conciousness
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
what is conciousness
large and loaded but involves CNS
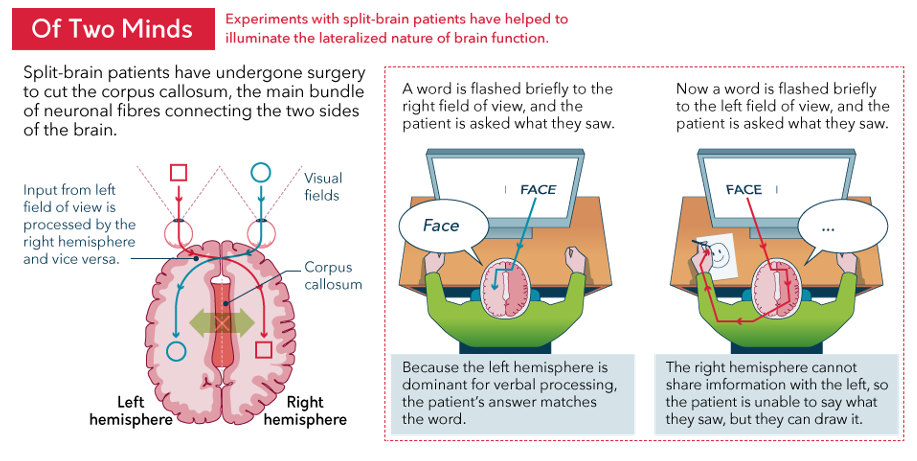
split brain
corpus callosum cut in epileptics, and sides cannot communicate
visual neglect
lesions in right parietal lobe, not aware of left stimuli, patients dont sense anything wrong, dorsal path interupted
ADHD
very common, suggest genetics but no gene found, causes unknown, treated with adderall
sleep
periodic, natural loss of conciousness, when brain is very active
sleep measurments
EEG, EOG (eye movements), EMG (muscle tension)
stages of sleep
1, 2, slow wave, and REM
beta waves
awake and alert, 13-30 hZ, low amp, erratic
alpha waves
awake and relaxed, 8-12 hZ, more amp, when ur getting sleepy
stage 1
light sleep, theta waves , 2-7 hZ
stage 2
lightish sleep, sleep spindles and k complexes, 3/min and 1/min relatively
slow wave sleep
deep sleep, 4hZ, high amp, about 20 mins to reach
REM
90 mins after SWS, vivid dreams, easy to wake up, desynchronized
sleep atonia
we appear paralyzed minus the occasional twitch
roffwarg et al
1962, eyes move like we are watching the dream, brain uses active parts as if we were doing activity in dream
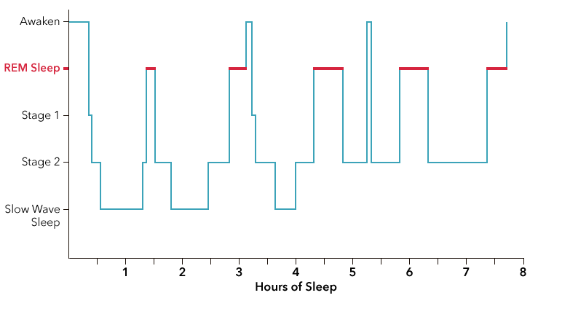
hypnogram
sleep stage graph, shows 90 min cycles
why do we sleep?
recovery for the body and brain
SWS functions
restores the brain via reduced bloodflow
REM functions
protects consolidation of memory
activation synthesis hypothesis
dreams have no meaning, consequence of whatever else is going on in the cortex
evolutionary hypothesis
dreams being a survival, enhances daytime performances
dyssomnias
recurring problems falling and staying in sleep
narcolepsy
uncontrollable sleep attacks, genetic
sleep apnea
stopping in breathing when sleeping
night terrors
high arousal and scary sleep dreams
insomnia
the inability to fall asleep or remain asleep, treated by new behaviours
conditioned insomnia
lack of sleep via anxiety
ideopathic insomnia
begins in childhood with no known cause
hypersomnia
excessive daytime sleepiness, often caused by sleep apnea