Exam I - Complement and Cytokines
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
Complement
a major immune defense mechanism which is the central reaction responsible for the development of inflammation. Serves as a link between the innate and adaptive immune systems. Functions by labeling pathogens for elimination via a lytic transmembrane pore.
Innate immunity
immunity which is an immediate reaction to an a foreign antigen.
Adaptive immunity
immunity which is a delayed reaction and involves antibodies and cells.
mast cells
cells that release histamine which binds to receptors on blood vessels to increase blood flow and blood vessel permeability
histamine
Mast cells release this compound which binds to receptors on blood vessels to increase blood flow and blood vessel permeability
Diapedesis
movement of cells such as leukocytes through blood vessel walls into the surrounding tissues.
Opsonization
function of complement which involves the coating of a foreign cells and tagging them for destruction by phagocytes. Ie) C3b
C3b
complement protein which especially enhances the efficiency of phagocytosis via opsonization
Chemotaxis
function of complement which involves chemical mediated cell movement via serum proteins. Stimulates the movement of neutrophils and monocytes toward sires of antigen deposition.
Serum proteins
free floating proteins in the blood serum which often function in chemotaxis in the pathway of complement reaction. Ie) C3a, 4a, 5a etc.
Cytolysis
function of complement which involves the lysis of cells such as bacteria, virus infected cells, and tumor cells. Cell lysis occurs through the formation of a membrane attack complex leading via the loss of osmotic integrity.
Lytic transmembrane pore
pore formed in response to the actions of complement membrane attack complex. Results in foreign cell lysis
Priming
function of the complement which involves the activation of secondary immune response.
Anaphylatoxins
proteins that promote vasodilation and increased vascular permeability via stimulation of mast cells and basophils to release histamine. his results in an increased blood flow to the site of infection allowing for more complement proteins, antibodies, and immune cells to reach the site of infection. Ie) C3a C5a
C3a and C5a
what are two examples of anaphylatoxins?
C1
complement protein that is composed of three proteins (1 q, 2 r, 2 s). It binds to the Fc region of the antibody in order to trigger the classical complement pathway.
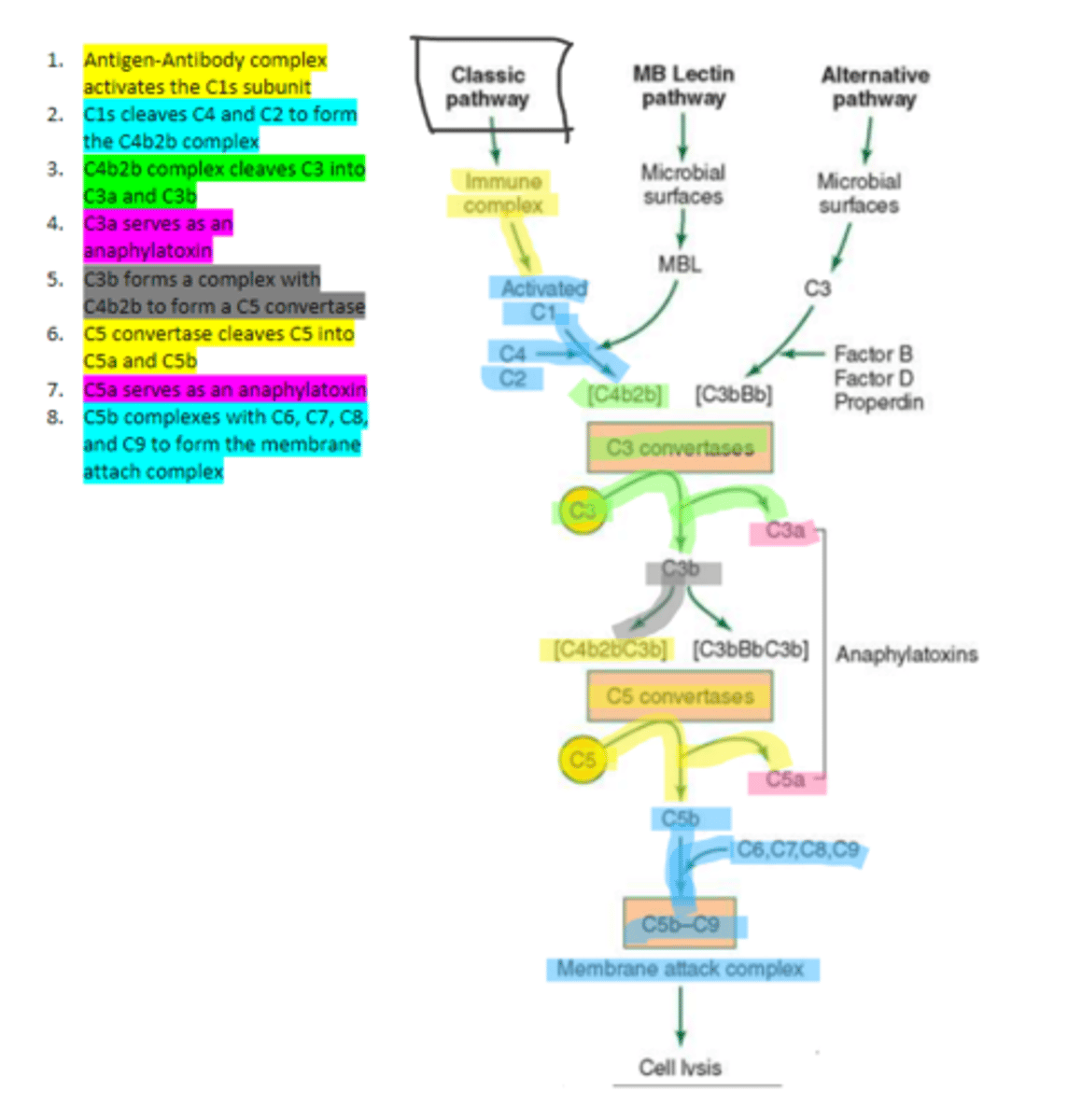
C1q
complement protein which is an aggregate of polypeptides that binds to the Fc portion of IgG and IgM in the classical pathway
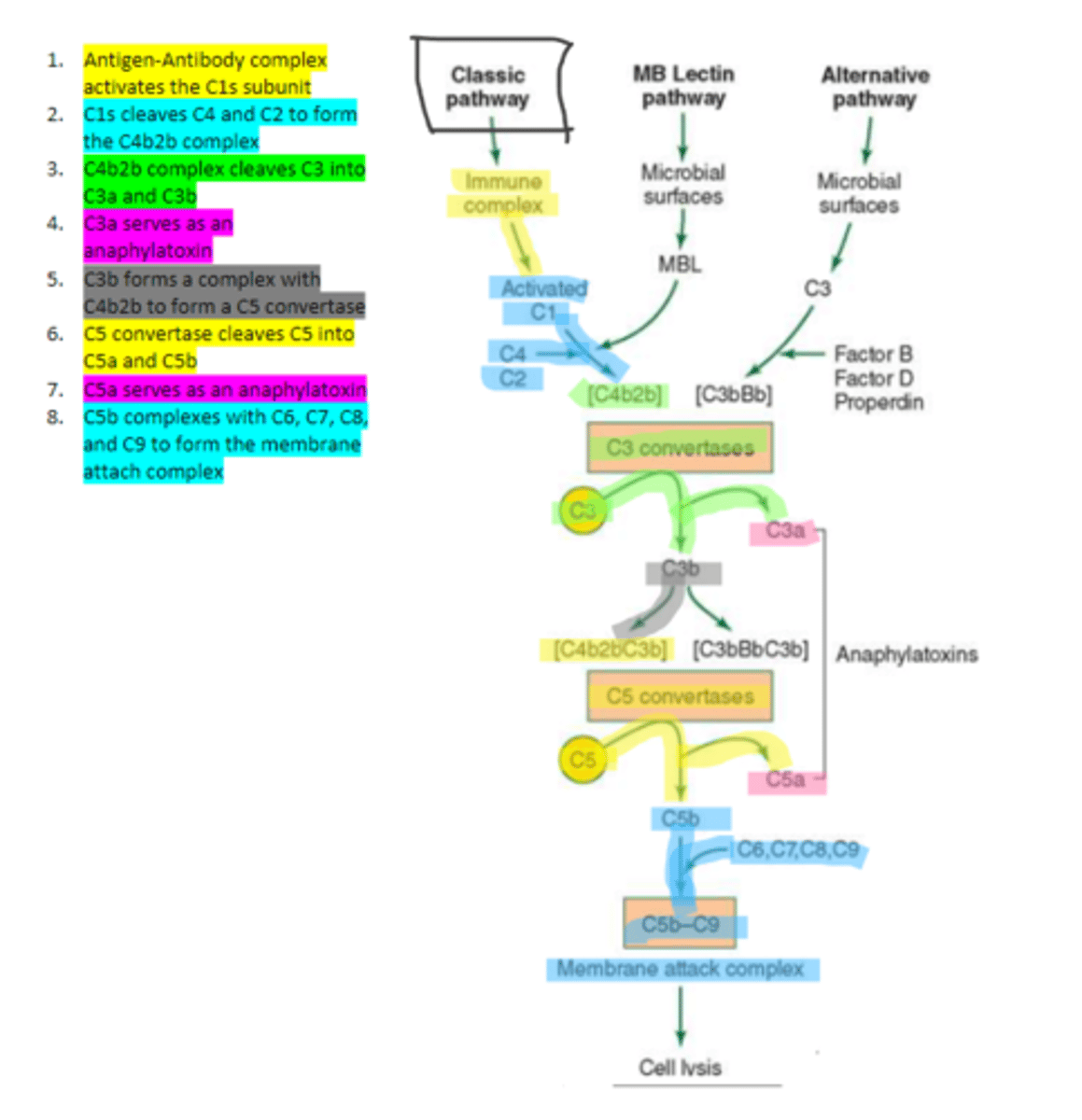
C1s
the first subunit of C1 complement protein which becomes activated by the binding of the immune complex during the classical pathway. Functions to cleave C4 and C2 form a C4b2b complex
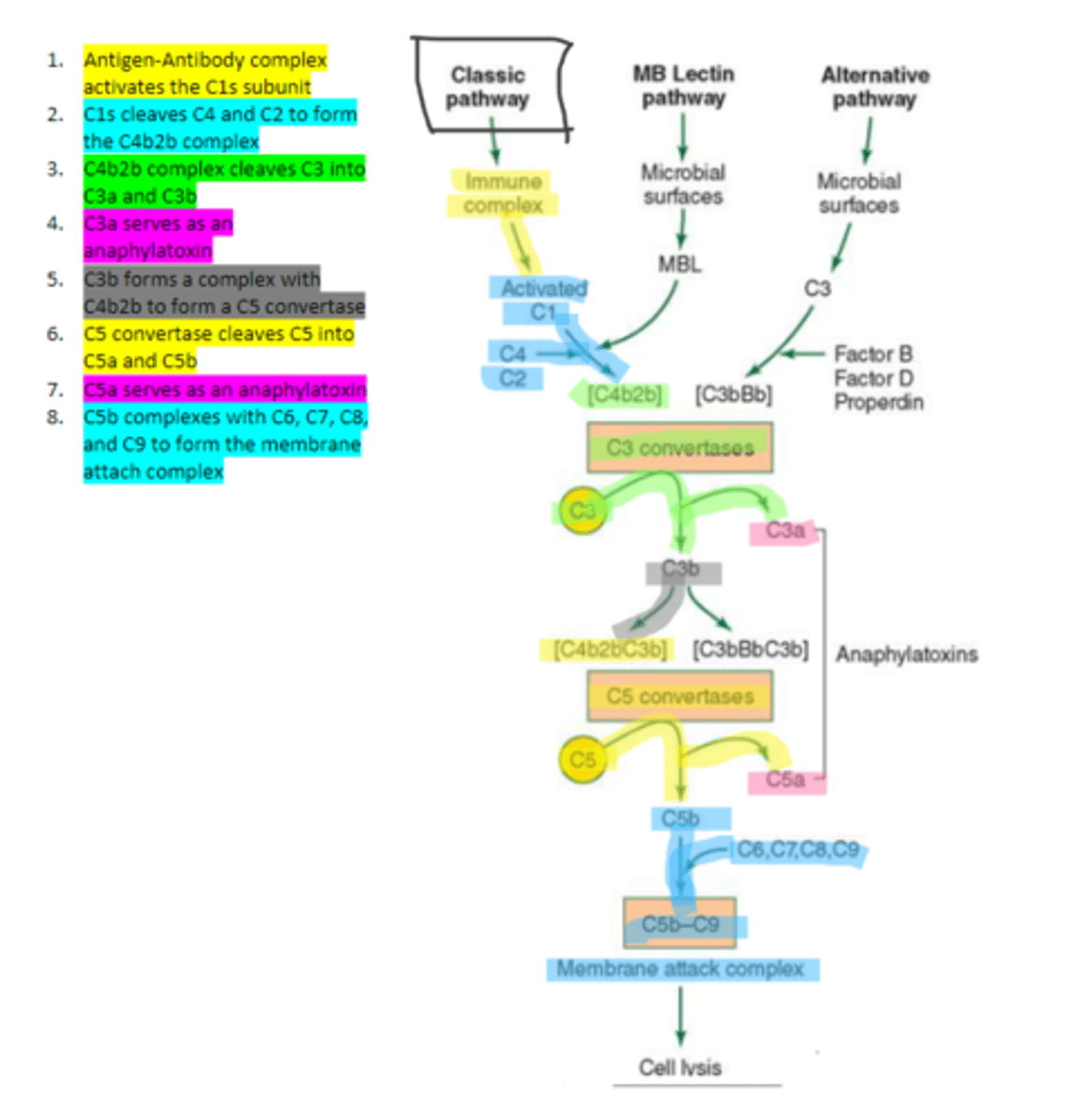
C4b2b
an active C3 convertase formed by the cleaving of C4 and C2 via C1s in the complement pathway. It functions to cleave C3 molecules into two fragments, C3a and C3b that go on to function as anaphylatoxins and mediators of opsonization respectively.
