BCH 4024 Exam 4
1/206
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
207 Terms
“Central Dogma”
A way to describe flow of genetic information in the cell
DNA is replicated → DNA is transcribed into RNA → RNA is translated into protein
In prokaryotes, DNA is in the…; in eukaryotes, DNA is in the…
Cytoplasm; nucleus
In Streptococcus pneumoniae, smooth cells produce…, while rough cells…
Polysaccharide capsule; don’t produce this capsule because they don’t have genetic material to make it
What strain of Streptococcus pneumoniae causes pneumonia?
Smooth; because the capsule protects it from host’s immune system
Avery’s experiment
Used smooth and rough strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae
Relied on “bacterial transformation” technique
Heated up smooth cells, causing DNA to be released into environment (cell free extract)
Mixed modified (with proteinase, RNase, or DNase) cell free extract with living rough cells
Rough cells took up smooth DNA and conditionally transformed into smooth cells
Bacterial transformation
External DNA is taken up by a bacterial cell, changing characteristics of the cells
First Avery’s Experiment
Treated smooth cell free extract with proteinase; rough cells still transformed into smooth cells
Second Avery’s Experiment
Treated smooth cell free extract with RNase; rough cells still transformed into smooth cells
Third Avery’s Experiment
Treated smooth cell free extract with DNase; rough cells DID NOT transform into smooth cells
What did Avery’s Experiments show?
DNA IS in fact the genetic information of the cell
Know nucleotide structures
Know nucleotide structures
Nucleotide
Nitrogenous base, sugar, and AT LEAST one phosphate
On ribose of nucleotides, what is on the 3’ and 2’ Cs, respectively
3’: OH
2’: OH in ribose (RNA), H in deoxyribose (DNA)
On ribose of nucleotides, what is on the 1’ C?
Glycosidic bond connecting ribose to nitrogenous base
How many rings do purines and pyrimidines have, respectively?
Purines: 2
Pyrimidines: 1
Nucleoside
Nucleotide minus the phosphate
What bond links nucleotides together?
Phosphodiester linkage
between 3’ OH and 5’ phosphate
What direction are polynucleotide sequences written?
5’ → 3’
Chargaff’s rules
DNA has concentrations in which A=T and G=C
Base composition varies between species
Base composition the same in different cells within individual organism
Base composition does NOT change with age/nutrition/environment
Photo 51
First x-ray diffraction image of DNA (by Rosalind Franklin)
DNA is double stranded, helical, and reveals information about turns
Repeating unit of DNA
dNMP
DNA contains… chains
Two unbranched polynucleotide chains
DNA backbone
Sugar and phosphate portion
… hydrogen bond(s) between As and Ts, and… hydrogen bond(s) between Gs and Cs
2; 3 (Watson and Crick base pairing)
Sugar/phosphate backbone of DNA is connected via…
Phosphodiester bonds
What bonding connects base pairs?
Hydrogen bonds (non-covalent bonding)
What does dNMP stand for?
2’-deoxyribonucleoside 5’-monophosphate
Why AREN’T DNA strands bonded covalently?
Bonds need to be easily breakable/reversible to separate strands for replication
Separating two DNA strands is termed…
Denaturing
Tm (melting temperature)
Temperature at which a solution of DNA is 50% denatured
What DNA regions are higher in Tm?
GC-rich regions; more hydrogen bonds, more energy input to break
Annealing
When complementary single strands of DNA come together through base pairing (i.e., opposite of denaturing)
In a living cell, >99% of DNA is in… conformation
B-DNA
B-DNA conformation
Right-handed helix
10.5 base pairs per turn of helix
Base pairs lying perpendicular to backbone
Hydrophobic portion of bases on interior
Base pairs exposed in major/minor grooves
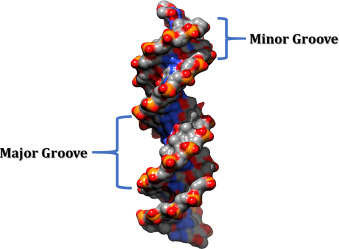
Major and minor grooves
Major: where a lot of nitrogenous bases exposed
Minor: where less nitrogenous bases exposed
A-DNA
Conformation of dehydrated DNA
Z-DNA
Seen in GC-rich regions
RNA’s 2’-hydroxyl on ribose sugar makes it a more… molecule
Fragile; can break phosphodiester bonds
RNA sequences are always read from…
5’ → 3’ direction
G-U base pairing
Allowed when RNA base pairs with itself or another RNA molecule
What types of structures does RNA have, if any?
Primary structure: sequence
Secondary structure: base pairing within same RNA molecule (e.g., stem loops)
Tertiary structure: interaction of various secondary structures
Gene
DNA sequence that encodes something functional
Includes regulatory sequences
Genome
Complete set of genetic information of all genes within a cell
Chromosome
DNA molecule that encodes genes
In a genome, the positions of genes are… within a species
Fixed
What is special about the E. coli genome?
