Genetics: Dominance, Multiple Alleles, Epistasis & Cytoplasmic Inheritance
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Complete Dominance
A relationship in which one allele is completely dominant over another

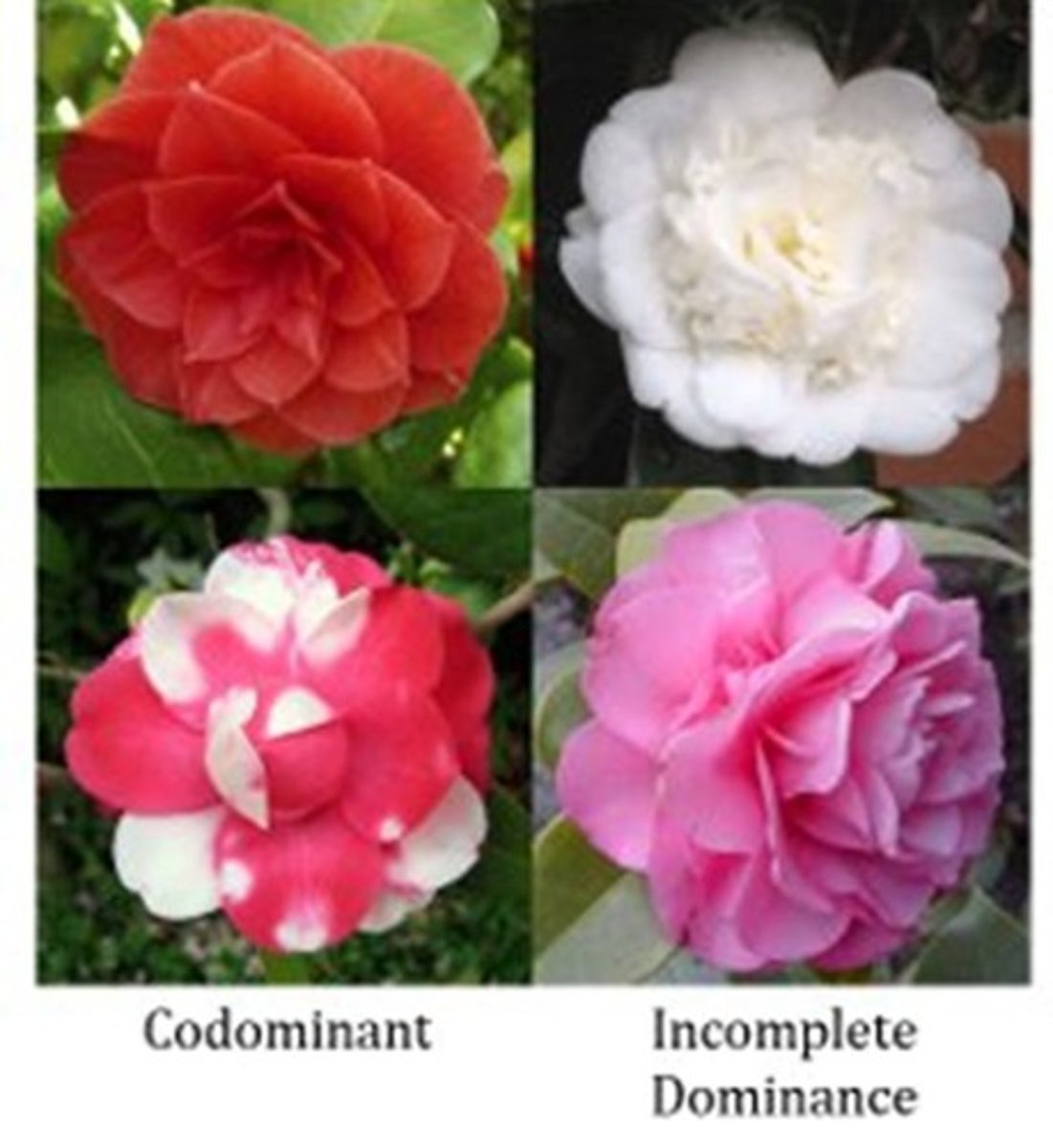
Incomplete Dominance
Phenotype of the heterozygote is in between the phenotypes of the two homozygotes; results when alleles have an additive effect.