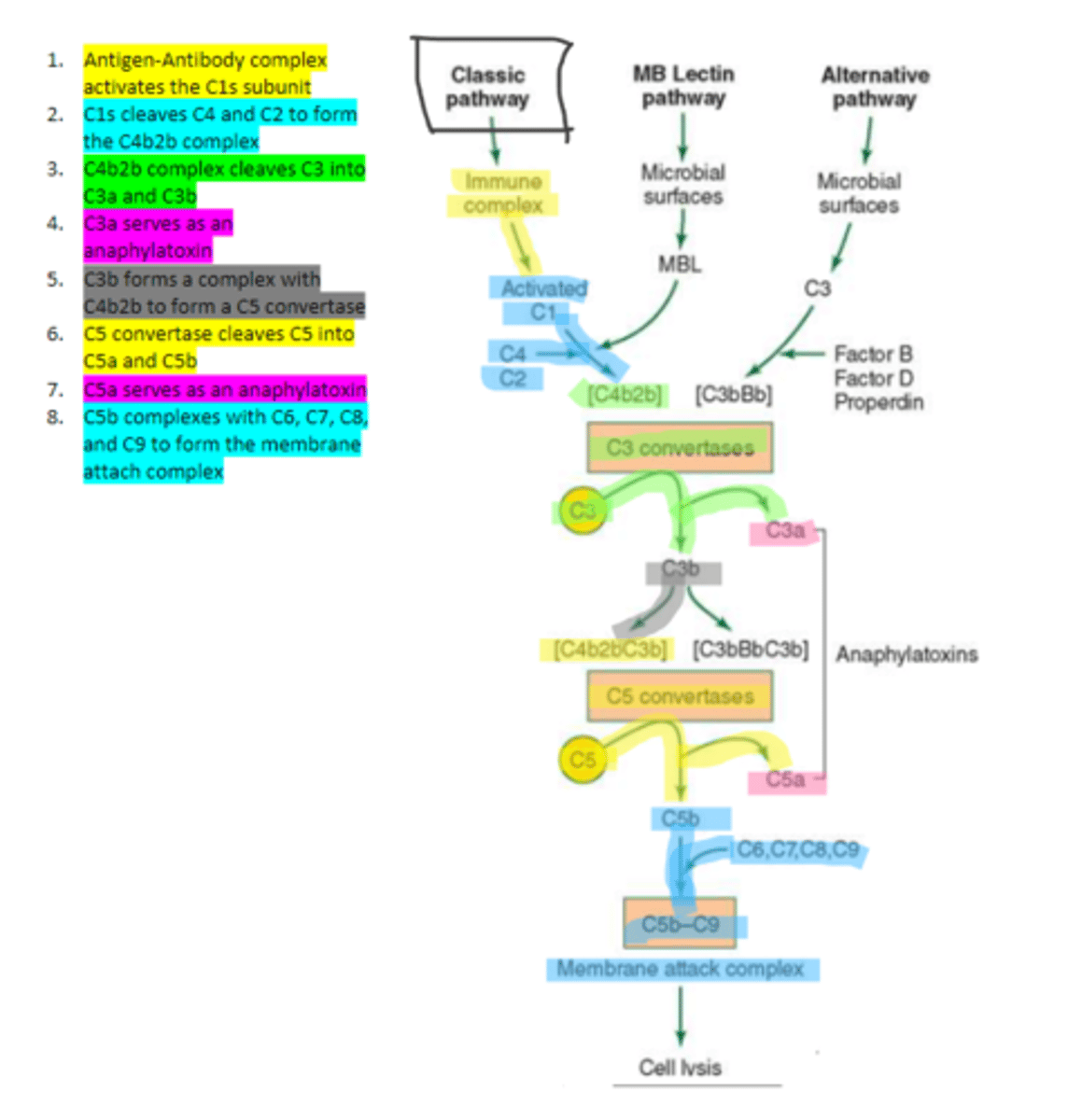
C3b
complement protein that forms a complex with C4b2b to produce C5 convertase in the classical pathway
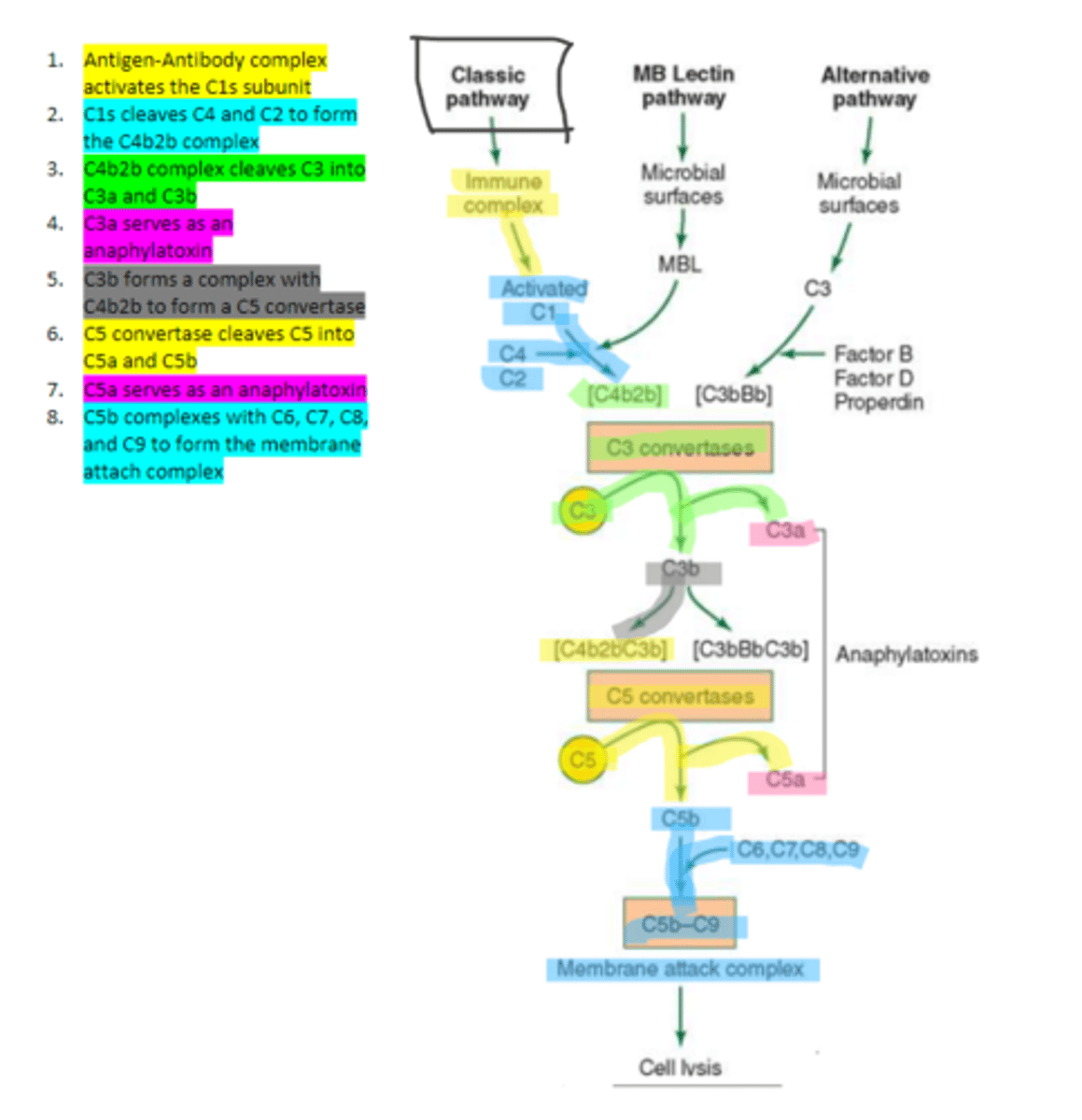
C5 convertase
enzyme formed by C3b and C4b2b complexing. Functions to cleave C5 to form C5a and C5b in the classical pathway
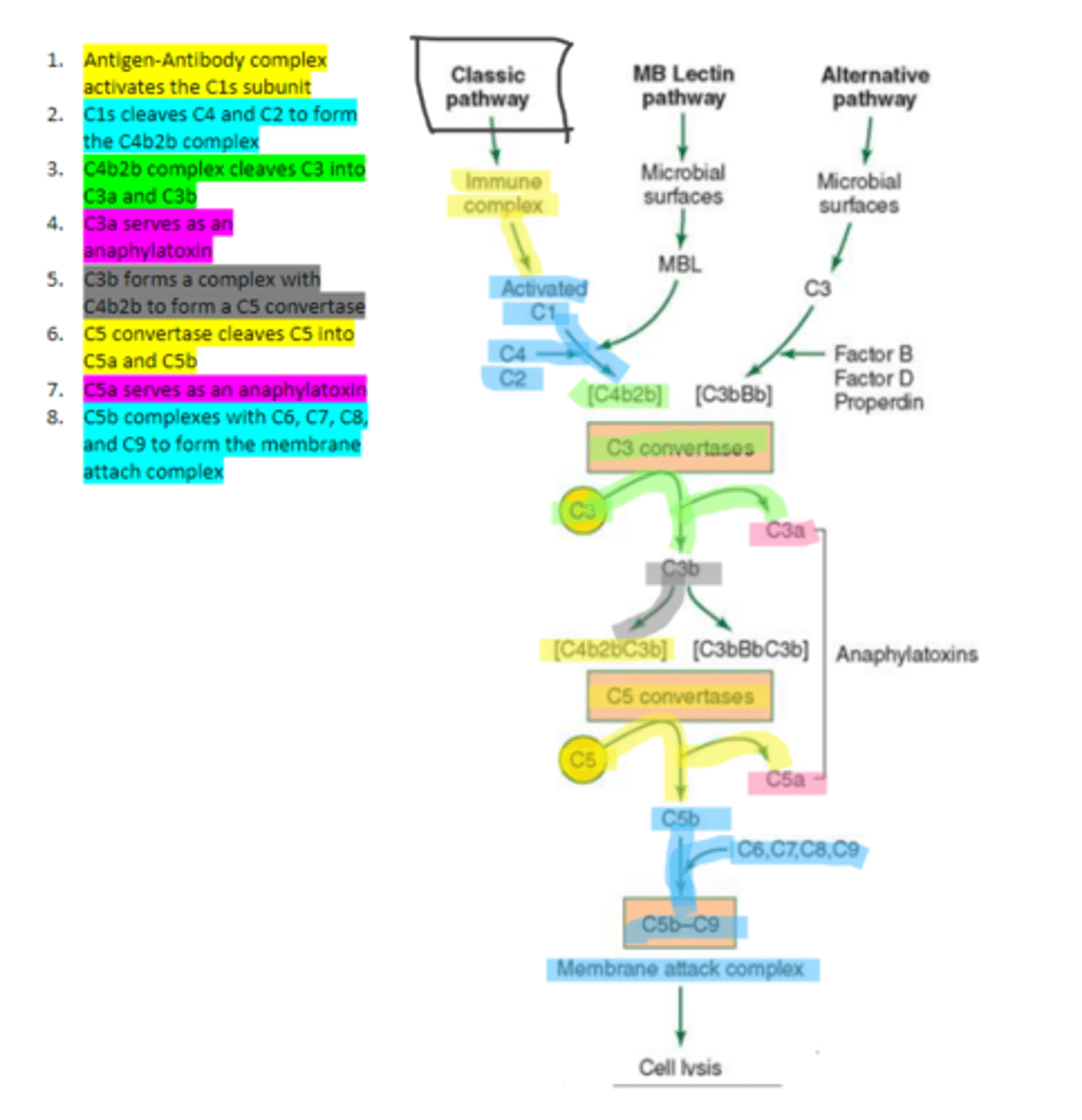
