functional groups
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
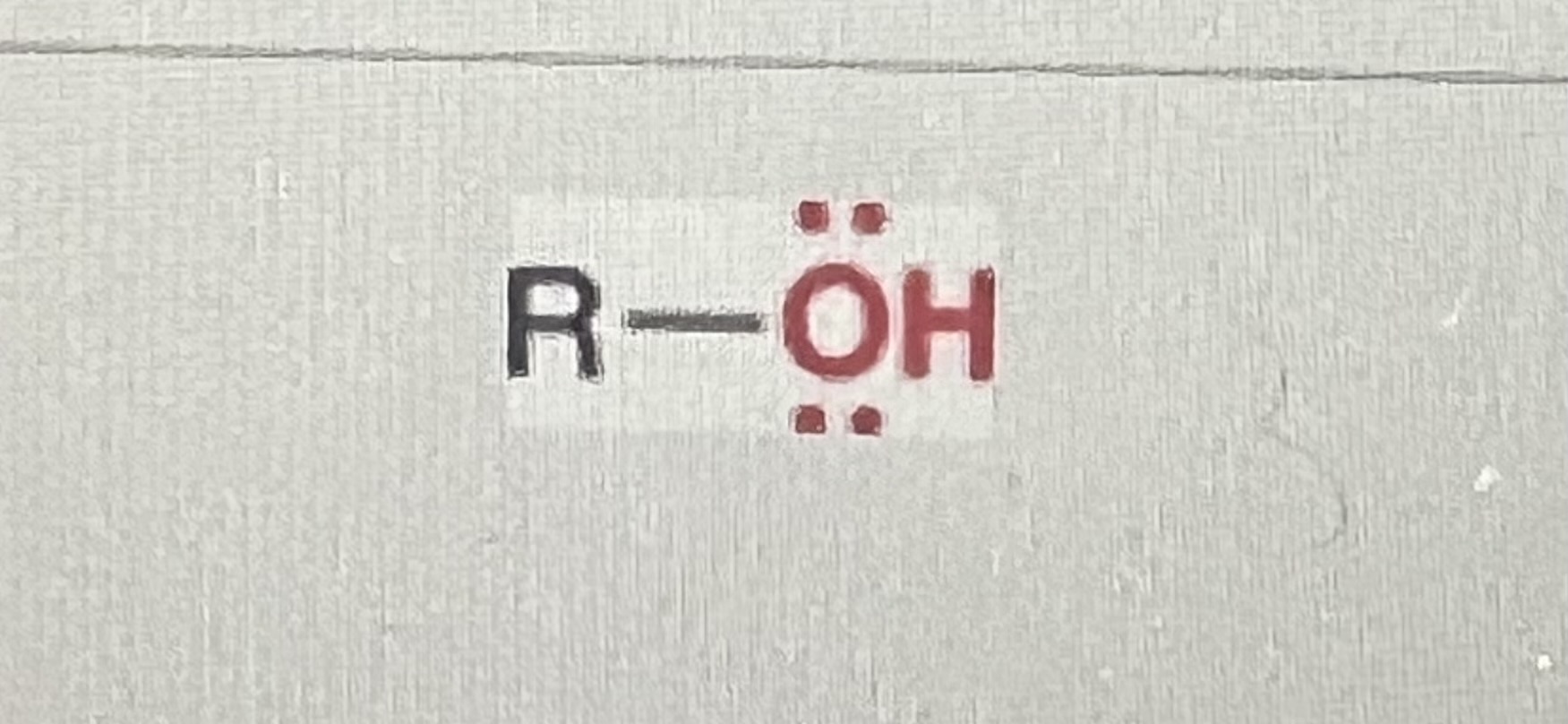
alcohols:
generic structure: R-OH
(R=alkyl)
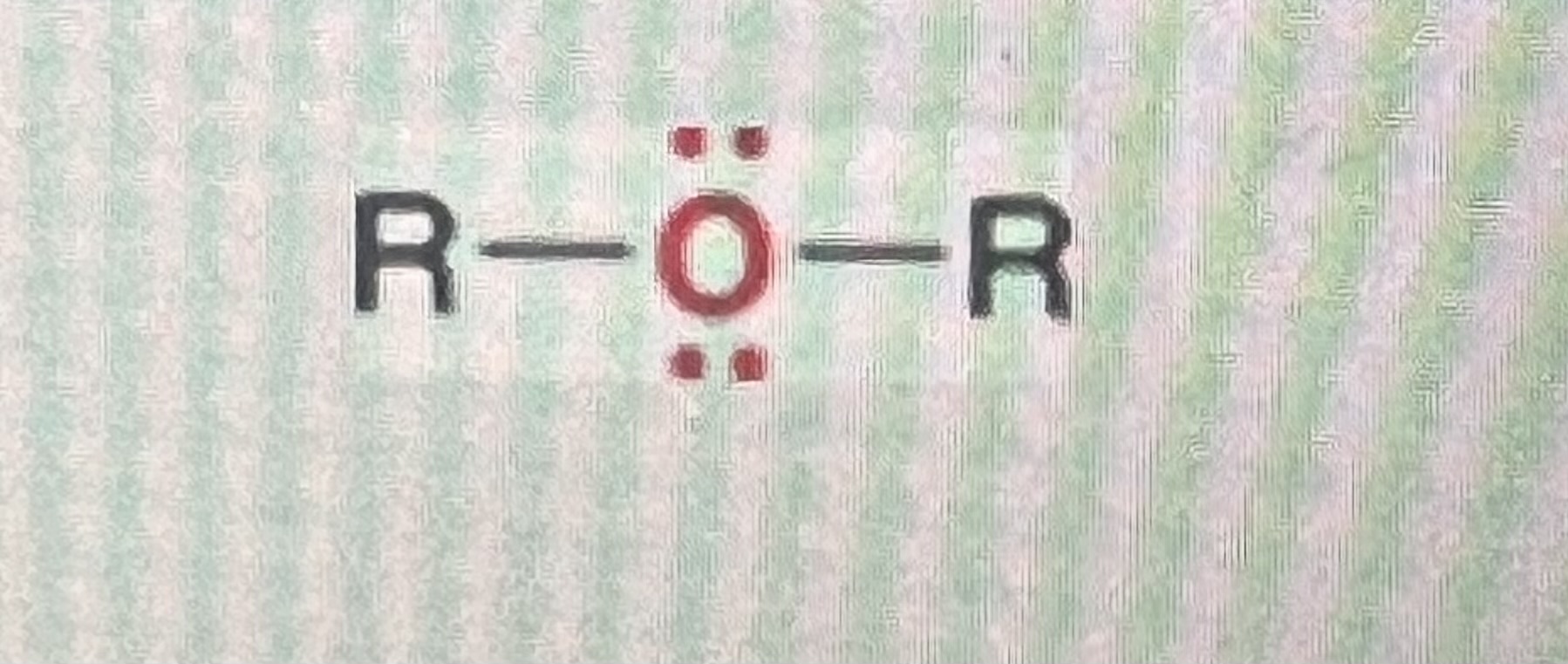
ethers:
generic structure: R-O-R
(R=alkyl)
