Lesson 5.2. Antihypertensive Drugs
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
137 Terms
Descending Loop of Henle
Target of Osmotic Diuretics
hydroxyl groups (-OH)
Osmotic Diuretics are characterized by the presence of ____________________.
Mannitol
Osmotic Diuretic Drug
gold standard
Mannitol is the ______________ diuretic
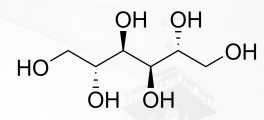
Mannitol Structure
intraluminal osmotic pressure
Mechanism of Action of Osmotic Diuretics:
a. increases ______________________________
b. leading to more __________________ leading to more urine output.
a = ?
water in the tubule
Mechanism of Action of Osmotic Diuretics:
a. increases ______________________________
b. leading to more __________________ leading to more urine output.
b = ?
requires large doses for effectiveness
Disadvantage of Osmotic Diuretics
intracranial/intraocular pressure
Use of Osmotic Diuretics
Acetazolamide, Brinzolamide, Dorzolamide, Methazolamide
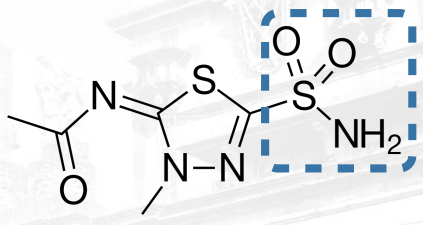
Drugs under Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors
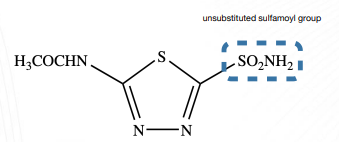
C-5 position
SAR of Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors:
a. The ____________ must be unsubstituted for optimal activity.
b. The ________________ is essential for binding to the carbonic anhydrase enzyme.
c. The sulfamoyl group is attached to ____________________.
a = ?
sulfamoyl (-SO2 NH2) group
SAR of Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors:
a. The ____________ must be unsubstituted for optimal activity.
b. The ________________ is essential for binding to the carbonic anhydrase enzyme.
c. The sulfamoyl group is attached to ____________________.
b = ?
5-sided ring
SAR of Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors:
a. The ____________ must be unsubstituted for optimal activity.
b. The ________________ is essential for binding to the carbonic anhydrase enzyme.
c. The sulfamoyl group is attached to ____________________.
c = ?
Acetazolamide Structure
Brinzolamide Structure
Dorzolamide Structure
Methazolamide Structure
Proximal Convoluted Tubule
target of Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors
reabsorption of bicarbonate (HCO3)
MOA of Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors:
a. Inhibits carbonic anhydrase, so it blocks the ___________________________.
b. Leads to increased secretion of _______________________________, resulting in diuresis.
a = ?
Na, HCO3, and water
MOA of Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors:
a. Inhibits carbonic anhydrase, so it blocks the ___________________________.
b. Leads to increased secretion of _______________________________, resulting in diuresis.
b = ?
Glaucoma
Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors are useful in treating _______________ by reducing aqueous humor formation and intraocular pressure.
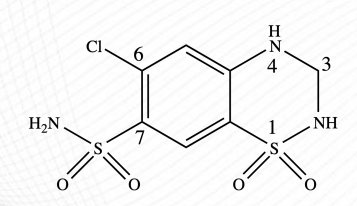
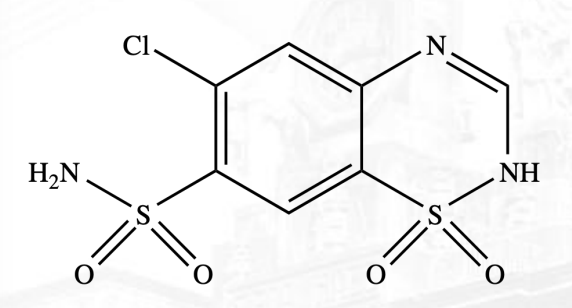
Hydrocholorothiazide, chlorothiazide
Drugs under Thiazides
Distal Convoluted Tubule
target of thiazides
benzothiadiazine
ring structure of thiazides
C3-C4 saturation
SAR of Thiazides:
a. ________________ increases activity by approximately 10-fold.
b. ________________ enhances diuretic potency and prolongs DOA.
c. ________________________________ essential for diuretic activity.
d. ________________ decreases polarity, leading to a longer DOA.
a = ?
