2. Documentation, Reporting & Nursing Informatics
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
What does nursing documentation provide a record of?
Nursing documentation provides a record of the patient’s status, events, tests, procedures, changes in condition, actions taken by the nurse, patient response, and outcomes.
Why do we chart in nursing?
We chart to communicate clearly, ensure continuity of care, provide a legal record, support quality and safety, and document interventions and patient responses.
Why do we have standard nursing terminologies and do-not-use abbreviations?
Standard nursing terminologies and do-not-use abbreviations reduce confusion, prevent errors, ensure clarity, and improve communication among healthcare providers.
Why do we have standardized documentation formats?
Standardized documentation formats ensure consistency, make information easier to find, support continuity of care, and facilitate interdisciplinary communication.
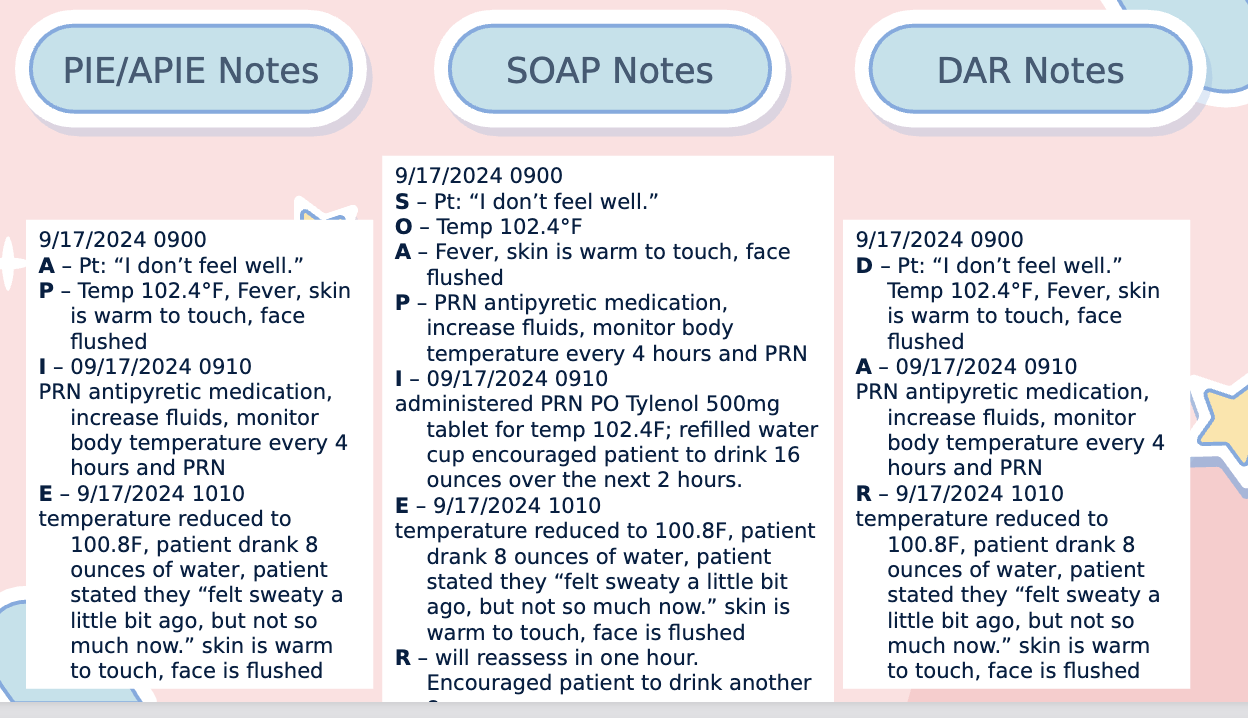
What are examples of formatted nursing documentation?
Examples include:
PIE/APIE notes (Problem, Intervention, Evaluation / Assessment, Problem, Intervention, Evaluation)
SOAP notes (Subjective, Objective, Assessment, Plan)
DAR notes (Data, Action, Response)
Why is formatted charting used in nursing?
Formatted charting provides a structured, consistent method for documenting care, making it easier to track patient progress and communicate with the healthcare team.
Examples
What are some common forms of nursing documentation?
Common forms include:
Bar-coded medication administration
Kardex (quick reference patient care summary)
Admission and discharge summaries
What are some legal issues related to nursing documentation?
Legal issues include:
Nurses’ notes are considered legal documents
Every entry must include date, time, and signature
Notes should never be altered or obliterated
Errors must be corrected using proper procedures
Charting should be done as soon as possible after care is provided
What is informatics?
