ANA 110 (Salmeron)--University of Kentucky--Exam 1
1/201
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
202 Terms
The heart is a ______
double pump
Left side of heart
pumps blood through miles of blood vessels in body
Right side of heart
- pumps blood to lungs
- can pick up oxygen and unload carbon dioxide
Where is the heart located?
mediastium of thoracic cavity
Apex of heart
directed inferiorly to the left
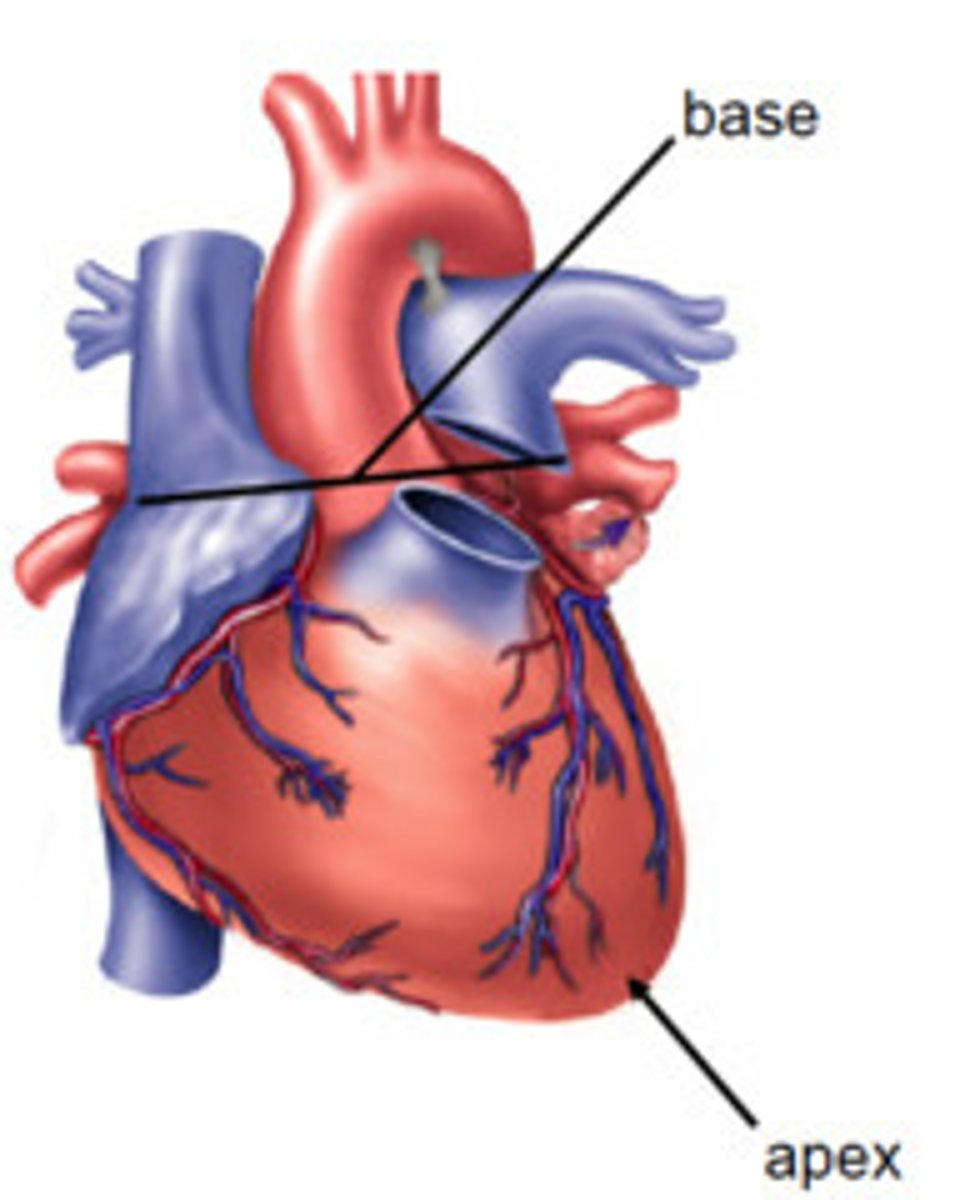
Base of heart positioned how?
