Chapter 2: Atoms, Ions, and Molecules~ the building blocks of matter
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
what are the three subatomic particles and their charge and mass?
Electron- negative (-), mas of .0005 amu
Proton- positive (+), mass of 1 amu
Neutron- no electrical charge, mass of 1 amu
Radioactivity
is the spontaneous emission of high-energy radiation and particles by materials
beta particle
is a particle that is emitted during radioactive decay and is equivalent in mass and charge to a high energy electron: B (aka just high energy electrons)
alpha particle
is a particle that is emitted during radioactive decay and is equivalent in mass and charge to a 4He nucleus: a (are about 10,000 times more massive than B particles)
Rutherford’s gold foil experiment
Ernest Rutherford shined a beam of a (positively charged) particles on a thin sheet of gold foil.
Doing this he tested Thomson’s plum pudding model. If Thomson’s model was correct than all the alpha particles would go right through.
Most a particles passed straight through but some deflections occurred which Rutherford concluded were because a tiny fraction of a particles encountered small regions of high positive charge and large mass.
Rutherford discovered the…
nucleus which contains the positively charged center of an atom that contains nearly all the atom’s mass
Thomson’s plum pudding model
featured a positive sphere of matter (dough) with negative electrons (chocolate chips) embedded in it.
Isotopes
are atoms of an element containing the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons.
Nuclide
refers to any atom of any element that has a particular number of neutrons in its nucleus, it is a specific isotope of an element.
Symbol used to represent a particular nuclide:
A- mass number: which indicates the total number of nucleons (neutrons and protons) in the nucleus of an atom
Z- atomic number: number of protons in an element (same for all isotopes of a particular element)
C- charge
X- represents the symbol for the element
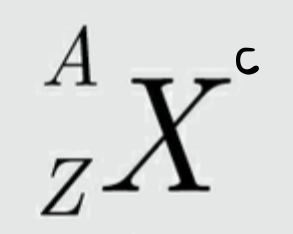
periodic table of elements
is a chart of the elements in order of their atomic numbers and in a pattern based on their physical and chemical properties
PT periods
horizontal rows
PT groups or families
18 columns
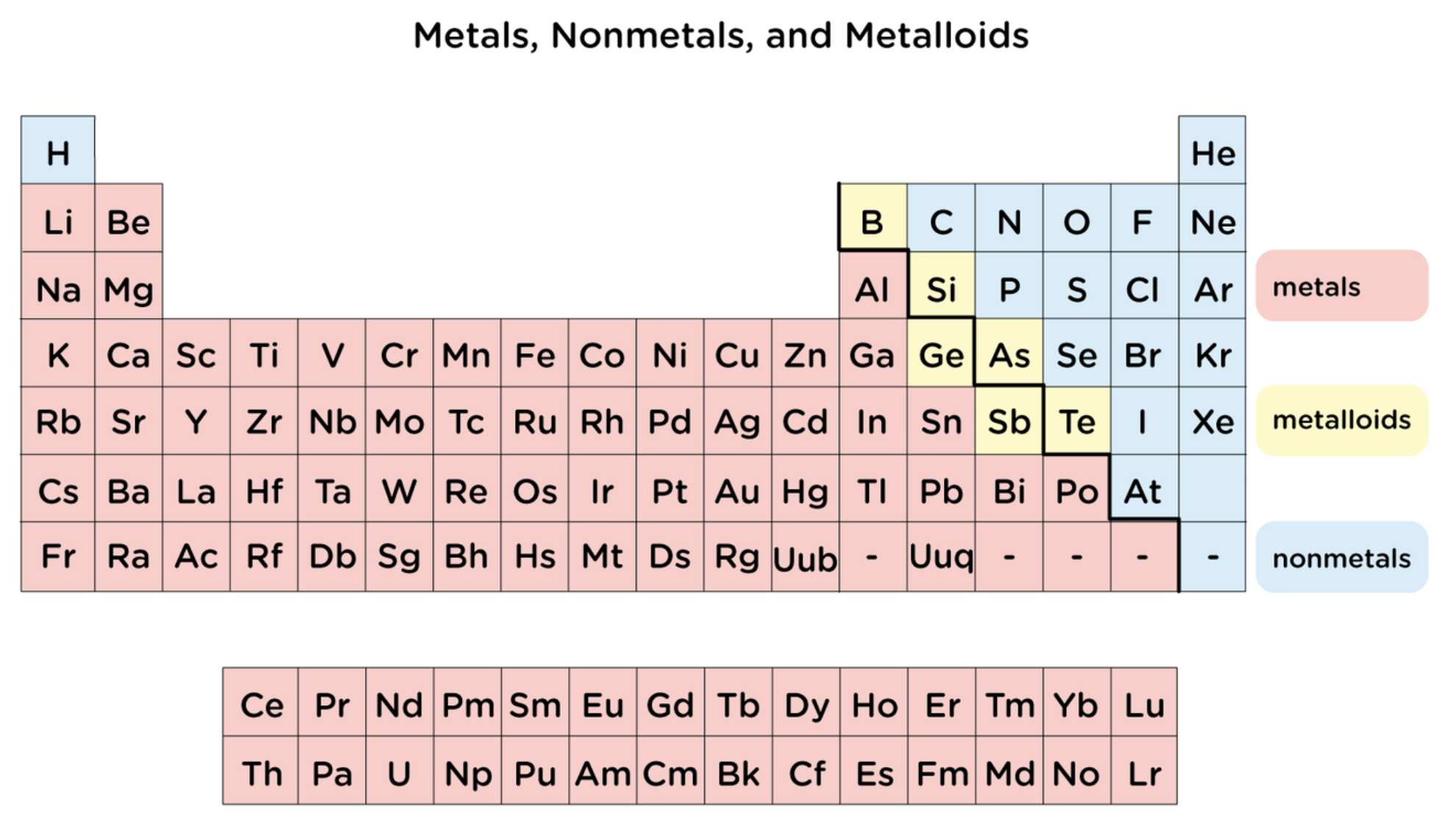
