Chem 11 Chapter 1
1/92
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Prep for Wed Quiz
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
matter
any substance, composed of particles(atoms and molecules)
Chemistry
Study of matter and its properties
states of matter
solid liquid gasa and plasa
solid
particles are not able to move freely. Has definite shape and volume
Liquid
particles can move but that movement is somewhat limited because of this type of strucutre. The shape is defined by the container. Volume is fixed.
Gas:
atoms or particles can move freely and has indefinite shape and volume.
Matter is a pure substance if
if it is made of one type of substance
matter is a mixture
if it is made out of multiple substances
If a pure substance can be separated, it is a
compound
if a pure substance can't be serperated its an
element
Element
can not be serpated into simplier particles
Compound
2 or more elements
Molecules
ex. water
homogenous mixture
a mixture in which the composition is uniform throughout
heterogeneous mixture
A mixture that is not uniform in composition; components are not evenly distributed throughout the mixture. ex.
The conservation of Matter(mass)
matter cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction
Chemistry laws
outline the properties of atoms and molecules based on theories of atomic structure.
energy
In a nuclear reaction atoms can be turned into
When a log burns completely
the mass that formed the log is tunred into gas release into the air.
The law of definte porportions states that:
All samples of a given compound have the same portion of the consistent elements, regardless of their source or how they were prepared.
potential energy is released when
chemical bond is broken.
The law of multiple porportions
when two elements call them A and B form to diffrent components the massses of element B that combine with 1g of element A can be expressed as a ratio of small whole number..
The law of definite proportions______________
applies to two or more samples of the same compound, whereas the law of multiple proportions applies to one compound.
amount of a substance 6.022×10^(23)
mole denoted as mol
Electric current
Ampere denoted as A
unit of measurement for the brightness:
Candela denoted as cd
Boiling point Celcius
100c
boilding point kelvin
373k
Freezing point Celcius
0c
Freezing point kelvin
273k
absolute zero farinheit
-459.67f
absolute 0 kelvin
0k
Giga
G scientific notation 10^9
Mega
M 10^6
Kilo
K 10^3
Deci
D 10^-1
Centi
C 10^-2
Milli
m 10^-3
Micro
μ 10^-6
Nano
n 10^-9
Pico
p 10^-12
unit conversion values
are exact and have infinte number of sig figs
ex. 536
All nonzero values are significant: (give example)
4 sig figs
.1235
6709
4 sig figs
2 sig figs
.0045
1 sig fig
How many sig figs in 7000
4 sig figs
How many sig figs in 24040
2 zeros are important if
6.00 x 10^-2
.00600
3 sig figs
4 sig figs
how many sig figs in : 6709
Dalton’s Atomic Theory states:
All elements are composed of Atoms
All atoms of an element have the same mass and Properties
Atoms combine in sample whole #ratios to form molecules
Atoms of one element cannot change into atoms of another element
Nuclear Atomic Model states:
The mass of an atom is primarily in the nucleus (all protonos and neutrons are contained in nucleus)
The volume of an atom is mostly empty space with electrons dispersed
All atoms are neutral
The number of protons always equals
the number of electrons
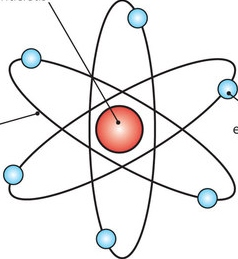
The most popular atomic model
is the bohr model which shows electrons rotating the nucleus also called the solar system model.
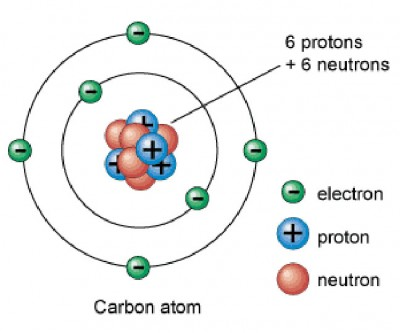
Protons are _____ charged
positively
Neutrons are ________ charged
neutral and aren’t charged
Electrons are _______ charged
negatively charged
charge of an electron is _____ __ _____ ______ ______ ____ proton
equal to but opposite in sign to
Atomic number=
# protons
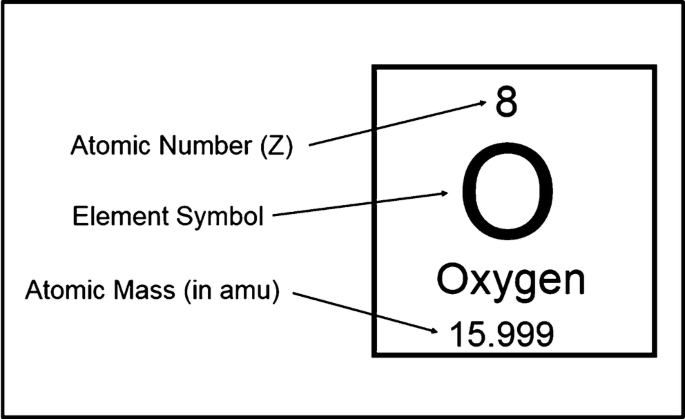
mass number=
number of protons plus the number of neutrons
Isoptopes of elements have diffrent # of ______ but the same number of ______
protons, neutrons
elements stay netural because the ______ number is not changing.
