gen physics 1- 2nd mast
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
45 degrees angle
With a constant initial velocity, in what degree of angle
Should an object be thrown to have its maximum range?
25 degrees angle
With a constant initial velocity, an object thrown at 65-degree angle will have the same range with an object launched at _____
d
Which would hit the ground first if dropped from the same height in a vacuum - a feather or a metal bolt?
a. the metal bolt
b. the feather
c. they would be suspended in a vacuum
d. they would hit the ground at the same time
d
When an object is launched at 0 degrees angle..
a. the object will not have a maximum point
b. the object will have a parabolic trajectory
c. the object will have a 0 range
d. the object will have a 0 height
c
What values are always known for a freefalling object?
a. vi = -9.8 m/s, a = -9.8 m/s2
b. vi = -9.8 m/s, a = 0 m/s2
c. vi = 0 m/s, a = -9.8 m/s2
d. d = -9.8 m, vi = 0 m/s
d
What values are always known for a freefalling object?
a. vi = -9.8 m/s, a = 0 m/s2
b. vi = -9.8 m/s, a = -9.8 m/s2
c. d = -9.8 m, vi = 0 m/s
d. vi = 0 m/s, a = -9.8 m/s2
c
The velocity of an object at the moment of launching and crashing are
a. moment of launching has greater velocity
b. moment of crashing has greater velocity
c. the same
d. both has 0 velocities
d
The standard acceleration due to gravity (or standard acceleration of free fall), is the nominal gravitational acceleration of an object in a vacuum near the surface of the Earth. It is defined by standard as:
a. 9.8 m/s
b. 9.8 m/𝑠^2
c. 9.8 m
d. -9.8 m/𝑠^2
Galileo Galilei
The scientist the claimed that all objects, regardless of their weights, fall at the same acceleration and conduct the experiment in the Leaning Tower of Pisa is __________.
gravity
The phrase “what goes up must come down” is because of
parabola
The path of a projectile motion has a shape of a
air resistance
The factor that might affect the rate of fall of an object is
c
The factor that might affect the rate of fall of an object is
a. Falling objects accelerate at -9.8 m/s^2
b. Falling object move at constant velocity
c. It depends on the mass: heavy objects accelerate, light objects do not
d. Falling objects accelerate at 100 m/s^2
height
It is the vertical distance, that is, the distance from where it was launched to the top-most point of its path
terminal velocity
It is the steady velocity achieved by an object freely falling
gravity
It is the pulling force directed towards the center of the Earth which has a value of -9.8 m/s^2
trajectory
It is the path of a projectile
free fall
It is the motion of an object under the effect of gravitational force only
range
It is the horizontal distance traveled by the projectile
maximum height
It is the height of the object when it is at the top of its path
air resistance
It is the force of friction or drag acting on an object in a direction opposing its motion as it moves through air
vertical line motion
It is another term of "Free Fall"
projectile motion
It is a combination of horizontal motion caused by the velocity of projection and vertical motion caused by the earth’s gravitational pull
projectile
It is a body thrown with an initial velocity (velocity of projection) and moves under the influence of gravity
a
Inside a vacuum chamber...
a. all objects regardless of mass falls at the same velocity
b. air resistance is stronger
c. objects with lesser weight will have a greater velocity
d. gravity in changing
zero
A stone is thrown vertically upward with a velocity of 30 m/s until it reaches its maximum height. The velocity of the stone at its maximum height is:
vacuum chamber
A place where there is an absence of matter and air resistance
air resistance
A parachute is an evidence of
c
An object thrown upwards will have a
a. increasing speed
b. irregular speed
c. decreasing speed
d. constant speed
d
A freely-falling body is one whose motion depends entirely on the __________.
a. mass of the object
b. wind in the area
c. height of the building
d. force of gravity acting on the body
a
A falling object will have an __________ 9.8 m/s every second of its motion
a. additional
b. a multiplier of
c. a decrease of
d. constant of
a
A baseball catcher throws a ball vertically upward and catches it in the same spot as it returns to the mitt. At what point in the ball’s path does it experience zero velocity and nonzero acceleration at the same time?
a. at the top of its path
b. the instant it leaves the catcher’s hand
c. the instant before it arrives in the catcher’s mitt
d. midway on the way up
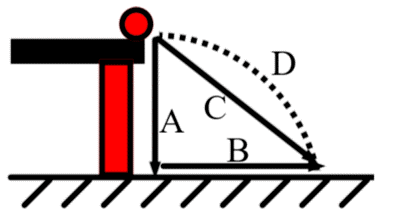
trajectory
Identify the part of a projectile motion labeled as "D"
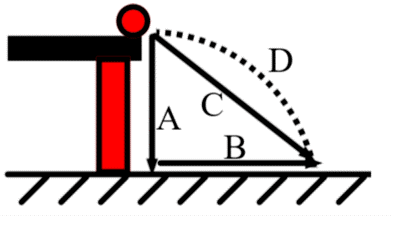
Range
Identify the part of a projectile motion labeled as "B"
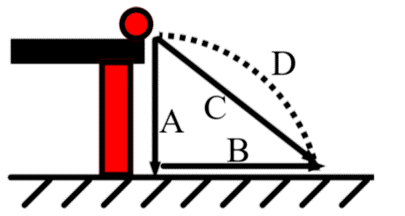
Height
Identify the part of a projectile motion labeled as "A"
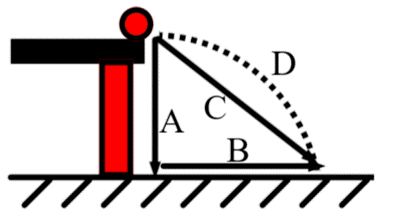
Line
Identify the part of a projectile motion labeled as "C"