Management final sophomore year 2024
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
The relationship between motivation and performance
effort
nature of motivation
the reason for people's actions, willingness and goals
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Deficit principle:
Satisfied need no longer motivates behavior
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Progression principle:
The need at one level does not become activated until the lower level need in the hierarchy is satisfied
what does Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs mainly focus on?
what factor or factors motivate people
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs weaknesses
five levels of need are not always present
order is not always the same
cultural differences
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs needs:
Self-actualization
esteem
belongingness
security
physiology
Alderfer’s ERG Theory
Existence needs:
Material well-being
Relates to Maslow’s physiological and safety needs
Alderfer’s ERG Theory
Relatedness needs:
How one individual relates to his/her social environment
Relates to Maslow’s belongingness and external self esteem needs
Alderfer’s ERG Theory
Growth needs:
Desire for personal growth and development
Relates to Maslow’s internal esteem and self-actualization
Process Perspectives on Motivation
Expectancy theory:
Motivation depends on how much we want
something and how likely we are to get it
Expectance theory factors
Effort to Performance Expectancy or Expectancy (E)
is the probability that effort will lead to performance
Expectance theory factors
Performance to Outcome Expectancy or Instrumentality (I)
is the perception that performance leads to an
outcome. Outcome is the consequence or reward for
performance
Expectance theory factors
Attractiveness or Valence (V)
is how much a particular outcome/reward is valued
Expectancy theory equation
M = E x I x V
expectancy theory
motivated behavior to occur
Effort-to-performance must be greater than 0
Performance-to-outcome must be greater than 0
Sum of valences must be greater than 0*
One or more valences may be negative!
Equity Theory
Individuals equate value of rewards to effort and
compare it to other people
Edwin Locke’s Goal-Setting Theory
Employees will be motivated by goals that have 4
characteristics: difficulty, specificity, acceptance, and commitment
Edwin Locke’s Goal-Setting Theory: Difficulty:
Extent to which a goal is challenging and requires effort
Edwin Locke’s Goal-Setting Theory: Specificity:
Clarity and precision of the goal
Edwin Locke’s Goal-Setting Theory: Acceptance:
Extent to which persons accept a goal as their own
Edwin Locke’s Goal-Setting Theory: Commitment:
Extent to which an individual is personally interested in reaching a goal
Reinforce desirable behaviors: Positive Reinforcement
strengthens behavior by providing a desirable consequence
Reinforce desirable behaviors: Avoidance or Negative Reinforcement
strengthens behavior by allowing escape from an undesirable consequence
Eliminate undesirable behaviors: Punishment weakens
behavior by providing an undesirable consequence
Eliminate undesirable behaviors: Extinction weakens
behavior by not providing a desirable consequence
Reinforcement Theory
Explains the role of rewards as they cause behavior to
change or remain the same over time
Variable Work Schedules
Compressed work schedule:
allows an employee to work a traditional 35-40 hour workweek in less than five workdays. For example, a full-time employee could work four 10-hour days instead of five 8-hour days.
Flexible Work Schedules
Flextime
Job sharing
Telecommuting
Flextime
flexible hours schedule that allows workers to alter their workday and decide/adjust their start and finish times
Job sharing
Job sharing or work sharing is an employment arrangement where two people, or sometimes more, are retained on a part-time or reduced-time basis to perform a job normally fulfilled by one person working full-time
Telecommuting
the practice of working from home, making use of the internet, email, and the telephone
Communication
The process of transmitting information from
one person to another
3 basic forms of communication: Interpersonal Communication (oral/written)
between persons
3 basic forms of communication: Networks and Teams
Between people is work groups
3 basic forms of communication: Organizational Communication
Between groups/units
Oral vs written
Oral Communication: when the spoken word is used to express meaning
Written Communication: when the written word is used to transmit meaning.
Nonverbal Communication definition
The communication exchange that does not use
words or uses words to carry more meaning than
the strict definition of the words themselves
Nonverbal Communication elements
Images are the kinds of words people elect to use
Settings
Body Language, facial expression, inflection of
your voice
Communication Networks
Patterns through which members
of a group or team communicate
Vertical Communication
Communication that flows up and down
the organization, usually along formal
reporting lines.