Elements in periodic table can be broadly categorized as..
metals, nonmetals, and metalloids
metals
tend to conduct heat and electricity
are malleable and ductile
all but mercury are shiny solids at room temperature
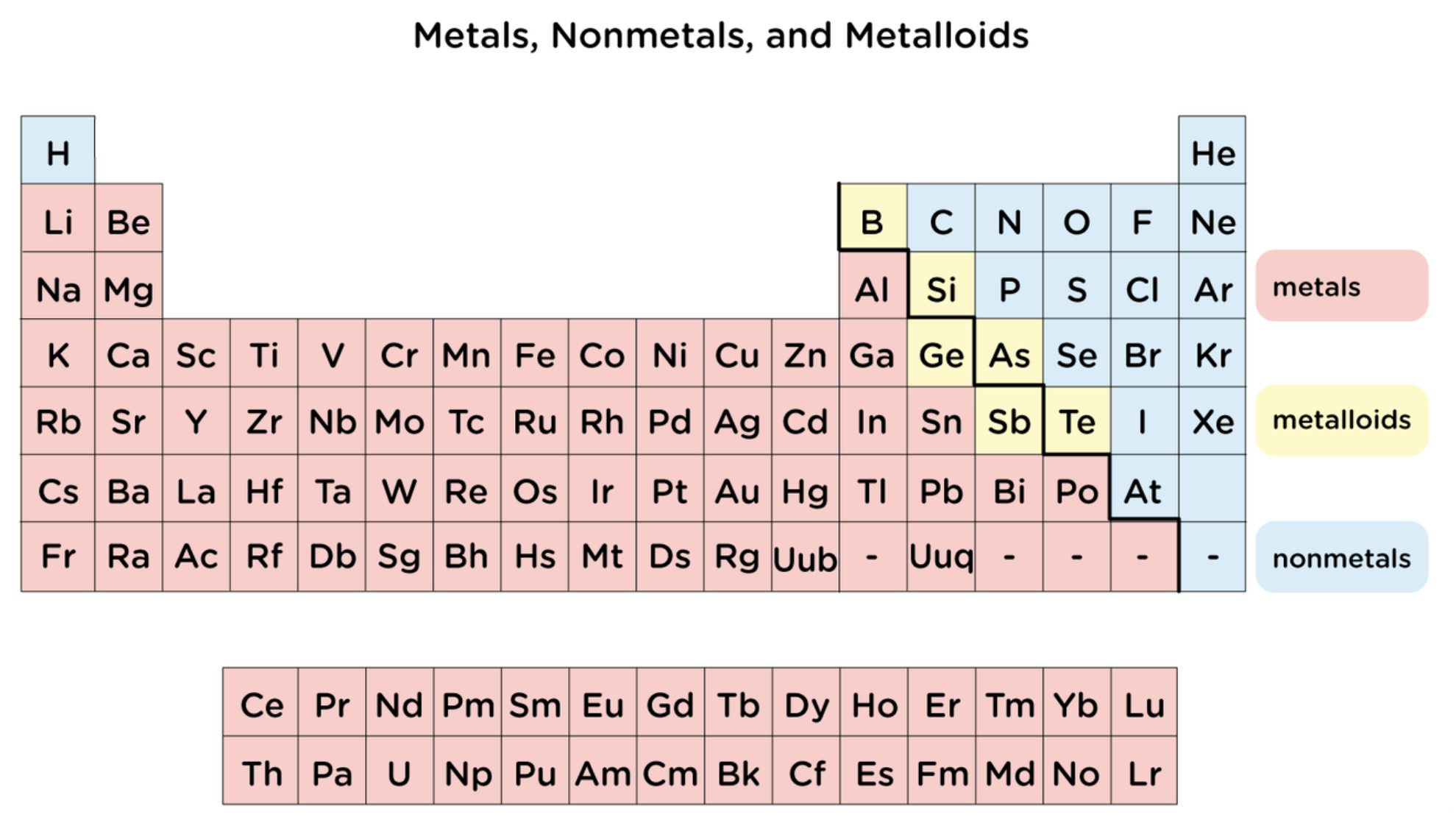
nonmetals
are poor conductors of heat and electricity
most are gasses at room temperature
the solids among them are Iodine (I2) which is brittle and Bromine (Br2) which is liquid at room temperature
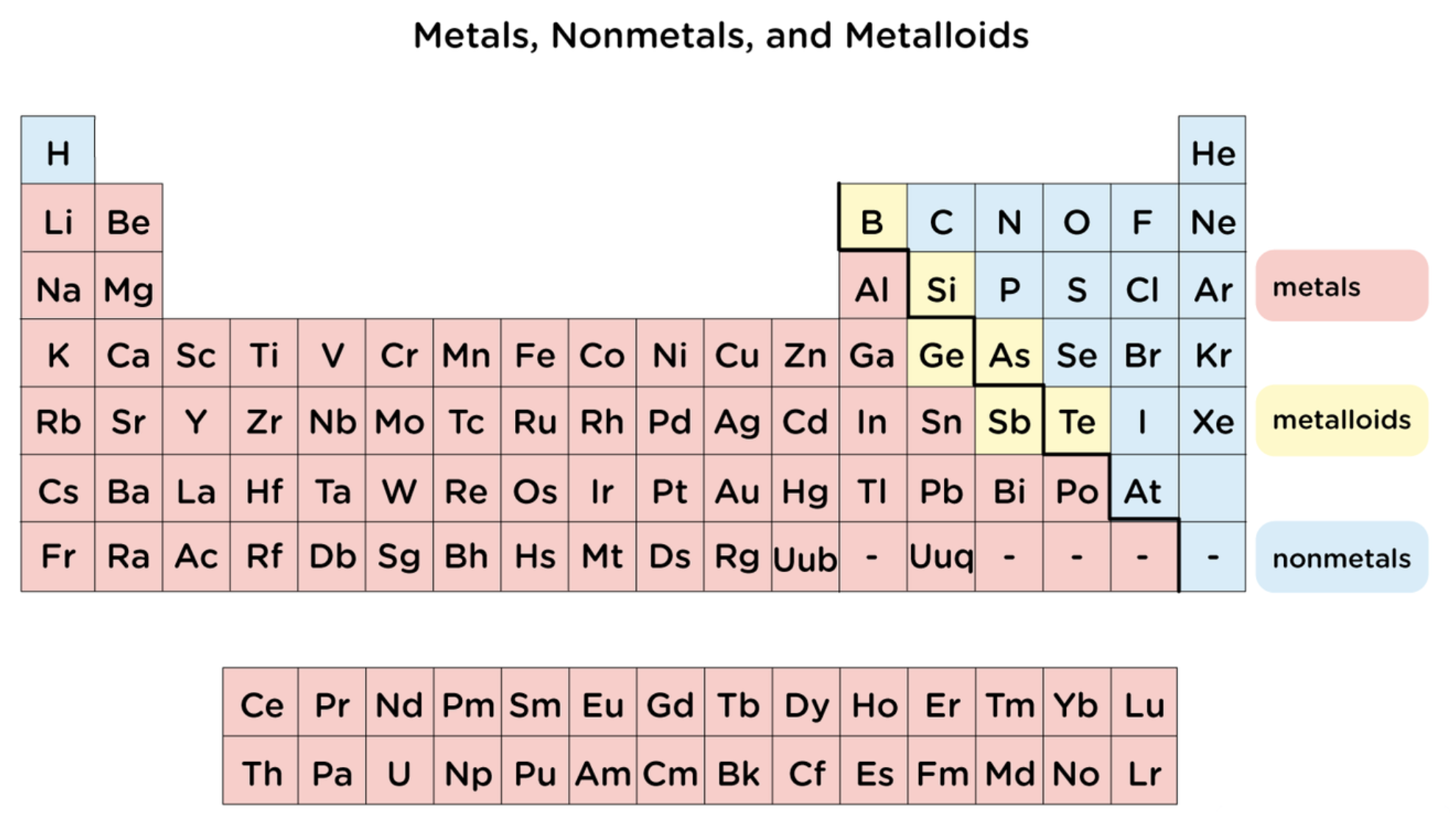
metalloids
have some properties of metal and some of nonmetals
shiny like metals but brittle like nonmetals
semiconductors
average atomic mass
is the weighted average of the masses of all isotopes of an element, calculated by multiplying the natural abundance of each isotope by its mass in unified atomic mass units and then summing the products
molecular mass
is the mass in u of one of a molecular compound. It is the sum of the average atomic mass of the atoms that are chemically bonded together in it.
formula unit
is the smallest electrically neutral unit of an ionic compound. Formula mass is used for ionic compounds because there are no molecules present.