Informatics is a broad academic field encompassing artificial intelligence, cognitive science, computer science, information science, and social science.
What is medical informatics?
Medical informatics relates to health care and describes a distinct specialty in the discipline of medicine, focusing on managing and using medical information.
What is nursing informatics?
Nursing informatics is the use of health information systems to support nursing practice, including documentation, patient care, and data management.
nursing science
computer science
information science
What is the role of data collection in informatics?
Data collection supports patient assessment, labs, procedures, results, and interventions by organizing and storing accurate information.
What is point-of-care technology?
Point-of-care technology helps with reduction of errors and improves assessments by allowing nurses to document and access information directly at the bedside.
How does informatics support continuity of care?
Informatics ensures access to previous visits and research, promoting consistent and coordinated patient care.
What is the first step in the Nursing Informatics process?
Data – raw facts collected (e.g., vital signs, lab results).
What comes after data in the Nursing Informatics process?
Information – organized and interpreted data that has meaning (e.g., trends in vital signs).
What is the third step in the Nursing Informatics process?
Knowledge – applying information to clinical practice (e.g., recognizing a patient is hypertensive).
What is the final step in the Nursing Informatics process?
Wisdom – using knowledge and experience to make sound clinical decisions (e.g., initiating interventions to manage blood pressure).
What are virtual visits used for in healthcare?
Connecting with patients for follow-ups (Telehealth).
What is a key feature of technology in the Information Age?
It is rapidly changing, creating new ways to use tech in the hospital.
What must nurses always follow when using technology?
Facility policy and additional expectations.
What must be ensured when using telehealth technology?
HIPAA compliance.
Which term means “organized data”? Informatics Wisdom Knowledge Information
Information
How does nursing informatics increase time with patients?
By reducing paperwork and streamlining documentation.
What advantage does informatics provide regarding patient data?
Better access to real-time information.
How does informatics improve documentation?
Enhances quality, accuracy, and consistency of records.
What type of errors does informatics help reduce?
Errors of omission (missed or forgotten care).
How does informatics affect hospital costs?
Reduces costs by improving efficiency and decreasing duplication.
How does informatics impact nurse job satisfaction?
Increases satisfaction by simplifying workflow and reducing burdens.
How does informatics support accreditation compliance?
Ensures documentation meets standards set by accrediting agencies.
What advantage does a common clinical database provide?
Improves interdisciplinary communication and continuity of care.
How does informatics improve access to diagnostic test results?
Provides faster, organized, and real-time access for providers and nurses.
What benefit does bar-code medication administration provide?
Ensures medication safety by reducing errors and verifying patient identity.
How does decision support and computerized provider order entry (CPOE) help?
Assists with clinical decisions, reduces transcription errors, and standardizes orders.
How does informatics improve record management?
Maintains accurate, organized, and easily retrievable patient records across the continuum of care.
What is the benefit of informatics in research access?
Provides access to large databases and evidence-based resources to improve practice and patient outcomes.
How does informatics support networking in healthcare?
Enhances collaboration by connecting healthcare providers, departments, and institutions to share information effectively.
How is distance learning supported through informatics?
Provides online access to classes and educational materials, making learning flexible and accessible from any location.
How are simulations used in nursing education with informatics?
Offers realistic practice scenarios that improve clinical skills and decision-making without risk to patients.
What role do online discussion boards play in informatics and education?
Facilitate peer-to-peer learning, collaboration, and knowledge sharing in virtual settings.
How are social media sites used in education and patient support?
Provide platforms for professional networking, education, and health-related discussions.
What benefit do support groups provide outside the classroom through informatics?
Connect individuals with shared experiences, offering education, encouragement, and emotional support online.
Where can you find reliable sources for nursing and healthcare information?
Peer-reviewed journals, textbooks, government websites, professional organizations, and reputable medical databases (e.g., PubMed, CINAHL, Cochrane Library).
How do you know if a source is reliable?
A source is reliable if it is evidence-based, peer-reviewed, current, authored by experts in the field, and free from bias or commercial influence.
Website Evaluation Criteria

Quick Quiz-
Which of the following is an advantage
of standardized terminology? (Select
all)
It promotes
consistent
documentationIt enables data from
different geographic
regions to be
comparedIt provides a
common means of
communicationIt enables nurses to
compare data
across populations
All of them
What is a key ethical concern regarding the creation and retention of documentation?
Ensuring that documentation is accurate, complete, and maintained according to legal and professional standards.