C3 lipophilic substituent
SAR of Thiazides:
a. ________________ increases activity by approximately 10-fold.
b. ________________ enhances diuretic potency and prolongs DOA.
c. ________________________________ essential for diuretic activity.
d. ________________ decreases polarity, leading to a longer DOA.
b = ?
C6 EWG and C7 sulfonamide
SAR of Thiazides:
a. ________________ increases activity by approximately 10-fold.
b. ________________ enhances diuretic potency and prolongs DOA.
c. ________________________________ essential for diuretic activity.
d. ________________ decreases polarity, leading to a longer DOA.
c = ?
N2 substitution
SAR of Thiazides:
a. ________________ increases activity by approximately 10-fold.
b. ________________ enhances diuretic potency and prolongs DOA.
c. ________________________________ essential for diuretic activity.
d. ________________ decreases polarity, leading to a longer DOA.
d = ?
HTN (alone/combination), edema related to heart, liver, and renal diseases
Use of Thiazides
Na/Cl Cotransporter (NCC)
MOA of Thiazides:
a. Inhibits ____________________ which increases the release of these ions in the urine.
b. Decreases ____________________, leading to increased urinary excretion of these ions.
c. Reduces _________________ by enhancing its reabsorption in the DCT, which may cause hypercalcemia.
d. The resulting _________________________ can potentiate digoxin toxicity.
a = ?
reabsorption of K and Mg
MOA of Thiazides:
a. Inhibits ____________________ which increases the release of these ions in the urine.
b. Decreases ____________________, leading to increased urinary excretion of these ions.
c. Reduces _________________ by enhancing its reabsorption in the DCT, which may cause hypercalcemia.
d. The resulting _________________________ can potentiate digoxin toxicity.
b = ?
calcium excretion
MOA of Thiazides:
a. Inhibits ____________________ which increases the release of these ions in the urine.
b. Decreases ____________________, leading to increased urinary excretion of these ions.
c. Reduces _________________ by enhancing its reabsorption in the DCT, which may cause hypercalcemia.
d. The resulting _________________________ can potentiate digoxin toxicity.
c = ?
hypercalcemia, hypokalemia and hypomagnesia
MOA of Thiazides:
a. Inhibits ____________________ which increases the release of these ions in the urine.
b. Decreases ____________________, leading to increased urinary excretion of these ions.
c. Reduces _________________ by enhancing its reabsorption in the DCT, which may cause hypercalcemia.
d. The resulting _________________________ can potentiate digoxin toxicity.
d = ?
Hydrochlorothiazide Structure
Chlorothiazide Structure
Indapamide Structure
Thick Ascending Loop
Target of Loop Diuretics
Furosemide, Torsemide, Bumetanide, Ethacrynic Acid
Drugs of Loop Diuretics
thiazides
SAR of Loop Diuretics:
a. Sulfonamide-containing diuretics similar to ___________________.
b. known as _________________________.
c. has a _______________________.
a = ?
high-ceiling loop diuretics
SAR of Loop Diuretics:
a. Sulfonamide-containing diuretics similar to ___________________.
b. known as _________________________.
c. has a _______________________.
b = ?
fast onset, short DOA
SAR of Loop Diuretics:
a. Sulfonamide-containing diuretics similar to ___________________.
b. known as _________________________.
c. has a _______________________.
c = ?
Na/K/Cl cotransporter
MOA of Thiazides:
a. Inhibits ______________________
b. Leads to loss of ____________________________, which leads to diuresis
a = ?
Na, Cl, Ca, and Mg
MOA of Thiazides:
a. Inhibits ______________________
b. Leads to loss of ____________________________, which leads to diuresis
b = ?
