Chemistry - 5 Chemical Changes
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
Alkali
a soluble hydroxide
Base
substance that can neutralise acids
Acid
any compound that forms H⁺ ions in solution
Neutral
neither acidic nor alkaline
Dissolving sodium hydroxide in water
sodium hydroxide (water→) sodium ions(aq) + hydroxide ions(aq)
Indicators [4]:
- litmus paper
- universal indicator
- phenolphthalein
- methyl orange
Litmus paper [3]
acid: red
neutral: no change
basic: blue
Universal indicator
an indicator with a different colour for each pH value.
Phenolphthalein [3]
acid: colourless
neutral: colourless
basic: pink
Methyl orange [3]
acid: red-orange
neutral: yellow
basic: yellow
pH scale
measurement system used to indicate the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in solution; ranges from 0 to 14

Neutral solution + universal indicator
green
Acidic solution + universal indicator
red - yellow
Basic solution + universal indicator
blue - purple
pH meter
a device used to measure the pH of a solution

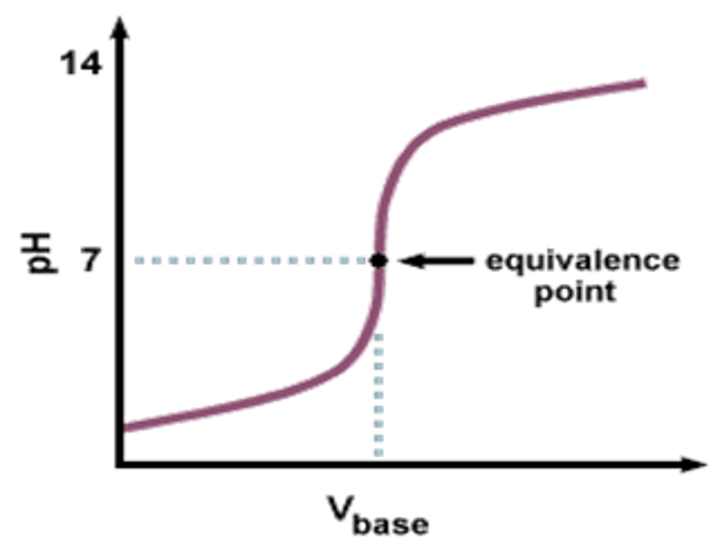
Equivalence point
the point in a titration where the number of moles of hydrogen ions equals the number of moles of hydroxide ions (middle of vertical drop)
Ionise
the reaction of a molecular substance with a solvent to form ions in solution.
Acids are classed as strong or weak depending on how they...
ionise in water
In aqueous solutions, acid molecules...
ionise and release H⁺ ions
Strong acids ... in aqueous solutions
fully ionise
How can we tell if an acid is weak?
it is a reversible reaction
Weak acids ... in aqueous solutions
partially ionise
Carbonic acid
H₂CO₃
Ethanoic acid
CH₃COOH
Citric acid
C₆H₈O₇
As the pH scale decreases by one unit...
the concentration of hydrogen ions increases by ten times
Concentration of acid
number of moles of acid molecules per unit of volume
Concentration vs. strength
concentration is the amount of solute dissolved in a given amount of solution while strength refers to the solute's tendency to form ions in water
Ethanoic acid dissolving in water
CH₃COOH ⇌ CH₃COO⁻ + H⁺
All acids contain...
hydrogen ions
Hydrochloric acid
HCl
Sulfuric acid
H₂SO₄
Nitric acid
HNO₃
What metals can react with acids?
metals more reactive than hydrogen (reactivity series)
What is the reaction between a metal and an acid?
a displacement reaction; the more reactive metal displaces the less reactive hydrogen in its acid
Salt
a compound formed when the hydrogen in an acid is wholly, or partially, replaced by metal (or ammonium) ions
Metal and acid
metal + acid → salt + hydrogen
Hydrochloric acid produces metal ... salts
chloride
Sulfuric acid produces metal ... salts
sulfate
Why does magnesium react rapidly with acid?
magnesium is more reactive than hydrogen; it has a stronger tendency to form positive ions
Chloride ions
Cl⁻
Sulfate ions
SO₄²⁻
Nitrate ions
NO₃⁻
The metal is ...
oxidised
The hydrogen ions are ...
reduced
The reaction of a metal and an acid is a ... reaction
redox
Base
compounds that can neutralise acids
An alkali is a base that...
is soluble in water
acid and base
acid + base → salt + water
Ammonium ion
NH₄⁺
Limiting reactant
a reactant that is totally consumed during a chemical reaction, limits the extent of the reaction, and determines the amount of product
Acid and alkali
acid + alkali → salt + water
In neutralisation, the ... reacts with the ... to form water
H⁺, OH⁻
Ionic equation for neutralisation
H⁺(aq) + OH⁻(aq) → H₂O(l)
Acid and ammonia solution
acid + ammonia solution → ammonium salt + water
Ammonia + water
NH₃ + H₂O → NH₄OH
How would you create a pure, dry sample of crystals from the reaction of an acid and an alkali? [3]
- carry out titration with indicator to find how much alkali completely reacts with the acid
- combine those volumes again, without indicator
- crystallise and dry crystals
Acid and metal carbonate
acid + metal carbonate → salt + water + carbon dioxide
Ore
a rock that contains a large enough concentration of a mineral making it profitable to mine
Oxidation
loss of electrons
Reduction
gain of electrons
Reactivity series
a list of metals which shows them in order of their reactivity, with the most reactive at the top
alkali metal and water
alkali metal + water → metal hydroxide + hydrogen
How can we test for orders of reactivity? [2]
- water (more reactive elements)
- dilute acid (less reactive elements)
Reactivity series:
potassium
sodium
lithium
calcium
magnesium
aluminium
CARBON
zinc
iron
tin
lead
HYDROGEN
copper
silver
gold
Reactivity series mnemonic
Please Stop Lustfully Calling Me A 'Cute Zoe'; Instead Try Letting Him Come - Susan's Guy
Displacement reaction
a reaction in which a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from an aqueous solution of the latter's ions.
A more reactive metal will...
displace a less reactive metal from an aqueous solution of one of its salts
Ionic equation
an equation in which ions are explicitly shown
Spectator ion
ion that does not participate in a reaction (not oxidised or reduced)
OILRIG
oxidation is loss, reduction is gain
Half equation
an equation for a redox reaction which considers just one of the species involved and shows explicitly the electrons transferred to or from it.
Redox reaction
an oxidation reaction paired with a reduction reaction
Displacement reactions are also known as...
redox reactions
Oxidising agent
substance that gains electrons
Reducing agent
substance that loses electrons
Where are metals from?
the Earth's crust
Whether it is worth extracting a particular metal depends on [3]:
- how easy it is to extract from its ore
- how much metal the ore contains
- the changing demands for a particular metal
How is copper extracted from copper ores? [5]
- ore is ground up into powder
- mixed with water and chemical that makes copper compound repel water
- air is bubbled through mixture
- copper compound floats to top as froth while rocky bits sink
- concentrated compound is scraped off to be extracted from
How are unreactive metals often found?
in their native state rather than as compounds
metal oxide and carbon
metal oxide + carbon → metal + carbon dioxide
What metals can be reduced using carbon?
metals less reactive than carbon
What metals can be reduced using hydrogen?
metals less reactive than hydrogen
How are metals more reactive than carbon extracted?
electrolysis of the molten metal compound