Single, circular
What types of chromosomes do humans have?
Linear chromosomes
In the nucleus, chromosomes are found…
Wrapped around proteins
Meier-Gorlin Syndrome
DNA replication initiation impaired, from mutated helicase gene (MCM5)
Small ears, no kneecaps, gaps in skull
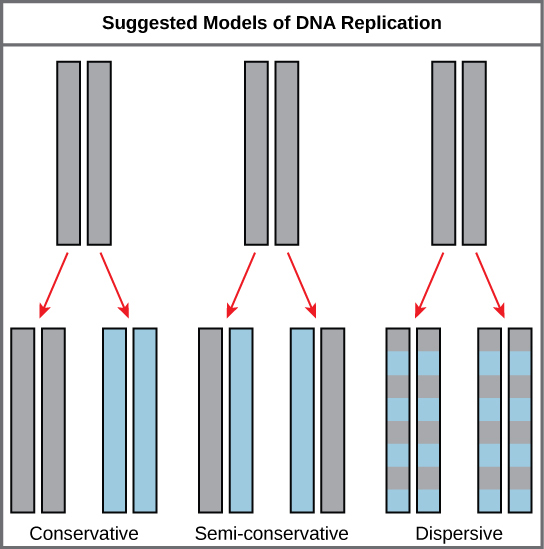
Conservative replication
Yields one original DNA molecule and one entirely newly synthesized DNA
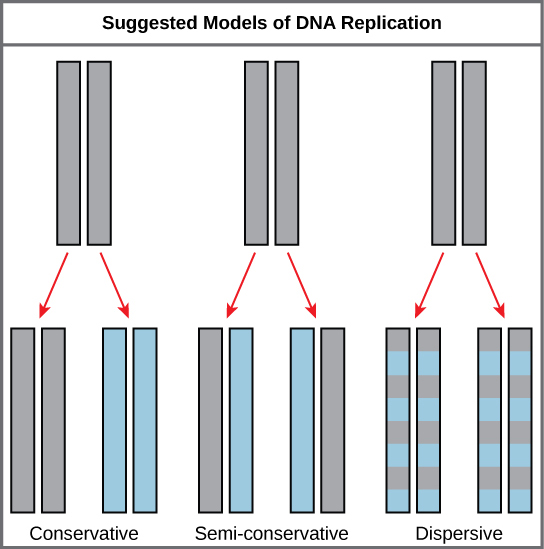
Semi-conservative replication
Yields two DNA molecules, each with one parental and one newly synthesized strand
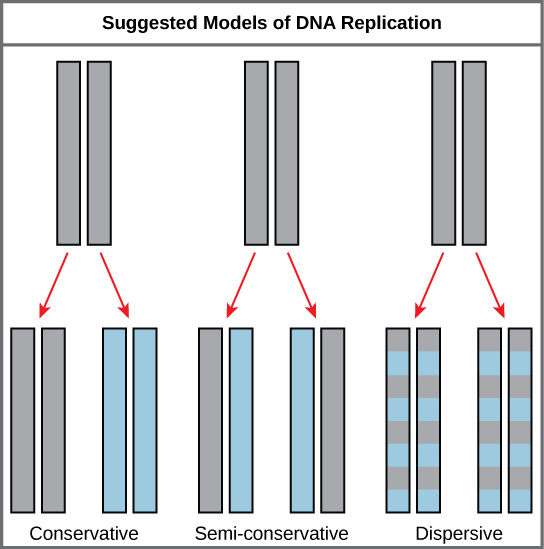
Dispersive replication
Yields two DNA molecules that are hybrids (or mixtures) of parental and newly synthesized DNA
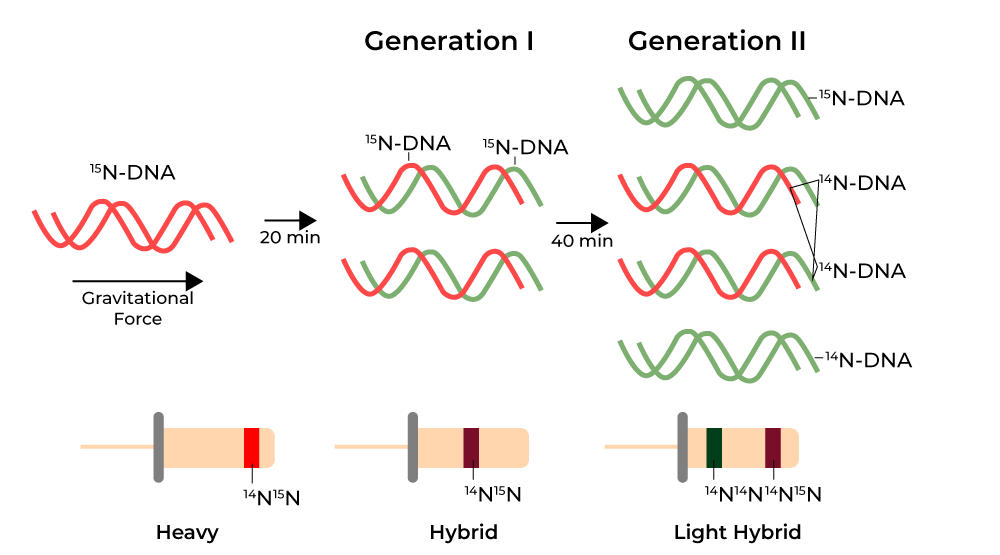
Meselson and Stahl experiment
All parental DNA labeled with 15N → saw single heavy density band
Allowed to replicate in 14N medium → saw single hybrid density band
Allowed to replicate again in 14N medium → saw one hybrid density band, and one light density band
Concluded that DNA replication is semi-conservative
Meselson and Stahl used… cells
E. coli
Meselson and Stahl used… culture media
(1) regular culture media and (2) culture media with heavy isotope of N
Meselson and Stahl used… technique
CsCl density gradient
CsCl density gradient
If CsCl is put into centrifuge, a density gradient is created down tube (heaviest density at bottom); DNA will migrate to equivalent density
DNA polymerase substrate
dNTP
DNA polymerase
Catalyzes extension of DNA strand one dNMP at a time
DNA polymerase synthesizes in… direction
5’ → 3’
DNA polymerase catalytic mechanism
3’ hydroxyl of 3’ nucleotide attacks a phosphate of incoming dNTP, releasing PPi
What is required at active site of DNA polymerase?
Two Mg2+ ions; stabilizes charges to set up conditions for nucleophilic attack
DNA polymerase requires a… and…
Template; DNA or RNA primer
DNA polymerase replication is…
Accurate; avoids mutations
Nucleases: DNase is specific for…, while RNase is specific for…
DNA; RNA
Nucleases can…
Remove bases from DNA/RNA
Exonuclease
Breaks phosphodiester bond at one end of polynucleotide chain
Exonucleases can work in the… direction
5’ → 3’ OR 3’ → 5’
Endonuclease
Breaks a phosphodiester bond within a polynucleotide chain
Endonucleases can be… or…
Sequence-independent; -specific
Endonucleases can make… break(s)
Single-strand (nick) or double-strand
Excinuclease
Breaks two phosphodiester bonds within a single polynucleotide chain
Restriction endonucleases
Endonucleases that only break phosphodiester bonds at specific DNA sequences (restriction sites)
