Wk 6: Cardio Lipid and Carditis (PII)
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Which blood vessels have the least amount of elastic tissue? Which has the most?
Least: Venule/capillary
Most: Aorta
Which blood vessels have the least amount of smooth muscle? Which has the most?
Least: Venule/capillary
Most: Artery/precapillary sphincter
Name the cross-section of a small artery from innermost to outermost layer
Intima
Internal elastic lamina
Media
External elastic lamina
Adventitia
How are cholesterol and triglycerides transported throughout the body?
Cholesterol and triglycerides are water-insoluble so they use: lipoproteins which are:
water-soluble phospholipid outer layer carrying apolipoproteins
What are apolipoproteins?
Co-eznymes, receptor ligand and regulators of lipoprotein metabolism
Which apolipoprotein is associated with promoting cholesterol removal from tissues in HDL?
Apo-A
Which apolipoprotein is associated with chylomicrons
Apo-B; B48
Apo E
Which apolipoprotein is associated with triglyceride metabolism?
Apo-CI, C-II and C-III
What are lipoprotein(a) / Lp(a)?
LDL particle w/ added apo(a) attached to apo(b)
linked to cardiovascular disease (CVD) and valvular aortic stenosis (VAS)
Clinical trials indicated Lp(a) is linked w/ increase risk of MI,CAS, ischemic stroke
Which type of lipoprotein has the highest amount of protein?
HDL
Which type of lipoprotein has the highest amount of cholesterol esters?
LDL
Which type of lipoprotein has the highest amount of triglycerides?
Chylomicrons
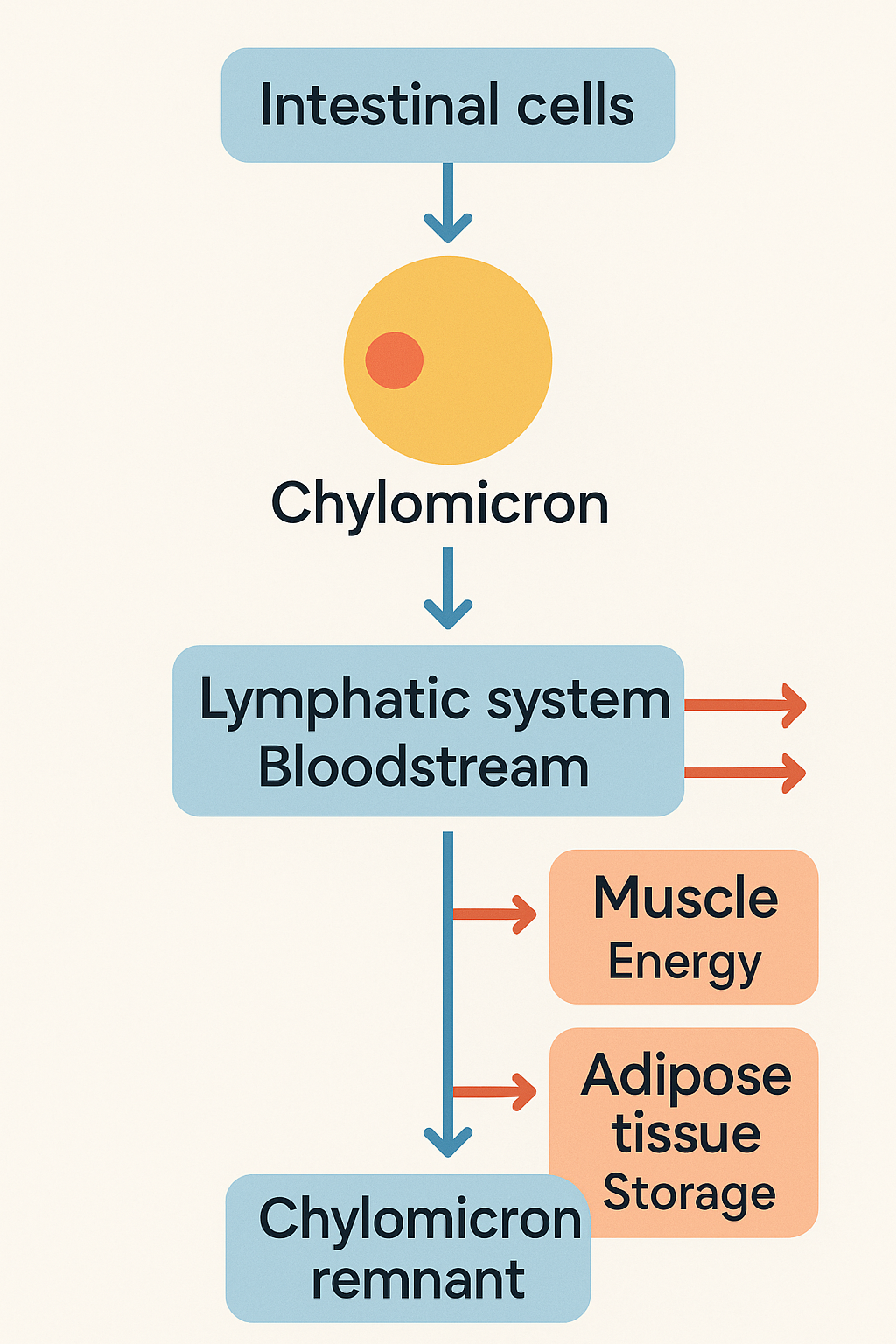
What is the purpose of chylomicrons and LPL?
(Apo B-48) Chylomicrons: transports fats that we eat from gut → rest of the body, how?
LPL’s breaks it down to release the fatty acids → free fatty acids
deliver fat to muscle: for energy
deliver to adipose tissue: for fat storage
What are VLDL?
(Apo B-100) created by the liver after it absorbs leftover chylomicrons and fats.
Also transport and distribute fat for energy and repair.
Necessary in small amounts
What is the relationship between VLDL and LPL?