-if one of the R-groups were to be a hydrogen, the structure would be considered and alcohol
sulfides:
generic structure: R-S-R
(R=alkyl)
-similar to ethers, but Oxygen is replaced with Sulfur
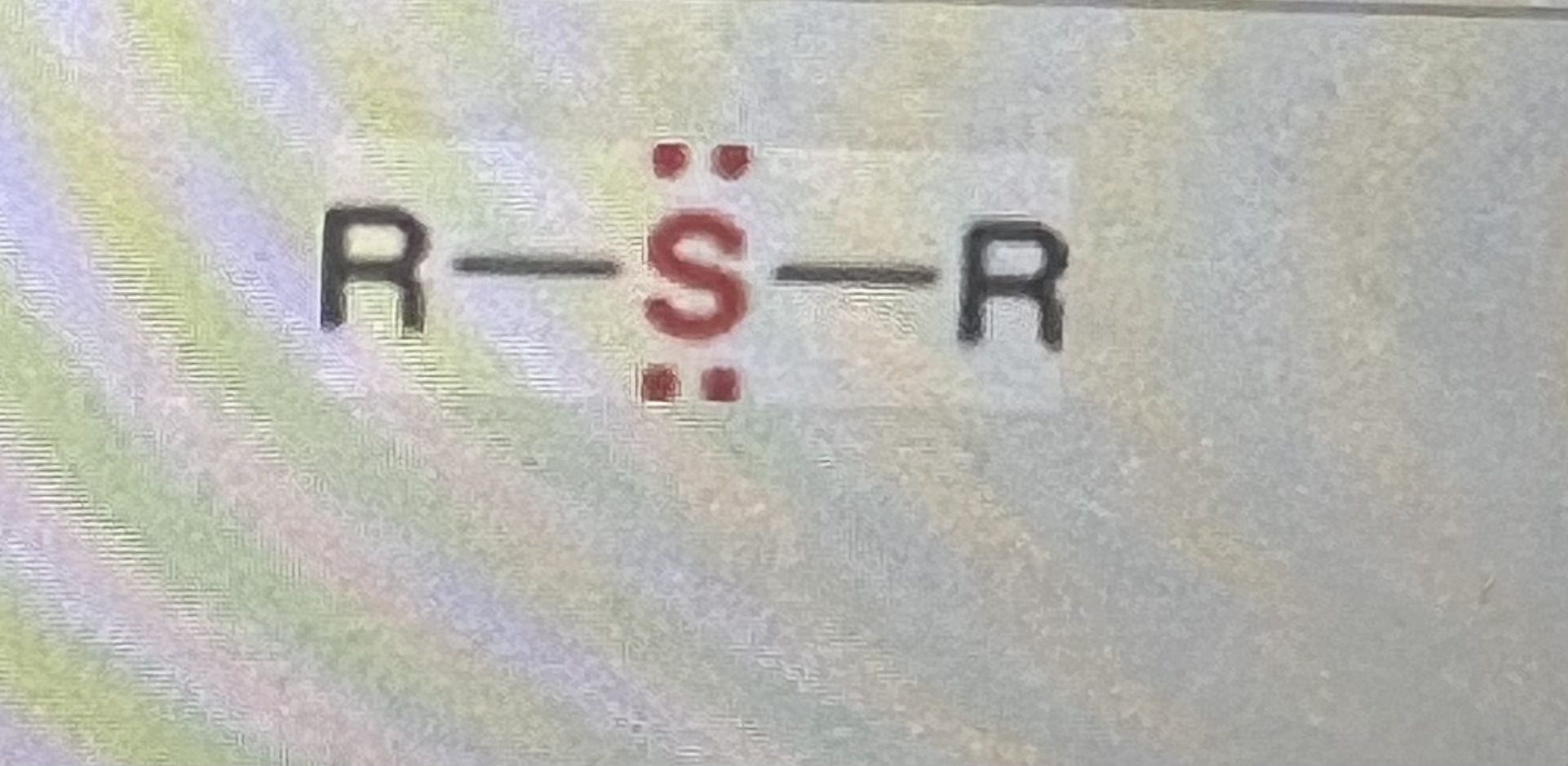
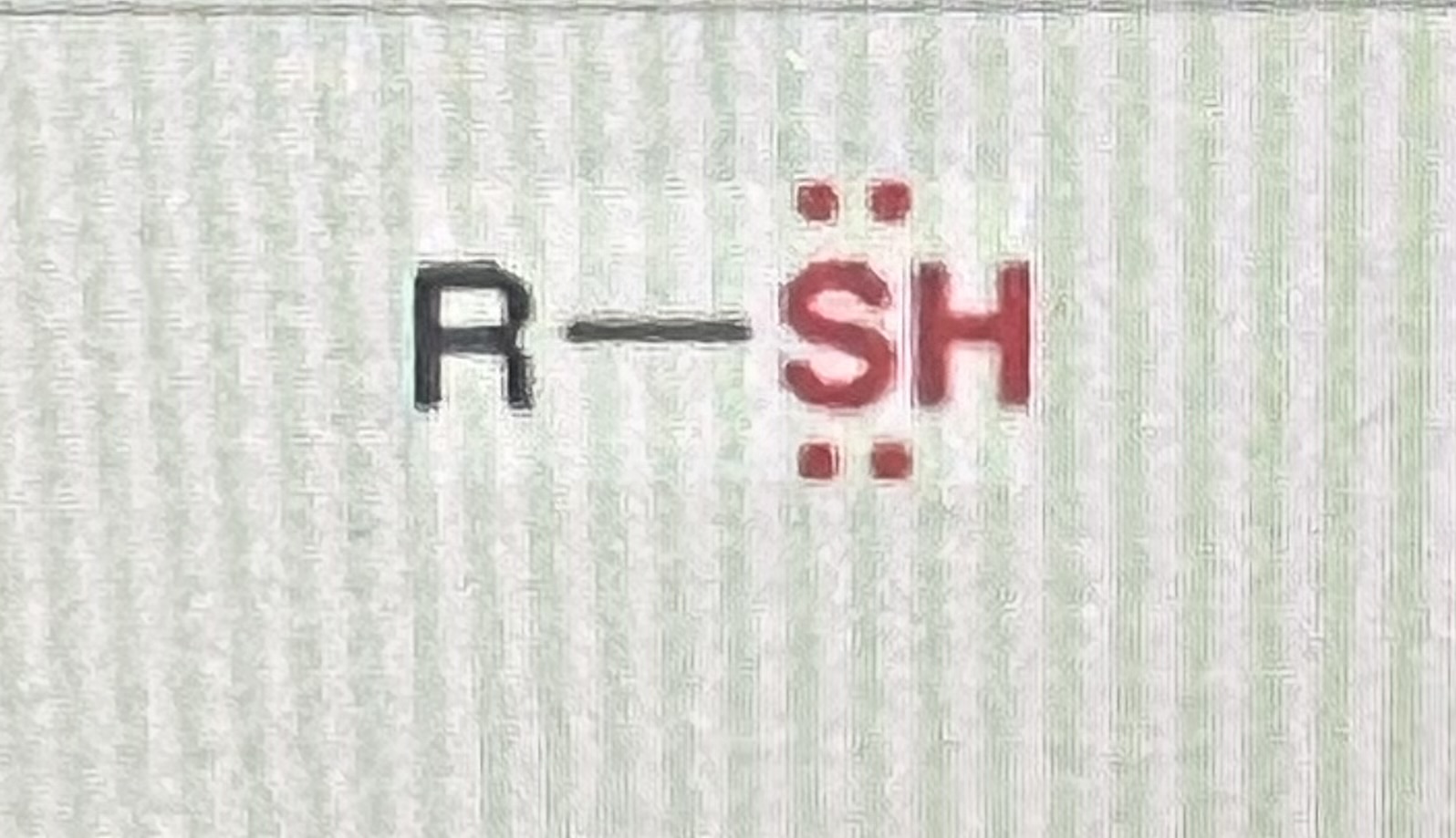
