prokaryotic cells + viruses
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
includes replication x
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
what is a bacterial cell wall made up of?
murein (peptidoglycan)
list 8 ways in which prokaryotic cells differ from eukaryotic cells
much smaller
'cytoplasm lacks membrane bound organelles
smaller ribosomes (70S)
no nucleus - instead have a single circular DNA molecule which is free in the cytoplasm and not associated w/ protein
murein cell wall
have 1≤ plasmids (some)
have a capsule surrounding the cell (some)
have 1≤ flagella (some)
what are the 3 main structural components of a virus?
genetic material
capsid
attachment protein
give 3 structural features found in all virus particles and describe their function":
capsid - protects genetic material
genetic material - codes for viral protein
attachment protein - to bind to receptors on cell
name the 7 key structural components of a general bacterial cell
flagellum
genetic material (circular and plasmids)
cytoplasm
ribosomes
capsule
murein cell wall
cell membrane
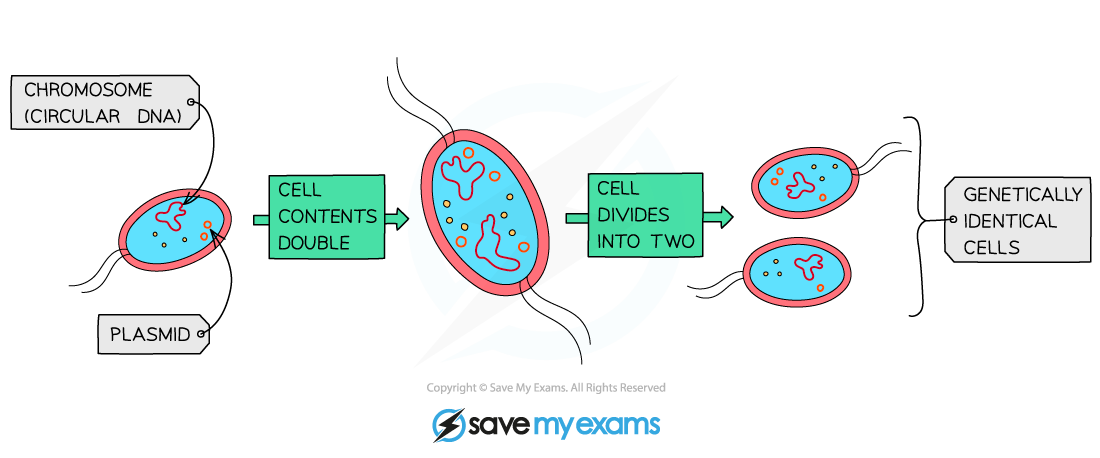
describe the process of binary fission:
circular DNA and plasmids replicate (main DNA loop only replicated once but plasmids can be replicated many times)
cell grows and DNA loops move to opposite poles of cell
cytoplasm begins to divide and new cell walls begin to form
cytoplasm divides and 2 daughter cells are produced w/ 1 copy of circular DNA but a variable no. of copies of plasmids
how do viruses replicate themselves (generally)?
use attachment proteins to bind to complementary receptor proteins on cell surface membrane
inject DNA/RNA into host cell - organelles help to replicate viral particles
why are viruses described as acellular and non living?
not made of cells/no cell surface membrane
no metabolism/nutrition
cannot independently move/respire/replicate/excrete
give one reason why antibiotics are ineffective against viruses:
any 1 from:
do not have bacterial structure/enzymes
do not have metabolism
do not have cell wall/murein