LPL breaks down the triglycerides in VLDL also in the capillary walls (muscle, fat tissue) to release free fatty acids
Comparing VLDL and chylomicron, chylomicron has higher amounts of triglycerides. What can contribute to the lower levels to VLDL?
Chylomicron (90%) vs VLDL (55%)
Triglycerides are removed from VLDL by lipoprotein lipase (LPL) which → IDL then → LDL
What is the main role/characteristics of LDL?
Major cholesterol transporter in humans
Degradation of Apo B-100 → release of cholesterol (>> cholesterol)
What are PCSK9?
Regulates LDL receptors by binding to LDL receptors → internalization and degradation
What is the main role/characteristics of HDL?
Reverses cholesterol transport
inhibit lipoprotein oxidation and maintain endothelial integrity
Synthesized >liver but also intestine
How does HDL and CETP relate to VLDL and LDL?
Cholesteryl Ester Transfer Protein (CETP) transfer/trades cholesterol esters from HDL to VLDL/LDL with triglycerides between lipoproteins
Goal: remove cholesterol by giving it to VLDL/LDL and taking up triglycerides to balance lipid contents between HDL and others
Define primary hyperlipidemia that can progress to atherosclerosis
Inherited disorders →
lipoprotein lipase deficiency (type I)
Defective LDL receptors (Type IIa)
Define HTN that can progress to atherosclerosis
Increase of shear stress w/ damage to endothelium
Define hypothyroidism and how that can progress to atherosclerosis
Decreased formation LDL receptors in liver
How does oxidized LDL contribute to dyslipidemia → atherosclerosis
Accumulates in subintimal macrophages (scavenger receptor mediated uptake) → cellular dysfunction/apoptosis/necrosis
Stimulates pro-inflammatory cytokines → stimulate macrophages migration → foam cells → endothelial injury = plaque formation
Stimulate smooth muscles cells to move from the media to intima → takes up oxidized LDL → foam cells
+ proliferation bc of the laying of collagen and matrix molecules
What is a result from cholesterol-loaded macrophages?
→ lipotoxicity to the endoplasmic reticulum → apoptosis and plaque necrosis
What is a result from cholesterol crystals from necrotized macrophages?
