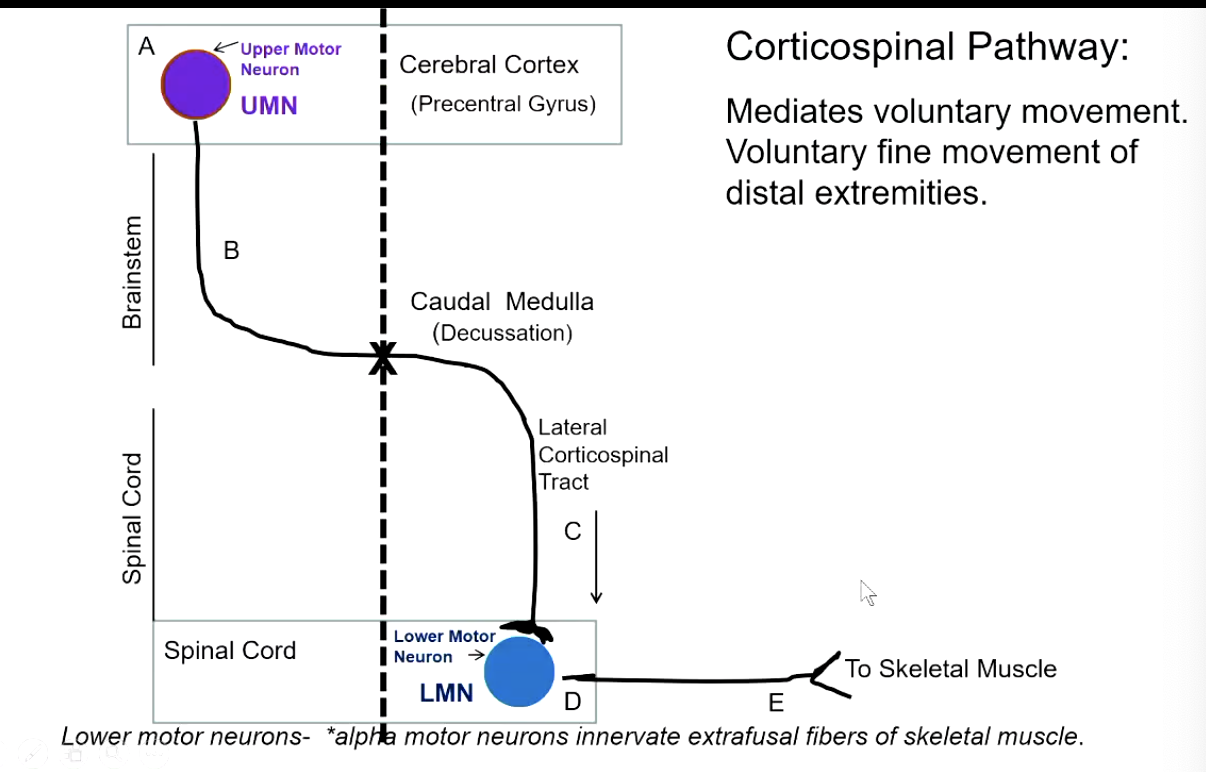
t/f: if there is a lesion in the lateral corticospinal tract, it is a upper motor neuron lesion.
true!
only lesions in ventral horn or axons leaving to skeletal muscle are considered lower motor neuron lesions
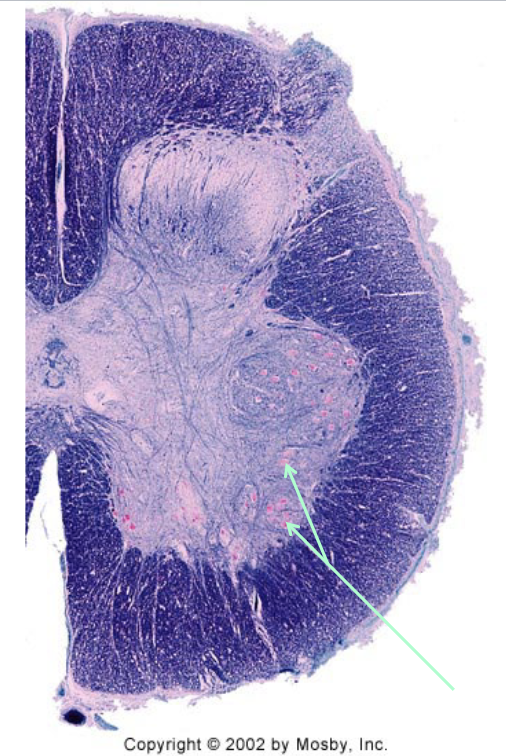
Clusters of lower motor neurons in the anterior horn at S4.
