Supporting Systems & Movement in Animals – Comprehensive Review
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A comprehensive set of Q&A flashcards covering skeleton types, bone and cartilage structure, human axial and appendicular skeletons, joints, muscle anatomy and physiology, injuries, and diseases to aid exam preparation.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
What are the three main types of animal skeletons?
Hydrostatic skeletons, exoskeletons, and endoskeletons.
Which animals typically possess hydrostatic skeletons?
Soft-bodied invertebrates such as coelenterates (jellyfish, anemones), annelids (earthworms) and nematodes (roundworms).
How does a jellyfish move using its hydrostatic skeleton?
By contracting its bell, forcing water out and propelling the body forward.
State two disadvantages of hydrostatic skeletons.
1) Restricted range of movement and size; 2) Rapid water loss limits them to moist/aquatic habitats.
What polysaccharide forms the arthropod exoskeleton?
Chitin.
List two advantages of an arthropod exoskeleton.
• External protection for organs • Wax cuticle reduces water loss.
Why must arthropods moult?
Because the rigid exoskeleton limits growth; shedding (ecdysis) allows a larger exoskeleton to form.
Name two disadvantages of exoskeletons.
Limited mobility and growth; heavy if scaled up to large size.
Which vertebrate groups possess cartilaginous endoskeletons?
Sharks and rays.
State three advantages of an endoskeleton.
1) Grows with the body 2) Internal protection for organs 3) Provides muscle attachment for movement.
What are the two main supportive tissues of vertebrate endoskeletons?
Cartilage and bone.
Describe hyaline cartilage.
Glossy, flexible cartilage with chondrocytes in lacunae and abundant collagen; lines joints and reduces friction.
What is the function of fibrocartilage between vertebrae?
Acts as a shock absorber and permits limited movement.
Which mineral is most responsible for bone hardness?
Calcium salts (calcium phosphate).
What is the basic structural unit of compact bone?
The Haversian system (osteon).
Compare compact and spongy bone in one sentence.
Compact bone is dense and strong; spongy bone is lighter, with trabeculae aligned along stress lines and contains red marrow.
Name the four bone shape categories with one example each.
Long (femur), short (carpals), flat (scapula), irregular (vertebra).
What is the diaphysis of a long bone?
The shaft composed mainly of compact bone.
What is found in the medullary cavity of an adult long bone?
Yellow (fatty) marrow.
Give two functions of red bone marrow.
Produces red blood cells (erythrocytes) and white blood cells (leucocytes).
Which structure covers the outer surface of bone and aids repair?
Periosteum.
How many vertebrae are in the human spine?
33 vertebrae.
Name the first two cervical vertebrae in order.
Atlas and axis.
What is an intervertebral disc composed of?
A fibrous cartilage ring surrounding a gelatinous centre (nucleus pulposus).
List three functions of the vertebral column.
Supports the head, protects the spinal cord, provides attachment for ribs and back muscles.
Distinguish true, false, and floating ribs by attachment.
True ribs attach directly to sternum; false ribs attach indirectly via cartilage; floating ribs attach only to vertebrae.
What bones form the pectoral girdle?
Clavicle and scapula.
Why is the shoulder joint more mobile than the hip joint?
Its shallow glenoid cavity and minimal ligamentous attachment allow a wide range of motion.
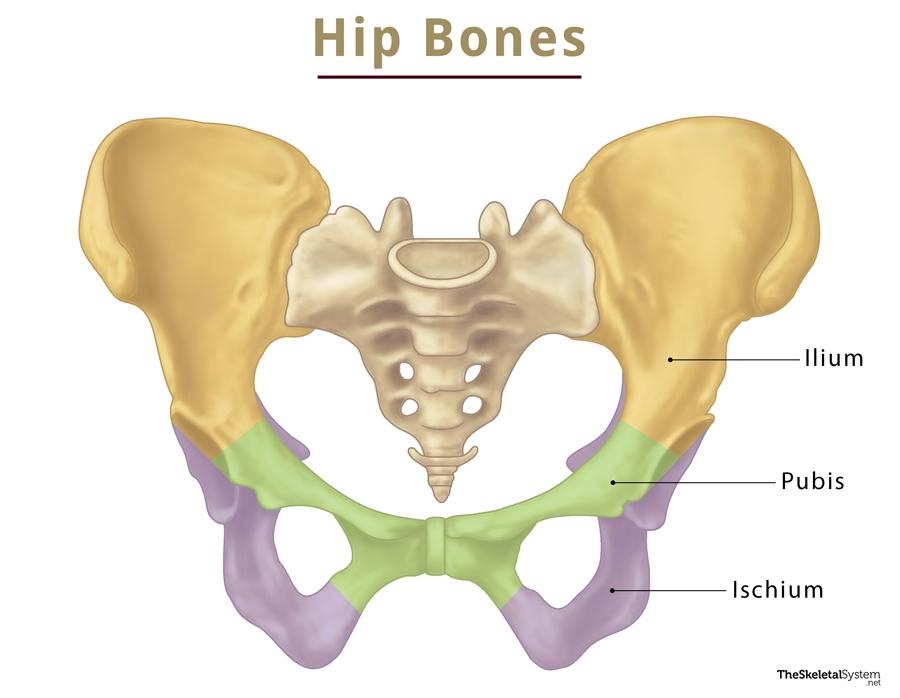
Which three bones fuse to form an adult hip (coxal) bone?
