[HISTOLOGY SLIDES] Cartilage and Bone (Laboratory)
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Fibrocartilage; intervertebral disc, articular disc, glenoid and acetabular labra
What type of cartilage is in the image? Where is this specific type of cartilage found?
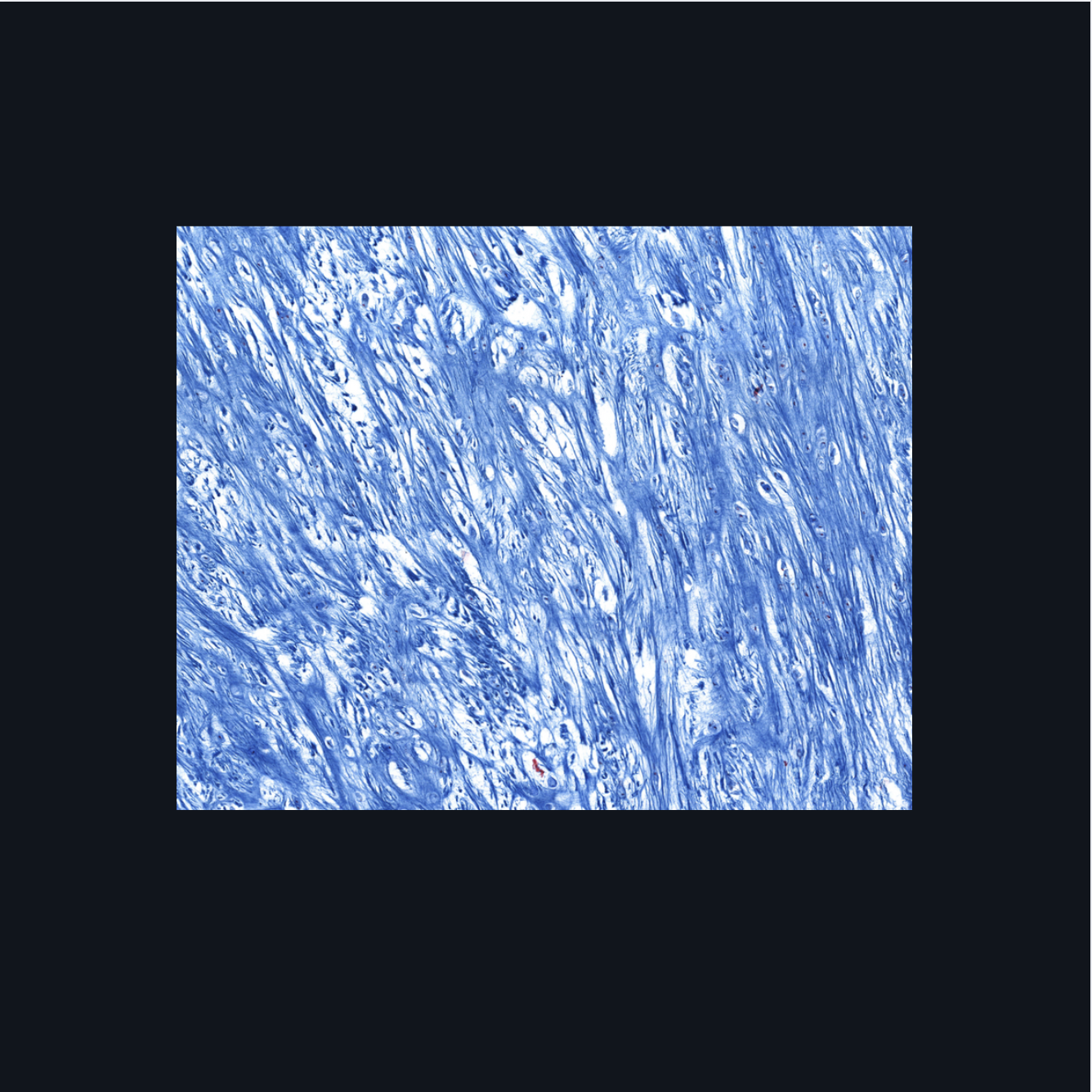
Collagen fibers
This type of cartilage is abundant in what fibers?