what are clinical presentations of upper motor neuron lesions?
hyperreflexia
spastic paralysis
increased muscle tone (pronounced in upper extremity flexors and lower extremity extensors)
Clasp Knife reflex
Clonus (rapid muscle contraction)
Babinski sign present
large area of body affected (level of lesion and below)
what is clonus?
rapid series of alternating muscle contractions in response to a sudden stretch
most common in ankles
tested by rapidly flexing foot upward
knees
tested by rapidly pushing patella toward toes
sign of upper motor neuron lesion
what are clinical presentations of lower motor neuron lesions?
flaccid paralysis
loss of deep tendon reflexes
decreased muscle tone
atrophy
fasciculations (anterior horn cell involvement)
segemental distribution of deficit
what are Fasciculations?
Spontaneous contractions of muscle fibers visible through the skin as small twitches.
Seen in anterior horn cell disease.
Sign of LMN lesion
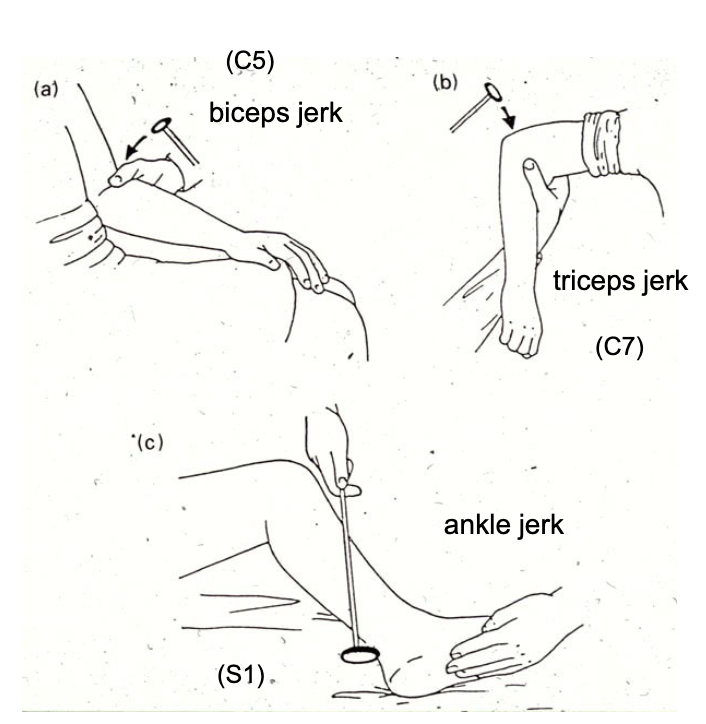
exaggerated reflexes during deep tendon reflex testing is a sign of…?