Stimulates inflammation and recruitment of neutrophils
What is a result from aging plaques?
Attraction of T cells and monocytes which creates cycle of necrosis and inflammation
Formation of fibrous cap over aging plaques
What can result from fibrous cap formation over aging plaques?
Plaques with defective or broken caps are prone to rupture → trigger thrombosis + blocking blood flow
What is one strong contributor to severe hypertriglyceridemia? (HTG)
Impaired lipolysis of TG in TRLs by LPL
TRL delivering TG to LPL but there is a malfunction
GPIHPB1 ensures LPL is at the location (capillary endothelial), so mutation there can contribute as well.
What is the most frequent mutation in LPL gene for primary (genetic) cause of HTG?
Autosomal recessive inheritance
What is APOC2 Deficiency?
loss of function mutation in both APOC2 allele → functional lack of LPL activity + hyperchylomicronemia
What is APOA5 Deficiency?
Loss of function mutation in both APOA5 allele causes familial chylomicronemia syndrome (FCS)
What is GPIHBP1 Mutation?
Interfere w/ synthesis or folding → FCS
Autoantibodies to protein
What is LMF1 Deficiency?
Both alleles lose function due to mutation affecting LPL processing and folding → FCS
What medical condition can contribute to hypercholesterolemia (Elevated LDL)?
Hypothyroidism and estrogen deficiency
What is the major cause that causes hypercholesterolemia (Elevated LDL-C)?
Polygenic predisposition exacerbated by 2nd factors like diet
What type of disorder is associated with primary (genetic) causes of hypercholesterolemia (Elevated LDL) from familial hypercholesterolemia?
Autosomal dominant disorder w/ elevated plasma LDL-C but nl TG lvls
Define homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) in primary causes of elevated LDL-C
If a person inherits two defective LDLR genes (either identical or different mutations), they have homozygous FH which → very high LDL cholesterol and early, aggressive cardiovascular disease.
Heterozygous FH most common
What is the most common genetic mutation found in FH?
LDLR mutation
What other genetic mutations are found in FH?
APOB mutation: Apo B-100 reduces LDL receptor binding affinity → familial defective apoB (FDB)
PCSK9 mutation: gain-of-function mutations → enhance PCSK9 activity → fewer LDL receptors → less LDL-C removed from blood
What’s the difference between acute and subacute infective endocarditis?
Acute: + fever that rapidly damages cardiac structures, radiates and can progress to death within weeks
Subacute: Slow course that causes slow cardiac damage, rarely metastasizes and grad. progresses
Which organisms is commonly associated with community acquired and IVDU?
Strep: community associated
Staph: healthy care associated, IVDU (R sided)
How does endothelial injury contribute to infection invasion?
Direct infection by organism
Development of platelet-fibrin thrombus → nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis (NBTE)
How causes NBTE and the results of it?
Example: arise from hypercoagulable state
Results: site for bacteria to attach during transient bacteremia with MSCRAMMs
→ surface adhesin molecules by organisms
microbial surface components recognizing adhesin matrix molecules
How does adherent organisms respond to bactericidal activity and microbicidal peptides released by platelets in endocarditis?
Proliferatie to form dense microcolonies
→ combo of fibrin deposition + platelet aggregation = infected vegetation
What is the common causes to myocarditis?
Viral infections
What are the effects of the enteroviral protease 2A when it comes to myocarditis?
Promote viral replication and infection through degradation of myocarditis protein dystrophin which are needed for myocyte stability
Also can activate TK to benefit further viral entry
Besides Beck’s Triad, what is another PE finding that can lead us towards cardiac tamponade?
Paradoxical pulse
inspiratory decline in systolic arterial pressure thats greater than >10 mmHg
What other condition can have cardiac tamponade?
1/3 in constrictive pericarditis
others:
Hypovolemic shock
acute and COPD
PE
What can the R ventricle cause during inspiratory enlargement?
Leftward bulging of interventricular septum
→ compress and reduces:
L ventricular vL
stroke vL
Arterial systolic pressure (paradoxical pulse)