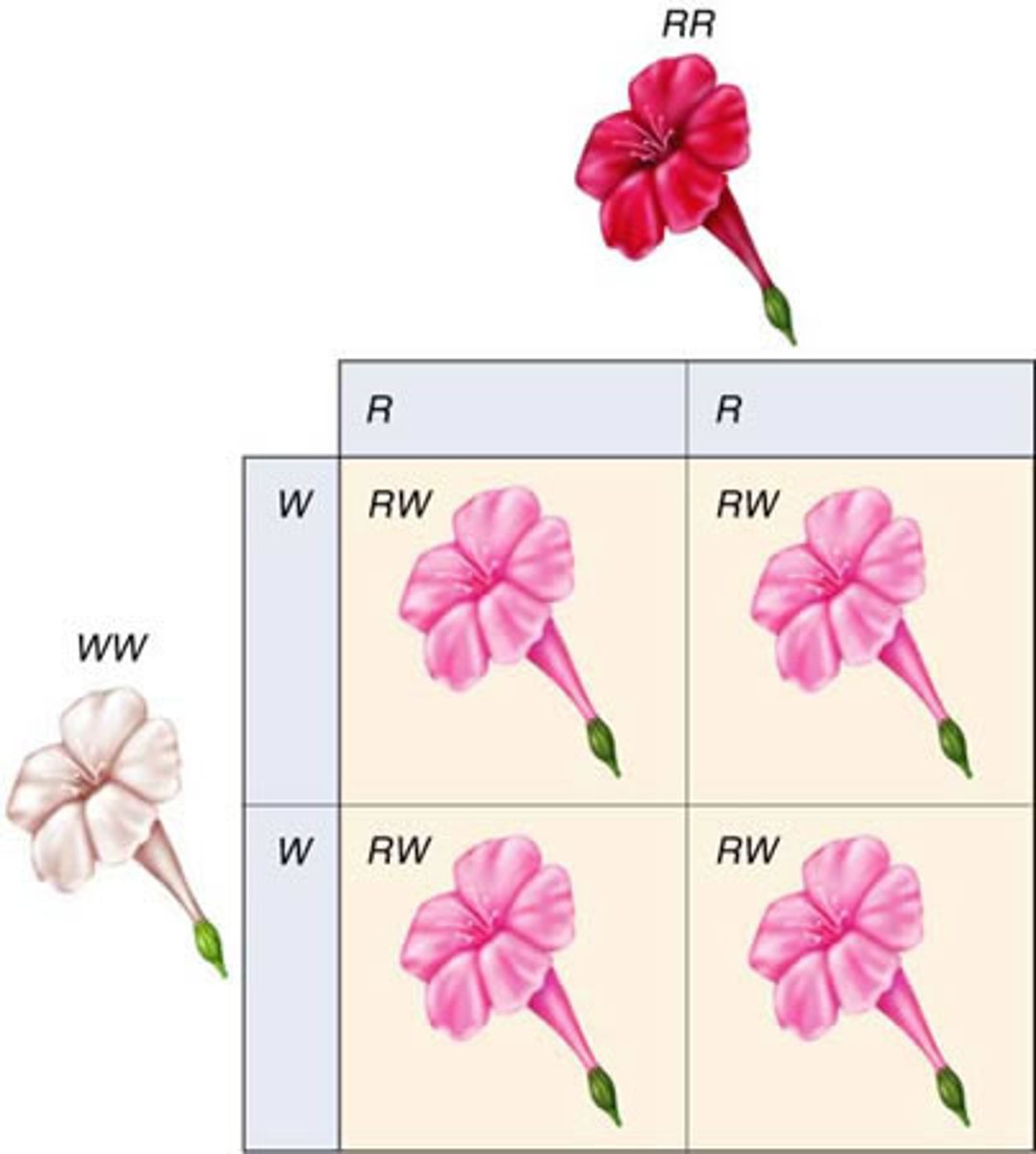
Co-dominance
Phenotype of the heterozygote includes the phenotypes of both homozygotes.