ex. KCl or CaCl2
Mole (mol)
is an amount of a substance that contains a number of particles (atoms, ions, molecules, or formula units) equal to the Avogadro constant.
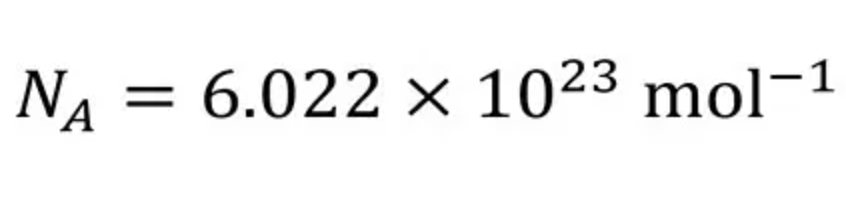
molar mass
the mole serves as an important link between the atomic mass values in the periodic table and measurable masses of elements and compounds.
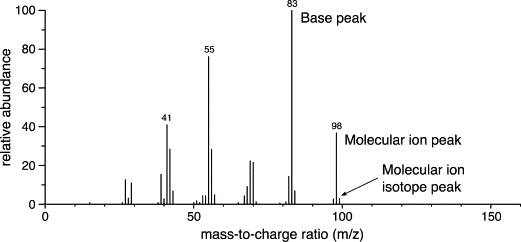
mass spectrometer
is a device that separates and counts ions according to their ratio of mass (m) to charge (z), m/z
molecular ion
(m/z) is an ion formed in a mass spectrometer when a molecule loses an electron after being bombarded. with high-energy electrons. The molecular ion has a charge of 1+ and has essentially the same molecular mass as the molecule from which it came.
mass spectrum
When the ions and the molecular ion are separated according to their m/z values and then reach a detector, the resulting signals are used to create a graphical display called a mass spectrum in which the m/z values of the ions are plotted on the horizontal axis and the intensity (the number ions with a particular m/z value) on the vertical axis.