Ilium, ischium, and pubis.
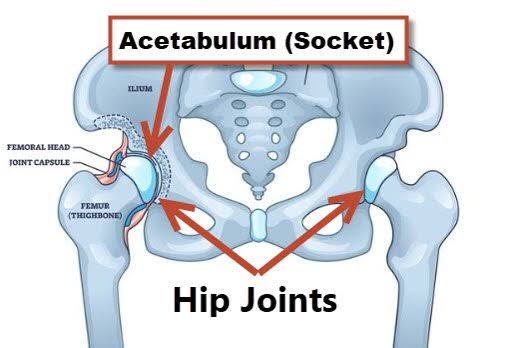
Name the deep socket of the hip joint.
Acetabulum.
Which is the longest and strongest bone in the body?
Femur.
How many bones make up the human wrist (carpals)?
Eight carpals.
Define ligament.
A band of strong, elastic connective tissue that links bone to bone and stabilises joints.
Define tendon.
A collagen-rich, inelastic cord attaching muscle to bone.
What fluid lubricates synovial joints?
Synovial fluid.
State the six main types of synovial joints.
Ball-and-socket, hinge, pivot, plane (gliding), condyloid, and saddle.
Give an example of a pivot joint.
Atlas–axis joint in the neck.
What is a bursae and its function?
A fluid-filled sac reducing friction between tendons/ligaments and bone.
Describe a simple (closed) fracture.
Bone breaks cleanly but does not penetrate the skin.
What is osteoporosis?
Age-related loss of bone mass causing porous, fragile bones.
List two lifestyle factors that help prevent osteoporosis.
Weight-bearing exercise and a calcium/vitamin D-rich diet.
What childhood disease results from vitamin D deficiency?
Rickets.
Explain what a slipped disc is.
Protrusion of the nucleus pulposus through ruptured cartilage, pressing on spinal nerves.
Define arthritis in one sentence.
A group of disorders causing joint inflammation, pain, and stiffness.
Differentiate osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Osteoarthritis is non-inflammatory wear-and-tear of cartilage; rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune inflammatory disorder of synovial membranes.
What causes gouty arthritis?
Deposition of urate crystals in joint tissues due to high blood uric acid.
Which protein filaments slide during muscle contraction?
Actin slides over myosin.
Name the functional contractile unit of a myofibril.
Sarcomere.
What ion triggers exposure of actin binding sites?
Calcium ions (Ca²⁺).
What supplies energy for cross-bridge cycling?
ATP hydrolysis to ADP + Pi.
What is a motor unit?
One motor neuron and all the muscle fibres it innervates.
Explain muscle tetanus (in physiology).
A fused, sustained contraction due to rapid, repeated stimulation.
Why are biceps and triceps called antagonistic muscles?
Because contraction of one (biceps) flexes the elbow while contraction of the other (triceps) extends it, producing opposite actions.
Describe Duchenne muscular dystrophy in two facts.
X-linked recessive absence of dystrophin; progressive muscle degeneration appearing in early childhood.
What is the largest and strongest tendon in the body?
Achilles tendon.
List two common causes of skeletal muscle cramp.
Electrolyte imbalance (low Ca²⁺/Mg²⁺/K⁺) and dehydration.
Define sprain.
Stretched or torn ligament at a joint.
What is a bunion?
An enlarged, inflamed bursa at the base of the big toe due to shoe pressure.
Which connective tissue sheath surrounds an entire skeletal muscle?
Epimysium.
What percentage of cartilage is water?
About 80 %.
Name two roles of the S-shaped curvature of the spine.
Absorbs shock and helps maintain balance in upright posture.
Which hormone drop in post-menopausal women accelerates bone loss?
Oestrogen.
What is the foramen magnum?
Large opening at the base of the skull through which the spinal cord exits.
Which vertebrae allow nodding and rotation of the head?
Atlas (C1) for nodding; axis (C2) for rotation via the odontoid process.
Why is the clavicle frequently fractured?
It is slender, transmits forces from the upper limb to the axial skeleton, and is superficially located.
Identify two ways synovial joints reduce friction.
Articular (hyaline) cartilage and synovial fluid.
What name is given to muscles that assist the prime mover?
Synergists.
State the function of fontanelles in an infant skull.
Allow skull compression during birth and accommodate rapid brain growth.
What are trabeculae?
Thin bony plates forming the lattice of spongy bone.