Properties of restriction sites
Short
Palindromic
4-6nt long
Palindromic sequences
Both strands of DNA have same sequence when read 5’ → 3’
AATT and TTAA
High-fidelity DNA polymerases have…
Two active sites:
Catalytic site for DNA synthesis
3’ → 5’ exonuclease site for removing mis-incorporated nucleotides (like a backspace button)
DNA synthesis begins at…
An origin of replication sequence
How is DNA synthesized starting at the origin?
In both directions; bidirectional synthesis
DNA is synthesized by DNA Pol at sites called…
Replication forks
For every origin of replication, there is(are)… replication fork(s)
2
Parent DNA is unwound by…
Helicase
DNA synthesis at the leading strand occurs…, while DNA synthesis at the lagging strand occurs…
Continuously; discontinuously
Okazaki fragments are synthesized by…
A series of discontinuous 5’ → 3’ reactions at the lagging strand
Supercoils
From under- or over-winding DNA
Topoisomerases
Enzymes that add/remove supercoils in DNA by cutting phosphodiester bonds → unwrapping helix → resealing strands
DNA gyrase
Bacteria-specific topoisomerase that introduces supercoils (in addition to removing them ahead of replication fork)
Why would DNA gyrase introduce supercoils?
To compress DNA for packaging
Fluoroquinolones
Antibiotics that target bacterial DNA gyrase
Fluroquinolones block…
Ability to reseal DNA, causing double-strand breaks
Fluoroquinolones are effective in fighting bacterial infections because they have…
Selective toxicity; DNA gyrase is not present in humans and therefore our cells are not threatened by fluoroquinolones
What is the regulated step in the control of DNA synthesis?
Initiation
oriC
Origin of replication in E. coli; a unique 245 bp sequence
DnaA protein
First protein that comes in for DNA replication in E. coli; binds to R and I sites
DNA unwinding element (DUE)
AT-rich segment where strand separation occurs
Why does DUE bind to an AT-rich region?
In these regions, DNA strands bound using 2 H bonds only, requiring less energy/making it easier to separate them
How is DnaA activated?
Binds ATP
DnaA proteins bind to oriC →
Positive supercoil → DNA denaturation at DUE → replication bubble formed
What does DnaC doe when it binds to ATP?
Loads a DnaB helicase at both ends of replication bubble
Why is it important that DnaA is very slow to release ADP after dissociating?
It prevents dissociated DnaA from binding ATP and initiating replication at the same origin as before (each origin can only be used once)
Dam methylase
Methylates oriC DNA to regulate initiation