Sensation and Perception
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is sensation?
Sensation is the conversion (transduction) of physical, chemical, or electromagnetic stimuli into electrical signals.
What is perception?
Perception is the interpretation and organization of sensory input
What are sensory receptors?
Sensory receptors are specialized excitable cells (often neurons or receptor cells) that detect specific types of stimuli
They convert physical, chemical, or electromagnetic input into electrical signals via sensory transduction
How do sensory neurons transmit stimuli from the periphery to the brain?
Sensory Ganglia act as a relay station for incoming sensory signals from the periphery.
After entering the CNS, sensory signals are routed to specific cortical regions for analysis
What are the major types of sensory receptors?
“Please Help Neurons Transmit Our Olfactory Taste”
Photoreceptors, Hair cells, Nociceptors, Thermoreceptors, Osmoreceptors, Olfactory, Taste
What is a threshold in sensory systems?
A threshold is the minimum intensity of a stimulus required to initiate signal transduction.
What is the absolute threshold in sensory systems?
The absolute threshold is the minimum intensity of stimulus energy required to activate a sensory system.
What is the threshold of conscious perception?
The threshold of conscious perception is the minimum stimulus intensity and duration required to generate a neural signal that reaches awareness.
What is the difference threshold or just-noticeable difference (JND)?
The difference threshold (or JND) is the minimum change in stimulus intensity required for a person to detect a difference between two stimuli.
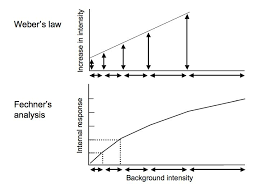
What does Weber’s Law state about the just-noticeable difference (JND)?
Weber’s Law states that the JND is proportional to the magnitude of the original stimulus
This proportion remains approximately constant across a wide range of stimulus intensities
What is Signal Detection Theory?
SDT explains how nonsensory factors—like expectations, motives, attention, and prior experience—influence our ability to detect stimuli.
What are the four possible outcomes in a signal detection experiment, and how do they reveal response bias?
Hit: Correctly detecting a present stimulus
Miss: Failing to detect a present stimulus
False Alarm: Reporting a stimulus when none was present
Correct Rejection: Accurately stating no stimulus was present
Response Bias
Reflects the subject’s tendency to say “yes” or “no” regardless of actual stimulus
Adaptation:
refers to a decrease in response to a stimulus over time
Eye:
an organ specialized to detect light in the form of photons
What are the primary functions of the cornea in vision?
gathers and filters incoming light
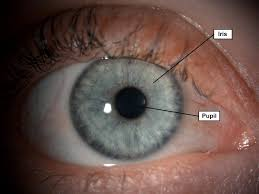
What is the iris of the eye?
colored, circular structure that divides the front of the eye into the anterior and posterior chambers
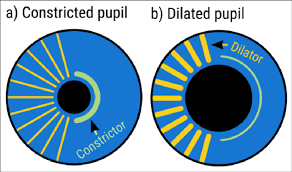
what muscles control pupil size?
the two muscles of the iris, the dilator and constrictor pupillae, open and close the pupil.
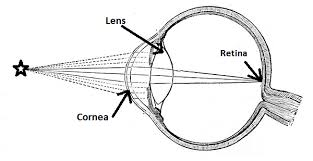
What is the role of the lens in vision?
refracts incoming light to focus it on the retina
How is the lens held in place?
is held in place by suspensory ligaments connected to the ciliary muscle
How does the ciliary body regulate intraocular fluid?
The ciliary body produces aqueous humor, a clear fluid
The Canal of Schlemm acts as a drainage channel for aqueous humor
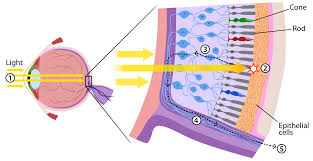
What photoreceptors are in the retina and what do they do?
The retina contains rods and cones.
Rods detect light and dark
Cones come in three forms (short-, medium-, and long-wavelength) to detect colors.
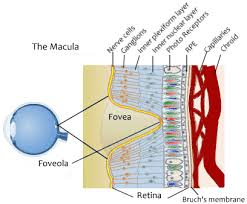
Where are cones located?
The retina contains mostly cones in the macula, which corresponds to the central visual field.
The center of the macula is the fovea, which contains only cones.