Topic 6
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Chorionic meaning
To do with the placenta
Are hormonal units of foetus & mother integrated/separate
Fetal, placental & maternal compartments form an integrated hormonal unit → feto-placental-maternal (FPM) unit → creates the Endocrine Environment
Role of the Endocrine Environment
Maintains and drives the processes of pregnancy and pre-natal development
What type of protein is Human Chorionic Gonadotrophin
Glycoprotein
Human Chorionic Gonadotrophin molecular weight
30,000
Human Chorionic Gonadotrophin is produced by what cells
Trophoblastic Cells
Human Chorionic Gonadotrophin subunits
α Subunit = Common with FSH, TSH, LH
β subunit = Hormone Specific
When does Human Chorionic Gonadotrophin begin to be excreted
Implantation
How many days after fertilisation can Human Chorionic Gonadotrophin be detected in blood
8 days
How many days after fertilisation can Human Chorionic Gonadotrophin (HCG) be detected in urine
14 days
When do HCG secretion levels peak
2 Months of Gestation
Role of hCG
Prevents Ovulation
↑ Endometrial Growth
Thyroid-stimulating
↑ Testosterone
Maintains the corpus luteum for 12 weeks
Makes sure uterine environment is receptive to pregnancy - angiogenesis, recruits Treg cells, inhibits dendritic cells)
Effect on immune system → changes function of T cells
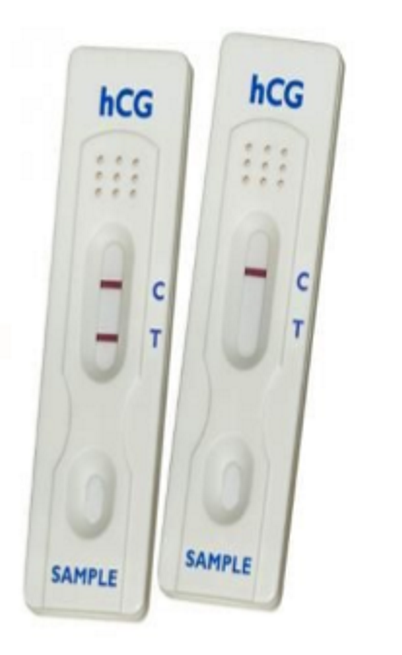
How do pregnancy tests work
On the T line there’s an antibody to hCG
If there’s hCG present, it will bind to the antibody & cause the colour change
Human Chorionic Somatomammotrophin (hCS) molecular weight
38,000
Human Chorionic Somatomammotrophin (hCS) is similar to what other 2 hormones
Similar to Growth Hormone and Prolactin
They have a Common Progenitor
hCS is synthesised by what
Placenta
When is hCS secreted
Week 5 Post Fertilisation
Low levels of hCS indicate what? why?
Low levels indicative of placental insufficiency as its secretion is Directly Proportional To Placental Size
hCS (human chorionic somatomammotropin) is also known as what
hPL (human placental lactogen)
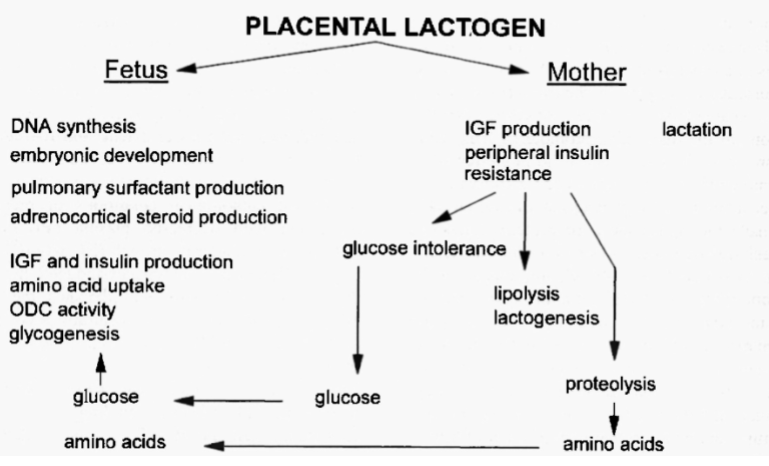
Effects of hCS (human chorionic somatomammotropin) on foetus & mother
Mother uses fat for energy more than glucose because foetus uses glucose
How do steroid levels in pregnancy compare with that of the menstrual cycle
Progesterone and Oestrogen Levels are higher
Sources of steroids throughout pregnancy
Corpus luteum in 1st trimester
Placenta starts taking over @ week 8 (luteal-placental shift)
Placenta is the main source by week 12
Why is the timing of the luteal-placental shift clinically important
Removal of the ovaries (with CL) before the luteal-placental shift leads to miscarriage
