Optic Nerve Anomalies & Diseases
1/179
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
180 Terms
metamorphopsia
blue yellow defects
minimal difference
normal
normal
minimal to no difference
prolonged recovery
normal or central scotoma
what might you see on the following tests for early macular or retinal disease?
amsler grid
color vision
color comparison
APD
contrast sensitivity
brightness comparison
photostress test
VF
scotomas w/o metamorphopsia
red-green defects
gross differences, desaturation of all colors
+APD
decreased contrast
gross differences
normal recovery
arcuate, cecocentral, central, altitudinal
what might you see on the following tests for early optic nerve disease?
amsler grid
color vision
color comparison
APD
contrast sensitivity
brightness comparison
photostress test
VF
disc margins
neuroretinal rim
cup
NFL
vessels
mirror images of ONH (uni vs bilateral)
what are some key characteristics to look at during ONH evaluation?
persistent hyaloid artery
congenital
appearance:
short stub of vessel projecting into vitreous
may run forward to lens
single vessel, no return to disc
most are bloodless but some may still have blood
complications:
rare vitreous hemorrhage
glial tissue & glial membrane
congenital
appearance:
Bergmeister’s papilla arises from the center of the optic disc, consists of a small tuft of fibrous tissue & represents a remnant of the hyaloid artery
gray tissue/membrane may block full view of optic disc or a section
usually nasal
usually no cupping is seen
complications:
none
corkscrew prepapillary vascular loop
congenital
appearance:
aberrant development of retinal vasculature system (arterial usually but can be venous)
unilateral vessel loop arising from disc & returning to disc
extends up to 1/3 into vitreous cavity
may be partially enclosed w/ glial tissue
concurrent cilioretinal arteries in 75% of cases
complications:
must r/o acquired loops
rare BRAO/CRAO, TMB, recurrent vitreous hemorrhage, subretinal hemorrhage
myelinated retinal nerve fiber (MRNF)
congenital
incidence: 0.3-1%
males = females
oligodendrocytes sheath axons
bilateral in 8% of cases
contiguous w/ ONH in 33% of cases
associations:
myopia
strabismus
amblyopia
appearance:
retinal dense white opacification w/ soft feathered or frayed edges, fine striations following RNF, tend to fan out
isolated patches seen away from ONH in mid-periphery
size varies from ½ DD to several DDs
complications:
rarely macula is involved, but if so, decreased VA)
relative VF defect
must r/o CWS, retinal ischemia, or pale disc
papilledema is partially translucent grayish-white appearance of true edema compared to MNF w/ denser white w/ feathered edge & obscures vessels at disc margin
how do you differentiate between papilledema & MNF?
crescents of optic disc
congenital or acquired, must determine
appearance:
pigment, choroidal, or scleral
usually temporal
complications:
must r/o pathological myopia, ROP, circumpapillary atrophy, glaucoma, elderly, POHS, angioid streaks, choroiditis
posterior staphyloma
important ddx for optic disc crescents
outward protrusion of all layers of posterior globe
hallmark for pathological myopia (increased elasticity)
may occur secondary to infection or trauma
circumpapillary staphyloma
dx aided by ultrasound
appearance:
unilateral anomaly w/ normal optic nerve lying at the base of staphyloma (deep cup-shaped ectasia)
blood vessels have normal pattern
atrophy & pigment
complications:
variable effects on VA & VF
lacquer cracks & CNVM
frontonasal dysplasia
situs inversus
congenital
appearance:
temporal branches of CRA & CRV merging more nasally from disc before returning to normal temporal location
eg: OD ONH vascular pattern appears more like an OS pattern
complications:
none
may be associated w/ tilted disc syndrome
malinserted optic disc
may be tilted in any direction
most common: tilting of horizontal axis
elevation of nasal aspect w/ temporal depression
simple myopic tilted disc
possible scleral crescent
possible VFdefect
r/o causes for disc edema
tilted optic disc syndrome
tilting of vertical disc
true tilted disc syndrome
usually nasal retinal choroidal ectasia
VF defect corresponds to ectasia, possibly bitemporal
does not respect vertical meridian
r/o other causes of VF defect
appearance:
ONH exits eye at oblique angle
often bilateral
partial coloboma w/ tilting of vertical axis of disc w/ situs inversus
tilted downward & nasal, giving the disc a D shape
inferior-nasal scleral crescent & inferior nasal partial retinal choroidal staphyloma
superior temporal disc elevated
complications:
myopic & astigmatic w/ oblique axis
lacquer cracks & CNVM (rare)
pseudo-bitemporal VF defect
the defect caused by tilted disc syndrome will not respect the vertical meridian
how do you differentiate between a bitemporal hemianopsia from tilted disc syndrome or optic chiasm defects like a pituitary tumor?
