Unit 6 Learning Catalytics
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Carbohydrates and fats are considered high-energy foods because they _____.
have no nitrogen in their makeup.
are easily reduced.
have a lot of electrons associated with hydrogen.
have a lot of oxygen atoms.
have a lot of electrons associated with hydrogen.
The free energy for the oxidation of glucose to CO2 and water is -686 kcal/mol and the free energy for the reduction of NAD+ to NADH is +53 kcal/mol. Why are only two molecules of NADH formed during glycolysis when it appears that as many as a dozen could be formed?
Most of the free energy available from the oxidation of glucose remains in pyruvate, one of the products of glycolysis.
Most of the free energy available from the oxidation of glucose is used in the production of ATP in glycolysis.
Glycolysis is a very inefficient reaction, with much of the energy of glucose released as heat.
There is no CO2 or water produced as products of glycolysis.
Most of the free energy available from the oxidation of glucose remains in pyruvate, one of the products of glycolysis.
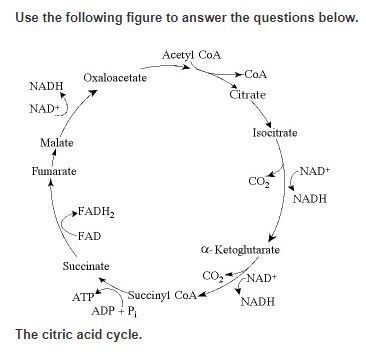 Starting with citrate, which of the following combinations of products would result from three acetyl CoA molecules entering the citric acid cycle (see the accompanying figure)?
|
3 ATP, 6 CO2, 9 NADH, and 3 FADH2
During aerobic respiration, electrons travel downhill in which sequence?
glucose → NADH → electron transport chain → oxygen
glucose → pyruvate → ATP → oxygen
glucose → ATP → electron transport chain → NADH
food → glycolysis → citric acid cycle → NADH → ATP
glucose → NADH → electron transport chain → oxygen
In chemiosmosis, what is the most direct source of energy that is used to convert ADP + Pi to ATP?
energy released from movement of protons through ATP synthase, down their electrochemical gradient
energy released as electrons flow through the electron transport system
energy released from substrate-level phosphorylation
No external source of energy is required because the reaction is exergonic.
energy released from movement of protons through ATP synthase, down their electrochemical gradient
In liver cells, the inner mitochondrial membranes are about five times the area of the outer mitochondrial membranes. What purpose must this serve?
It increases the surface for substrate-level phosphorylation.
It allows for an increased rate of glycolysis.
It increases the surface for oxidative phosphorylation.
It allows for an increased rate of the citric acid cycle.
It increases the surface for oxidative phosphorylation.
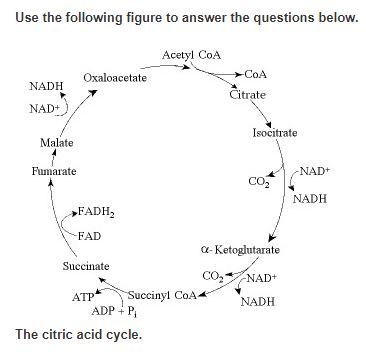
If the acetyl CoA concentration decreases, then the oxaloacetate concentration will ___________ and the citrate concentration will ________.
increase; increase
decrease; decrease
increase; decrease
decrease; increase
increase; decrease
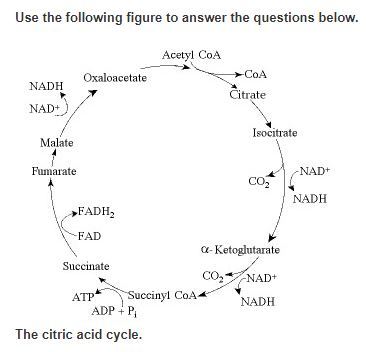
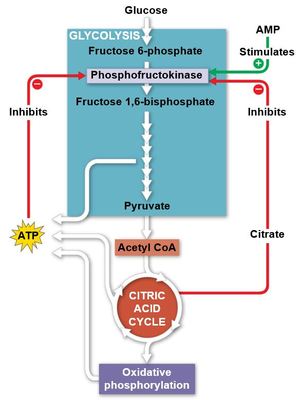
What condition(s) would increase ATP and carbon dioxide production?
Increase in acetyl CoA concentration
Increase in oxaloacetate concentration
Increase in malate concentration
Increase in ATP concentration
Increase in citrate concentration
Increase in acetyl CoA concentration
Increase in oxaloacetate concentration
Increase in malate concentration
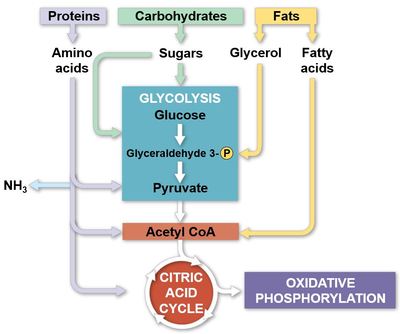
How would decreasing pyruvate transport affect the rate of oxidative phosphorylation?