C5b
complement protein that binds to C6 and C7 and inserts into the cellular membrane as a complex in the classical pathway
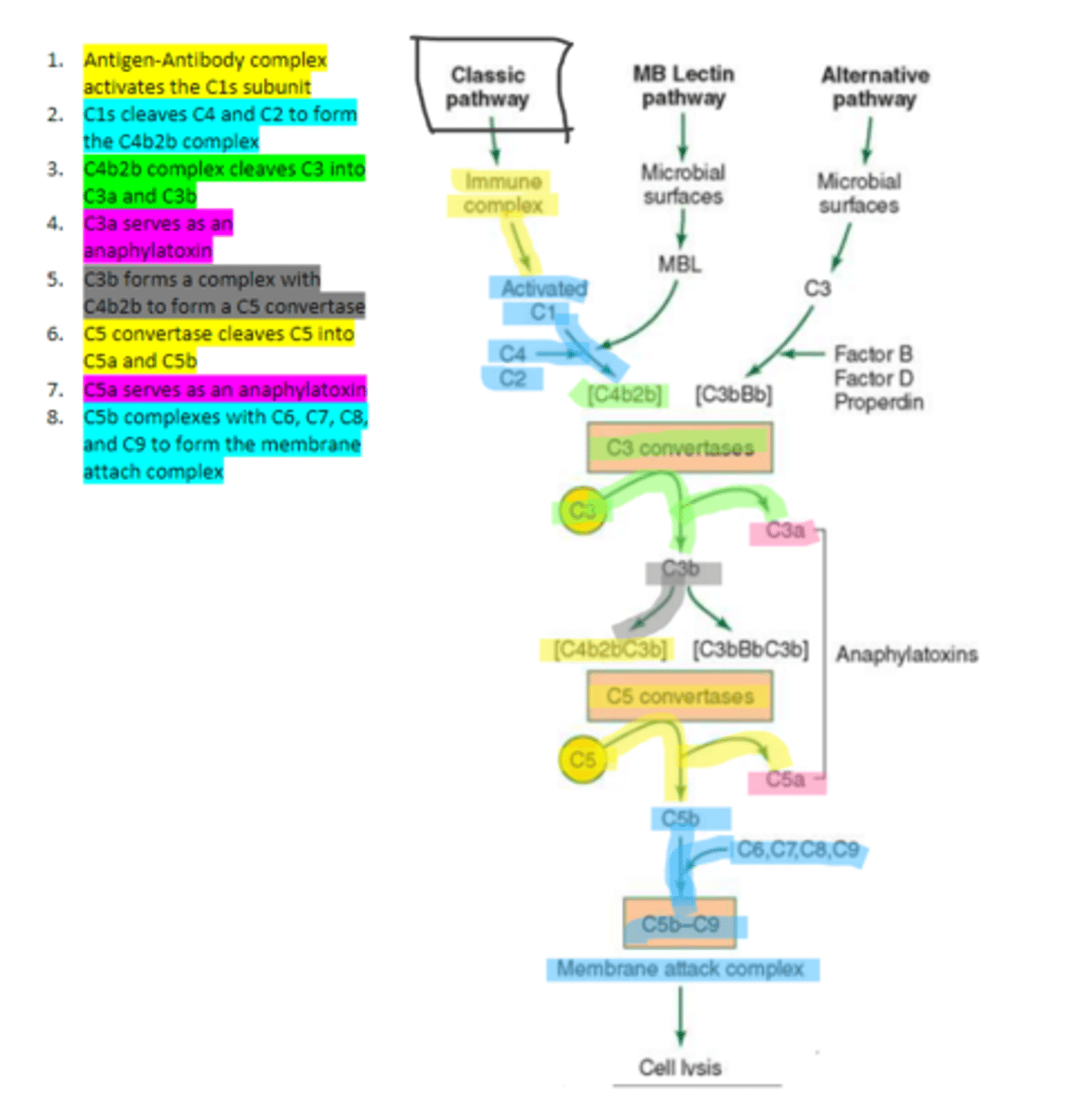
C8
complement protein that binds to the C5b, C6, C7 complex embedded in the cellular membrane in the classical pathway
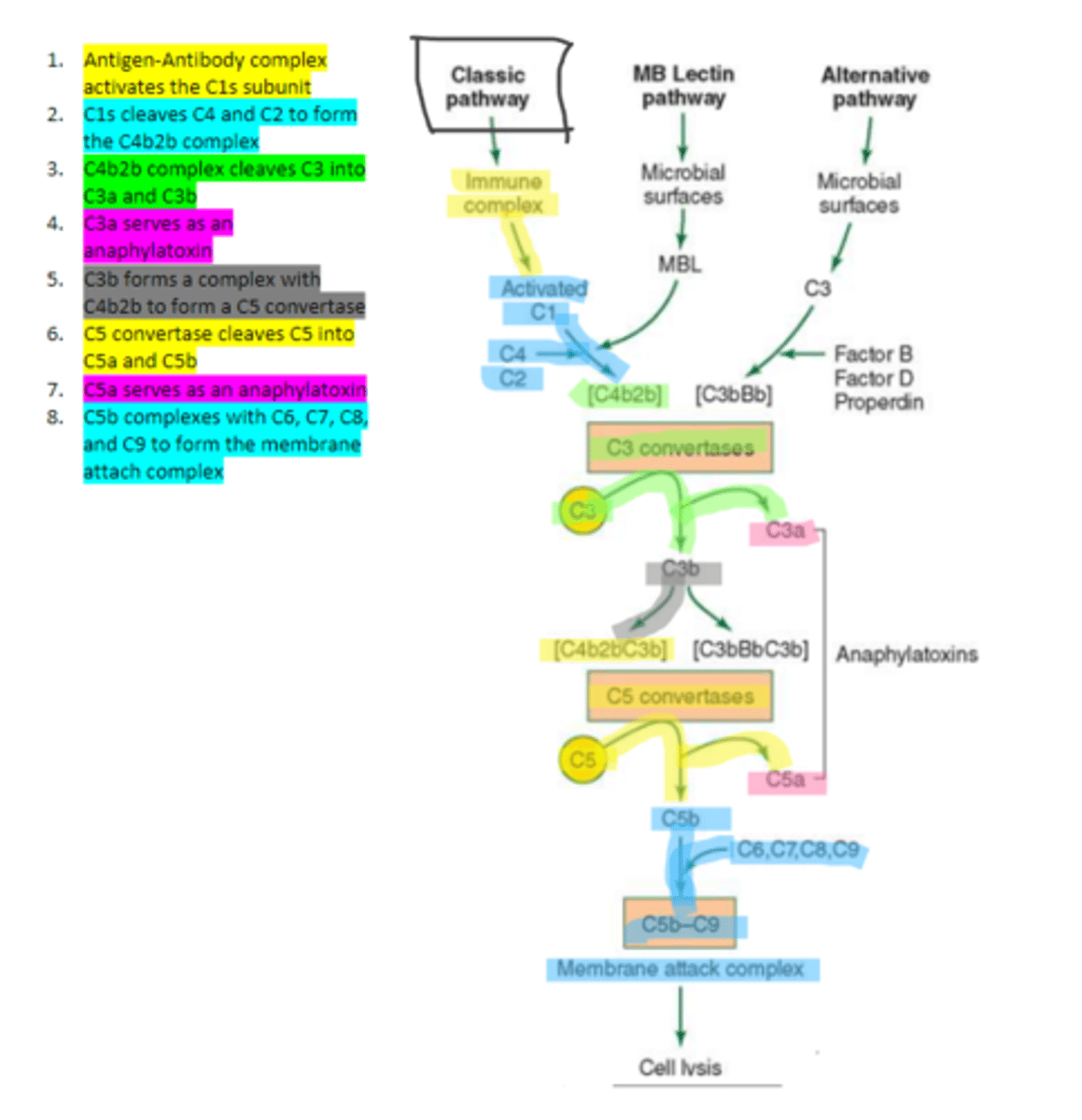