optic nerve pit
aborted or incomplete coloboma
appearance:
larger than normal ONH w/ crater like defect often found in temporal margin
usually unilateral
variable size, shape, depth, & location
focal, round, oval depression associated w/ peripapillary atrophy
olive-gray to yellowish-white coloration
complications:
CSR
retinoschisis
lamellar macular holes
arcuate/papillomacular bundle VF defects correlated to location
confusion w/ NTG if central pit
blur/distortion
coloboma of ONH
etiology: incomplete closure of embryonic choroidal fissure
rare, unilateral or bilateral
appearance:
inferior portion of ONH affected w/ significant excavation & pigment hyperplasia
white bowl-shaped excavation
depth of excavation varies
larger appearing ONH w/ unusual vascular pattern
associations:
coloboma of choroid/retina, lens, iris
complications:
variable VA: normal to NLP
associated VF defects
strabismus
micro-ophthalmos
RD
NTG confusion
must r/o systemic abnormalities
coloboma, heart defects, atresia of nasal choanae, retarded growth & development, genital &/or urinary anomalies, ear anomalies & sensorineural hearing loss
what is CHARGE syndrome?
dysplasia of optic nerve
etiology: AD, rare, associated w/ mutations of PAX2 gene
papillorenal syndrome or renal syndrome
appearance:
ON excavated w/ absence or attenuation of central retinal vessels & multiple cilioretinal vessels emanating & exiting from ONH edge
VA often normal w/ superior-nasal VF Defect
morning glory syndrome
etiology: variant of ON/central coloboma, variant of ON dysplasia
very rare
usually unilateral
females > males
systemic abnormalities:
basal encephalocele
hypertelorism + wide head, flat nose, midline notch in upper lip
CNS vascular anomalies
appearance:
larger than normal ONH
funnel-shape conical excavation
irregular pigmented PPA
white glial tissue at its base
unusual vascular pattern
vessels radiate from periphery of disc
abnormally straight
increased #
difficult to differentiate arterioles from venules
complications:
VA may be normal but often worse than 20/200
associated VF defects & severe decreased VA
r/o systemic abnormalities w/ neurological consult
at risk for non-rhegmatogenous RD
congenitally full disc (crowded optic disc)
result of a normal # of RGC axons passing through a small posterior scleral foramen
associations:
hyperopia
short axial legnth
optic disc elongation
optic atrophy
bilateral choroidal folds
2:1 to 3:2
what is a normal DM/DD?
>3.0
a DM/DD of _____ is optic nerve hypoplasia & correlates w/ poor visual outcomes
<2.0
a DM/DD of ____ is a large optic nerve
age
what needs to be considered when evaluating the DD/DM ratio?
increases
the DD/DM ratio _____ with age
decreases
the DM/DD ratio ____ with age
greater than or equal to 0.26
in premature infants, a normal DD/DM ratio is reported as ____ at birth
optic nerve hypoplasia
congenital
non-progressive
unilateral or bilateral
associations:
if unilateral, 50% w/ strabismus
if unilateral, may have RAPD
nystagmus if bilateral & poor VA
present in 50% of FAS & other gestational drug toxicities
septo-optic dysplasia
etiology: developmental defect: toxic, infectious, ischemia, or idiopathic
characteristics:
VA varies from 20/20 to NLP
VF defects vary
small disc (1/2 the size of normal), somewhat pale & dirty
dysplasia of RNF w/ decreased # of axons in ONH
double pigment ring sign
septo-optic dysplasia
rare
congenital defect during embryological development
optic nerve hypoplasia
absence of septum pellucidum, corpus callosum
hypopituitarism: GH deficiency → short stature
seizures
systemic work up
careful documentation
pt education
polycarbonate lenses
megalopapilla
congenitally larger than normal ONH
unilateral
otherwise normal in appearance
vessels may falsely appear narrow
DM/DD ratio less than or equal to 2.1
non-progressive
less
larger disc diameter = _____ distance to the fovea
less than or equal to 2:1
what is the DM/DD ratio in megalopapilla?