Decrease the rate.
Increase the rate.
There would be no change in rate.
1, Decrease the rate
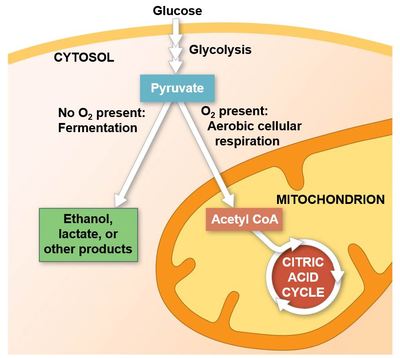
Match the type of respiration to the statement.
____ - increasing lactate concentration and low ATP production.
____ - low lactate concentration and high ATP production.
Anaerobic
Aerobic
Early investigators thought the oxygen produced by photosynthetic plants came from carbon dioxide. In fact, it comes from _____.
electrons from NADPH
water
glucose
air
water
When oxygen is released as a result of photosynthesis, it is a direct by-product of _____.
the electron transfer system of photosystem II
splitting water molecules
the electron transfer system of photosystem I
chemiosmosis
splitting water molecules
A spaceship is designed to support animal life for a multiyear voyage to the outer planets of the solar system. Plants will be grown to provide oxygen and to recycle carbon dioxide. Since the spaceship will be too far from the sun for photosynthesis, an artificial light source will be needed.
What wavelengths of light should be used to maximize plant growth with a minimum of energy expenditure?
green light
mixture of blue and red light
full-spectrum white light
UV light
mixture of blue and red light
What event accompanies energy absorption by chlorophyll (or other pigment molecules of the antenna complex)?
carboxylation reaction of the Calvin cycle occurs.
An electron is excited.
Electrons are stripped from NADPH.
ATP is synthesized from the energy absorbed.
An electron is excited.
As electrons are passed through the system of electron carriers associated with photosystem II, they lose energy. What happens to this energy?
It is lost as heat.
It excites electrons of the reaction center of photosystem I.
It is used to establish and maintain a proton gradient.
It is used to phosphorylate NAD+ to NADPH, the molecule that accepts electrons from photosystem I.
It is used to establish and maintain a proton gradient.
The electrons of photosystem II are excited and transferred to electron carriers. From which molecule or structure do the photosystem II replacement electrons come?
oxygen
photosystem I
the electron carrier, plastocyanin
water
water
In a plant cell, where are the ATP synthase complexes located?
thylakoid membrane and inner mitochondrial membrane
thylakoid membrane only
thylakoid membrane and plasma membrane
inner mitochondrial membrane only
thylakoid membrane and inner mitochondrial membrane
Which of the following statements best describes the relationship between photosynthesis and respiration?
Photosynthesis is catabolic; respiration is anabolic.
Photosynthesis occurs only in plants; respiration occurs only in animals.
Photosynthesis stores energy in complex organic molecules; respiration releases energy from complex organic molecules
Respiration runs the biochemical pathways of photosynthesis in reverse.
Photosynthesis stores energy in complex organic molecules; respiration releases energy from complex organic molecules
In photosynthetic cells, synthesis of ATP by the chemiosmotic mechanism occurs during _____.
neither photosynthesis nor respiration
photosynthesis only
respiration only
photosynthesis and respiration
photosynthesis and respiration
Carotenoids are often found in foods that are considered to have antioxidant properties in human nutrition. What related function do they have in plants?
They reflect orange light and enhance red light absorption by chlorophyll.
They shield the sensitive chromosomes of the plant from harmful ultraviolet radiation.
They serve as accessory pigments to increase light absorption.
They protect against oxidative damage from excessive light energy.
They protect against oxidative damage from excessive light energy.
The accumulation of free oxygen in Earth's atmosphere began with the origin of _____.
land plants
life and respiratory metabolism
chloroplasts in photosynthetic eukaryotic algae
cyanobacteria using photosystem II
cyanobacteria using photosystem II
Why are C4 plants able to photosynthesize with no apparent photorespiration?
They conserve water more efficiently.
They do not participate in the Calvin cycle.
They exclude oxygen from their tissues.
They use PEP carboxylase to initially fix CO2.
They use PEP carboxylase to initially fix CO2.
The alternative pathways of photosynthesis using the C4 or CAM systems are said to be compromises. Why?
C4 compromises on water loss and CAM compromises on photorespiration.
CAM plants allow more water loss, while C4 plants allow less CO2 into the plant.
Both minimize photorespiration but expend more ATP during carbon fixation.
Each one minimizes both water loss and rate of photosynthesis.
Both minimize photorespiration but expend more ATP during carbon fixation.