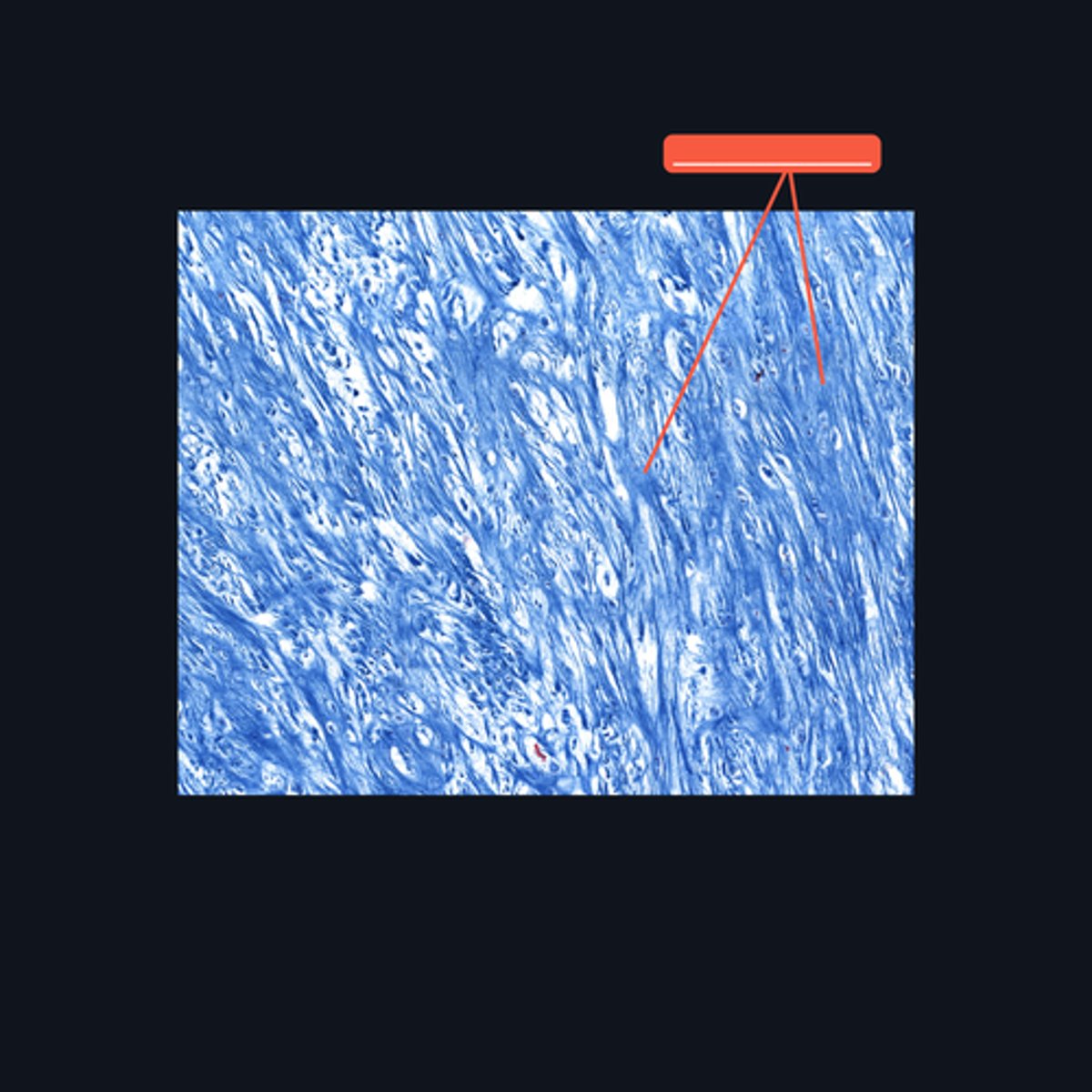
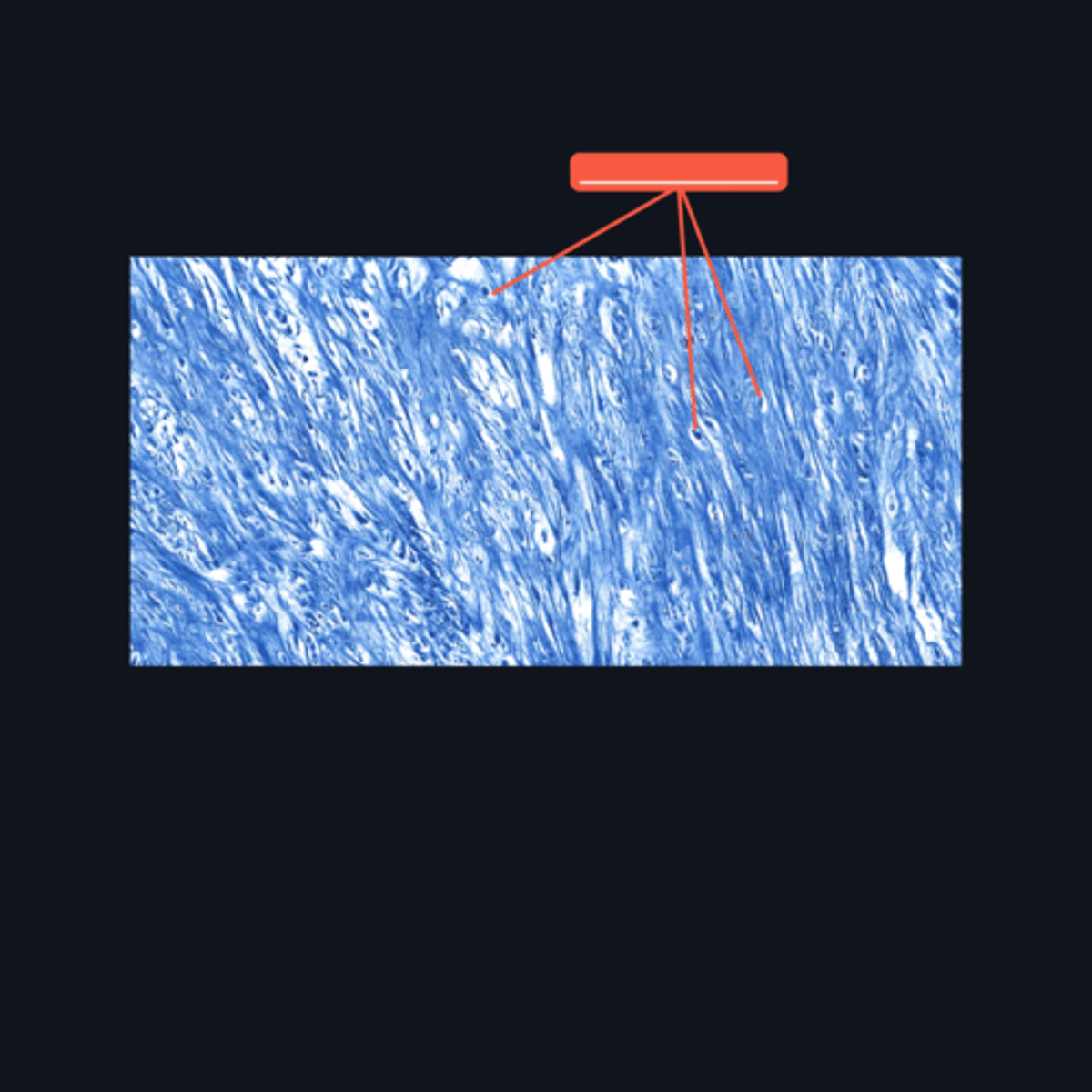
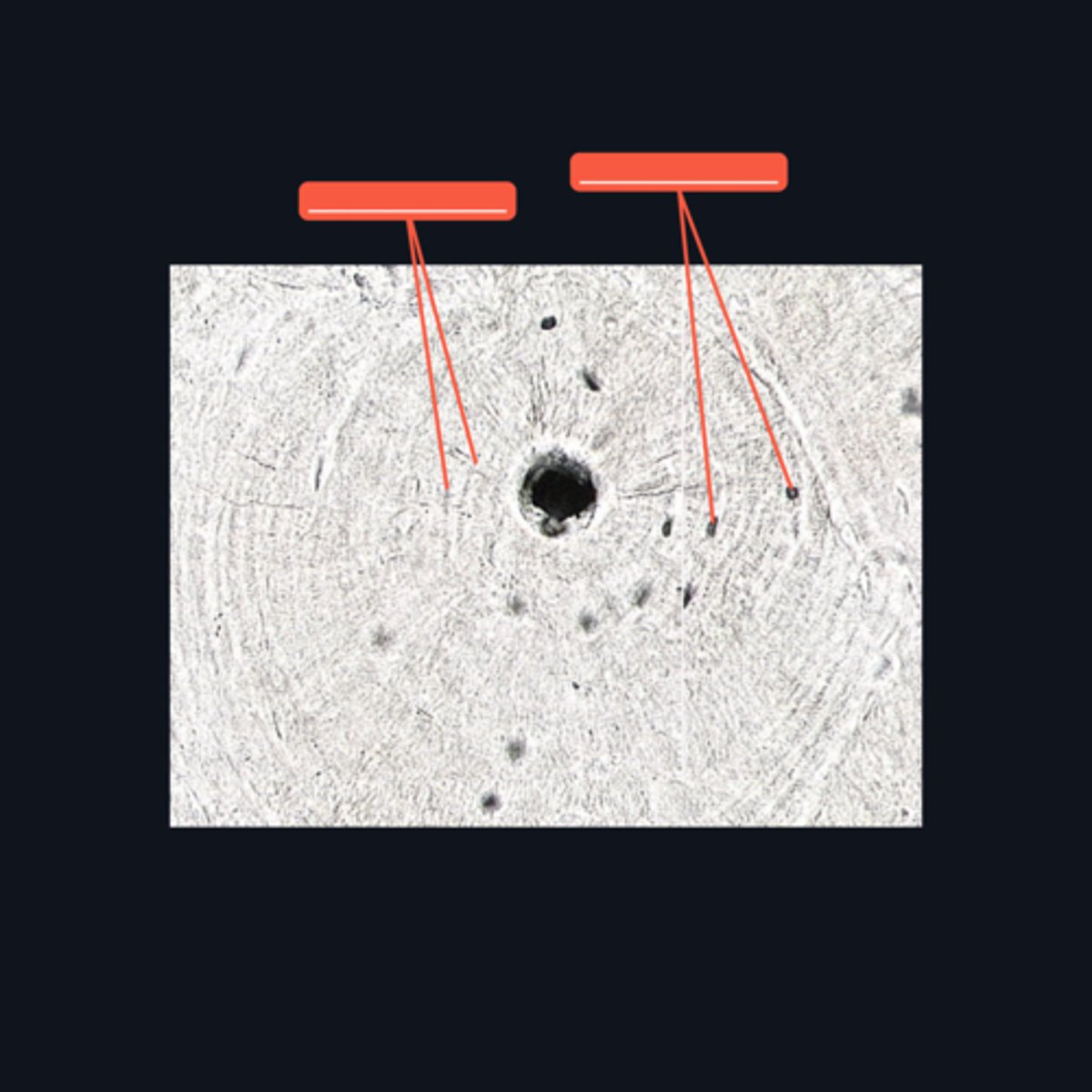
Dense regular connective tissue; chondrocytes; lacunae
This cartilage is commonly mistaken as _____. However, when examined closely, _____are contained in _____ (identify pointed structures), making it a cartilage.
