Intro to Microbio Lab
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Why do we use aseptic technique?
For safe handling and to avoid contamination.
What is the purpose of doing a four-quadrant streak
It allows for the isolation of single colonies of bacteria
Nutrient agar (NA) & Tryptic Soy Agar (TSA) plates
Support the growth of a wide range of organisms.
Gram Postive
purple, thick peptidoglycan layer
Gram Negative
pink, thin peptidoglycan layer
Monotrichous
single flagellum
Amphitrichous
flagella at both ends of cell
Lophotrichous
cluster of flagella at one or both ends
Peritrichous
flagella distributed over the entire cell
Motility Test Medium (MTM)
use of semi solid agar media to detect bacterial motility
Mesophiles
moderate temperature loving microbes. (20C-45C)
Psychrophiles
cold loving bacteria (-20C-20C)
Thermophiles
heat loving microbes (41C-122C)
Prodigosin pigment
Produced by Serratia marcesens
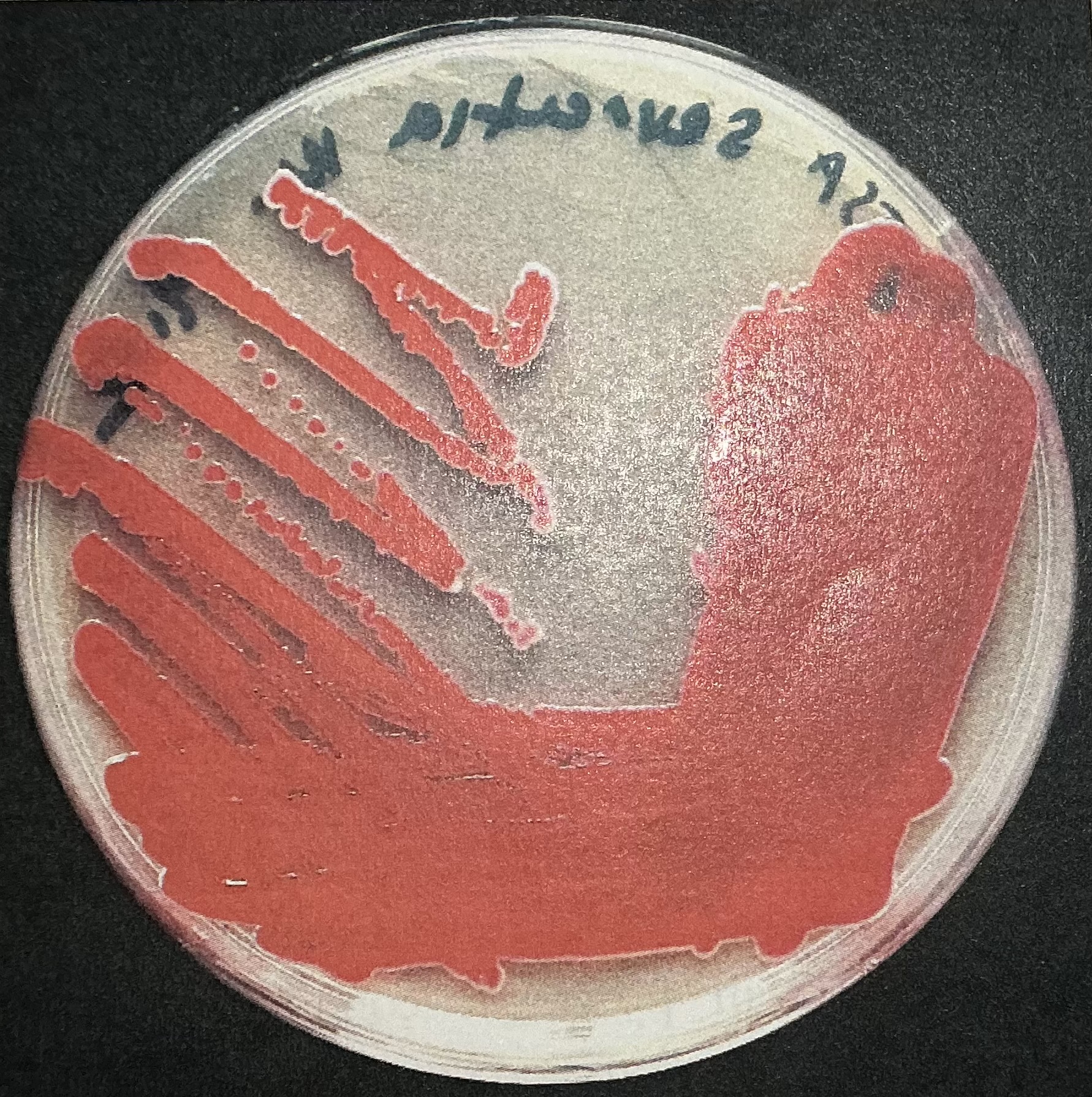
Pyocyanin pigment
Produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa
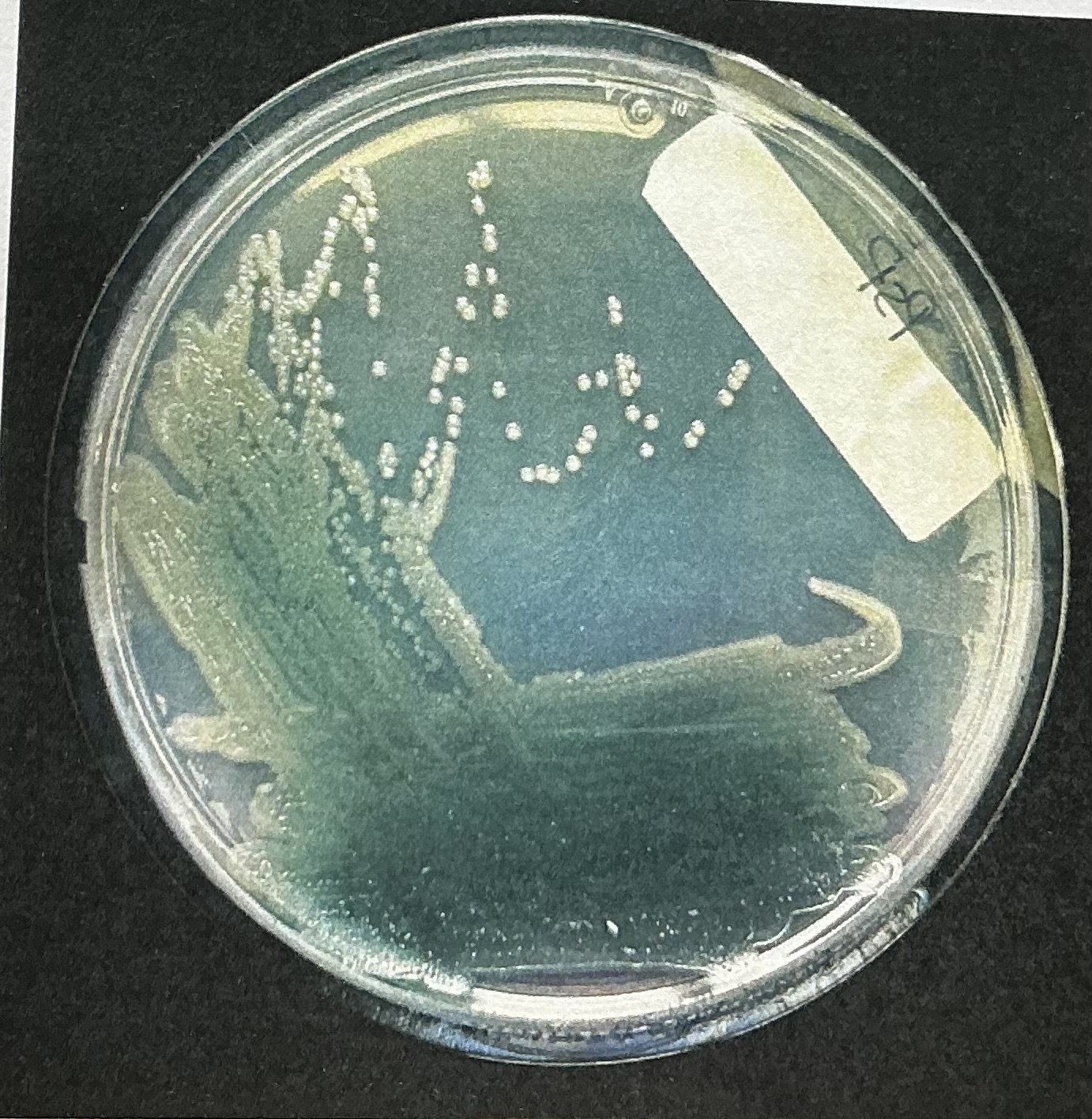
Canthaxanthin pigment
Produced by Micrococcus roseus

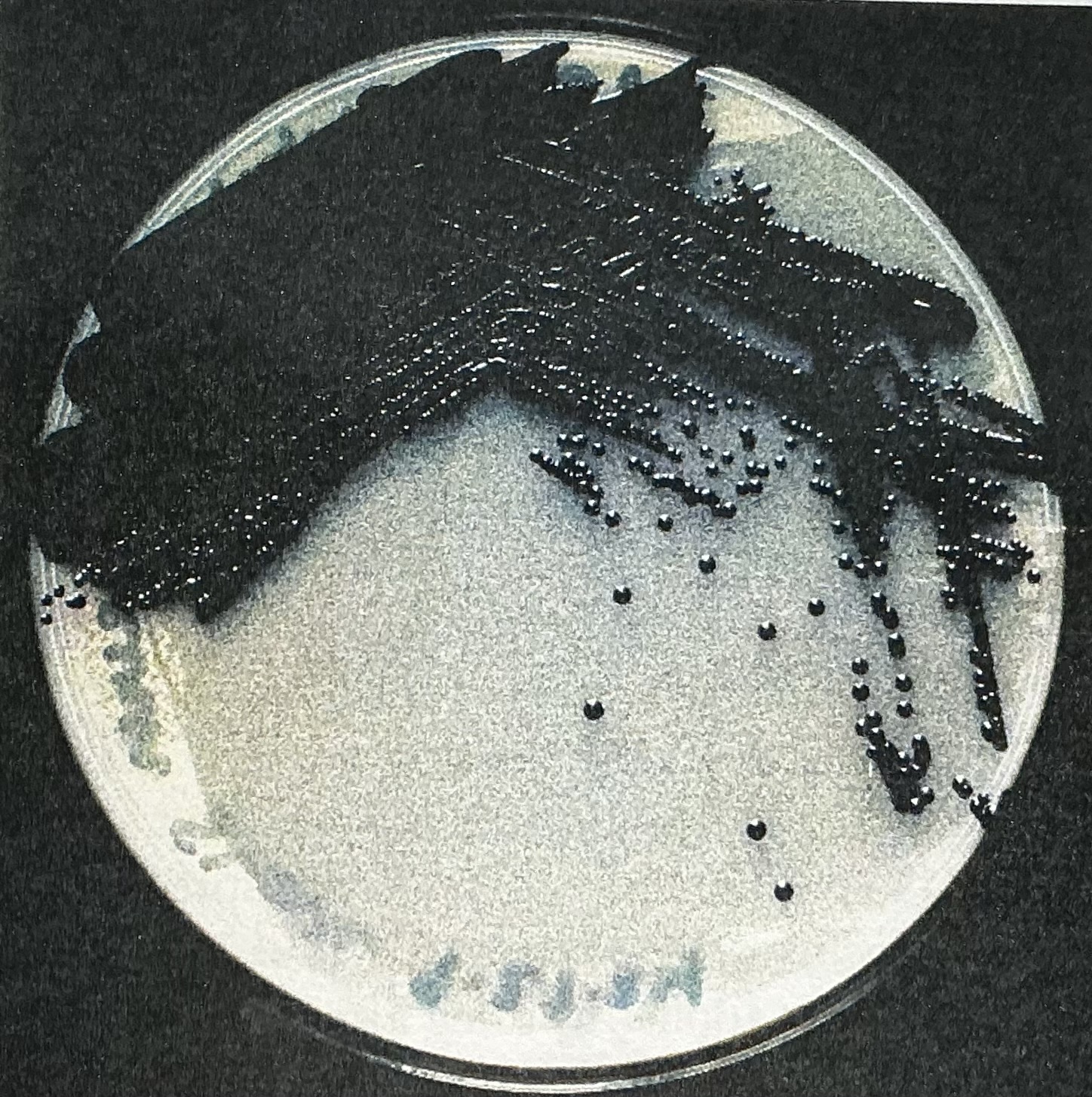
Violacein pigment
Produced by Chromobacterium violaceum
Phases of bacterial growth curve
Lag Phase, Exponential/Log Phase, Stationary Phase, and Death Phase
Lag Phase
The organisms are not dividing because they are adjusting
Exponential/Log Phase
The organism will start dividing and reproduce exponentially
Stationary Phase
As resources are reduced, growth levels off (Bacteria growth and Bacteria death balanced out)
Death Phase
As limiting factors intensify, bacteria start dying faster than reproducing.
Nutritive Media
Media types that provide sufficient nutrients to support the growth of a wide range of microorganisms.