Pregnancy continues normally if the ovaries are removed after the luteal-placental shift
What form of oestrogen is highest in the menstrual cycle & what is highest in pregnancy
Menstrual cycle = estadiol
Pregnancy = estriol
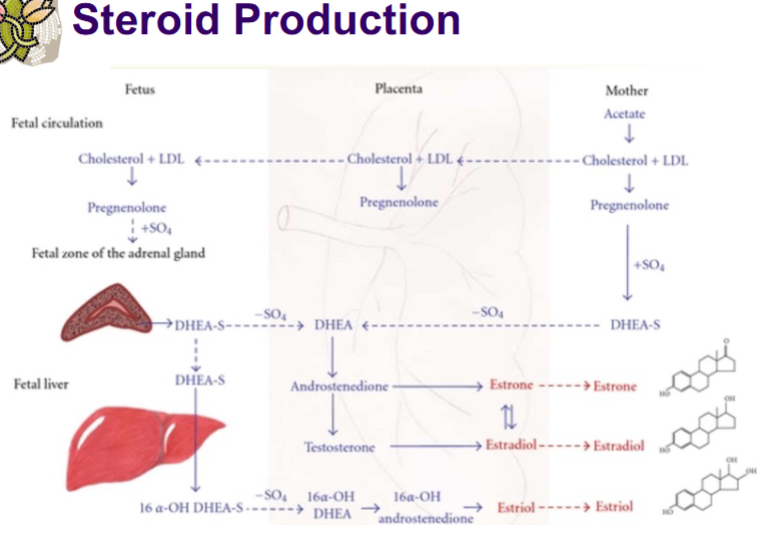
Pregnenolone forms from what, where (fetus/placenta/mother)
Formed from cholesterol (from LDL) in all 3 - foetus, placenta, mother
Where can pregnenolone be converted to DHEA
Foetal adrenal gland & in the mother (not the placenta)
Where is DHEA converted to oestrogen
Placenta
Progesterone is formed from what
Maternal Precursors
Do levels of progesterone vary much throughout pregnancy
Levels Increase Significantly Throughout Pregnancy
80-90% of progesterone is produced by what and sent where
By the placenta
Sent to both foetus & mother
Role of progesterone in mother
Decreases Uterine Contractility (so drop in progesterone indicates pregnancy coming to an end)
Inhibits Ovulation - Acting on GnRH, FSH and LH
Maintain Uterine Function - Placental Secretion and Function
Embryo Nutrition - Increases Decidual Cells & Uterine Secretion
Role of progesterone in embryo
Precursor for other Hormones:
Adrenal Hormones - Weak Androgen (Oestrogen)
Cortisol - Surfactant Production
Testicular Hormones - Testosterone (Foetal Differentiation)
What forms of oestrogen are present in pregnancy
Oestrone, Oestriol, 17b-Oestradiol
Is oestriol a strong/weak oestrogen
weak
Does oestrogen in pregnancy have a maternal/foetal/placental origin
All 3 (Placental Produced Oestrogens Transfer to Maternal and Foetal Compartments)
What do oestrogens form from
C-19 Steroids in the Adrenal Glands are converted into Weak Androgens (Dehydroepiandrostenedione (DHEA), 17-OH -DHEA) which are precursors to oestrogen
Role of Oestrogens in Pregnancy
Essential For Foetal Survival (Urinary Oestrogens Decreased with Foetal Death)
Myometrial Hypertrophy and Gap Junctions
Lacterous Duct development
Increase Uterine Size
Increase External Genitalia Size
Relaxes Pelvic Ligament
Increase Oxytocin Receptors
A small amount is needed to maintain pregnancy but a spike at the end allows for relaxation of pelvic ligament & increased oxytocin receptors)
What type of hormone is relaxin
Peptide hormone
Where is relaxin produced
Corpus luteum & placenta in pregnancy
Also produced in the prostate
Relaxin increases secretions of what hormones
LH
hCG
Role of Relaxin in pregnancy
Myometrial Relaxation - Facilitation of Implantation
Relaxation of Pelvic Ligament
Relaxation of Cervix
Effect of relaxin on myocardial overload
Decreases it
Effect of relaxin on renal function
Increases renal function

Effect of relaxin on cell preservation
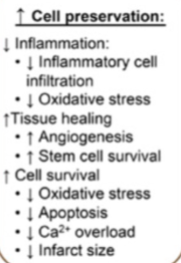
Effect of Relaxin on the ECM
Increased remodelling
