HBS Unit 4 Conclusion Questions
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Predict the potential effects of abnormally narrow renal arteries, a condition called renal artery stenosis, on the ability of the kidneys to carry out their functions. Explain how this might impact other body systems.
If the kidneys are not able to effectively filter waste and maintain water balance in the blood, the body’s ability to carry out other functions, such as dissolving minerals and nutrients for use in the body, moistening tissues, and lubricating joints, would be affected.
Describe how other organs or structures, aside from those in the urinary system, help you maintain a water balance.
The stomach and intestines play a role in the intake and absorption of water
Sweat glands release water when you sweat
The skin helps protect the body and plays a role in water loss and absorptio
How do the circulatory system and kidneys interact to create urine?
The kidneys remove unwanted or unneeded particles from the blood to produce waste (urine)
Capillaries are intertwined with the nephrons of the kidney
The glomerulus is a capillary bundle and is involved in the first stage of urine formation.
In the glomerulus, particles are filtered from the blood. Filtration occurs by selective permeability and passive transport along a concentration gradient.
Blood cells do not transfer to the filtrate (urine)
In the tubules of the nephron, additional passive transport occurs, along with the active transport of other wastes from the blood.
Figure 2 has two urine outputs from the same individual during the same day, with the same number of hours between bladder-voiding events. Explain what you think might cause this phenomenon.
With dehydration, urine becomes darker because it is more concentrated. Water is reabsorbed into the bloodstream within the kidneys before reaching the bladder. If someone is dehydrated the body will hold onto water, rather than excrete it. Minerals and other constituents of urine are continuously filtered from the blood, so excretion will still continue, but there will be less water to dilute these other urine components.
Certain drugs that treat high blood pressure cause vasodilation of systemic arteries and arterioles, including those in the kidneys. What effect would these drugs have on the eGFR?
Drugs for high blood pressure that cause vasodilation would increase GFR, because the drug works to widen the arteries and arterioles, lowering blood pressure and increasing surface area for filtration.
What are three actions that an individual can take to decrease their chances of CKD?
Three things an individual can do to decrease their chances of CKD are to limit alcohol and smoking, make healthy food choices, and incorporate physical activity into their daily routine.
If Isla had children with a man who was homozygous recessive for PKD 2, what are the chances that her children will have PKD 2? Use a Punnett square as needed to show your work.
There will be a 50% chance that her children will have PKD 2.
Explain how the code in your DNA relates to your physical appearance as well as the functioning of your body. How might a change in this code impact the body?
Protein synthesis, our code determines everything about us, not just our physical appearance, it has to do with predisposition of certain illnesses, it makes all the proteins that make up our body, if we change to code, we change the protein, if we change to proteins we change the functionality of the protein.
Urinalysis is an important diagnostic tool for the determination of medical disorders. However, urinalysis has many other uses. Describe one other reason a person may have their urine tested.
Drug testing for school, sport or job. Pregnancy test for women. to monitor health.
Explain why diagnostic tests are classified as a type of medical intervention.
Can help diagnose a disease.
Describe how a dysfunction in the body can affect the nephrons of the kidneys, and explain how urinalysis could detect this dysfunction.
High sugar levels in the body can affect the nephrons over time by destroying the lining of the nephrons with glucose. This could lead to chronic kidney disease. A urinalysis can detect it by detecting high levels of sugar (glucose)
Provide an example that illustrates how the structure of an organ (or accessory organ) in the digestive system is specifically linked to its function.
Teeth are hard and sharp. They can bite into and tear apart food into smaller pieces. At the same time, salivary amylase in the mouth helps to begin chemical digestion. The tongue helps us swallow food, so chemical digestion can continue in the stomach.
The stomach is a sac-like organ that is made of muscle and contains enzymes. Its muscles can expand as food enters. Its muscles provide mechanical digestion, while the acid inside provides chemical digestion of the food.
Why do the small and large intestines have such different lengths?
The variation in length is due to the function of each intestine. Because the small intestine continues to digest and then absorb nutrients from the food, it needs to be longer, so it has more time and more surface area to do this. The large intestine’s main function is to compact the remnants from the small intestine into waste and absorb the remaining water. Because there is not as much to absorb, the large intestine does not need to be as long as the small intestine.
Explain how both the digestive system and the urinary system work to conserve water in the human body.
The urinary and digestive systems both reabsorb water as substances pass through them. In the urinary system, water is reabsorbed from the filtrate and returned to the blood. In the digestive system, the large intestine absorbs the extra water from the remaining food before it is excreted as waste.
Explain the importance of using accurate and engaging medical illustrations and models in both medical education and popular media. Provide at least one example to support your explanation.
In medical education, accurate and engaging illustrations and models are used to teach students about anatomy, physiology, and pathology. In popular media, these illustrations and models can help educate the public about various medical conditions and treatments, such as the effects of smoking on the lungs, the progression of a disease such as cancer, or the mechanism of action of a drug.
Accurate and engaging media is especially important when considering the development of patient education materials. When patients receive clear and visually appealing illustrations and models, they are more likely to understand their medical condition, the recommended treatment plan, and potential risks and benefits associated with their care. This understanding can lead to improved patient outcomes and satisfaction with their healthcare experience.
Describe how a problem in a body system other than the digestive system can cause dysbiosis in the gut. Also, describe how a problem in the gut microbiome could cause disease in a body system other than the digestive system. Do additional research as needed.
If a person has a chronic inflammatory condition, such as rheumatoid arthritis or psoriasis, the immune system can be impacted, leading to systemic inflammation. This inflammation can disrupt the delicate balance of the gut microbiome, causing dysbiosis.
Conversely, imbalances in the gut microbiome can contribute to the development of neurological conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and multiple sclerosis. Dysbiosis can also affect the immune system, leading to chronic inflammation and autoimmune diseases, such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis.
What are the functions of the smooth muscle in the stomach and the villi in the small intestine? How do the structures help with function?
The smooth muscle in the stomach propels the food bolus to the intestine and continues the mechanical breakdown of food; the villi in the small intestine assist in food absorption.
The shape of smooth muscle is round in the center and tapered at the end, allowing it to tense and relax but still maintain tone, thanks to the rounded center.
The villi in the small intestine are small fingerlike projections (like a shag bath mat). Their structure helps increase the small intestine’s surface area for more efficient absorption.
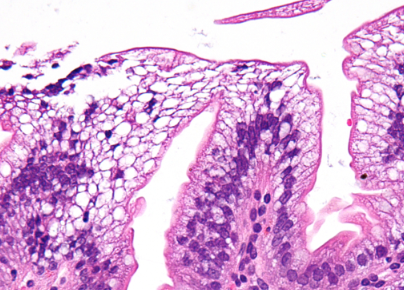
Abetalipoproteinemia is a rare, inherited disorder that is caused by changes (mutations) in the microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTTP) gene. The disorder affects fat absorption by the intestine and mobilization by the liver. Analyze Figure 10, Abetalipoproteinemia Biopsy from the Duodenum. What changes do you see in the tissue? Explain how those changes would cause impaired fat absorption.
The enterocytes or simple columnar epithelium cells have an accumulation of fluid and increased cytoplasm. Enterocytes’ function is to assist with absorption. In an individual with Abetalipoproteinemia, the enterocytes cannot function appropriately due to this fluid accumulation, and, therefore, cannot absorb nutrients appropriately.