16, C9
Polymerization of up to ___ molecules of ___on C5b in the cellular membrane produces the membrane attack complex resulting in cell lysis in the classical pathway
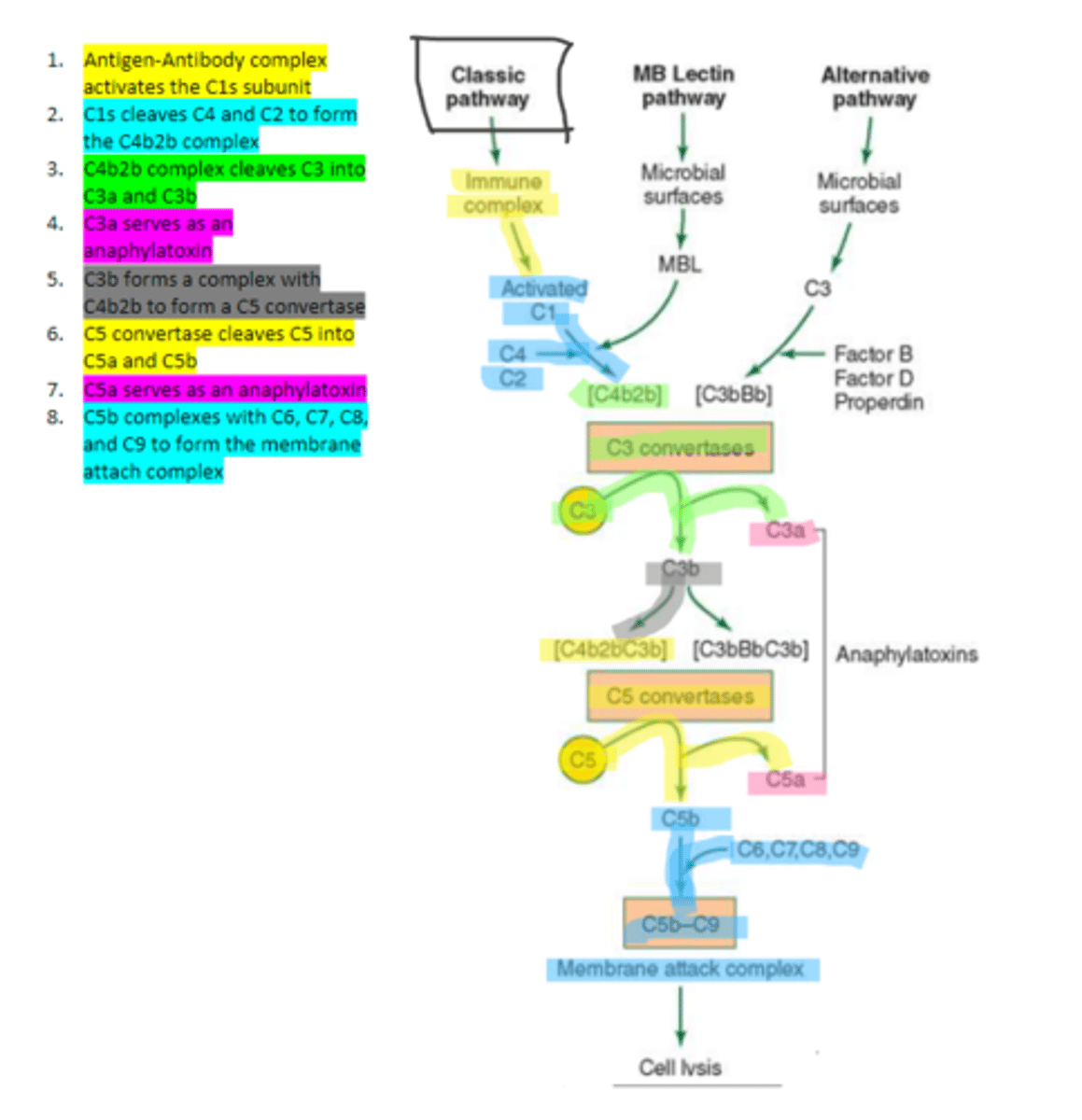
IgM and IgG (1, 2, and 3 NOT 4)
the only two immunoglobulins which can fix the classical complement pathway
MBL