pulmonary edema, HTN
Use of Loop Diuretics
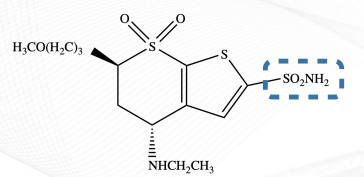
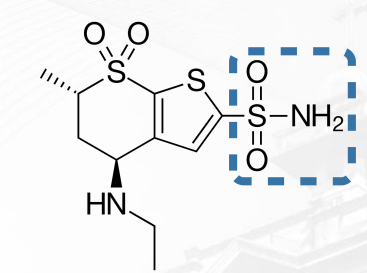
Furosemide Structure
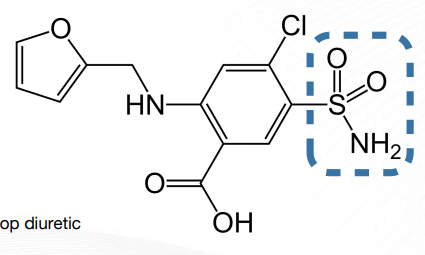
Bumetanide Structure
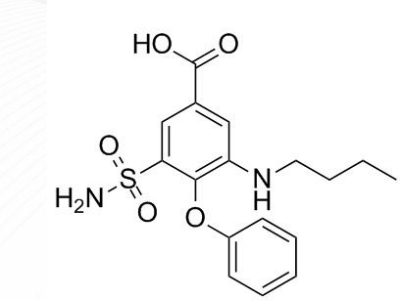
Torsemide Structure
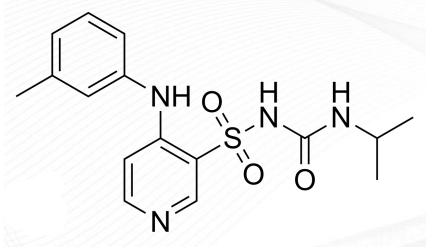
Ethacrynic Acid Structure
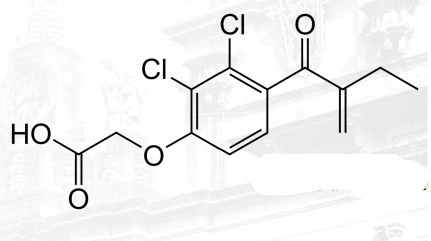
Spirinolactone and Eplerenone
Potassium-sparring Diuretics (Hormone-derived) drugs
Amiloride and Triamterene
Potassium-sparring Diuretics (Synthetic) drugs
aldosterone
MOA of K-sparring Diuretics:
a. Hormone-Derived: inhibits _________________ leading to K retention and Na and H2O secretion
b. Synthetic: inhibits ___________________ in CD, leads to Na and H2O excretion and indirectly decrease K excretion.
a = ?
Epithelial Na co-transporter (ENaC)
MOA of K-sparring Diuretics:
a. Hormone-Derived: inhibits _________________ leading to K retention and Na and H2O secretion
b. Synthetic: inhibits ___________________ in CD, leads to Na and H2O excretion and indirectly decrease K excretion.
b = ?
steriodal
The _____________ structure of K-sparring diuretics may cause sex-related changes.
Spironolactone Structure
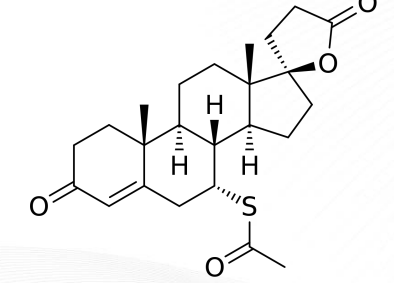
Eplerenone Structure
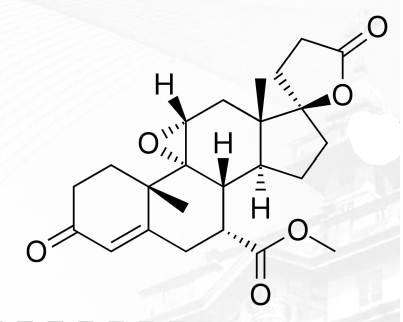
Amiloride Structure
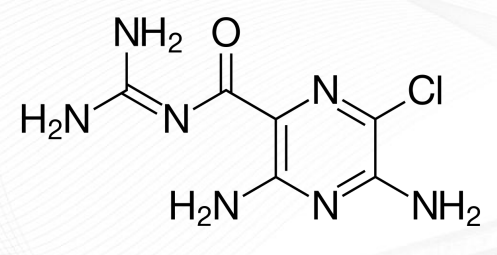
Triamterene Structure
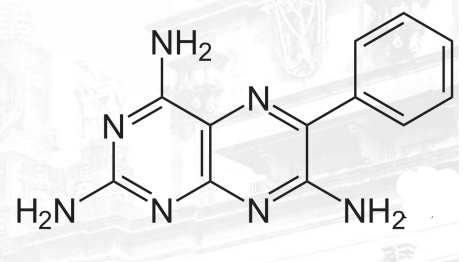
Nifedipine, Amlodipine, and Felodipine
Calcium Channel Blockers that are Dihydropyridines (DHP)
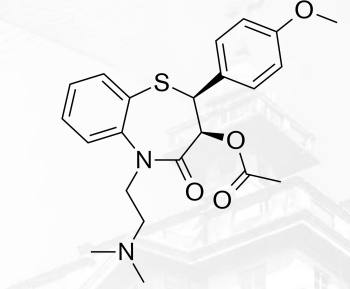
Diltiazem
Calcium Channel Blockers that are Benzothiazepine
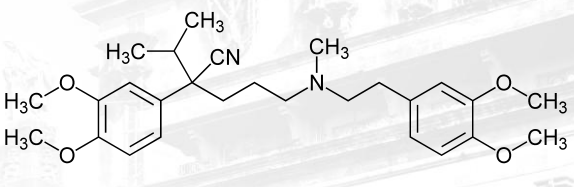
Verapamil
Calcium Channel Blockers that are Phenylalkylamine
L-type Ca channel
MOA of Calcium Channel Blockers:
a. blocks ___________________ which decreases Ca influx, leading to vascular relaxation.