What ethical and legal issues are involved in preservation of privacy and confidentiality?
Protecting patient information from unauthorized access or disclosure, in compliance with laws like HIPAA.
What concerns exist regarding the ownership of software in healthcare informatics?
Determining who legally owns the software and ensuring it is used according to licensing agreements.
What issues arise around ownership and integrity of data?
Ensuring data is accurate, secure, and not altered improperly, while maintaining ethical use of patient information.
How is prevention of computer fraud and misuse relevant to ethical and legal practice?
Protects patient data and hospital systems by preventing unauthorized access, tampering, or illegal use of electronic health records.
How does nursing informatics enable nurses to improve patient care and safety?
By providing real-time access to patient data, supporting clinical decisions, and reducing errors.
How does nursing informatics help gather evidence of best practice?
By collecting and analyzing data from multiple sources to guide evidence-based interventions.
How is point-of-care documentation and reference used in the future of nursing informatics?
Nurses can document and access patient information directly at the bedside, improving workflow and care accuracy.
How can nurses advocate for consumer access to health care information?
By supporting patient portals and educational resources, empowering patients to participate in their own care.
Why is transitioning care a critical concern in nursing?
Because it involves risks to patient safety, including miscommunication, errors in medication, and incomplete transfer of important information.
What patient information should be included in a hand-off report?
Patient identification and the reason for visit.
What clinical information is included in a hand-off report?
Review of systems, events from the last 24 hours, changes in condition, and upcoming tasks.
What are key qualities of an effective hand-off report?
It should be systematic, timely, and accurate to ensure patient safety and continuity of care.
How can communication problems impact patient safety during hand-offs?
Communication problems can be the primary cause of more than half of sentinel events.
How can standardized hand-off communication help?
A standardized approach can help avoid sentinel events and other errors, improving patient safety.
Why is communication considered a safety issue in nursing?
Because effective communication prevents errors, ensures continuity of care, and protects patients from harm.
How did informatics and standardized handoff reporting affect nurses’ knowledge?
Nurses had increased knowledge about patient priorities, improving their ability to provide focused care.
How did new nursing graduates feel after using standardized handoff reporting?
They reported feeling empowered and more confident in patient care.
What collaborative practices improved due to standardized handoffs?
Nurses were able to jointly teach at the bedside and collaboratively assess patients, enhancing teamwork.
How did nurses perceive the exchange of information and shift relationships?
Nurses perceived that appropriate information was being exchanged and that relationships between shifts improved.
How did patient satisfaction change after implementing EBP handoff reporting?
Patient satisfaction improved significantly in three areas:
Nurses kept patients informed
Friendliness and courtesy of the staff
Likelihood to recommend the hospital
What should you include in the Situation part of SBAR?
Identify yourself, your unit, the patient by name, and the reason for your report.
What information goes in the Background section of SBAR?
Include the patient’s reason for admission, significant medical history, vital signs, contraction pattern (if applicable), and other relevant context.
What should be communicated in the Assessment section of SBAR?
Provide your clinical impression, concerns, and evaluation of the patient’s current condition.
What is included in the Recommendation part of SBAR?
Clearly explain what you need, specify requests and time frames, make suggestions, and clarify expectations.
When are verbal and telephone orders typically used?
They are often limited to emergency situations.
Who is authorized to take a verbal or telephone order?
Registered Nurses (RNs) only; students cannot take these orders.
What steps must an RN follow when taking a verbal or telephone order?
Repeat the order verbatim to confirm accuracy.
Enter the order into the paper or electronic system.
Document it as a verbal/phone order with date, time, physician’s name, and RN signature.
What is an incident report?
A report completed when an unusual and unexpected event involving a patient, visitor, or staff member occurs.
What are some examples of incidents that require reporting?
Falls, medication errors, and equipment malfunctions.
How should an incident report be documented?
Factual, objective, and nonjudgmental, documenting details immediately to ensure accuracy.
What is the purpose of an incident report?
To record the details of the incident for accuracy and future reference, not for assigning blame.
What is the difference between an EMR (Electronic Medical Record) and an EHR (Electronic Health Record)?
EMR: Contains information for a single episode of care (e.g., one hospital stay).
EHR: Contains information about all encounters and visits across multiple providers and settings.
What was the Health on the Net (HON) Foundation, and what happened to it?
HON provided guidelines for reliable online health information, but it was discontinued in 2022.
What is Charting by Exception (CBE)?
A documentation method that records only abnormal or significant data, aiming to eliminate redundancy in patient records.