enzyme that binds to sugar residues such as mannose found in microbial surface polysaccharides such as lipopolysaccharides (LPS). Its triggers the activation of of C4 and C2. Allow following complement steps are common to the classical pathway.
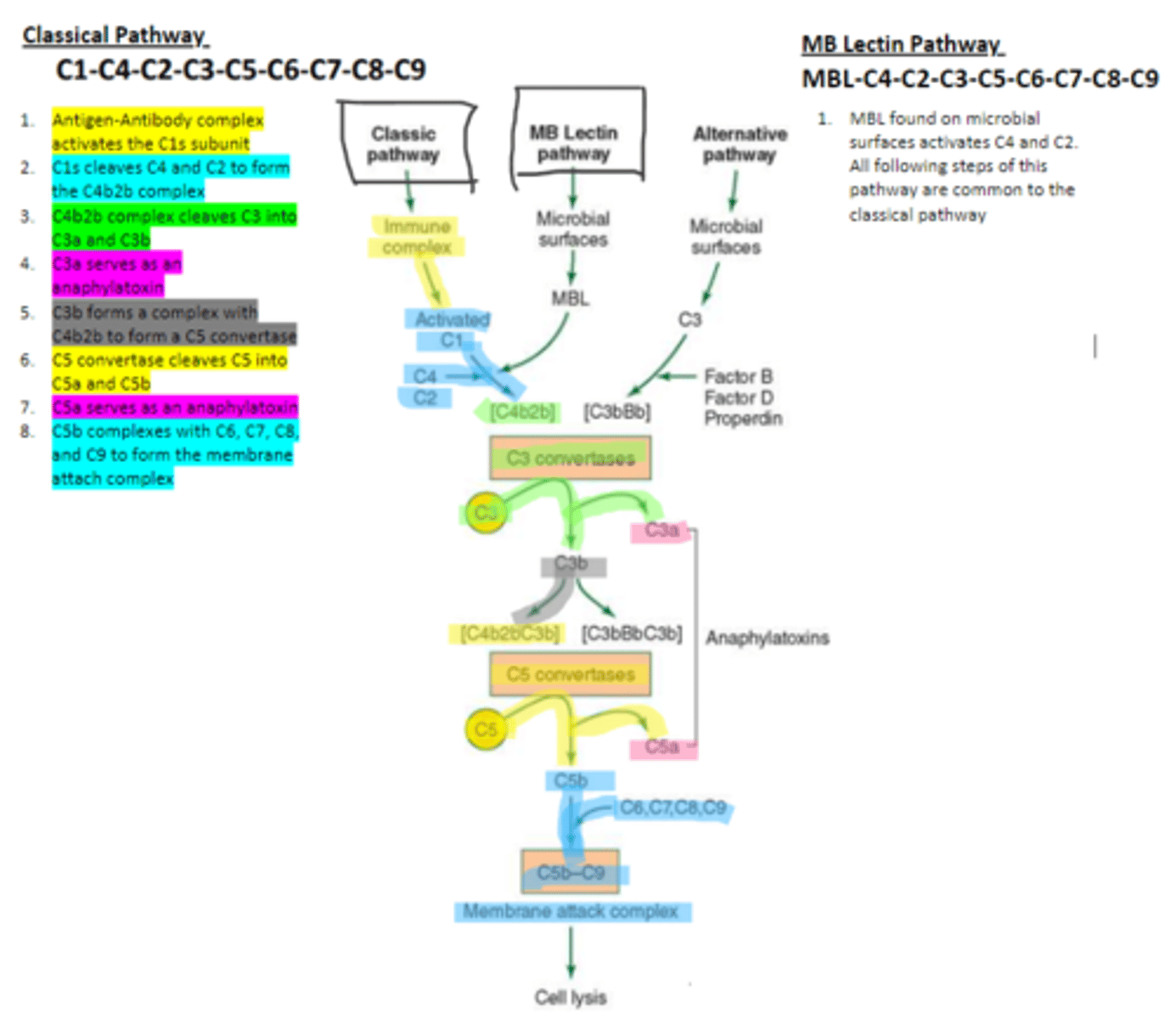
C4 and C2
Binding of MBL activates these two complement proteins.