b. _________ promotes vasodilation without cardiac effects
c. _________ promotes vasodilation and reduces heart rate
a = ?
DHP
MOA of Calcium Channel Blockers:
a. blocks ___________________ which decreases Ca influx, leading to vascular relaxation.
b. _________ promotes vasodilation without cardiac effects
c. _________ promotes vasodilation and reduces heart rate
b = ?
Non-DHP
MOA of Calcium Channel Blockers:
a. blocks ___________________ which decreases Ca influx, leading to vascular relaxation.
b. _________ promotes vasodilation without cardiac effects
c. _________ promotes vasodilation and reduces heart rate
c = ?
IHD, HTN, Angina management
use of Calcium-Channel Blockers
para-position
SAR of Calcium Channel Blockers:
a. ______________ of the phenyl substituent must remain unsubstituted.
b. ______________ of the phenyl substituent are for optimal activity; if bulky is used, it will lock at a C4 perpendicular orientation.
c. 1,4 DHP can tolerate larger substitutions at ________________ for enhanced activity.
d. _______________ is essential for activity.
e. In C3/C5 position, 1.____________ optimize activity while 2. _______________ enhance selectivity.
f. In C4, 1._______________ is for optimal activity while 2.___________________ decrease activity.
a = ?
X can be an ortho- or meta-
SAR of Calcium Channel Blockers:
a. ______________ of the phenyl substituent must remain unsubstituted.
b. ______________ of the phenyl substituent are for optimal activity; if bulky is used, it will lock at a C4 perpendicular orientation.
c. 1,4 DHP can tolerate larger substitutions at ________________ for enhanced activity.
d. _______________ is essential for activity.
e. In C3/C5 position, 1.____________ optimize activity while 2. _______________ enhance selectivity.
f. In C4, 1._______________ is for optimal activity while 2.___________________ decrease activity.
b = ?
C2/C6
SAR of Calcium Channel Blockers:
a. ______________ of the phenyl substituent must remain unsubstituted.
b. ______________ of the phenyl substituent are for optimal activity; if bulky is used, it will lock at a C4 perpendicular orientation.
c. 1,4 DHP can tolerate larger substitutions at ________________ for enhanced activity.
d. _______________ is essential for activity.
e. In C3/C5 position, 1.____________ optimize activity while 2. _______________ enhance selectivity.
f. In C4, 1._______________ is for optimal activity while 2.___________________ decrease activity.
C = ?
Unsubstituted N1
SAR of Calcium Channel Blockers:
a. ______________ of the phenyl substituent must remain unsubstituted.
b. ______________ of the phenyl substituent are for optimal activity; if bulky is used, it will lock at a C4 perpendicular orientation.
c. 1,4 DHP can tolerate larger substitutions at ________________ for enhanced activity.
d. _______________ is essential for activity.
e. In C3/C5 position, 1.____________ optimize activity while 2. _______________ enhance selectivity.
f. In C4, 1._______________ is for optimal activity while 2.___________________ decrease activity.
d = ?
symmetrical esters
SAR of Calcium Channel Blockers:
a. ______________ of the phenyl substituent must remain unsubstituted.
b. ______________ of the phenyl substituent are for optimal activity; if bulky is used, it will lock at a C4 perpendicular orientation.
c. 1,4 DHP can tolerate larger substitutions at ________________ for enhanced activity.
d. _______________ is essential for activity.