thiols:
generic structure: R-SH
(R=alkyl)
-similar to alcohol, replaces OH with SH
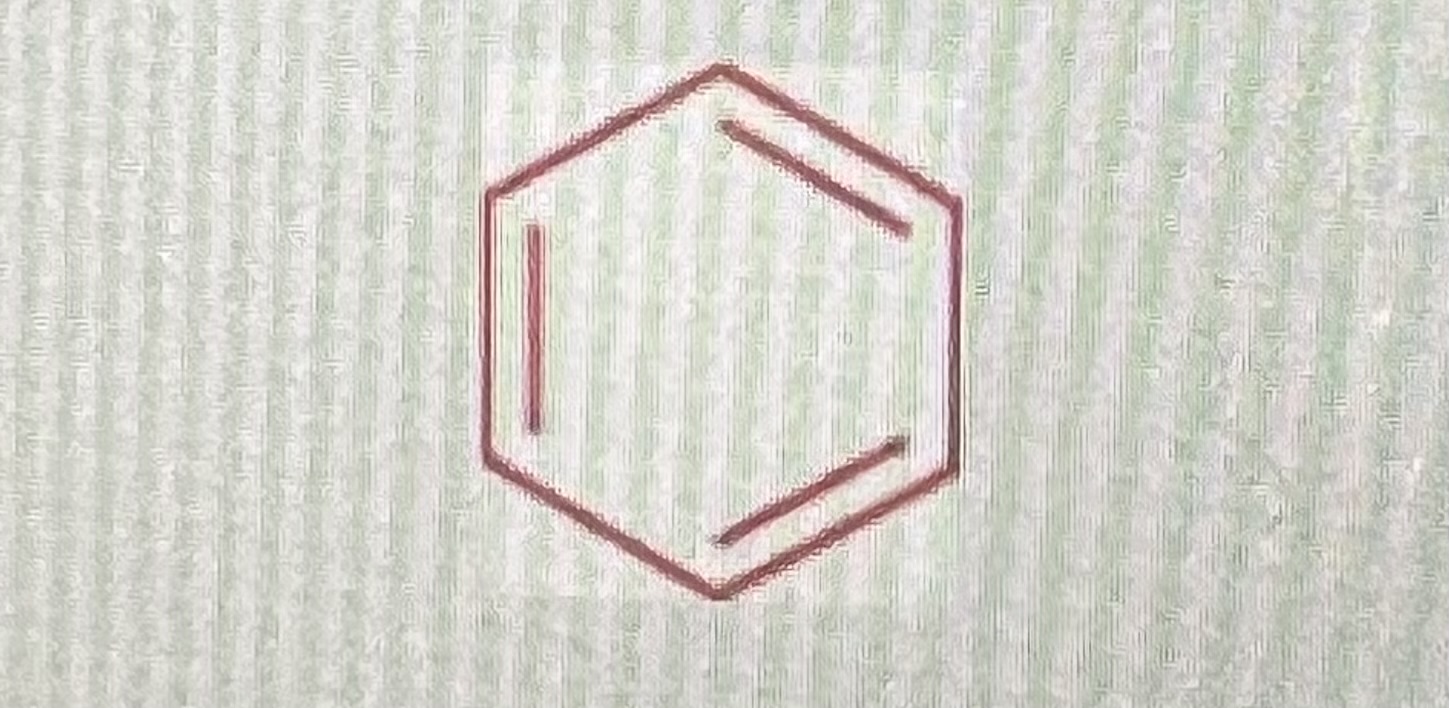
benzene:
-falls under the functional group aromatics
-aromatic compounds are in a ring structure with alternating double bonds