optic disc drusen
AD irregular pattern w/ incomplete penetrance
bilateral in 75-86% of cases, may be asymptomatic
occurs in 1% of the population
primarily found in whites
males = females
may be associated w/ RP & pseudoxanthoma elasticum
appearance:
buried in youth, elevated disc
irregular, superficial, transilluminate as glistening, yellowish, waxy calcifications by 2nd-3rd decade
drusen become more visible as they enlarge and move to surface
usually nasal, occasionally w/in adjacent RNFL
no hyperemia or dilation of surface microvasculature
complications:
usually asymptoamtic
VA rarely affected
VF loss
vascular complications: rare flame-shaped disc hemorrhages, AION, juxtapapillary choroidal neovascularization
no
are optic disc drusen & retinal drusen associated?
hyaline or colloid bodies of the ONH
calcified globular deposits anterior to the lamina cribosa that become more apparent w/ age
impaired RGC axonal transport → mitochondrial damage → axons deteriorate → material congeals & calcifies → axonal death
describe the pathophysiology of optic disc drusen
high reflectivity of drusen, posterior acoustic shadowing w/ larger lesions
how do optic disc drusen appear on B scan?
high reflectivity at junction of globe & optic nerve, size 1-4mm in diameter & up to 3mm thick
how do optic disc drusen appear on CT?
CT
what is a good test for determining of optic disc drusen are calcified?
round/oval hyper-autofluorescence w/ irregular edges
how do optic disc drusen appear on fundus autofluorescence?
autofluorescence present prior to injection, early & late nodular staining of the disc, hyper fluorescence w/o leakage, late circumferential peripapillary staining
how do optic disc drusen appear on fluorescein angiography?
elevated nerve head w/ underlying nodular shadowing & normal or thinner RNFL
how do optic disc drusen appear on OCT?
baseline VF
routine yearly exams
consider possibilities of systemic issues
disc is more susceptible to elevated IOP or AION so important to watch out for
how is optic disc drusen managed?
pseudo-papilledema
apparent disc swelling that simulates some of the features of papilledema
secondary to an underlying, usually benign, process
causes:
buried disc drusen
tilted or malinserted optic disc
crowded optic disc
optic nerve hypoplasia
myelination
hyaloid remnants
peripapillary hyperreflective ovoid mass-like structures (PHOMS)
hyperreflective, ovoid-shaped localized mass above & adjacent to Bruch’s membrane opening
common but nonspecific OCT marker of axoplasmic stasis in ONH
associations:
ODD
tilted disc
papilledema
NA-AION
CRVO
acute demyelinating optic neuritis
melanocytoma
benign primary tumor of ON
arise from dendritic melanocytes & can occur anywhere w/in the uveal tract, conjunctiva, & sclera
females > males
mean age: 50y
no apparent hereditary pattern or racial predilection
growth can occur over 5-20y w/ very low potential for malignant transformation
appearance:
elevated gray to black lesion
usually involved less than or 50% of the disc
may grow beyond borders of disc & involve juxtapapillary NFL
feathery or flayed edges similar to MNF
may involve juxtapapillary choroid
may have associated RPE degeneration
complications:
most eyes maintain good VA
optic disc edema
sheathing of retinal vessels
sub-retinal edema
enlarged blind spot & possibly other RNFL VF defects
RAPD
hypofluorescence due to blockage of choroidal fluorescence by polyhedral pigment cells
how does melanocytoma appear on FA?
hyperfluorescence due to increased vascularity
how does melanoma appear on FA?
hypofluorescence of tumor, iro-fluorescence of remaining retina
how does melanocytoma appear on funus autofluorescence?
dx and photo documentation
f/u every 3mo initially, then every year
if growth is noted, immediately refer to retinal oncologist
how do you manage melanocytoma?
increased thickness, presence of intrinsic vascularization & nodular
what are the risk factors for malignancy for a melanocytoma?
malignant transformation or ischemic necrosis
rapid enlargement of a melanocytoma can indicate:
2
malignant transformation of a melanocytoma occurs in __% of cases
astrocytic hamartoma
congenital abnormality of astrocytes in ON & NFL
benign, non-metastasizing but may grow associated & coincident w/ growth patterns
can appear anywhere in retina but tend to be on or near disc
unilateral or bilateral
associations:
tuberous sclerosis
neurofibromatosis
appearance:
Mulberry lesions
variable size & presentation
solitary or multifocal
non-calcified or calcified
complications:
decreased vision
VF defects secondary to optic nerve compression
dx:
B-scan, FA, neuro-imaging
systemic workup
non-calcified astrocytic hamartoma
astrocytic hamartoma type
dirty white, flat, oval lesion w/ relatively smooth surface
translucent or semi-translucent
may have associated RPE changes near the lesion that resemble CHRPE
may be germinative stage of the tumor
calcified astrocytic hamartoma
astrocytic hamartoma type
whitish-yellow, elevated, multi-lobulated, mulberry lesion
non-progressive
may glisten
may be an aged version of the smooth type of lesion
astrocytic hamartoma arise in inner retinal layers & typically obscure retinal vessels, may auto-fluoresce if calcified, highly vascularized that hyperfluoresce in all FA stages
how do you differentiate astrocytic hamartoma & optic disc drusen?