factors B, D, and properdin
In the alternative pathway of complement, infectious agents activate the system and trigger the cellular production of these three components
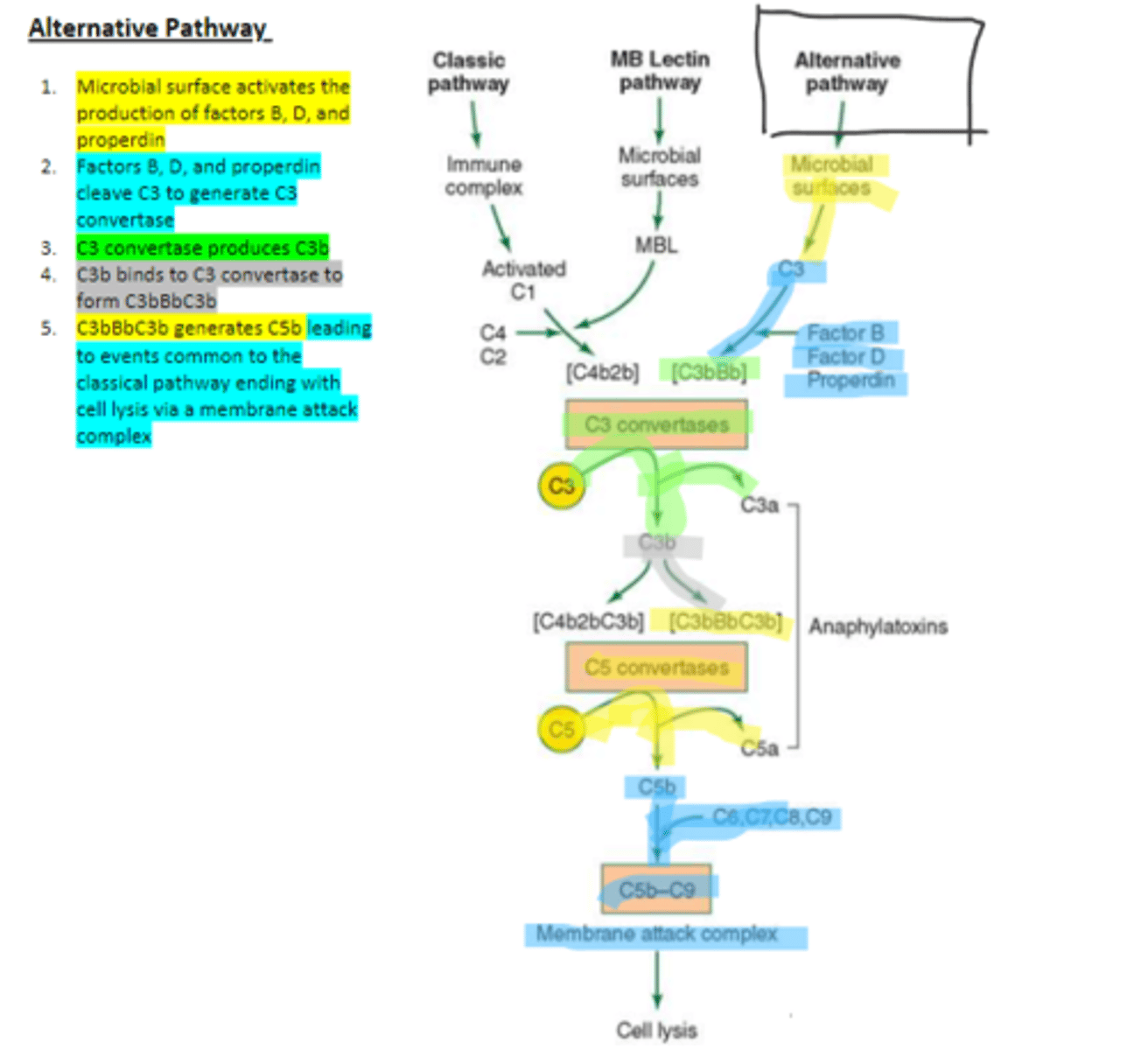
c3
Factors B, D, and properdin of the alternative complement pathway cleave ____ to generate C3 convertase
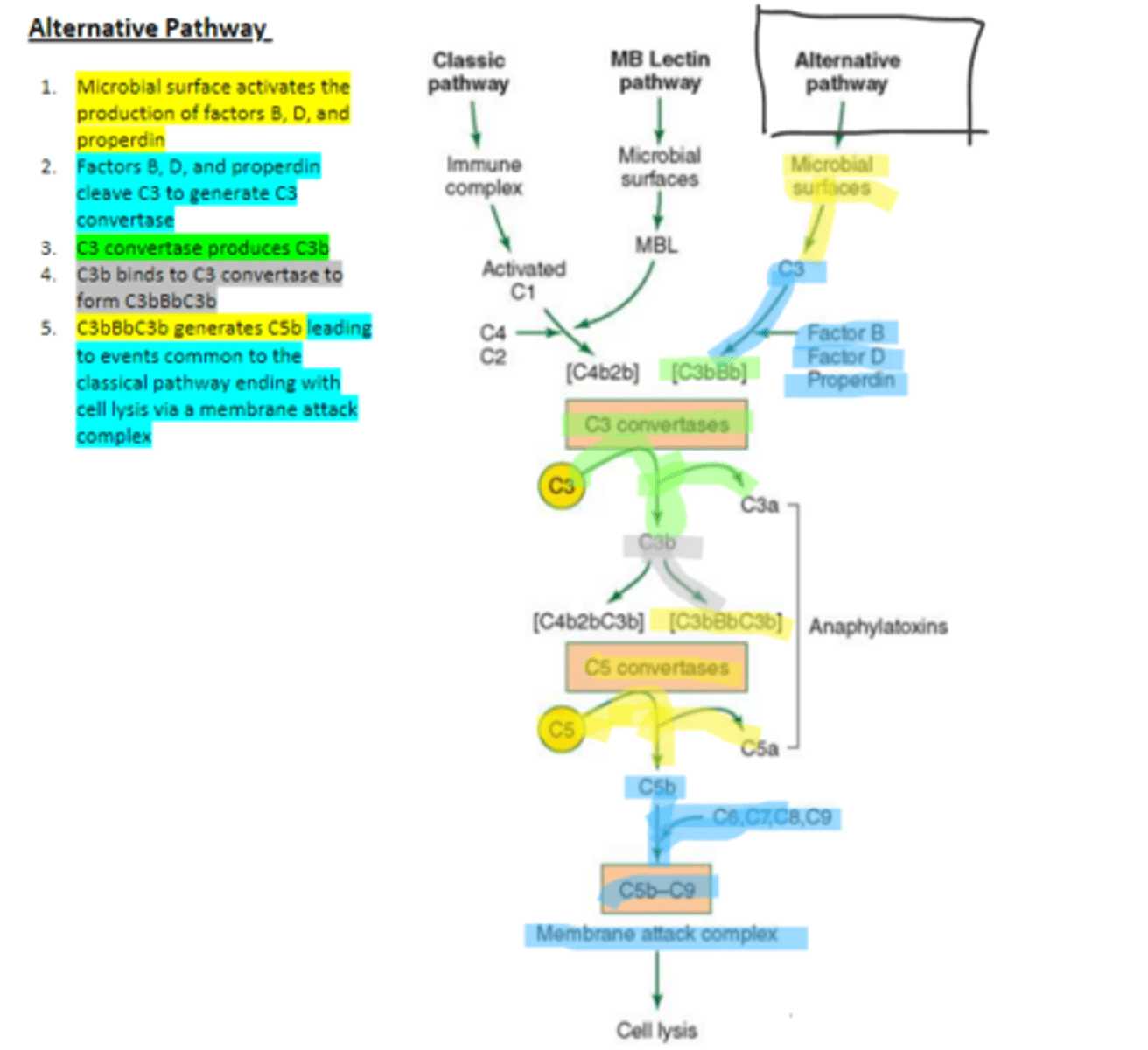
C3 convertase (C3bBb)
complement protein of the alternative pathway that produces more C3b.