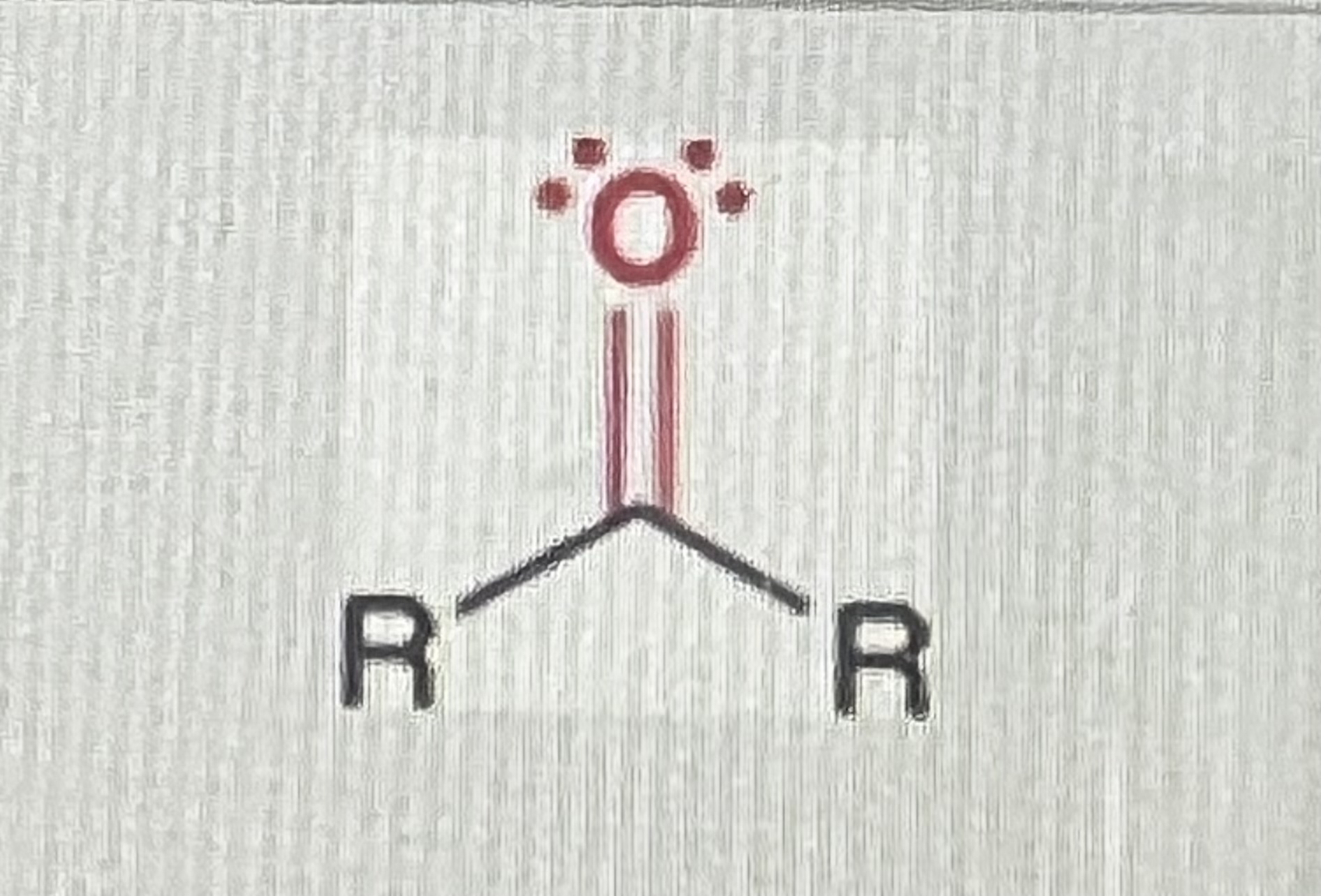
ketones:
(R=alkyl)
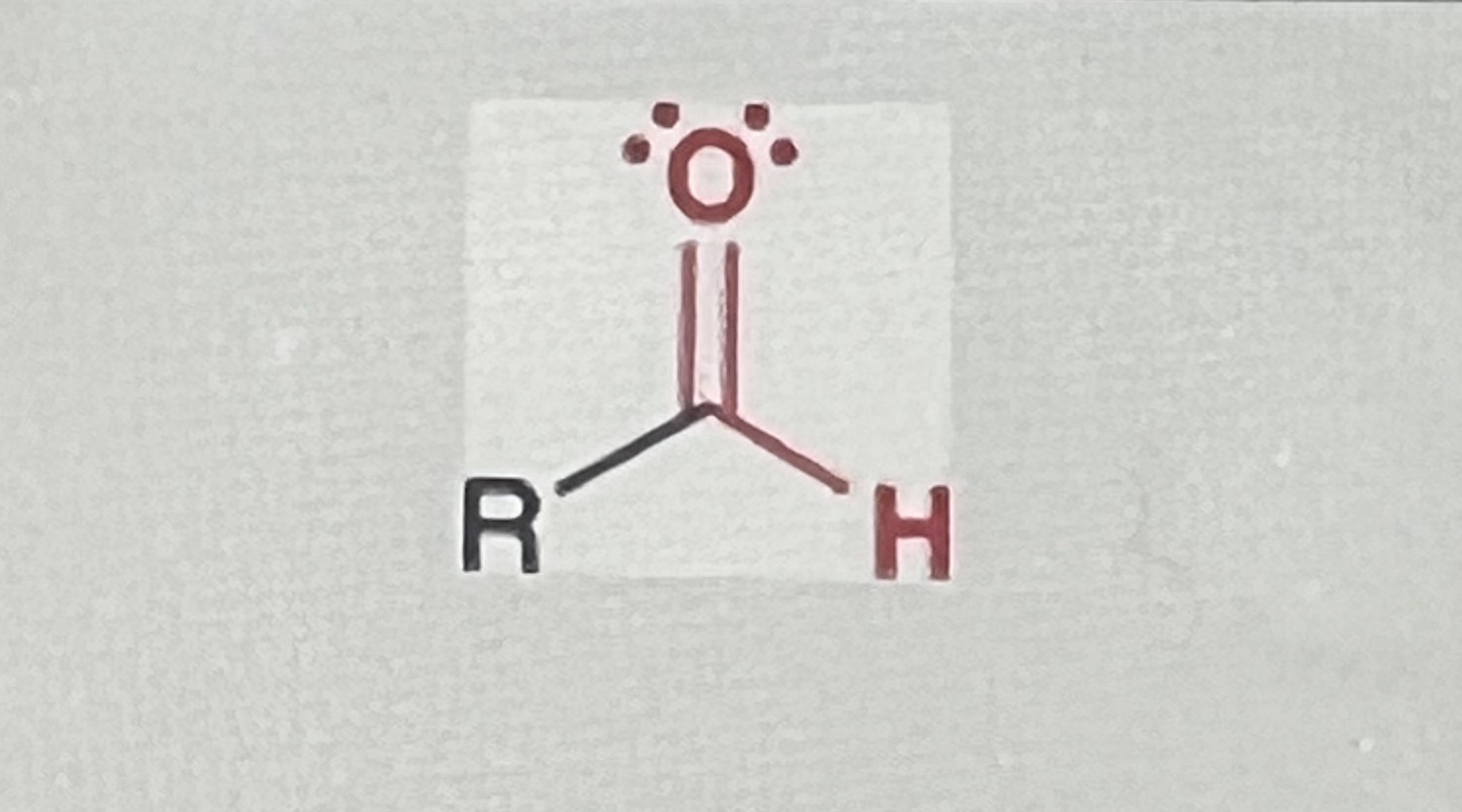
Aldehyde
(R=alkyl)
-one R-group MUST be hydrogen but both R-groups can be hydrogen, or if one R-group is hydrogen the other must be alkyl