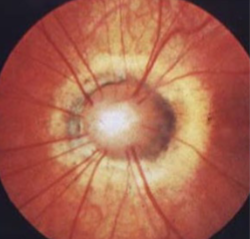
persistent hyaloid artery
persistent hyaloid artery
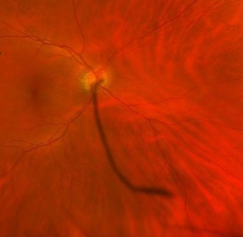
persistent hyaloid artery
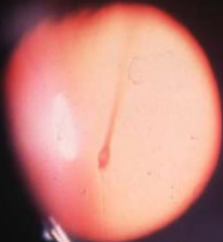
glial tissue
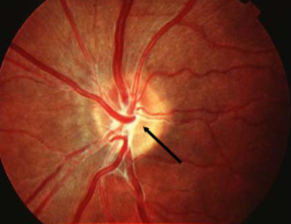
glial tissue
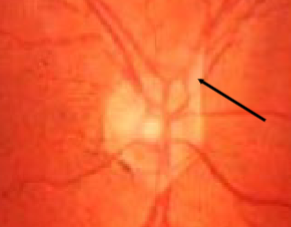
glial tissue
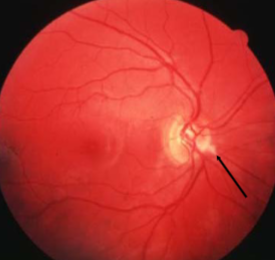
corkscrew prepapillary vascular loop
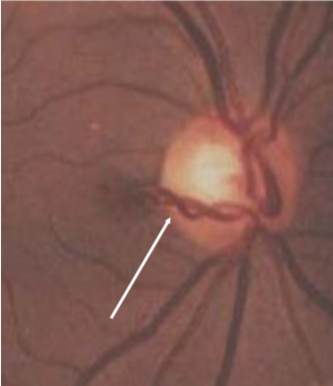
MNF
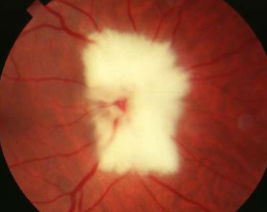
MNF
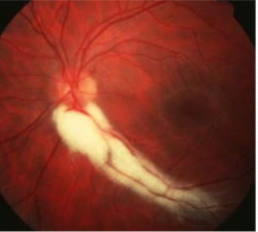
MNF
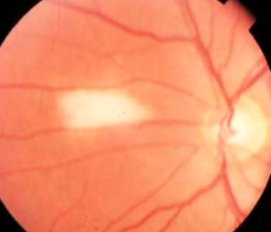
MNF
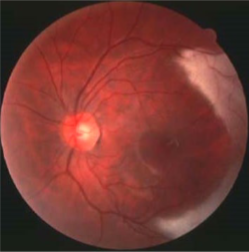
MNF

pigment crescent
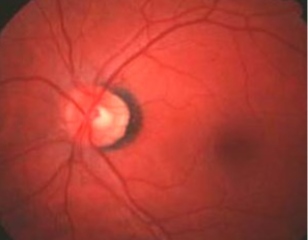
scleral crescent
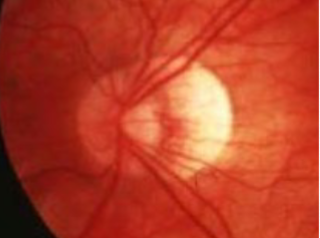
PPA w/ POHS
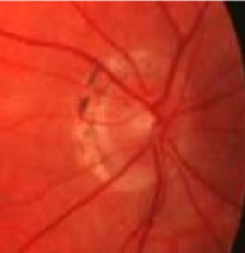