superiorly to the right
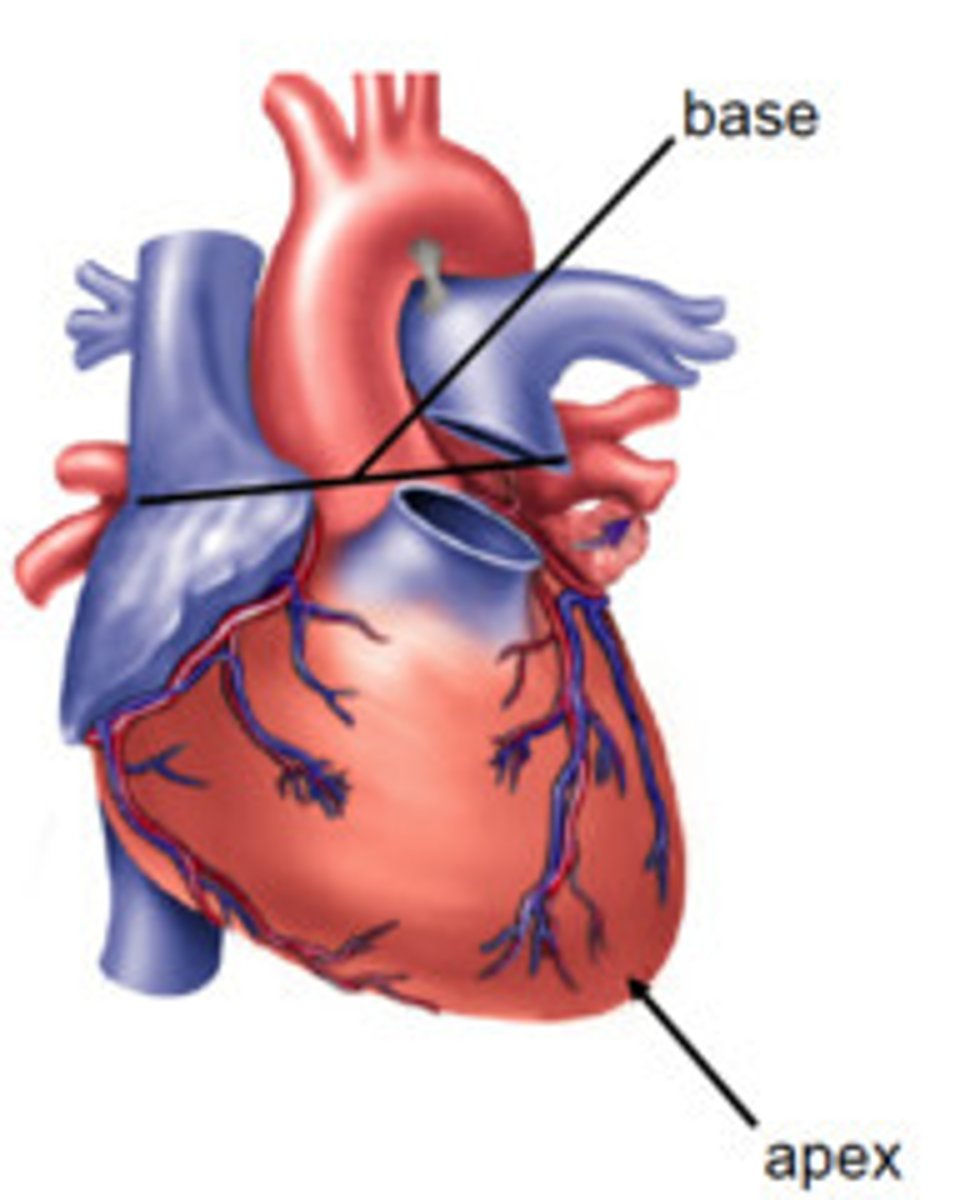
Pericardial fluid is between _______ and _______
parietal layer and visceral layer of serous pericardium
fibrous pericardium
- outer layer
- dense irregular connective tissue
- prevents overstretching
serous pericardium
- inner layer of pericardium
- double layer
- delicate
two layers of serous pericardium
parietal and visceral
parietal layer of serous pericardium
fused to fibrous pericardium
visceral layer of serous pericardium
is the outer layer of the heart
Epicardium =
visceral pericardium
Layers of heart wall
epicardium, myocardium, endocardium
Epicardium
- visceral serous pericardium
- contains blood and lymphatic vessels
Myocardium
- middle, cardiac muscle tissue layer
- involuntary
Endocardium
- endothelial layer overlying connective tissue
- lines heart chambers and heart valves
Anatomy of Layers of heart wall
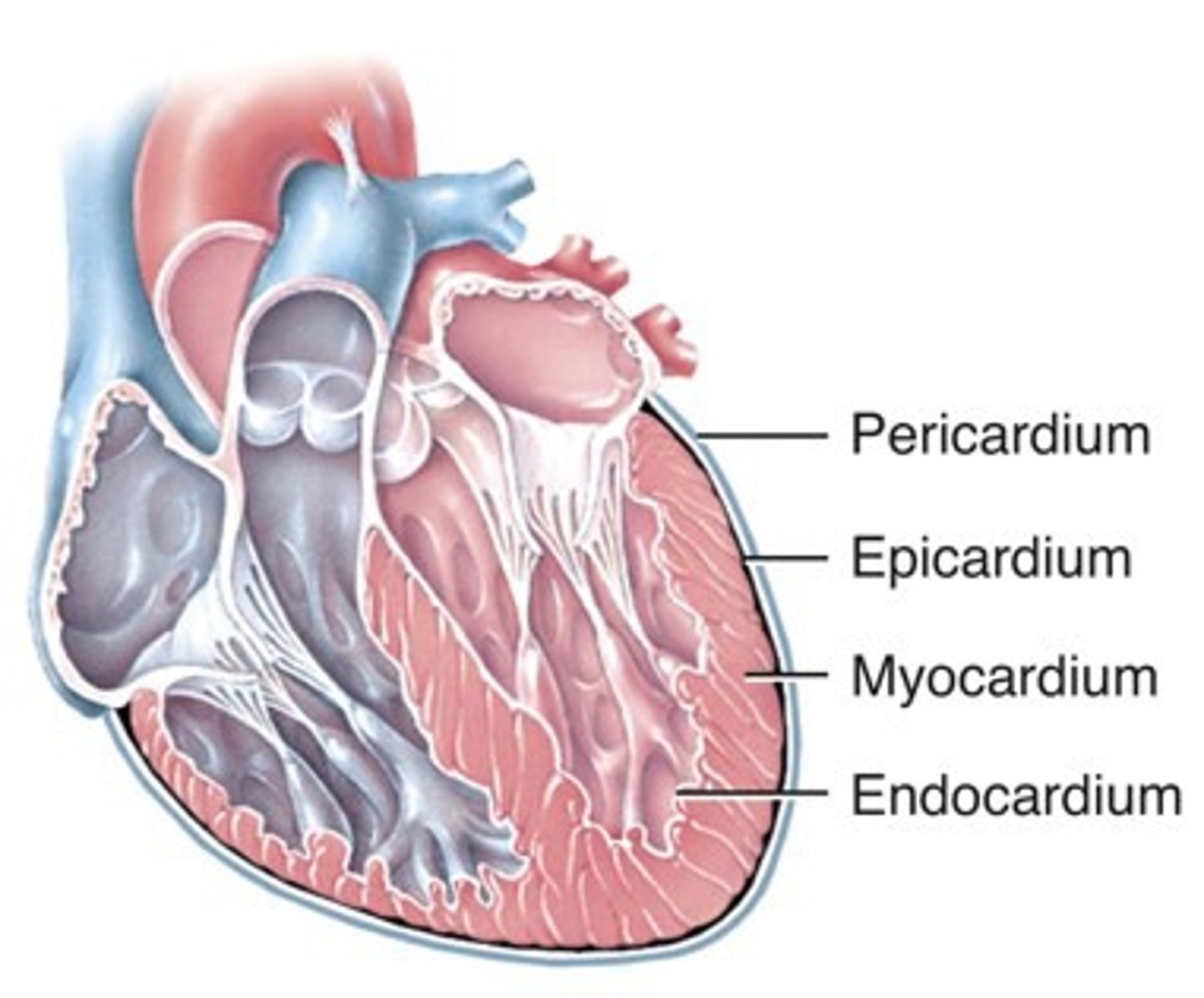
Chambers of the heart
two atria and two ventricles
What do atria do?