Both ketones and aldehydes contain:
A double bind between the carbon and oxygen, called a CARBONYL
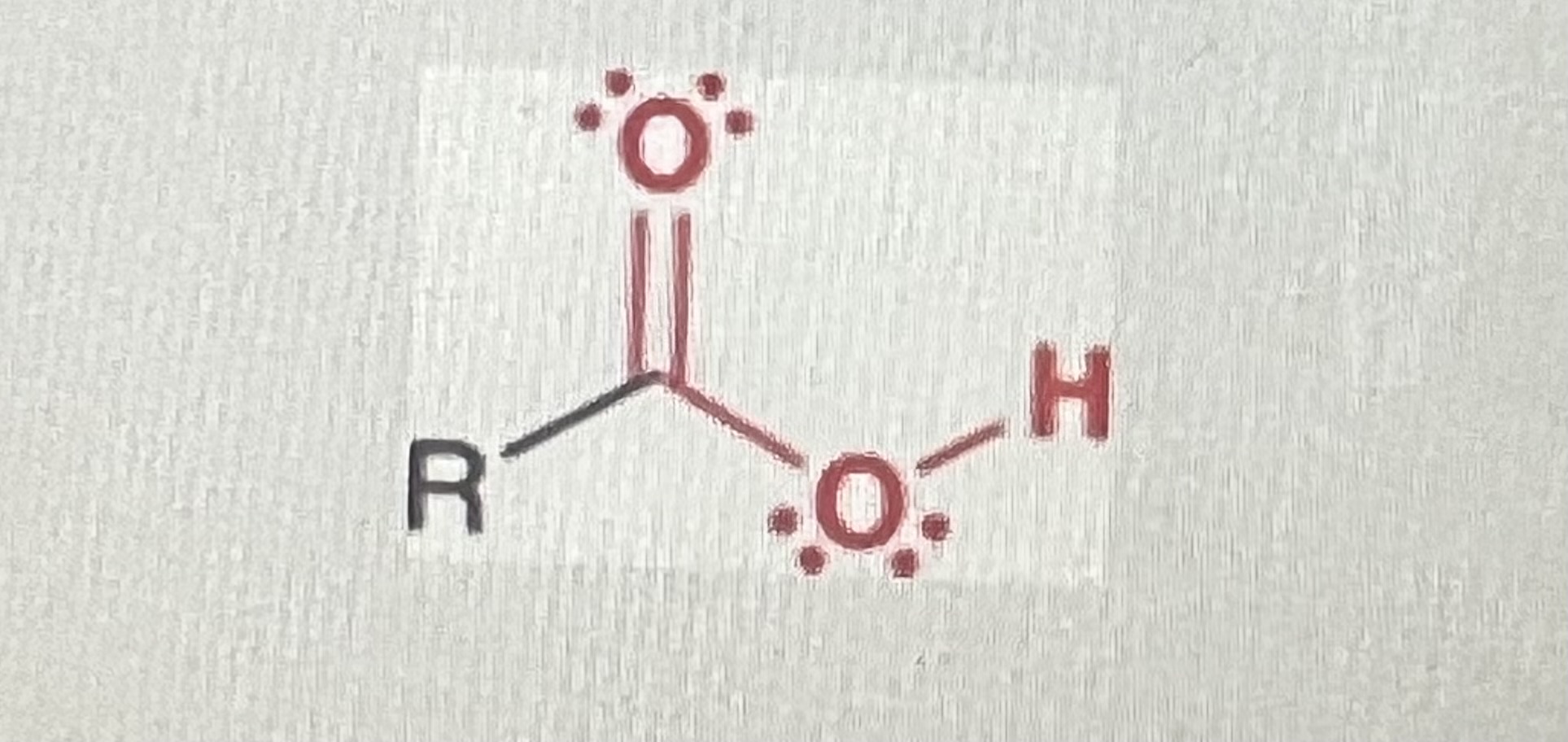
Carboxylic acids:
(R=hydrogen or alkyl)
-contains carbonyl but is NOT a ketone or aldehyde