C3 convertase
C3b binds to ____ to form C3bBbC3b in the alternative pathway
C3bBbC3b
the alternative pathway C5 convertase that generates C5b leading to the production of the membrane attack complex and cell lysis.
Proenzymes
enzymes that must be cleaved in order to form active enzymes.
regulated
Protein activity in the complement pathway is highly ____, meaning protein activities are controlled by a series of cascades. Proteins will not be activated unless the downstream events occur in order to activate them.
9
how many steps are in the complement pathway?
C5 convertase
enzyme which breaks down C5 into C5a and C5b. Involved in all three complement pathways.
C5a
complement protein that is an anaphylatoxin as well as a chemotactic factor. Involved in all three complement pathways.
membrane attack complex, cell lysis
All pathways of complement result in the formation of a _____ and ultimately ____
HIV, stomatitis stomatitis virus, mycoplasma
three microorganisms that can activate the classical pathway of complement
HIV
virus that can activate the lectin pathway of complement
epstein-barr virus, trypanosomes, leishmania spp, many fungi
four microorganisms that can trigger the alternative pathway of complement
Herpes keratitis
a viral infection of herpes simplex virus in the eye. Usually effects only one eye and is most often occurring on the cornea. Viral proteins presented on the infected cell surfaces serve as antigens for antibody production. Infection deeper than the corneal epithelium can cause scarring, vision loss, and sometimes blindness.
classical pathway
Herpes keratitis triggers which pathway of complement?
Cicatricial pemphigoid
autoimmune disease targeting basal epithelial cells of the conjunctiva.
Mooren's ulcer
autoimmune disease involving the wasting away of corneal tissue from the exterior. Involves the activation of mast cells by C5a and other complement events occur as well.
Cytokines
potent, low molecular weight multifunctional cell regulator proteins. Involved in hematopoiesis, immunity, infectious disease, tumorigenesis, homeostasis, tissue repair, and cell development and growth. They act as signaling molecules that bind to tyrosine kinase receptors on target cells in order to trigger a biological response via the bind to DNA.
Tyrosine kinase receptor
the main receptor class that is triggered by cytokines. Can auto phosphorylate causing a transduction of the signal to DNA in order to mediate a biological effect.
Immunoregulatory
class of cytokines including INF gamma, which play a major role in antigen presentation.
Proinflammatory
class of cytokines including IL1, IL6, TNF alpha, and IFNs, which are commonly seen in infectious disease and are involved in enhancing inflammatory response.
Anti-inflammatory
class of cytokines including TGF beta, IL10, IL11, and IFN beta, which are involved in downregulating an overactive inflammatory response.
Colony stimulation factors (CSFs)
class of cytokines which serve as growth factors during growth and differentiation.
INF gamma
name one immunoregulatory cytokine
IL1, IL6, TNF alpha
name three proinflammatory cytokines.
TGF beta, IL10, IL11, INF beta
name four anti-inflammatory cytokines.
differentiate
Naïve T cells use cytokines in order to ____ into other T cell subsets
Th1 cells
differentiated T cells that are generated in the presence of IL4 which function in the protection against bacteria and viruses.
Th2 cells
differentiated T cells that are generated in the presence of IL4 which function in the protection against parasites.
Th17
differentiated T cells that are generated in the presence of TGF beta and IL6 which function in the protection against fungi.
Treg cells
differentiated T cells that are generated in the presence of TGF beta which function in peripheral tolerance.
bacteria and virus
what do Th1 cells protect against?
parasites
what do Th2 cells protect against?
fungi
what do Th17 cells protect against?
LPS
a biomarker found in the cell wall of gram negative bacteria which can trigger a cytokine cascade.
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)
the first cytokine produced in response to the presence of LPS and triggers the production of IL1
IL1
cytokine that triggers the production of IL6 and IL8
Proinflammatory cytokines TNF alpha, IL1, and IL6 are biomarkers of septic shock (dangerously low blood pressure caused by infection)
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
formation of small blood clots within vessels that can occur in the formation of sepsis due to an increase in cytokine levels.
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
syndrome which can occur due to the formation of septic shock blood oxygen levels are low, alveoli collapse, and alveoli fill with fluid. Occurs due to an increase in cytokine levels.
Purified protein derivative (PPD)
a measured level of cytokine production in vitro used to monitor immune status. Ie) the detection of TB reactivity.
Inf alpha
cytokine which is an approved therapeutic agent for hepatitis C infection of liver cells. It prevents viral infection mechanisms and increases cytotoxic T lymphocyte activity.
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL)
immune cells whose activity is increased by Inf alpha
Inf beta
cytokine which is an approved therapeutic agent for the treatment of multiple sclerosis. It inhibits T cell activation, proliferation, and migration (across BBB) in order to prevent the immune system from targeting the myelin sheath of axons
TNF alpha
nhibitors of this cytokine are used to manage rheumatoid arthritis. Ie) Infliximab
Infliximab
a monoclonal chimeric antibody which targets TNF alpha in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.
IL2 and IL15
Inhibitors of these two cytokines are used in therapies related to transplantation and cancer.
inflammation
Dry eye is an indicator of surface _____ which is due to the activation and infiltration of pathogenic immune cells.
CD4+ T cells
cells of the conjunctiva that are primarily involved dry eye development
CD11b+ cells
cells of the cornea that are primarily involved in dry eye development.
IL1, TNF alpha, and IL6
in the first stage of DES formation, stress induces the secretion of these three cytokines by ocular surface tissues. These cytokines causes the activation and migration of APCs towards lymph nodes.
IL17 and IFN gamma
in the second stage of DES formation, APCs at the lymph node stimulate the production of these two cytokines via differentiated T cells, Th17 and Th1 cells respectively. IL17 inhibits T regulatory cells.
IL17
what do Th17 cells secrete?
IFN gamma
What do Th1 cells secrete?
IL17, MMPs, IFN gamma
in the third stage of DES formation, cytokines migrate to the ocular surface. Interaction of ____ with receptors on the ocular surfaces leads to the secretion of ____ and inflammatory cytokines causing epithelial damage. ______ causes upregulation of chemokine ligands as well as increased migration of immune cells to the ocular surface tissues.