e. In C3/C5 position, 1.____________ optimize activity while 2. _______________ enhance selectivity.
f. In C4, 1._______________ is for optimal activity while 2.___________________ decrease activity.
e.1. = ?
asymmetrical esters
SAR of Calcium Channel Blockers:
a. ______________ of the phenyl substituent must remain unsubstituted.
b. ______________ of the phenyl substituent are for optimal activity; if bulky is used, it will lock at a C4 perpendicular orientation.
c. 1,4 DHP can tolerate larger substitutions at ________________ for enhanced activity.
d. _______________ is essential for activity.
e. In C3/C5 position, 1.____________ optimize activity while 2. _______________ enhance selectivity.
f. In C4, 1._______________ is for optimal activity while 2.___________________ decrease activity.
e.2. = ?
phenyl ring
SAR of Calcium Channel Blockers:
a. ______________ of the phenyl substituent must remain unsubstituted.
b. ______________ of the phenyl substituent are for optimal activity; if bulky is used, it will lock at a C4 perpendicular orientation.
c. 1,4 DHP can tolerate larger substitutions at ________________ for enhanced activity.
d. _______________ is essential for activity.
e. In C3/C5 position, 1.____________ optimize activity while 2. _______________ enhance selectivity.
f. In C4, 1._______________ is for optimal activity while 2.___________________ decrease activity.
f.1. = ?
nonplanar alkyl/cycloalkyl group
SAR of Calcium Channel Blockers:
a. ______________ of the phenyl substituent must remain unsubstituted.
b. ______________ of the phenyl substituent are for optimal activity; if bulky is used, it will lock at a C4 perpendicular orientation.
c. 1,4 DHP can tolerate larger substitutions at ________________ for enhanced activity.
d. _______________ is essential for activity.
e. In C3/C5 position, 1.____________ optimize activity while 2. _______________ enhance selectivity.
f. In C4, 1._______________ is for optimal activity while 2.___________________ decrease activity.
f.2. = ?
Nifedipine Structure
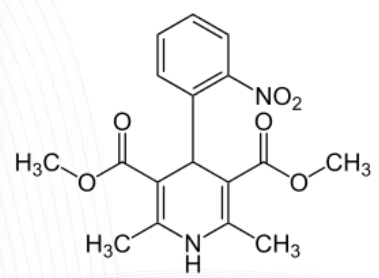
Amlodipine Structure
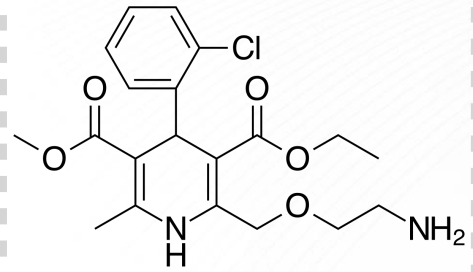
Felodipine Structure
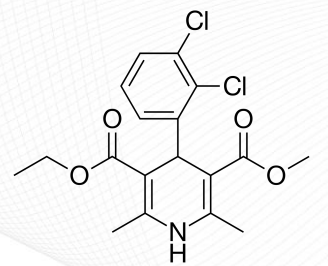
Nicardipine Structure
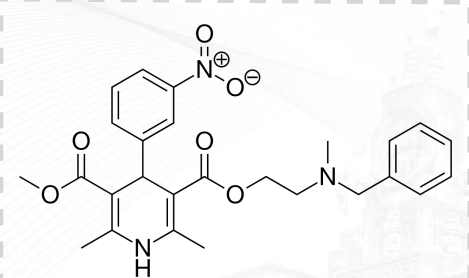
Diltiazem Structure
Verapamil Structure
RAAS Drugs
agents that act on the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone-system
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor (ACE Inhibitor)
Most agents are prodrugs and are hydrolyzed to active from(-prils to-prilats).
Severe Dry Cough and Hyperkalemia
ADR of ACE Inhibitors
Enalapril, Captopril, Lisinopril, Fosinopril
Drugs under ACE Inhibitors
angiotensin I to angiotensin II
MOA of ACE Inhibitors:
a. blocks the conversion of _________________________.
b. inhibits metabolism of ______________= leads to vasodilation.
a = ?
bradykinin
MOA of ACE Inhibitors:
a. blocks the conversion of _________________________.
b. inhibits metabolism of ______________= leads to vasodilation.
b = ?
hydrolysis
Metabolism of ACE Inhibitors:
a. for activation
b. for Fosinopril
a = ?
glucuronidation
Metabolism of ACE Inhibitors:
a. for activation
b. for Fosinopril
b = ?