-OH has to be directly attached to carbonyl carbon
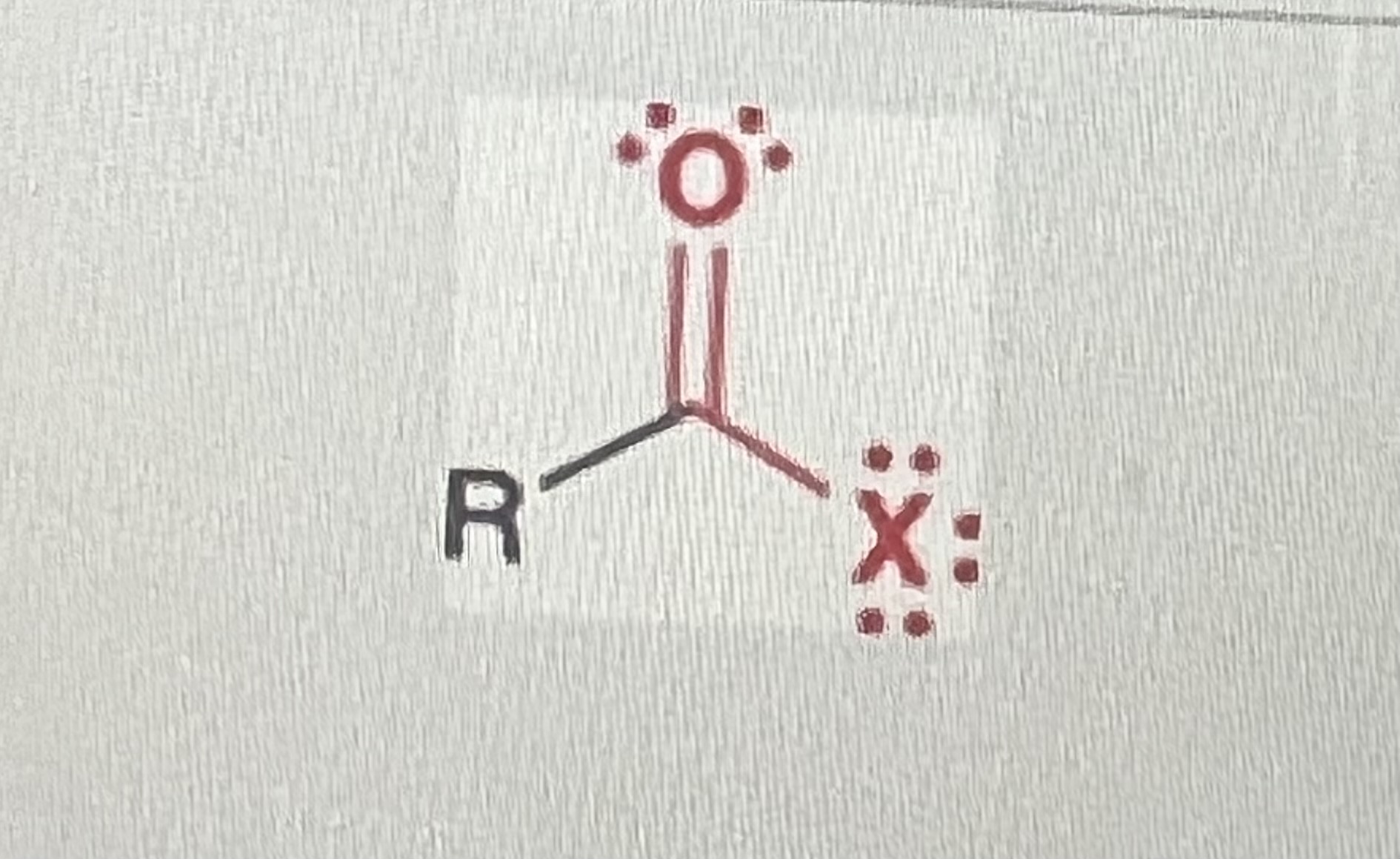
Acyl halides
(X=halogen, R=alkyl)
-contains CARBONYL and ACYL
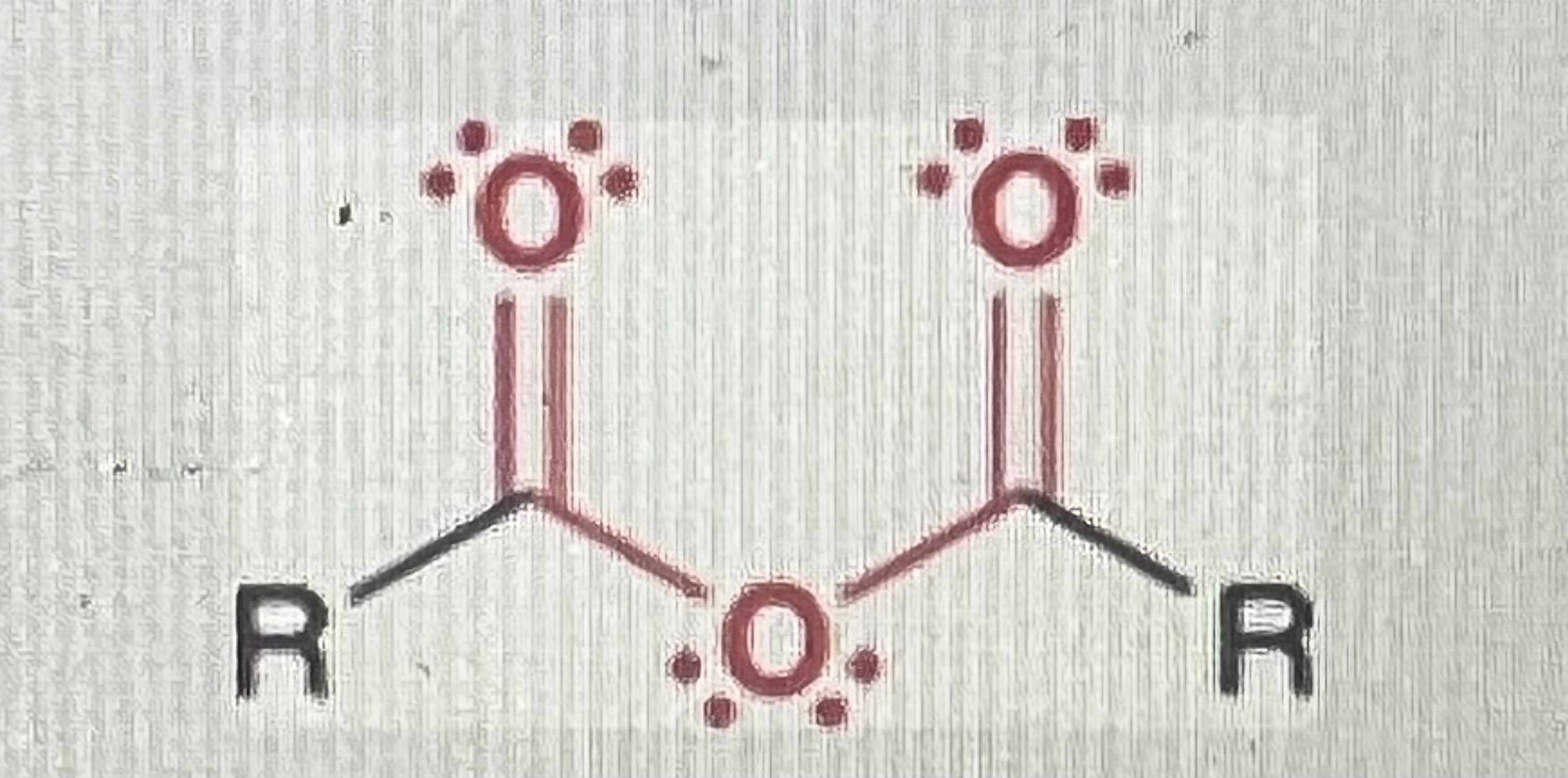
Anhydrides/ acid anhydrides:
Two Acyl groups with an oxygen attaching them (acid anhydride)