upper motor neuron lesion
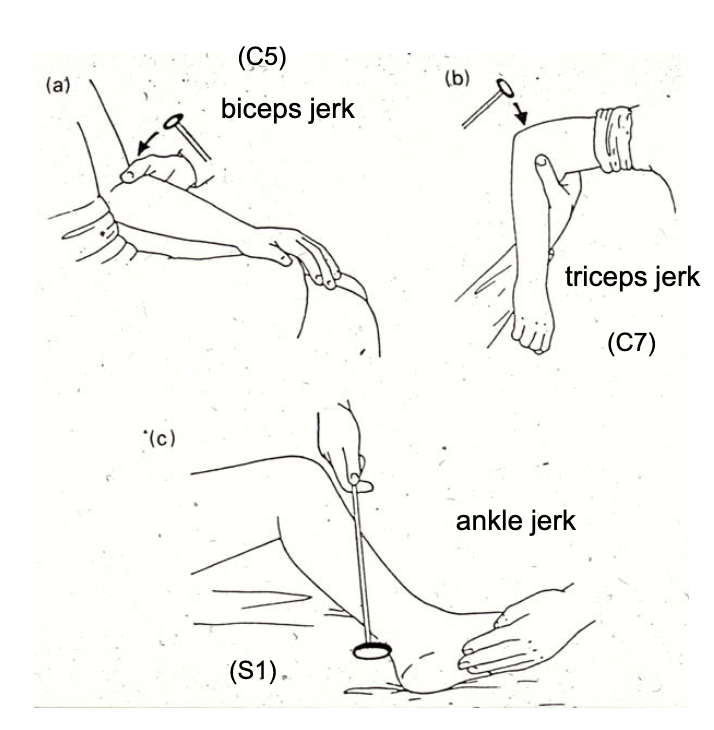
diminished reflexes during deep tendon reflex testing is a sign of…?
lower motor neuron lesion
Although spinal reflexes do not require supraspinal input, the lower motor neurons receive input from ________ that can modulate the intensity of the reflex.
cortex and brainstem
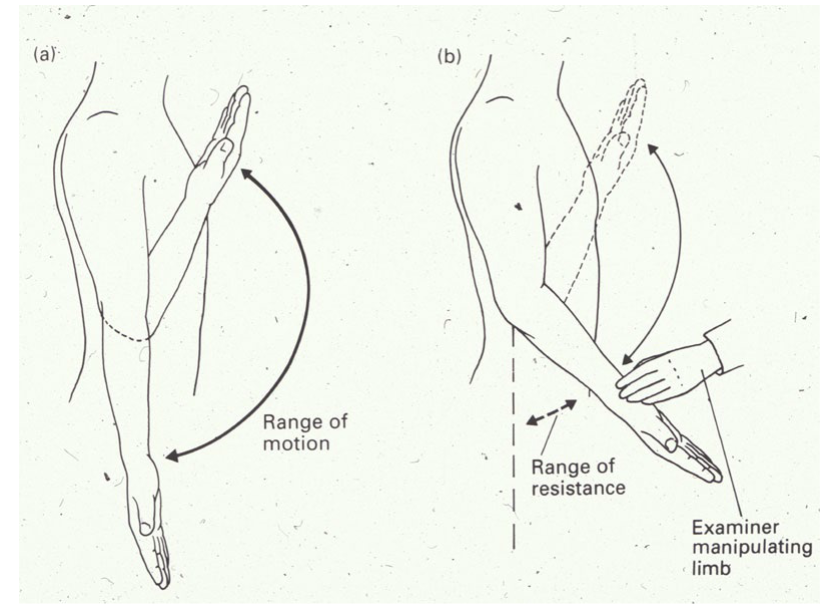
what is Clasp knife reflex?