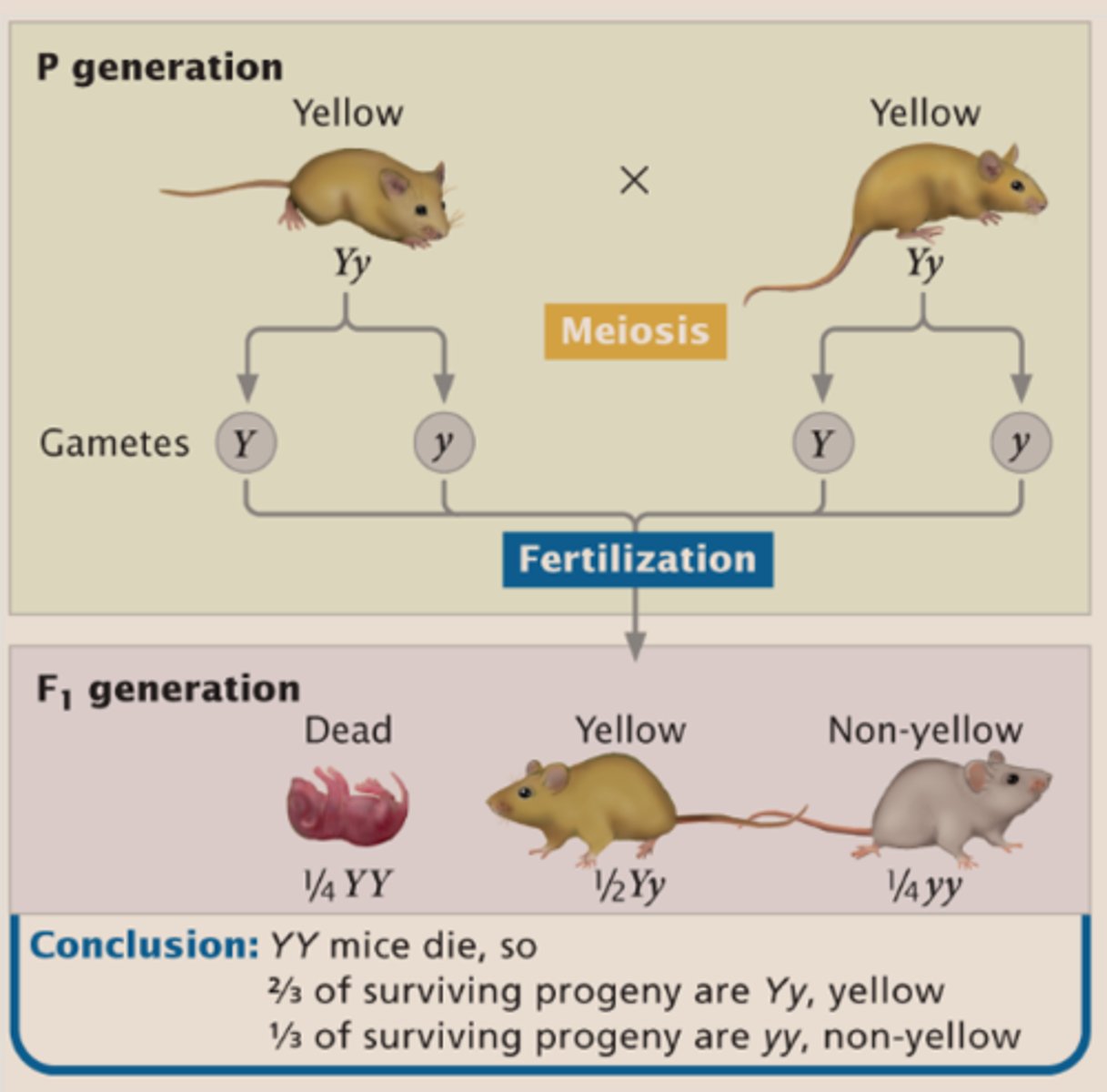
Lethal Alleles
The homozygous YY condition is LETHAL in early development.
Y= dominat for fur color
Y= recessive for lethality
Multiple Alleles
3 or more possible alleles exist in the population for a particular genetic locus
Genotype Calculation for Multiple Alleles
General rule - the number of possible genotypes: n = number of different alleles [n(n+1)] / 2.
