OCR GSCE Computing - Networks
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Network
A collections of computers and other hardware that has been connected together in order to allow communication and sharing of resources. Networks allow software to be installed and controlled across the network from a single computer.
LAN
Local Area Network - occupy an office
WAN
Wide Area Network - largest of which is the Internet
Advantages of Networks
Communication - email and the transferring of files is possible.
Sharing of resources - files on one computer can be accessed by another, multiple computers can share one printer, and within a LAN a connection to the Internet can be shared.
Network management - you can log onto any computer in a LAN and access all your files.
Router
Allows communication between a LAN and the Internet.
Hub
A device which lots of computers can be connected, usually with Ethernet cables. Computers connected can communicate with one another.
Switch
Performs the same job as a hub, but learns the locations of the computers and other devices plugged into it. Makes the network more efficient as fewer signals travel down the wrong cable.
Wireless Access Point
Any device that allows connection to the network without any cables.
Network Interface Card
Each computer added to a network must have these.
Client-Server Model
The server holds all the files. The clients request files from the server. Server also controls all security. If server is offline, all files cannot be accessed.
Peer-to-Peer Model
All computers have equal standing. They all store files and any peer can transmit a file to another peer. This is less secure than C-S. If one computer is offline, then the files could possibly be on another computer.
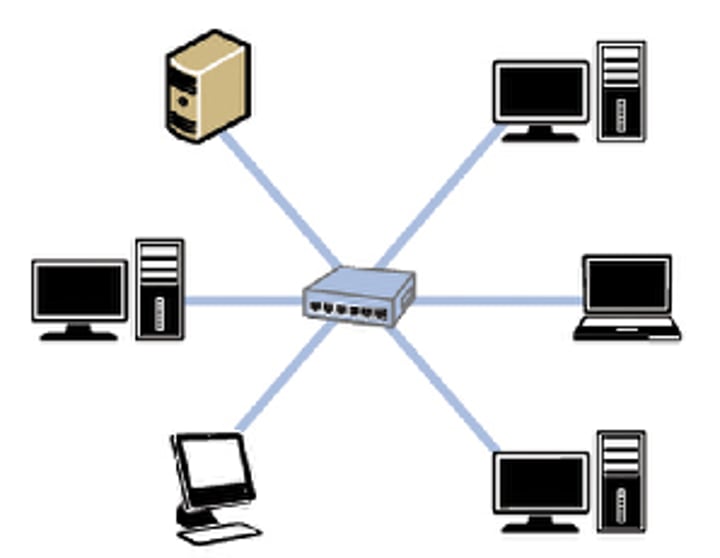
Star
All devices connected to central server or hub. All communication goes through central device. Faults are easy to find, system is secure. Lots of cables so more expensive.
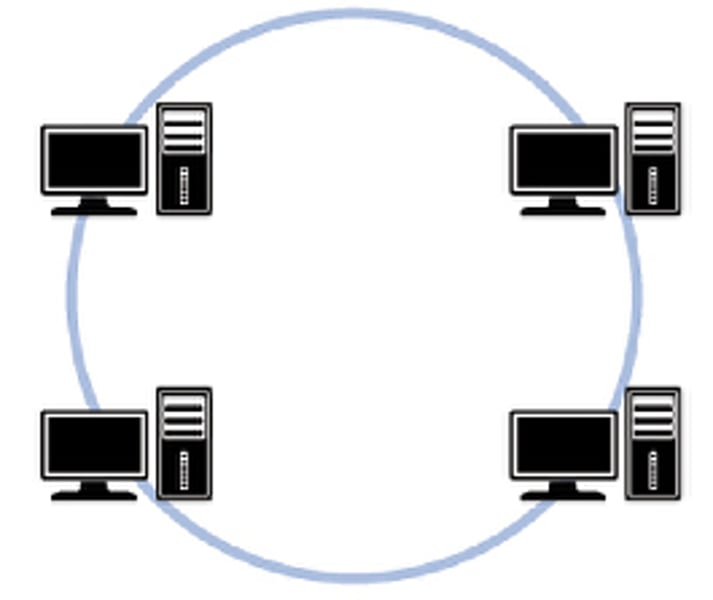
Ring
Each device is connected to 2 other devices. To communicate with a particular device, a signal has to pass through several other devices. No data collisions, high rates of transfer possible. Failure of single cable/device can break down network.
Internet Protocol (IP) Address
A unique number given to each device on a network.
Each website has its own IP address. Website > DNS > IP ADDRESS > allows access
Media Access Control (MAC) Address
A unique number, hard-wired into a device and cannot be changed. 12-digit hex number.
Packet
How data is sent across a network. Data is broken into small chunks. Header includes source address and destination of packet, as well as identification number to reassemble data. The packets do not need to take the same route or arrive in the same order that they left. If one packet is not delivered correctly, only that packet need to be re-sent, not all the data.
Protocol
A set of rules that computers must follow in order for communication to be successful.
HTTP - rules on how hypertext is moved around the Internet.
POP3 - accessing emails.
SMTP - used to send emails from one server to another.
FTP - how files are moved from one computer to another across the Internet.
Passwords
If you don't know the password, you can't access the computer.
User Access Levels
Passwords are tied to usernames. Different users can access different things. User have certain privileges on the network.
Encryption
Turn readable data into unreadable data. To decrypt data, the encryption key is needed.
Acceptable Use
Sets down what users are permitted to do on a network. Whether they can play games or access certain websites. What personal data should be entered. What punishments the user receives for violating the rules.
Backup
States what data will be backed up from the network, how often and where it will be stored.
The Internet
A worldwide network containing millions of computers and related hardware. To connect to the Internet, you need a router. If you are connecting to a communication line that does not work with digital signals you need a modem - converts digital to analogue.
HTML
Websites on the Internet are written with this. Used to tell a browser how to display each web page. It is an industry standard so different browsers display web pages in the same way. The capabilities of HTML increase with each version.
Compression
Files made smaller so they can be transmitted over a shorter time.
Lossless
File made smaller but all data is stored so when uncompressed the file will be exactly the same. PNG. GIF.