1. States of Matter GCSE
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
bonding for each state
☯ solid: strong
☯ liquid: weaker than solids
☯ gas: weak
arrangement for each state
☯ solid: regular
☯ liquid: random
☯ gas: random
shape of each state
☯ solid: stays the same shape
☯ liquid: takes the shape of its container
☯ gas: spreads to fill container
ability to compress each state
☯ solid: hard to compress
☯ liquid: hard to compress but might change shape
☯ gas: easy to compress
movement for each state
☯ solid: cannot move. only vibrates
☯ liquid: moves and flows easily
☯ gas: moves and flows easily, bounces off walls of container or each other
particle energy for each state
☯ solid: very little energy
☯ liquid: some energy
☯ gas: lots of energy
why is it easy to compress a gas and not a liquid or solid?
gases have more space between their particles and are easier to compress. solids and liquids don't have enough space between their particles for compression to happen.
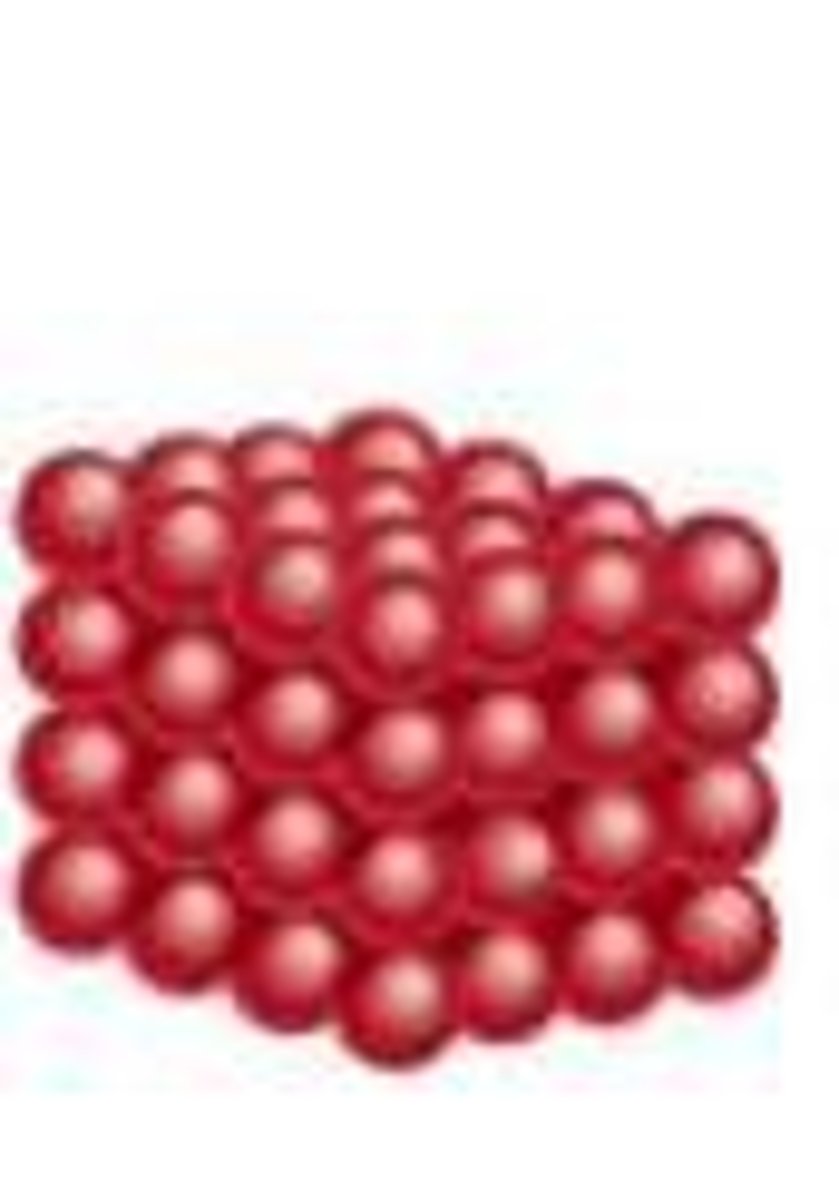
particle arrangement for a solid
tightly packed lattice structure

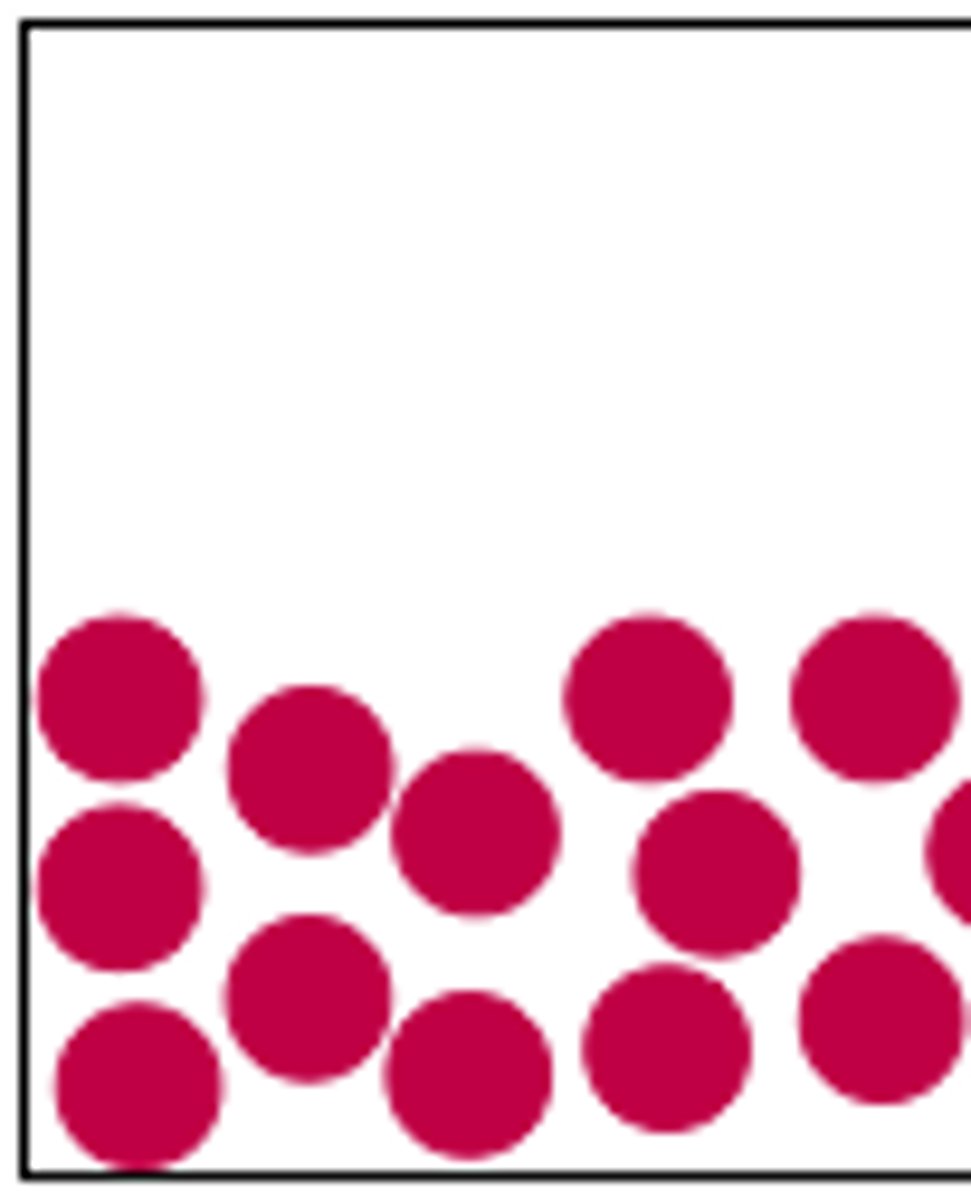
particle arrangement for a liquid
regular but not as tightly packed as a solid

particle arrangement for a gas
lots of space between particles which float and bounce off surfaces
solid to liquid
melting
liquid to gas
boiling and/or evaporation
gas to liquid
condensation
liquid to solid
freezing (or) solidification
solid to gas
sublimation
diffusion
the random movement of particles from a high concentration to a low concentration
speed of diffusion (fastest to slowest)
☯ gas
☯ liquid
☯ solid(cannot diffuse because the particles can only vibrate)
why is the white ring closer to the HCl?
ammonia is lighter than the hydrogen chloride and so, moves faster to form the white solid ring of ammonium chloride(NH₄Cl) closer to the hydrogen chloride
why does the solid ring not appear immediately?
air particles collide with the gas particles, slowing both NH₃ and HCl particles down.
what speed does gas travel at? (not essential)
500 m/s
boiling/evaporation (temperature difference)
boiling can only happen when a liquid is heated strongly.
evaporation can happen at any temperature.
boiling/evaporation (particles escaping)
boiling: many particles move fast enough to break all forces of attraction.
evaporation: some faster particles escape from the surface of the liquid to form a gas.
boiling/evaporation (bubbles)
boiling: yes
evaporation: no
melting and boiling point are below 25°C
gas
melting and boiling point are more than 25°C
solid
melting point is below 25, boiling point is more than 25
liquid