Chapter 13: Solutions
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Homogeneous Mixture
can be made up of almost any 2 phases of matter
Solute + Solvent
dissolved substance = solute and the substance it is dissolved in is the solvent
Solvent is the component present in the larger quantity or the volume
Common solutions involve a solid solute and a liquid solvent
Metal Alloys
are solid-solid soln of different metals
Like Dissolve Like
Substances dissolve in one another if the solute and solvent are
able to form intermolecular attractions.
• The energy released by the formation of solute–solvent attractions
helps to offset the energy required to overcome solute–solute and
solvent–solvent attractions.
• Most ionic compounds dissolve in water via ion–dipole attractions
formed between the charged ions and the polar water molecules.
Only made of carbon and hydrogen
nonpolar
Entropy
the degree of randomness or disorder in a system, is a factor in solution formation
• Solutions are typically less ordered than pure solids and pure liquids.
• Formation of a solution increases the entropy of the system.
• Entropy favors solution formation.
Unsaturated, Saturated, Super Saturated
example: water on its own is unsaturated
adding sugar until it cannot be dissolved further = unsaturated
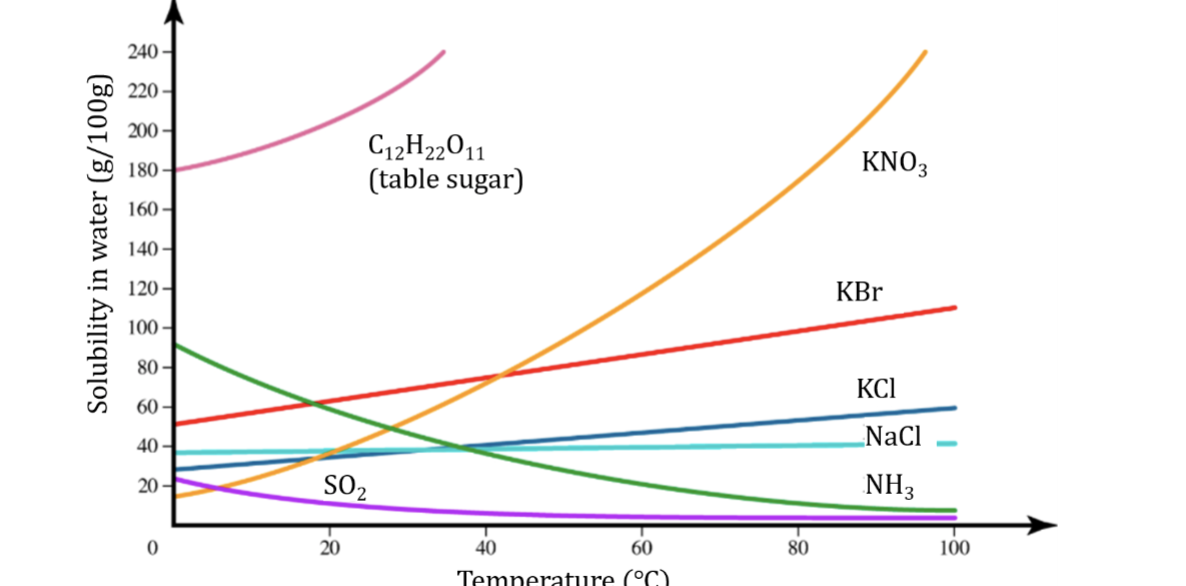
Fig. 13.4 Solubility v. Temperature for Some Solids Solutes in Water
Solubility of Gases
Unlike most solids, the solubility of gases decreases as temperature increases
Henry’s Law
• At any given temperature, the solubility of a gas in a liquid is
directly proportional to the partial pressure of the gas above
the surface of the liquid.
• Mathematically, Henry’s law is written as:
𝐜𝐨𝐧𝐜𝐞𝐧𝐭𝐫𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 𝐨𝐟 𝐝𝐢𝐬𝐬𝐨𝐥𝐯𝐞𝐝 𝐠𝐚𝐬 𝐢𝐧 𝐬𝐨𝐥𝐮𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 = 𝒌𝑷
• P is the partial pressure of the gas above the liquid and k is the
Henry’s law constant, which depends on the temperature, and is
different for each gas and solvent
memorize equation

Example 13.3

Organic Molecules in Water
• Polar organic molecules dissolve in
water better than nonpolar organic
molecules.
• Hydrogen bonding increases
solubility, since C–C and C–H bonds
are not very polar.
non polar = does not dissolve in water
Liquid/Liquid Solubility
miscible: liquids that mix in all proportions
immiscible: liquids that do not mix in one another
because hexane is nonpolar nad water is polar they are immiscible
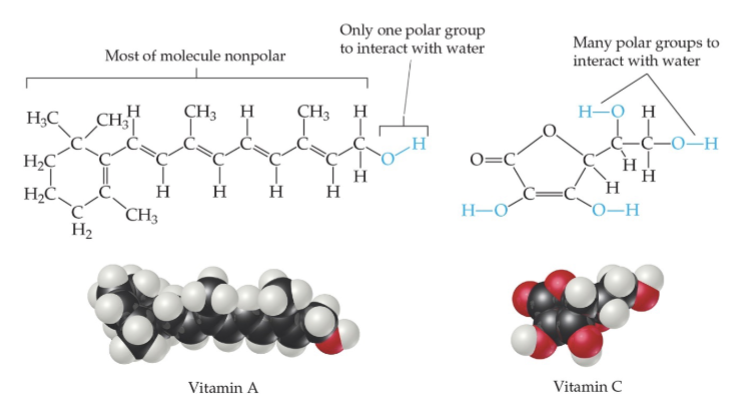
Solubility and Biological Importance
• Fat-soluble vitamins (like vitamin A) are nonpolar; they are
readily stored in fatty tissue in the body.
• Water-soluble vitamins (like vitamin C) need to be included
in the daily diet.