superior chambers that receive blood from veins
What do ventricles do?
inferior chambers that pump blood into arteries
Veins
blood to heart
Arteries
blood away from heart
First part of blood flow through heart (flow out)
1. blood to right atrium from superior and inferior vena cavae
2. blood passes right atrioventricular valve to enter right ventricle
3. Blood passes pulmonary semilunar valve
4. enters pulmonary artery which branches into right and left pulmonary arteries
Second part of blood flow though heart (back in)
1. blood returns to left atrium from lungs via pulmonary veins
2. passes left atrioventricular valve (bicuspid) to enter left ventricle
3. blood passes aortic semilunar valve to enter aorta artery
Three branches of aorta
brachiocephalic, left common carotid, left subclavian
Where does the right atrium receive blood?
superior and inferior vena cavae, coronary sinus straight from heart
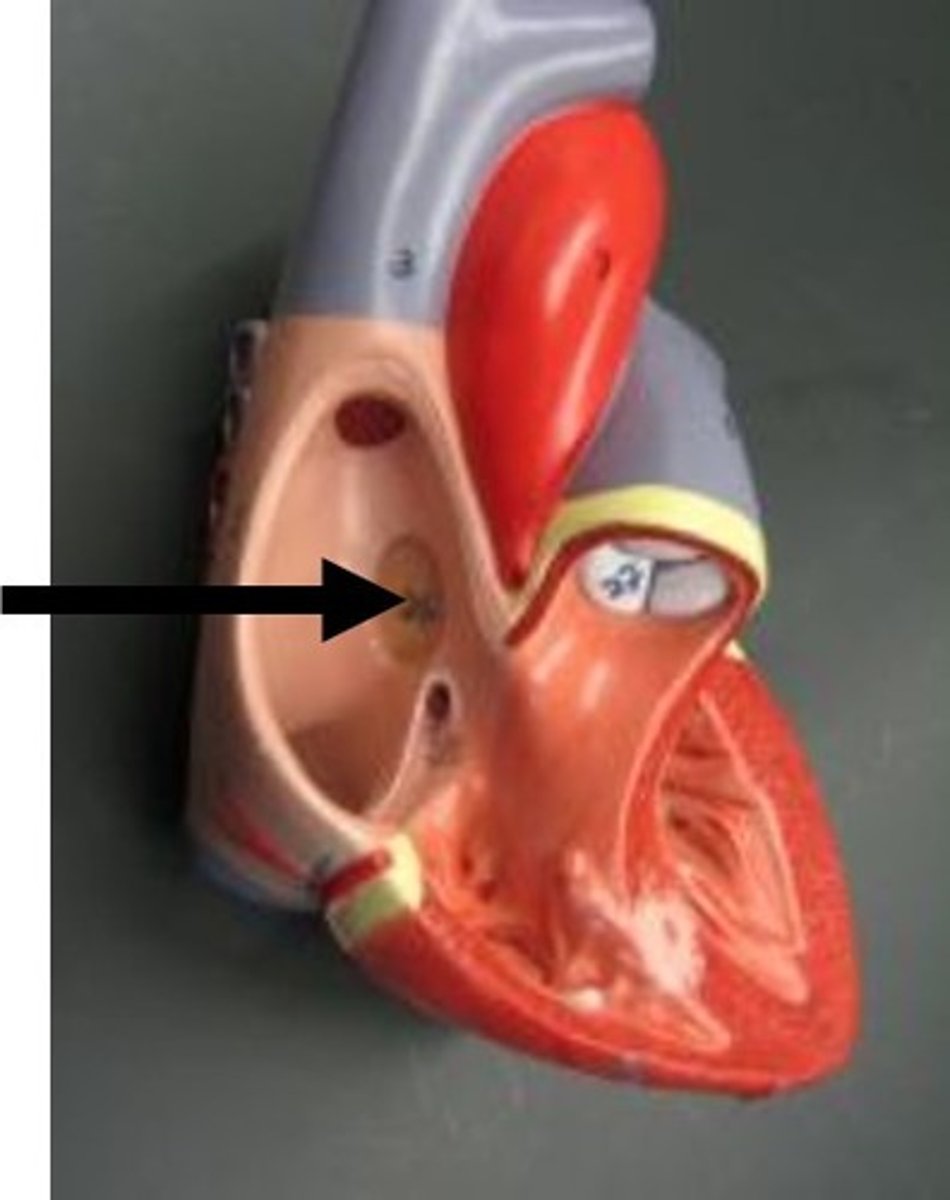
How is the right atrium separated from the left?