Captopril Structure
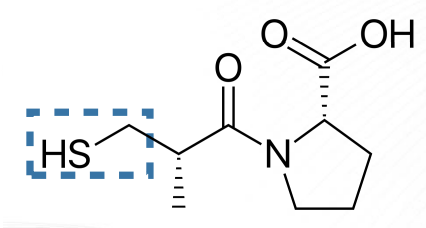
Captopril
fastest acting ACEI that may form dimers with cysteine
Lisinopril Structure
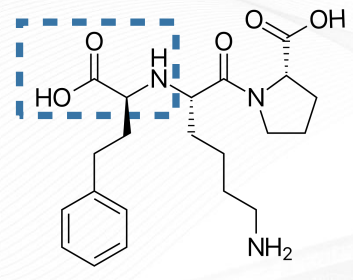
Lisinopril
excreted in the urine unchanged
Enalapril Structure
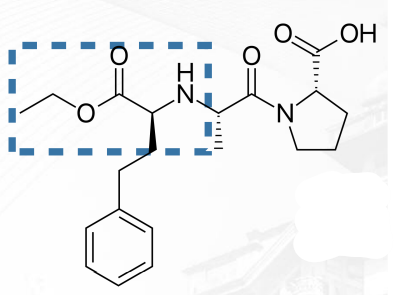
Enalapril
ester prodrug need activation and is excreted in the urine unchanged
Fosinopril Structure
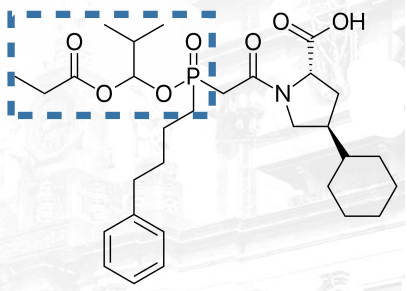
Fosinopril
ester prodrug need activation and undergoes glucuronidation
-COOH
SAR of ACE Inhibitors:
a. N-ring:
must have _________ for binding at the ACE cationic sites
________________________ = enhances potency
b. _________________ = essential for activity
__ are superiors in Zn-binding (but may cause skin rashes and loss of taste)
c. _____________ is useful for stereochemistry
d. _____________ of carboxylate or phosphate results to prodrug structure.
a.1. = ?
large heterocyclic rings
SAR of ACE Inhibitors:
a. N-ring:
must have _________ for binding at the ACE cationic sites
________________________ = enhances potency
b. _________________ = essential for activity
__ are superiors in Zn-binding (but may cause skin rashes and loss of taste)
c. _____________ is useful for stereochemistry
d. Esterification of carboxylate or phosphate results to prodrug structure.
a.2. = ?
Zn binding
SAR of ACE Inhibitors:
a. N-ring:
must have _________ for binding at the ACE cationic sites
________________________ = enhances potency
b. _________________ = essential for activity
__ are superiors in Zn-binding (but may cause skin rashes and loss of taste)
c. _____________ is useful for stereochemistry
d. _____________ of carboxylate or phosphate results to prodrug structure.
b = ?
-SH
SAR of ACE Inhibitors:
a. N-ring:
must have _________ for binding at the ACE cationic sites
________________________ = enhances potency
b. _________________ = essential for activity
__ are superiors in Zn-binding (but may cause skin rashes and loss of taste)
c. _____________ is useful for stereochemistry
d. ______________ of carboxylate or phosphate results to prodrug structure.
b.1. = ?
X (-CH3)
SAR of ACE Inhibitors:
a. N-ring:
must have _________ for binding at the ACE cationic sites
________________________ = enhances potency
b. _________________ = essential for activity
__ are superiors in Zn-binding (but may cause skin rashes and loss of taste)
c. _____________ is useful for stereochemistry
d. ______________ of carboxylate or phosphate results to prodrug structure.
c = ?
Esterification
SAR of ACE Inhibitors:
a. N-ring:
must have _________ for binding at the ACE cationic sites
________________________ = enhances potency
b. _________________ = essential for activity
__ are superiors in Zn-binding (but may cause skin rashes and loss of taste)
c. _____________ is useful for stereochemistry
d. ______________ of carboxylate or phosphate results to prodrug structure.
d = ?