-similar to carboxylic acid but hydrogen is replaced with a carbonyl carbon
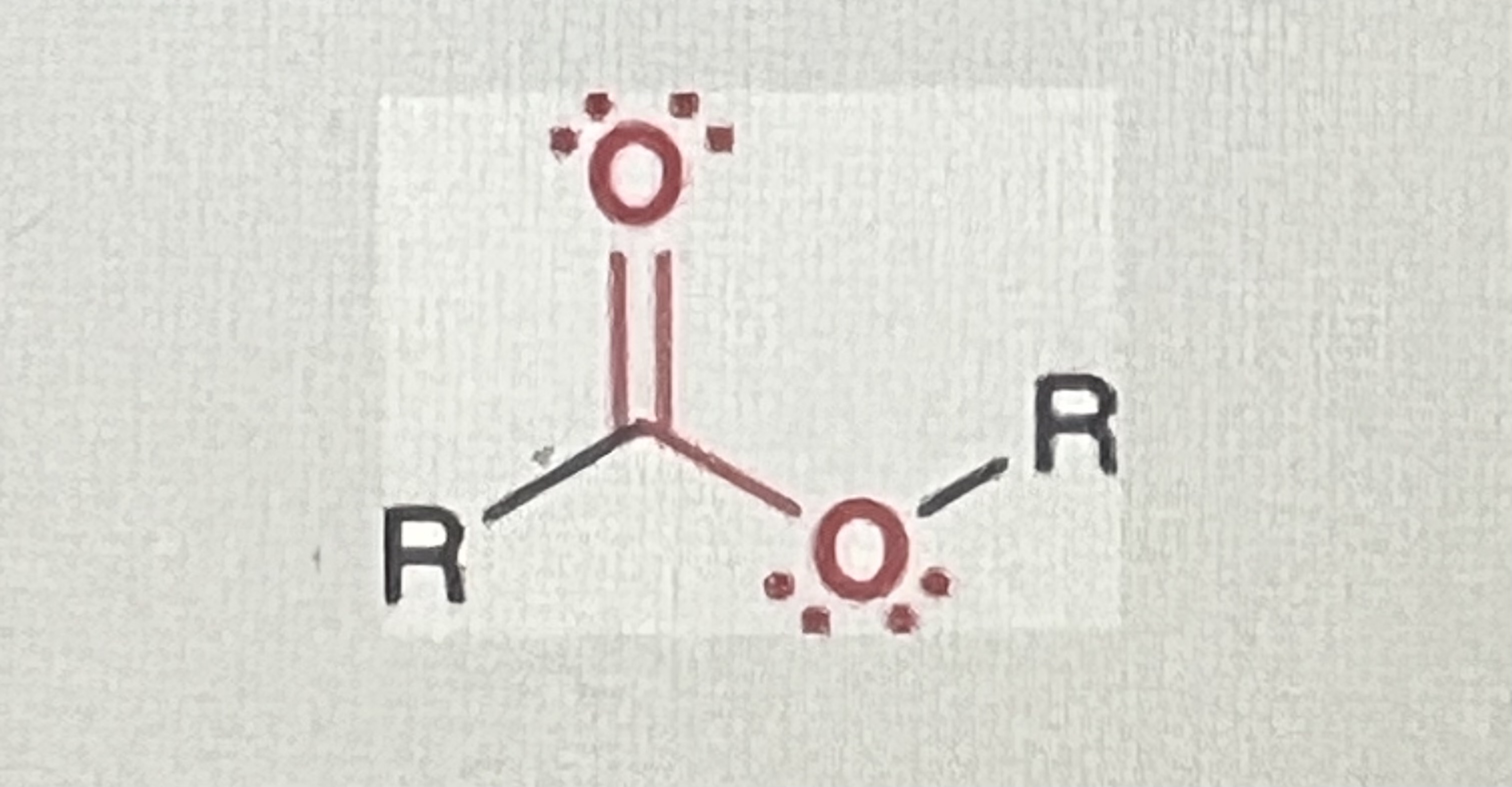
Esters:
contains carbonyl, R1 must be alkyl, R2 can be a hydrogen if necessary
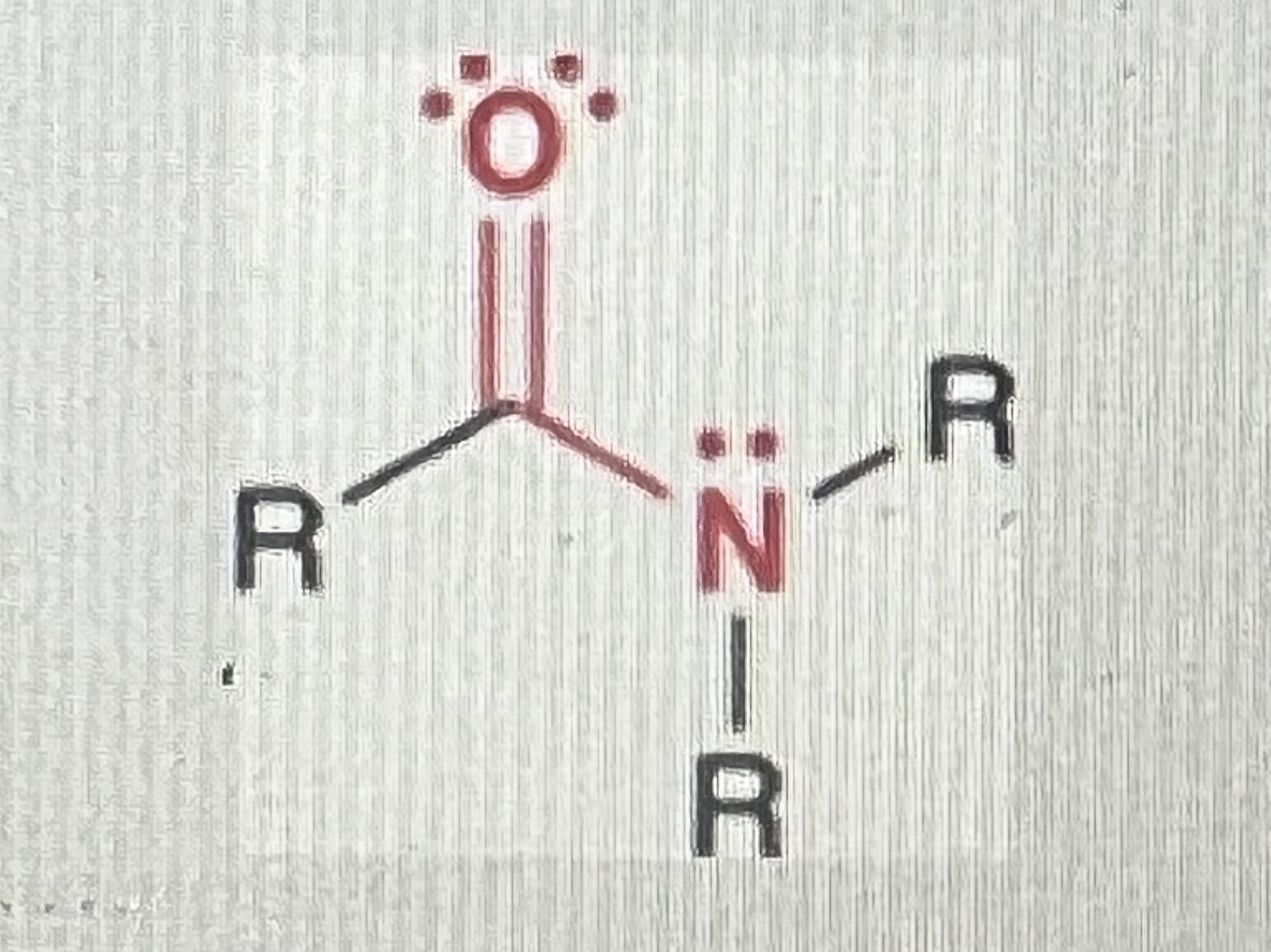