pathological myopia

posterior staphyloma
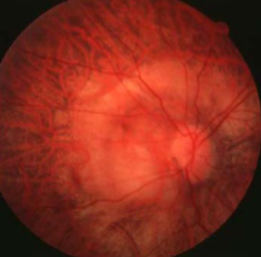
posterior staphyloma
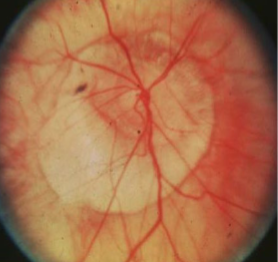
circumpapillary staphyloma

circumpapillary staphyloma
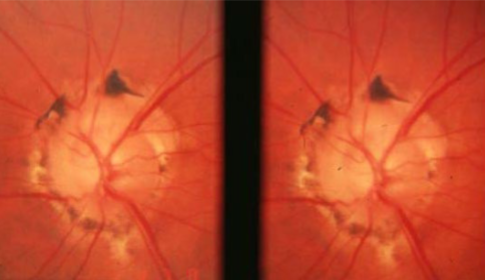
myopic disc w/ posterior staphyloma
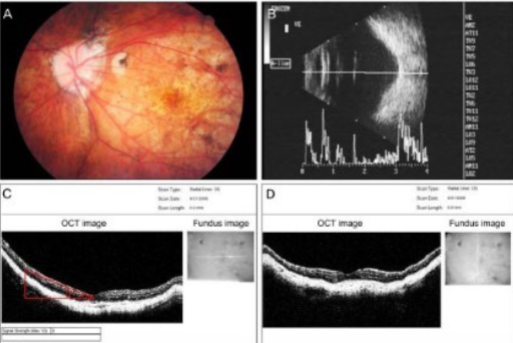
situs inversus
situs inversus
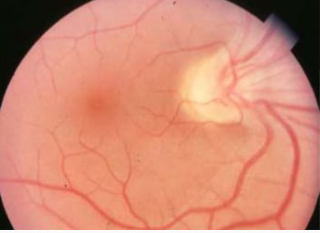
situs inversus
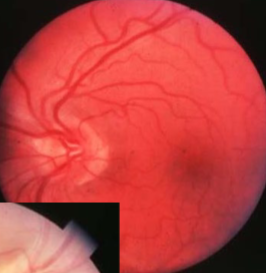
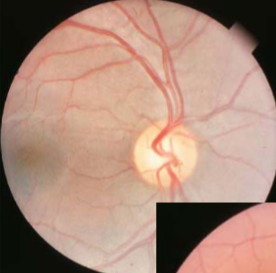
malinserted disc
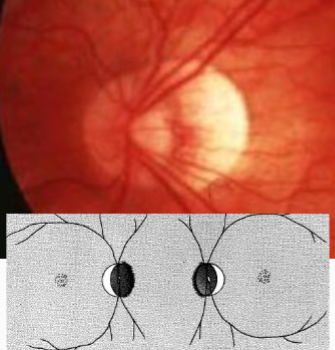
tilted disc
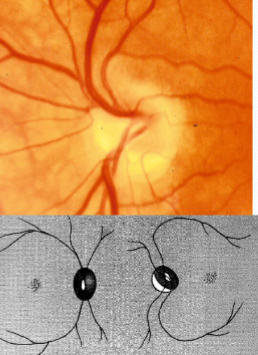
tilted disc
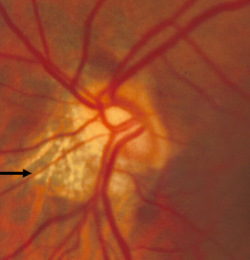
tilted disc
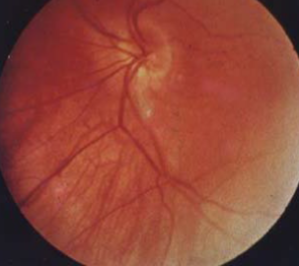
pseudo-bitemporal VF defect
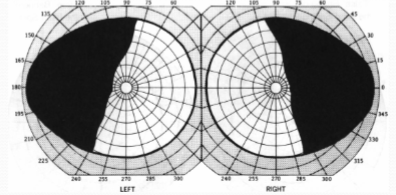