sign of UMN lesion
response to passive movements of the limb
collapse of resistance seen when a spastic, hypertonic limb is forcibly flexed or extended
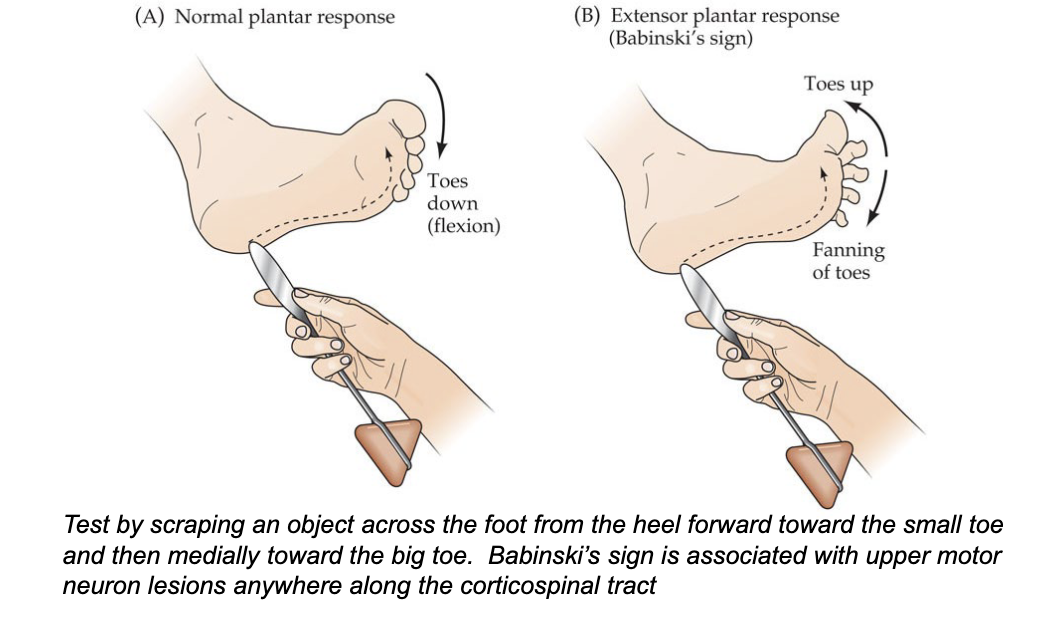
what is plantar response?
testing for Babinski’s sign
flexion = normal
extension (toes fanning and upward) = Babinski’s sign
is hyperreflexia a sign of UMN or LMN lesion ?
UMN
is spastic paralysis a sign of UMN or LMN lesion ?
UMN
is increased muscle tone a sign of UMN or LMN lesion ?
UMN
is clasp knife reflex a sign of UMN or LMN lesion ?
UMN
is clonus a sign of UMN or LMN lesion ?
UMN
is positive Babinski sign a sign of UMN or LMN lesion ?
UMN
is a large area of the body being affected a sign of UMN or LMN lesion ?
UMN
is decreased deep tendon reflexes a sign of UMN or LMN lesion ?
LMN
is flaccid paralysis a sign of UMN or LMN lesion ?
LMN
is decreased muscle tone a sign of UMN or LMN lesion ?
LMN
is atrophy a sign of UMN or LMN lesion ?
LMN
is fasciculations (anterior horn cell involvement) a sign of UMN or LMN lesion ?
LMN
is segmental distribution of deficit a sign of UMN or LMN lesion ?
LMN
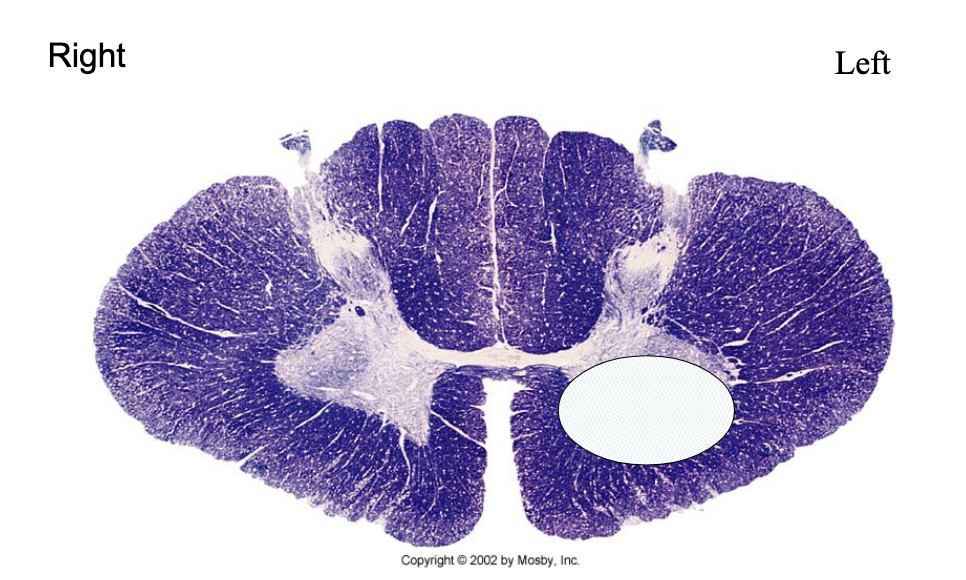
What is lesioned here? What clinical findings would you expect with this lesion?