EX: TSA and NA plates
Selective Media
Media types that promote the growth of "select" microbes, while preventing the growth of others
Differential Media
Media types that distinguish between organisms with unique characteristics due to difference in growth or appearance
Staphylococci
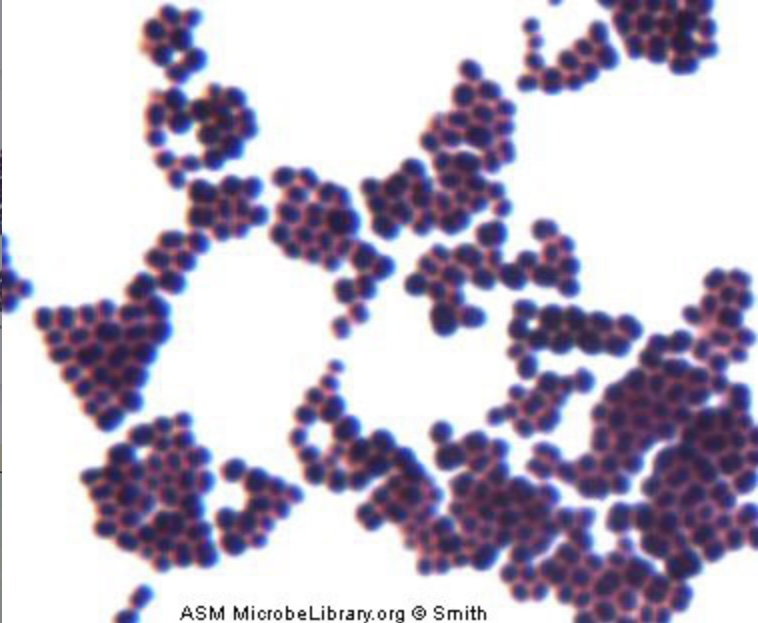
Steptococci
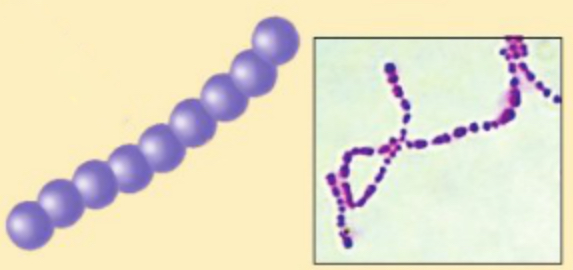
Sheep Blood Agar (SBA)
Differential Medium of Hemolysis
Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA)
Selective and Differential Medium. Staphylococci can grow on it and Streptococci cannot
Eosin Methylene Blue Agar (EMB)
Selective and Differential Medium. Distinguish organisms that can ferment lactose and organisms that can't
MacConkey Agar (MAC)
To isolate and identify enteric pathogens or non-pathogenic enteric bacteria. Can also distinguish lactose fermenters and non-lactose fermenters
Triple Sugar Iron Agar (TSIA)
Differential: Ability to ferment glucose/lactose/sucrose, reduce sulfur
Yellow Slant/Yellow Butt = carbohydrate fermentation
Red Slant/Yellow Butt = glucose fermentation only
Red Slant/Red Butt = no fermentation
Red Slant/No Change in Butt = no fermentation
Black Precipitate = sulfur reduction (requires acidic conditions)
Cracking or lifting of agar = Gas prodution
Citrate Utilization Test
Determines the ability of bacteria to use citrate as a sole carbon source for their energy needs
Positive - Blue
Negative - Green
Urease Test
Determines the ability of microorganisms to degrade urea by means of the enzyme urease.
Carbohydrate Fermentation
Determines if the microorganisms can metabolize that sugar
MRS Agar (De Man, Rogosa, and Sharpe)
Selective growth for bacteria from the genera: Lactobacillus, Streptococcus, Pediococcus, and Lenconostoc
Horizontal Gene Tranfer
passes genetic information between cells by a process independent of cell division and separate from reproduction
Three possible mechanisms of lateral gene transfer
Conjugation
Transformation
Transduction
Conjugation
In bacteria, the direct transfer of DNA between two cells that are temporarily joined.
Heat shock
A method that involves rapidly increasing and decreasing the temperature to increase membrane permeability in order to enhance the likelihood of bacterial transformation
Antibiotics
Substances that inhibit or kill bacteria
Disk diffusion/Kirby-Bauer method
-antibiotic embedded in filter disk diffuses into agar medium
-creates a concentration gradient, greatest near disk
Zone of inhibition
The zone where bacteria can't grow around a given antibiotic.
Mueller-Hinton agar
A common agar medium used for anti-microbial susceptibility testing.
Bacteriostatic
inhibits bacterial growth
Bactericidal
kills bacteria
Narrow spectrum antibiotics
Effective against specific bacteria like only for gram negative or only for gram Postive bacteria.
Broad spectrum antibiotics
antibiotics that affect a broad range of gram-positive or gram-negative bacteria