interatrial septum
fossa ovalis
remnant of foramen ovale
pectinate muscles of right atrium
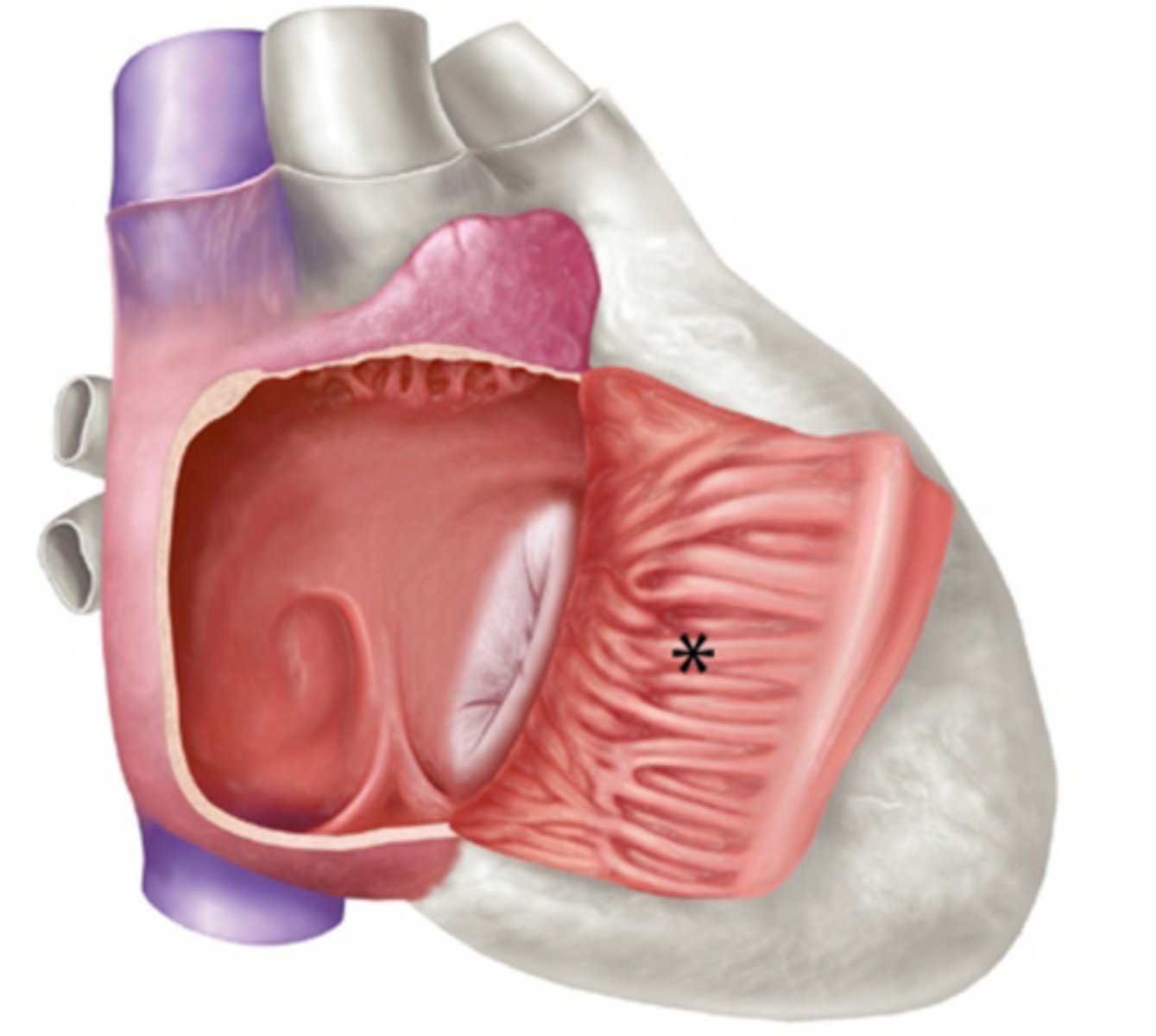
Tricuspid valve anatomy
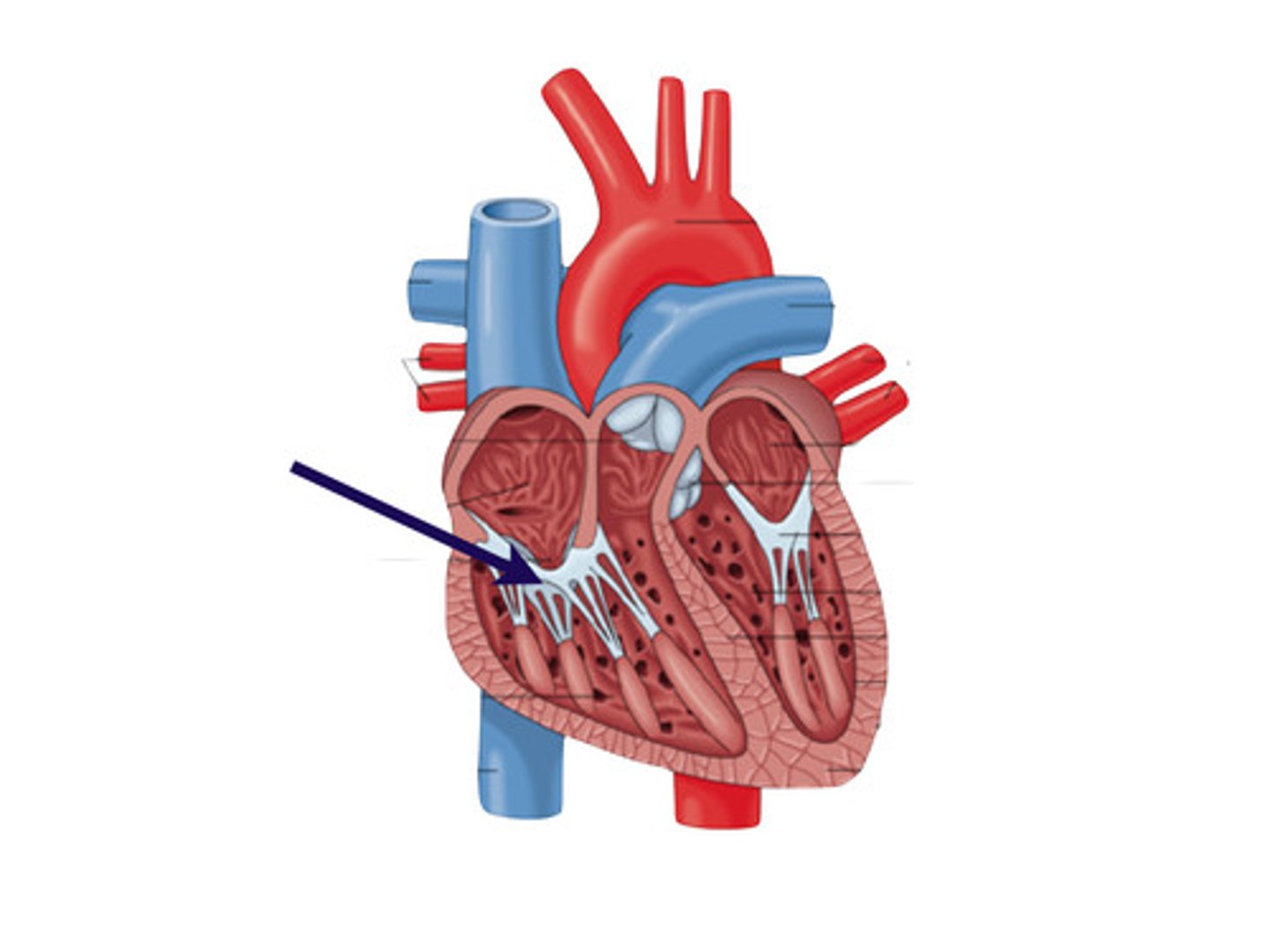
How does right ventricle receive blood?