Neutron
Atomic mass=
Σₙ(fractional isotope 1 x mass of isotope 1) + (fractional isotope 2 x mass of isotope 2) + ...
Ions:
have positive and negative charge and are a result of either gainig an electron or losing an electron.
Cation
minus an electron
anion
plus a electron
when multiplying two numbers the answer alwways has ______ sig figs.
THe least number of sig figs
when dividing two numbers the answer alwways has ______ sig figs.
The least amount of sig figs.
When adding or subtracting numbers the answer always has the _________ amount of sig figs
most
(1/2)MV²
Kenetic energy (KE)=
The SI unit of energy Joule (J):=
J=kg x ms²/S²
1 calorie (cal)
4.184 joules (J)
1 Calorie (Cal) or KIlo Calorie (kcal)
1000 cal= 4184 J
1 Kilowatt-Hour (kWh)
3.60 × 10^6 J
Condensation of water vapor into rain releasing energy in the form of heat
Exothermic; positive
Is the burning of natural gas in a stove exothermic or endothermic? What is the sign of the energy change?
Exothermic; negative
Cooking an egg: Heat energy is absorbed from the pan to cook the egg.
Endothermic; positive
contradiction because an endothermic reaction is defined as having a positive change in enthalpy, meaning it absorbs heat from its surroundings, while a negative ΔH signifies an exothermic reaction, where heat is released;
Endothermic; negative
Matter is a particele- it is composed of particles
The structures of those particles determine the properties of matter.
2 key concepts surrounding atomic matter
Nuclear model
What is this model Called:
Most of the atom’s mass and all of its positive charge are contained in a small core called the nucleus.
Most of the volume of the atom is empty space, throughout which tiny, negatively charged electrons are dispersed.
There are as many negatively charged electrons outside the nucleus as there are positively charged particles (named protons) within the nucleus, so that the atom is electrically neutral.
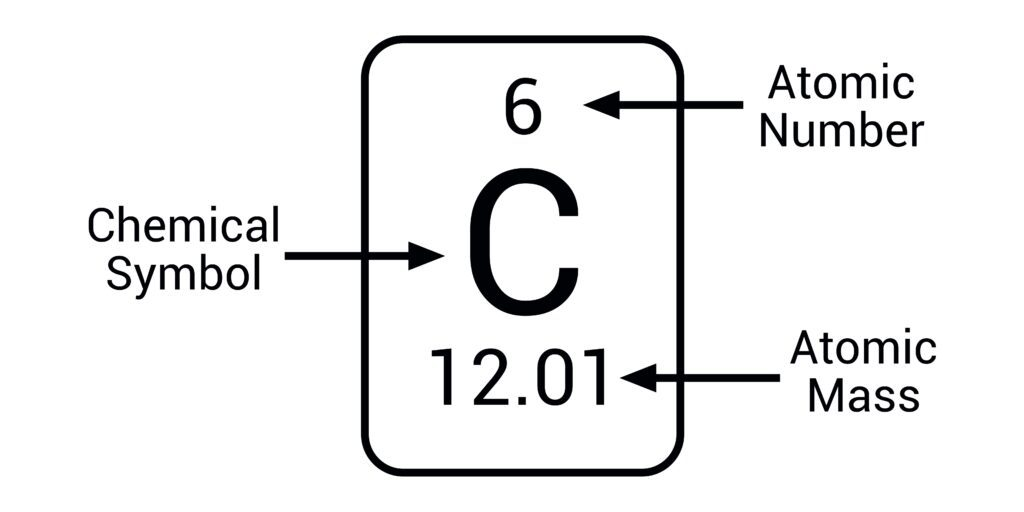
Mass number (A) =
number of protons (p) + number of neutrons (n)
number of protons in nucleus
Atomic number
Ratio ussed to convert between moles and atoms
1 mol atoms/ 6.022 × 10²³
Wave particle duality
electrons will have properties of particles (mass+volume) and electricity will also have wave properties.
Electromagnetic radiation
each wave has oscillating and mutually parrel and electronic and magnetic fields.
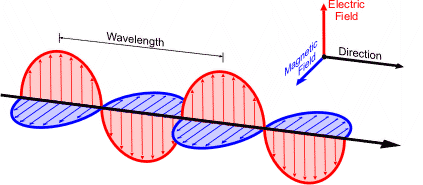
Wavelength λ
crest to crest distance amplitude
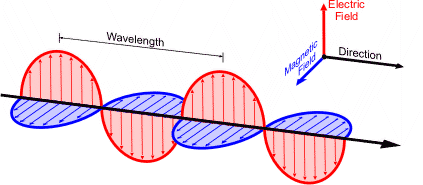
speed of light {c}
3.00 × 10^8 m/s
V=
c/λ
hertz (hz)
cycles/second
Frequency (v)
is the number of waves that pass a point in a given period of time
frequency
number of wave crest that pass a point in particular time frame
waves with higher amplidues are
brighter than waves with low amplitudes