LMN (in ventral horn cells)
atrophy, fasciculations, paralysis of hands (C7/8 affect hands)
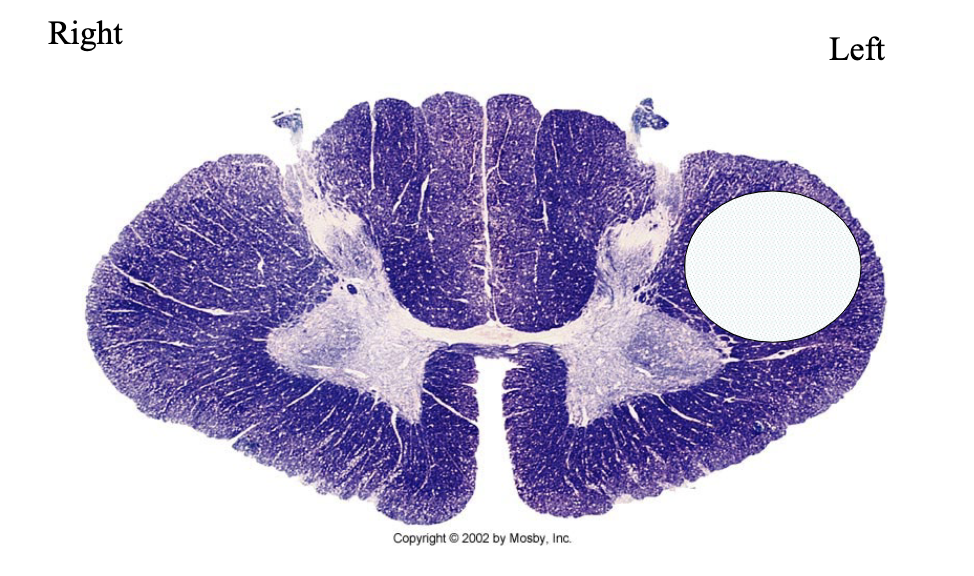
What is lesioned here? What clinical findings would you expect with this lesion?
UMN
increased muscle tone on left side (because we’re in spinal cord, if it was in brain stem it would be right side)
positive Babinski, Clonus
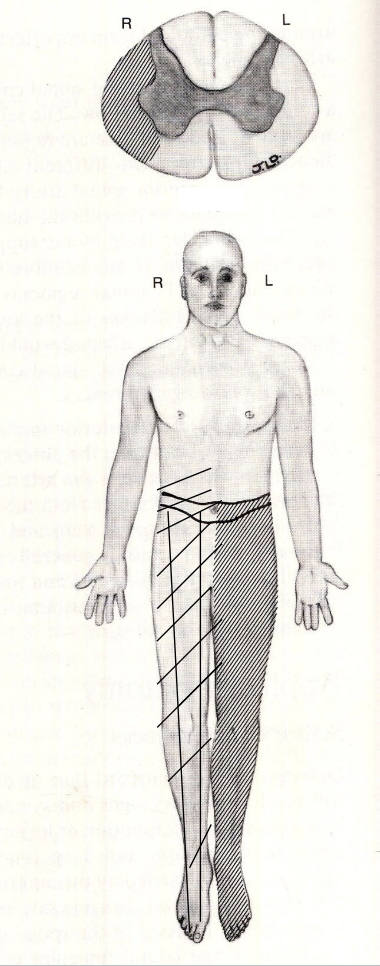
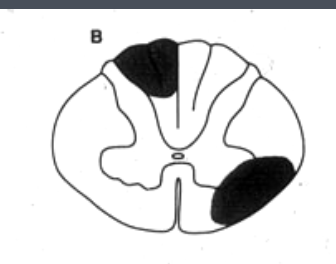
which sensory (ascending) pathway is lesioned here? which motor (descending) pathway is lesioned?