Important fact about multiple alleles
Each individual's diploid GENOTYPE still contains 2 alleles
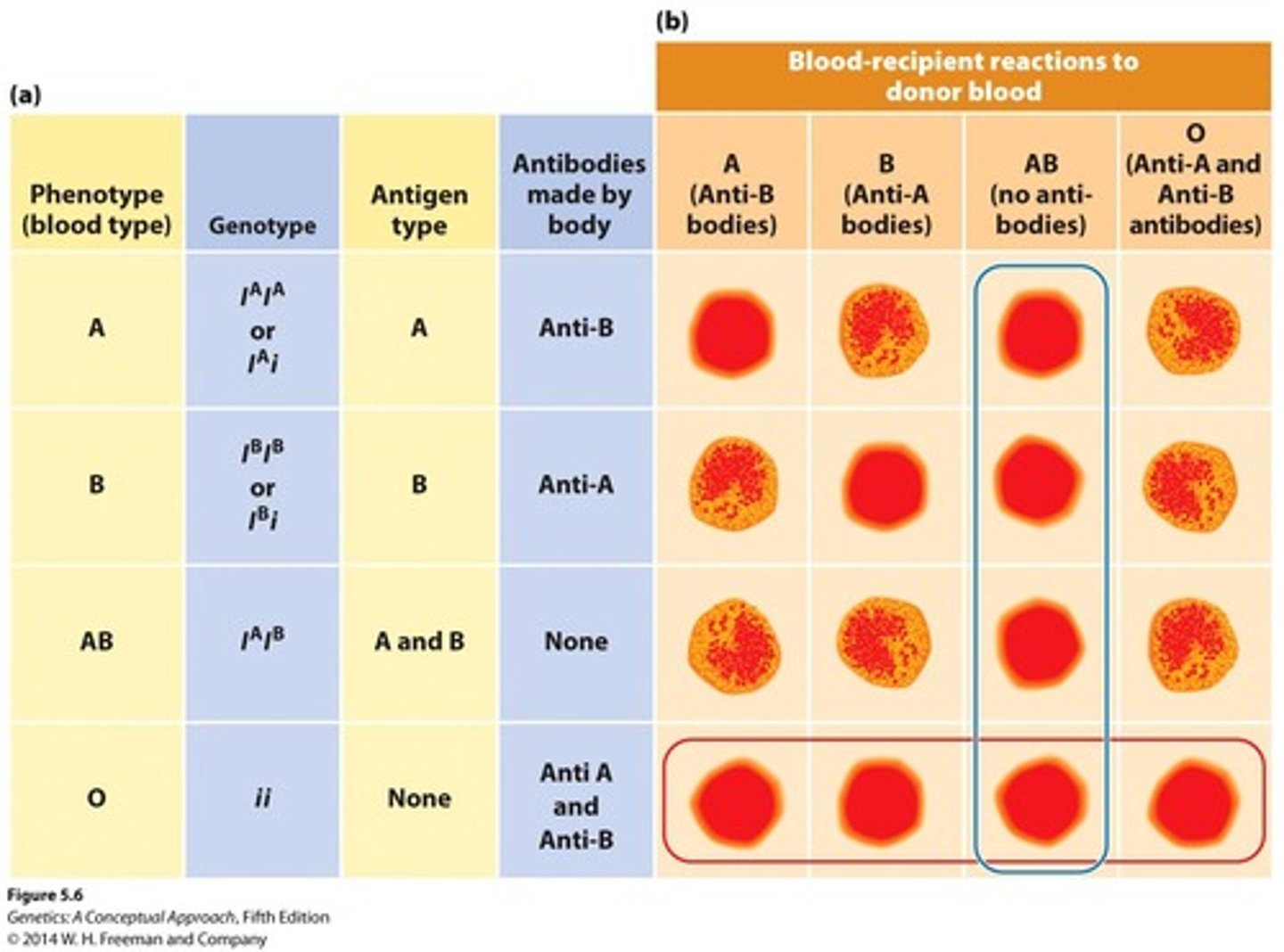
ABO Blood Groups
3 alleles; 4 phenotypes; 6 genotypes; demonstrates Complete & Co-dominance & Multiple Alleles.