Upward Communication is most subject to
distortion.
Downward Communication
Horizontal/Lateral Communication
Communication that involves persons at
the same level of the organization
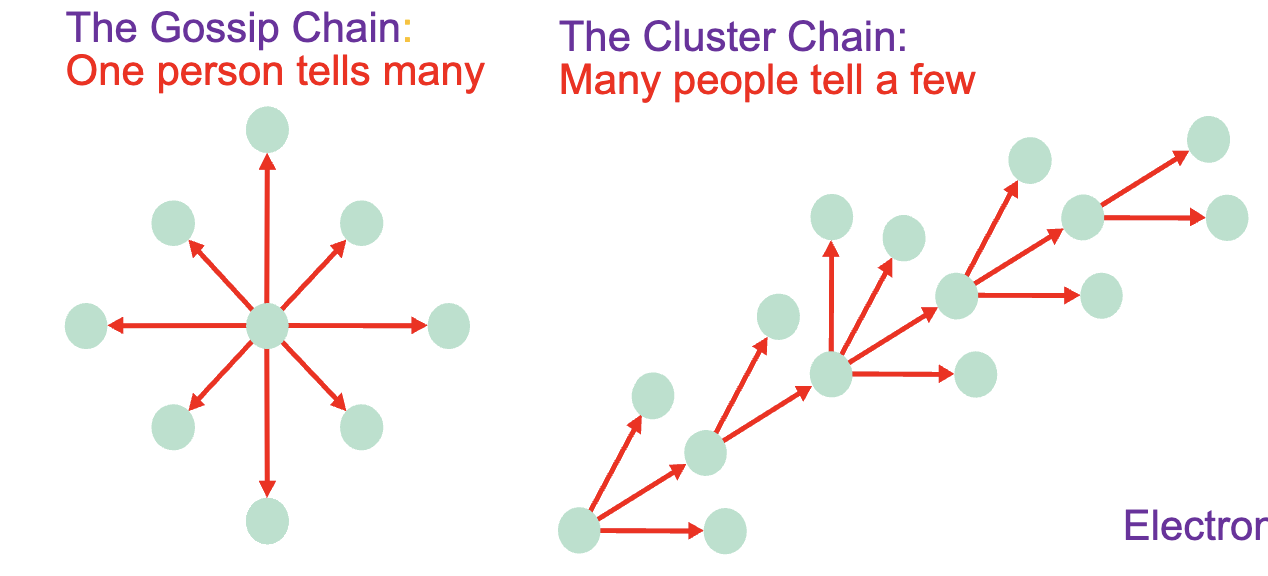
The grapevine communication
An informal communication network that can permeate an organization.
The Gossip Chain: One person tells many
The Cluster Chain: Many people tell a few
Benefits of Teams from the Organization’s Stand Point
Give more responsibility for task performance to the workers who do the tasks.
Empower workers by giving them greater authority and decision-making freedom.
Allow organizations to capitalize on the knowledge and motivation of their workers.
Enable the organization to shed its bureaucracy and to promote flexibility and responsiveness
Stages of Group Development: forming:
Attempting to define the task and how the
task will be accomplishedAbstract discussions of task-related
concepts/issues, frustrates some
members
Stages of Group Development: storming
Defensiveness, competition, and factions
Arguing among members, even when
they agree
Stages of Group Development: norming
Establishing and maintaining team ground
rulesMore friendliness and confiding in one
another
Stages of Group Development: performing
Ability of the group/team to prevent or work
through problemsClose attachment to the team
Role Ambiguity
When the sent role is unclear
Role Overload
When role expectations exceed an individual’s
capacities or when a person takes on too many
roles
Role Conflicts: interrole Conflict:
Conflict between roles
Conflicting demands for one role
from different sources
Role Conflicts: Intrasender Conflict:
When a single source sends contradictory messages
Role Conflicts: Person-role Conflict:
Discrepancy between role requirements and an individual’s values, attitudes, and needs
behavioral norms
Standards of behavior that a group accepts and
expects of its members.
