Reversible reactions and equilibria
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What is a reversible reaction?
It is where the reactants have a forward reaction which forms the products; however, the products react with themselves or decompose and have a backwards reaction, forming the reactants again.
How can a reaction indicate that it is reversible?
Using the symbol — ⇌
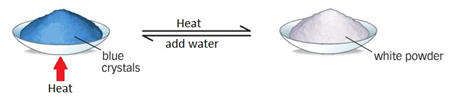
Describe the reversible reaction of the dehydration of hydrated copper (II) sulfate.
hydrated copper (II) sulfate ⇌ anhydrous copper (II) sulfate + water
CuSO4•5H2O ⇌ CuSO4 + 5H2O
Upon heating the blue hydrated copper sulfate, it turns white as it loses its water of crystallisation. Adding water to the anhydrous salt forms the hydrated salt again.
The forward reaction is endothermic (needs heating) and the backwards reaction is highly exothermic.
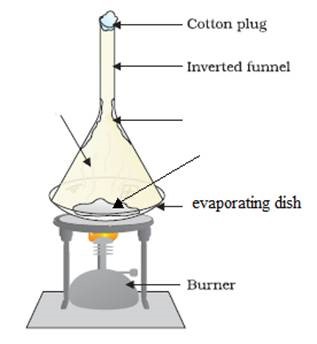
Describe the effect of heat on the reversible reaction ammonium chloride.
ammonium chloride ⇌ ammonia + hydrogen chloride
NH4Cl (s) ⇌ NH3 (g) + HCl (g)
Heating the ammonium chloride produces ammonia and hydrogen chloride gases; however, as the hot gases cool down, they recombine to form the solid ammonium chloride.
What is dynamic equilibrium?
When the rate of forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction, the overall reaction is in a state of equilibrium.
It is dynamic because the molecules on the left and right of the equation are changing into each other constantly but at the same rate.
What are the characteristics of a reaction at dynamic equilibrium?
the forward and backward reactions occur at the same rate
the concentrations of reactants ans products remain constant
What is condition required to reach dynamic equilibrium?
It must be in a sealed container/ closed system. So when no participating chemicals can escape and nothing else can enter.
What is the effect of a catalyst on equilibrium?
The presence of a catalyst does NOT affect the position of equilibrium but it does increase the rate at which equilibrium is reached
This is because the catalyst increases the rate of both the forward and backward reactions by the SAME amount and so does not affect the position of equilibrium.
What does the Le Chatelier’s principle state?
The principle states that when a change is made to the conditions of a closed system at equilibrium, the system will automatically move to oppose the change.
This principle is sued to predict the changes to the position of equilibrium when there are changes to the temperature and pressure.
What is the rule when shifting positions?
The position of equilibrium shifts to the right when the FORWARD reaction is favoured, meaning there are more products formed.
The position of equilibrium shifts to the left when the BACKWARDS reaction is favoured, meaning there are more reactants formed.
What effects does a change of pressure have on a system in equilibrium?
An increase in pressure will favour the reaction that has the LEAST number of molecules.
A decrease in pressure will favour the reaction that produces the GREATEST number of molecules.
In the case that the number of molecules on either side of the equilibrium is the SAME, there will be NO EFFECT om the positions.
What effects does a change in temperature have on a system in equilibrium?
An increase in temperature will shift in the direction of the ENDOTHERMIC reaction
A decrease in temperature will shift in the direction of the EXOTHERMIC reaction