Gene Interaction
The products of genes at different loci combine to produce new phenotypes that are not predictable from the single-locus effects alone.
Novel Phenotypes
trait affected by 2 or more different genes; genes cooperate to produce phenotype neither could produce alone
Agouti (A)
Determines distribution of pigment in each hair.
Black (B)
Determines whether pigment is black or brown.
Extension (E)
Determines whether pigment is deposited.
Spotting (S)
Determines whether spots will be present.
Epistasis
A gene that masks the effect of another gene at a different locus
Hypostatic gene
A gene whose expression is masked by the action of a gene at a different locus
Recessive Epistasis
9:3:4 ratio; a lab will be yellow if E locus is ee, regardless of genotype at B locus because NO pigment deposited.

Cytoplasmic Inheritance
Inheritance of characteristics encoded by genes located in the cytoplasm. Because the cytoplasm is usually contributed entirely by only one parent, most characteristics are inherited from a single parent.
Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON)
Results in sudden blindness in both eyes due to death of optic nerve.
Genetic Maternal Effect
The phenotype of the offspring is determined by the nuclear genotype of the mother.
Direction of Shell Coiling in Snails
Is Maternally Inherited; s+s and s+s+ mothers make a protein that results in dextral (right-handed) coiling.
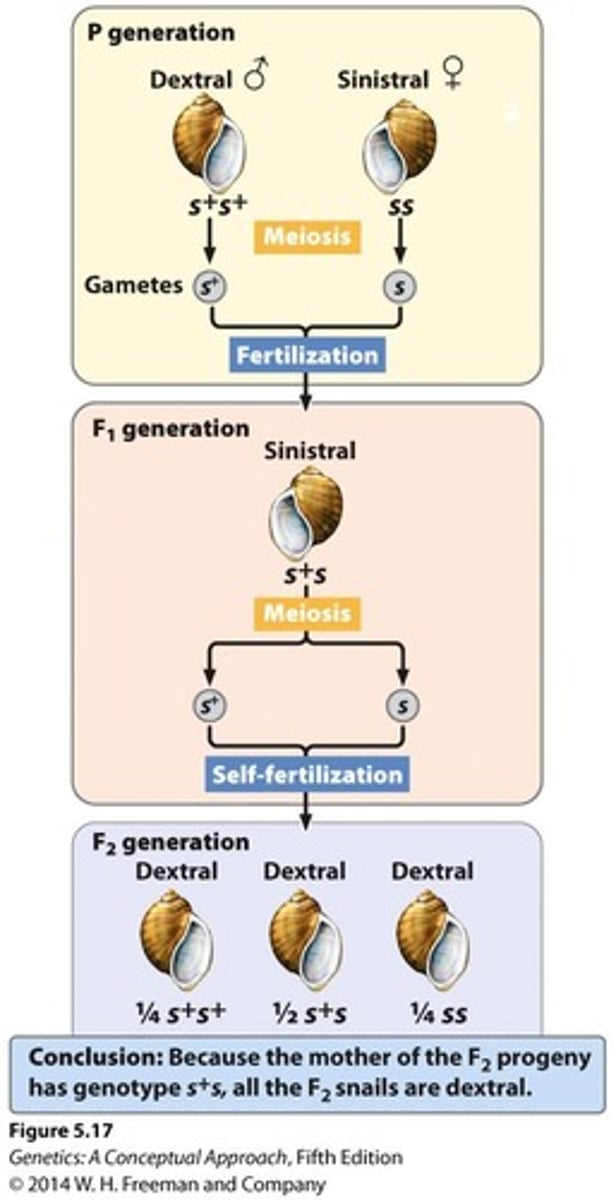
Dextral coiling
Result of s+s and s+s+ mothers depositing a protein into the egg.
Sinistral coiling
Result of ss mothers not depositing the protein into the egg.
F1 offspring coiling
Are sinistral even though their genotype is s+s, because their mother lacks an s+ allele.
F2 ss offspring coiling
Are dextral because their F1 s+s mother deposited the s+ gene product into the egg.
Cytoplasmic genes
Passed from the mother only, in the large egg.
Random segregation of mitochondria
Carrying a defect in a gene required for cellular respiration results in reduced ATP production.