from the right atrium
How is the right ventricle separated from the left?
interventricular septum
chordae tendineae
"heart strings"
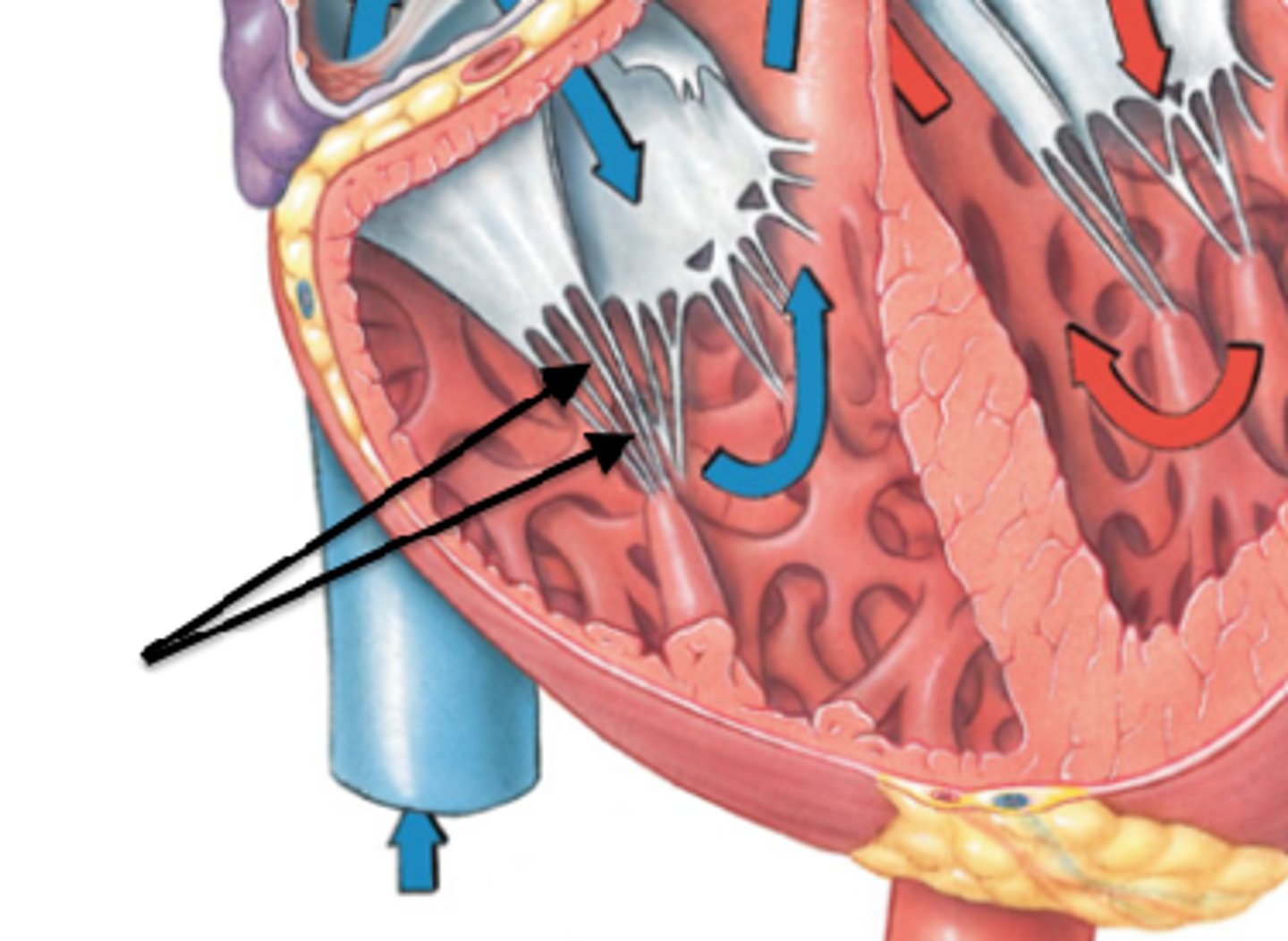
papillary muscles of ventricles
prevent backflow of blood
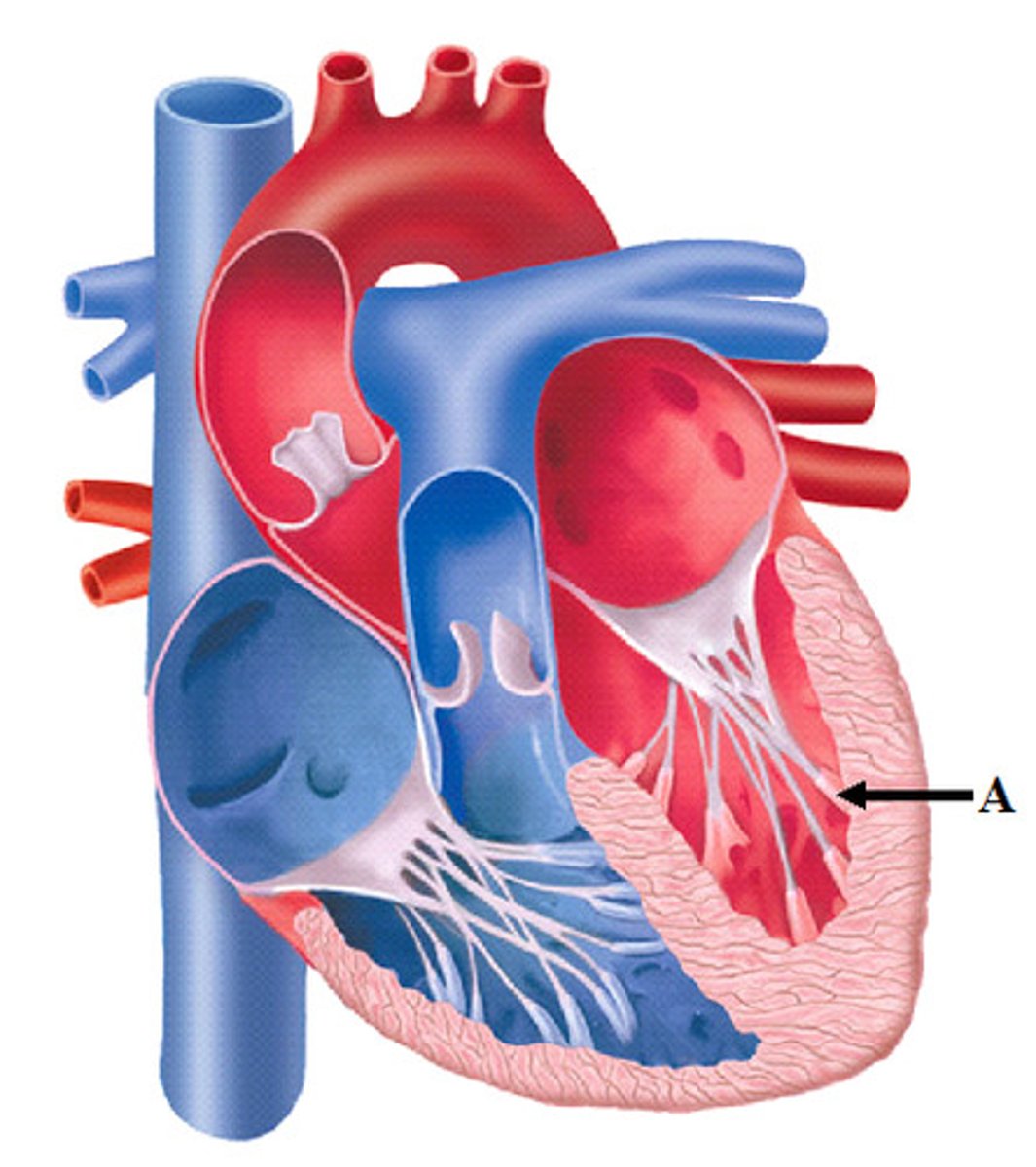
Trabeculae carnae
bundles of muscle that force blood out of ventricles
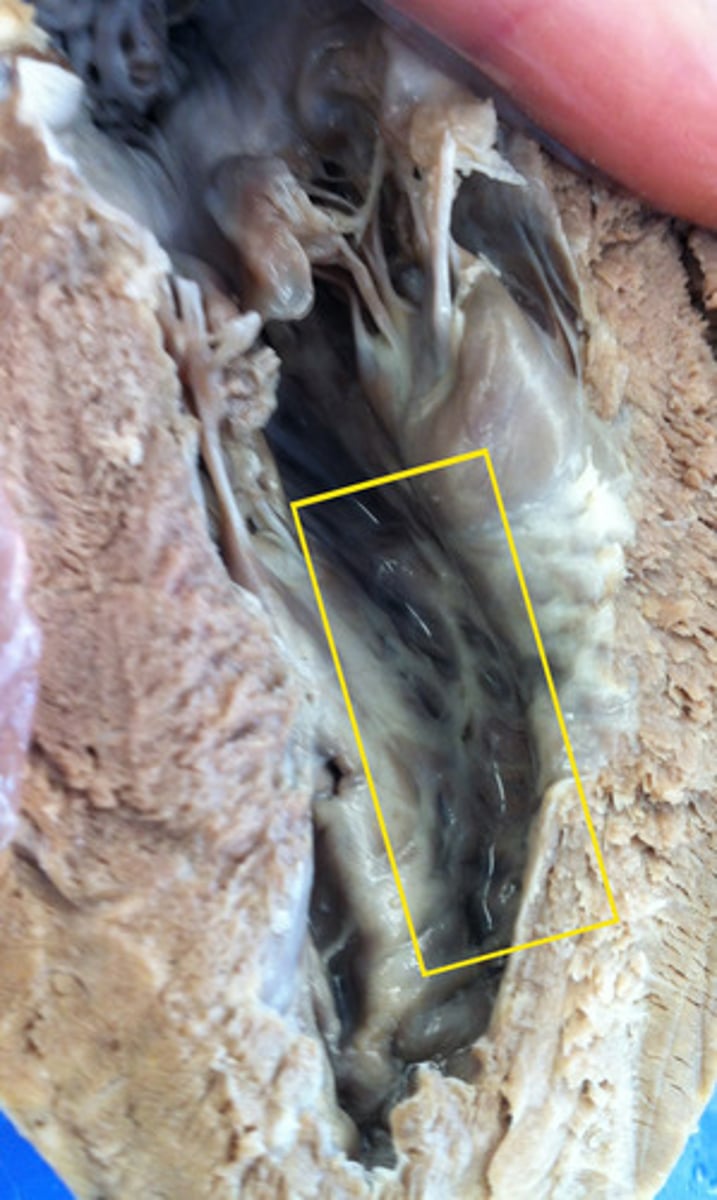
pulmonary semilunar valve anatomy
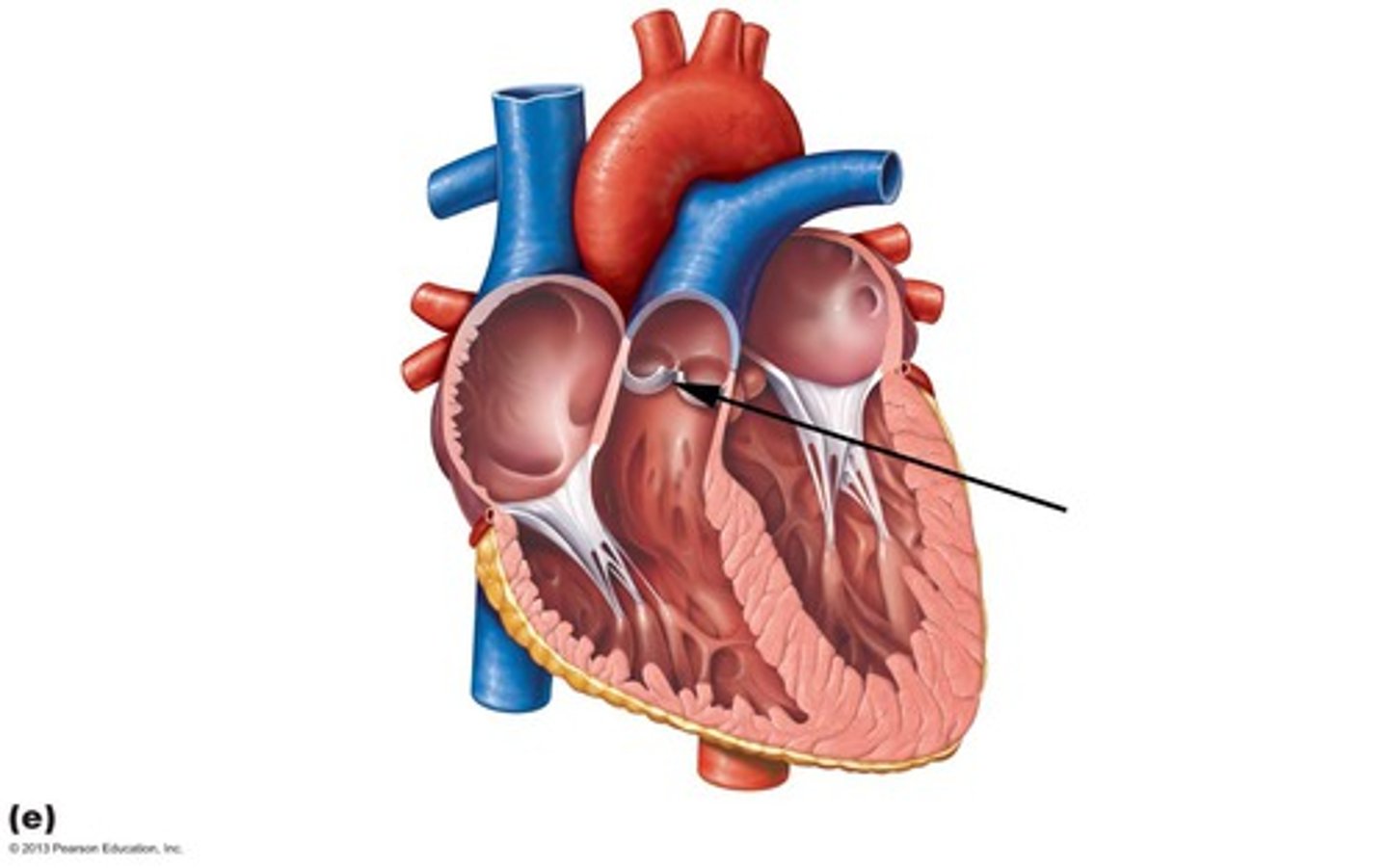
Circulation of oxygen-poor blood through lungs unloads ______ and picks up ____
CO2, O2
Left Atrium receives blood from where?
the four pulmonary veins
From left atrium, blood passes through the _______ into the _______
bicuspid (left atrioventricular valve), left ventricle
Left ventricle receives blood from where?
left atrium
Ligamentum anteriosum
connects aorta to pulmonary trunk as a remnant of fetal blood shunt
Atrial walls are (thicker/thinner) than ventricular walls
thinner
Why is the left ventricle thicker than the right?
The left ventricle must pump blood throughout the entire body and the right only has to go to the lungs.
Function of heart valves
open and close in response to pressure differences
Blood flows from areas of _____ to _____ pressures
high, low
Atrioventricular valves are between what?
atrium and ventricle
Semi-lunar valves are between what?
ventricle and artery
Tricuspid valve
right AV valve
Bicuspid valve
left AV valve
When heart valves open, what happens?
papillary muscles and chordae tendineae relax
What happens when heart valves close?
papilarry muscles and chordae tendineae are tight
What are the semi-lunar valves?
pulmonary (right) and aortic (left)
Pulmonary circulation
flow of blood from the heart to the lungs and back to the heart
systemic circulation
circulation that supplies blood to all the body except to the lungs
Coronary circulation
flow of blood to and from the tissues of the heart
Systematic circulation is powered by what?