tilted optic disc syndrome w/ situs inversus
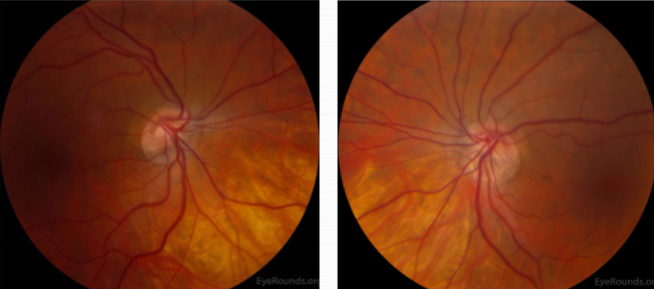
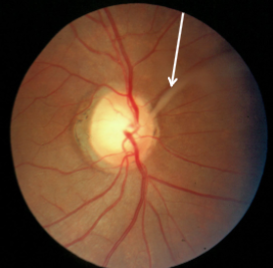
optic nerve pit
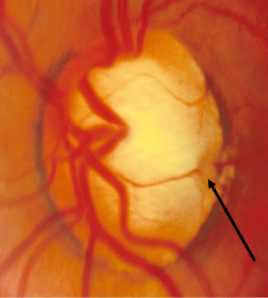
optic nerve pit
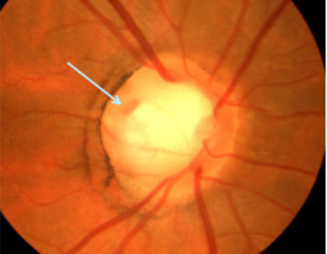
optic nerve pit
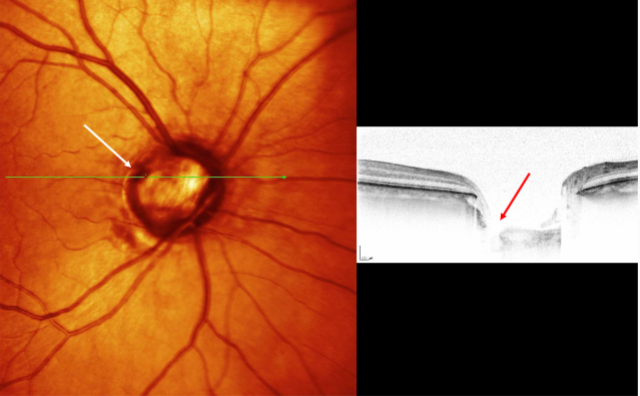
optic nerve pit
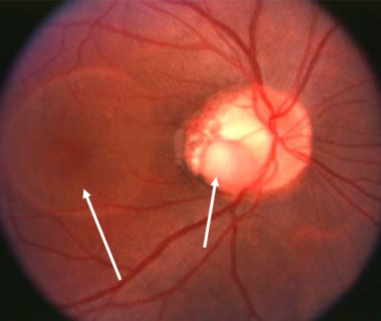
optic nerve pit & retinoschisis

optic nerve pit
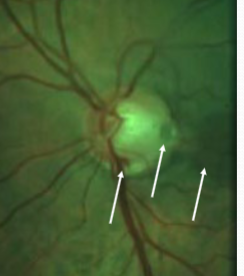
coloboma of ONH
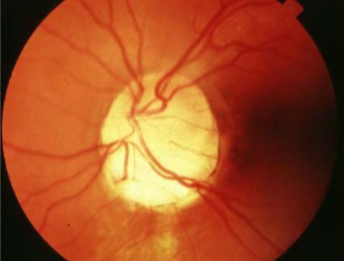
coloboma of ONH
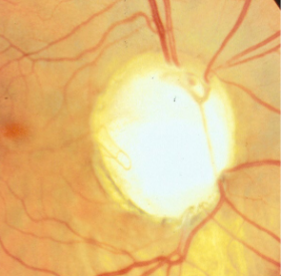
ONH coloboma
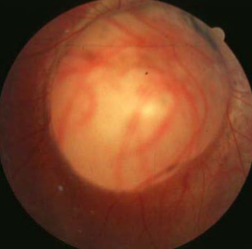
retinochoroidal & ONH coloboma

bridge coloboma
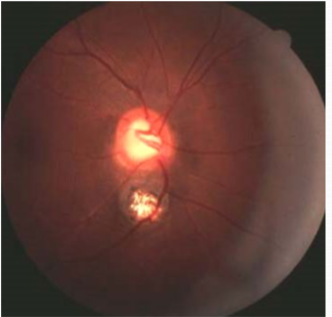
bridge coloboma
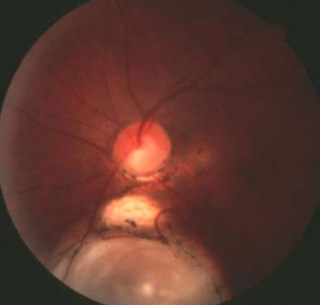
morning glory syndrome