Examples: output level, dress code,
promptness
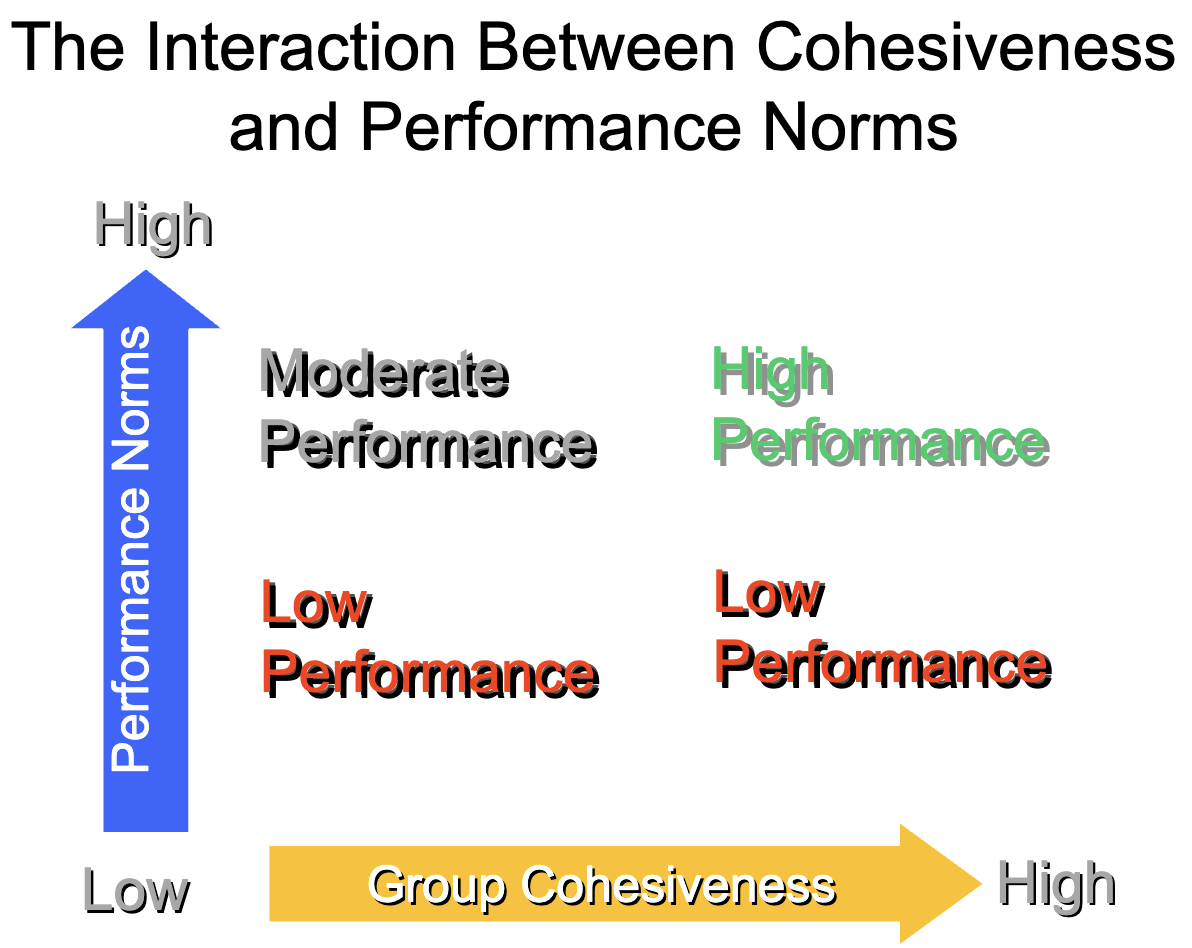
Group Cohesiveness
Tendency for a group to be in unity while working
toward a goal