Left ventricle
________ and ______ arteries supply oxygen-rich blood to myocardium of the heart
right, left coronary
Anastomoses
two or more arteries provide alternative routes in case of obstruction
Coronary veins
collect oxygen-poor blood into coronary sinus and empties it into right atrium
Great cardiac veins partners with what?
left anterior descending artery
Middle cardiac vein partners with what?
posterior interventricular artery
Sulci
surface grooves containing coronary blood vessels
Coronary sulcus contains what?
coronary sinus
anterior interventricular sulcus contains what?
Left anterior descending artery and great cardiac vein
posterior interventricular sulcus contains what?
posterior interventricular artery and middle cardiac vein
Intercalated discs
connect muscle fibers
desmosomes in discs provide ______
strength
Gap junctions of heart
connect beats of cells
autorhythmicity
heart beats on its own
sinoatrial (SA) node
pacemaker of the heart
Pattern of automatic depolarization of myocardium
1. SA node--right atrial wall
2. AV node and bundle---interventricular septum
3. right and left bundle branches--toward apex
4. Punkinhe fibers--upward in myocardium
Depolarization
Na+ comes in
Plateau
Ca2+ comes in, triggers contraction
Repolarization
K+ channels open and ions outflow
Long refractory periods between heart beats allows for what?
chambers to refill with blood
heart action potential picture
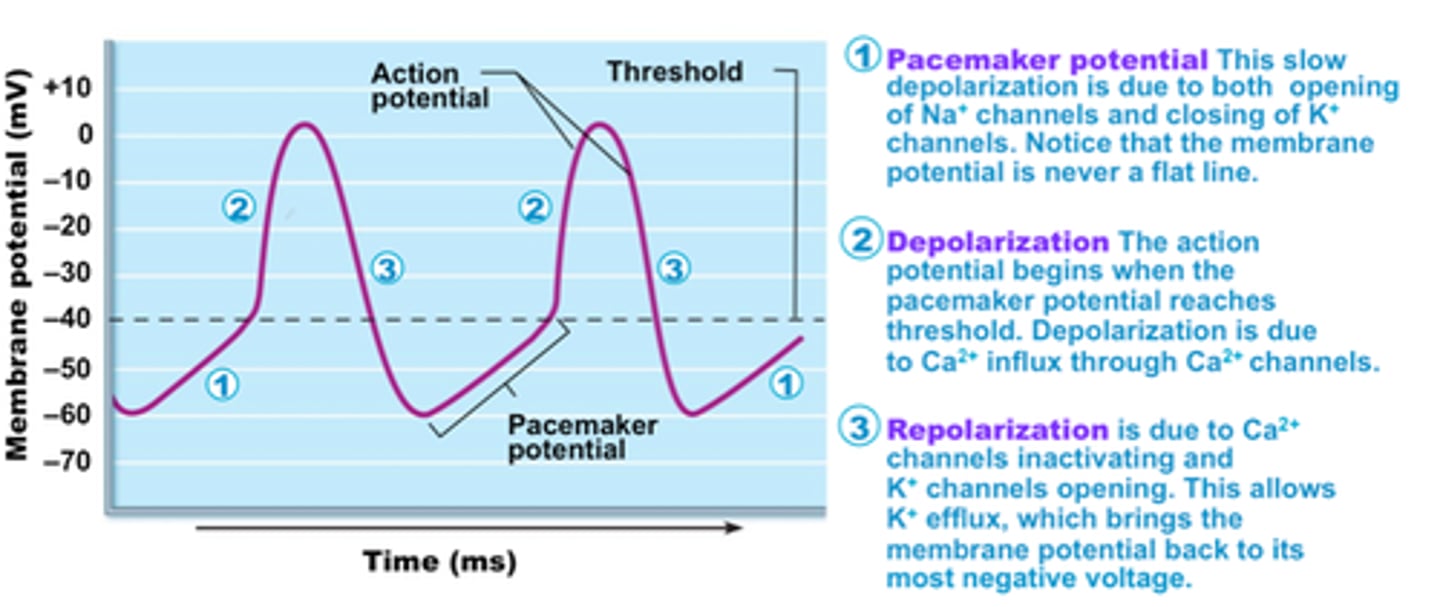
Thresh hold of SA node action potential
-50mV
Electrocardiogram
recording electrical charges of heartbeats
ECG waves explained
- P wave = depolarization (SA node)
- QRS complex = ventricular depolarization (AV node)
- T wave = ventricular repolarization
Diastole
Relaxation of the heart
Systole
Contraction of the heart
Sequence of systole to diastole
1. P wave
2. atrial systole
3. QRS complex
4. ventricular systole and atrial diastole begin
5. T wave
6. ventricular diastole occurs
Cardiac cycle
all events associated with a single heartbeat
What happens in a single heartbeat?
- two atria systole and diastole
- two ventricles systole and diastole
Heart sounds are caused by what?
closure of the heart valves
Lubb sound (S1)
closure of both AV valves as ventricles contract (ventricular systole)
Dupp sound (S2)
closure of both SL valves as ventricles relax (ventricular diastole)
End Diastolic Volume (EDV)
ventricles are full at end of atrial systole
Wiggers Diagram
different perspectives of cardiac cycle
isovolumetric contraction
all valves are closed
isovolumetric contraction occurs during when?
ventricular systole
ventricular ejection
blood is forced through semi-lunar valves
What happens after ventricular ejection?
end-systolic volume
End Systolic Volume (ESV)
volume of blood remaining in each ventricle after systole
isovolumetric relaxation
AV valves still closed
Isovolumetric relaxation happens when?
A and V diastole of cardiac cycle
Cardiac Output (CO)
Amount of blood pumped in 1 minute (~5 L)
Cardiac output equation
heart rate x stroke volume
Stroke volume
The amount of blood ejected from the heart in one contraction.