(ascending) spinothalamic = contralateral deficit at level of lesion and below
(motor) corticospinal = ipsilateral deficit at level of lesion and below
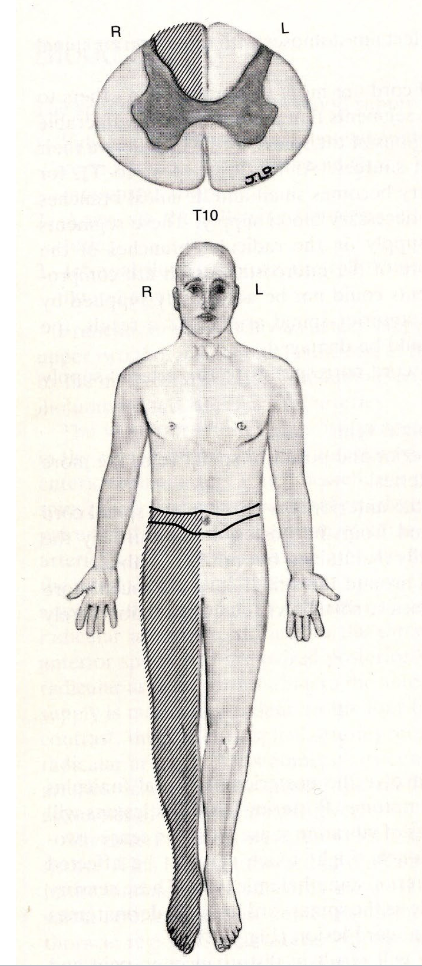
which sensory (ascending) pathway is lesioned here? which motor (descending) pathway is lesioned?
(ascending) dorsal column = ipsilateral deficit at level of lesion and below
(motor) none
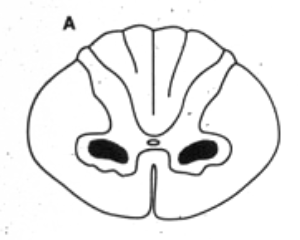
LNM bilaterally → polio
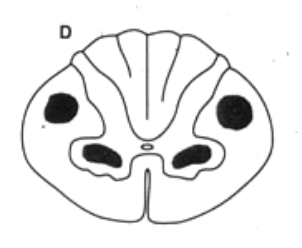
UMN and LMN bilaterally → ALS
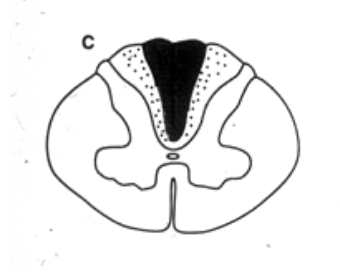
tabes dorsalis
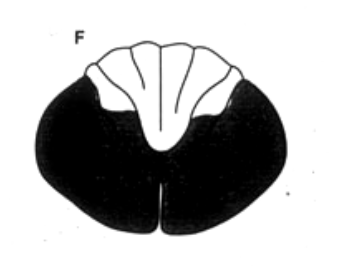
spinothalamic and corticospinal, LNM
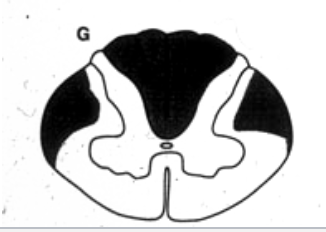
dorsal columns + lateral corticospinal tract → B12 Deficiency, Freidrichs Ataxia
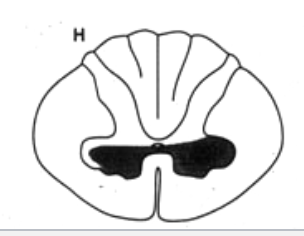
ventral white commissure, lateral corticospinl tract → Syringomyelia
corticospinal tract, dorsal columns → multiple sclerosis