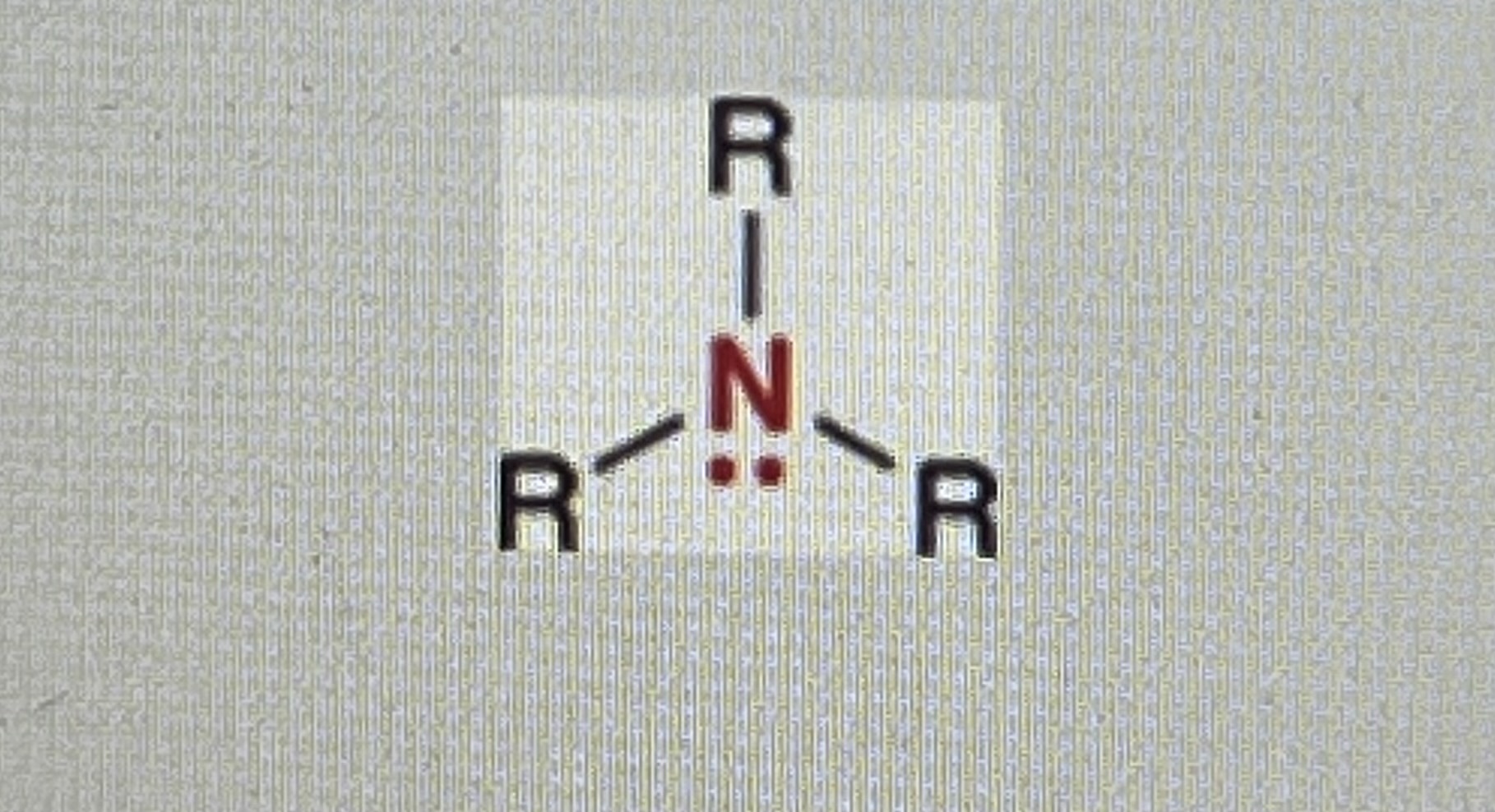
Amines:
(R=hydrogen or alkyl)
When you have a nitrogen atom connected to up to three R-groups
Amides:
(R= hydrogen or alkyl)
Contains carbonyl carbon, similar to carboxylic acids, oxygen is replaced with nitrogen