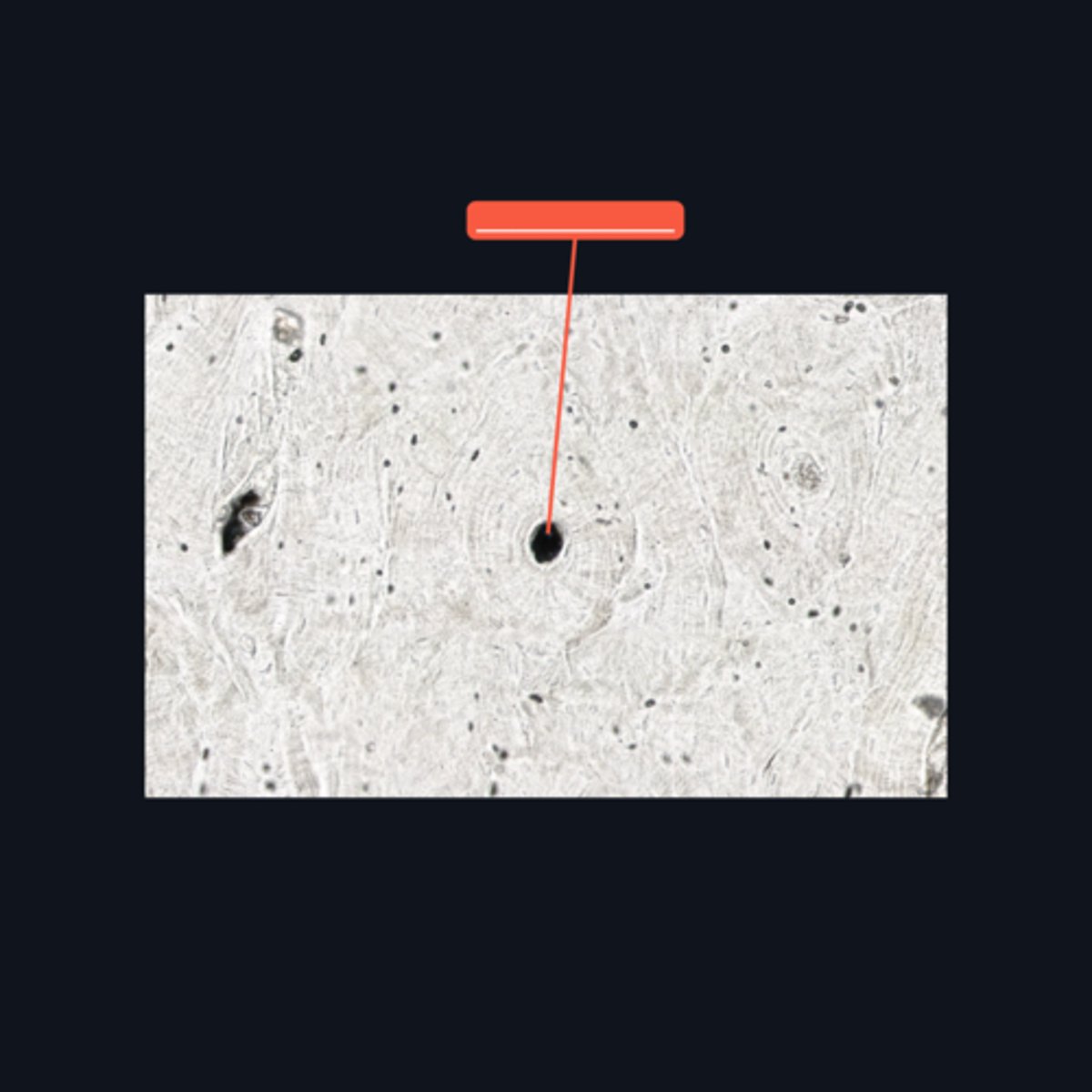
Haversian canal or Canal of Havers
It refers to a longitudinal channel where most of the bone lamellae and their associated osteocytes and lacunae are concentrically arranged

Haversian system or Osteons
This makes up the bulk of compact bone. It consists of several (4-20) bony lamellae with their associated lacunae and osteocytes
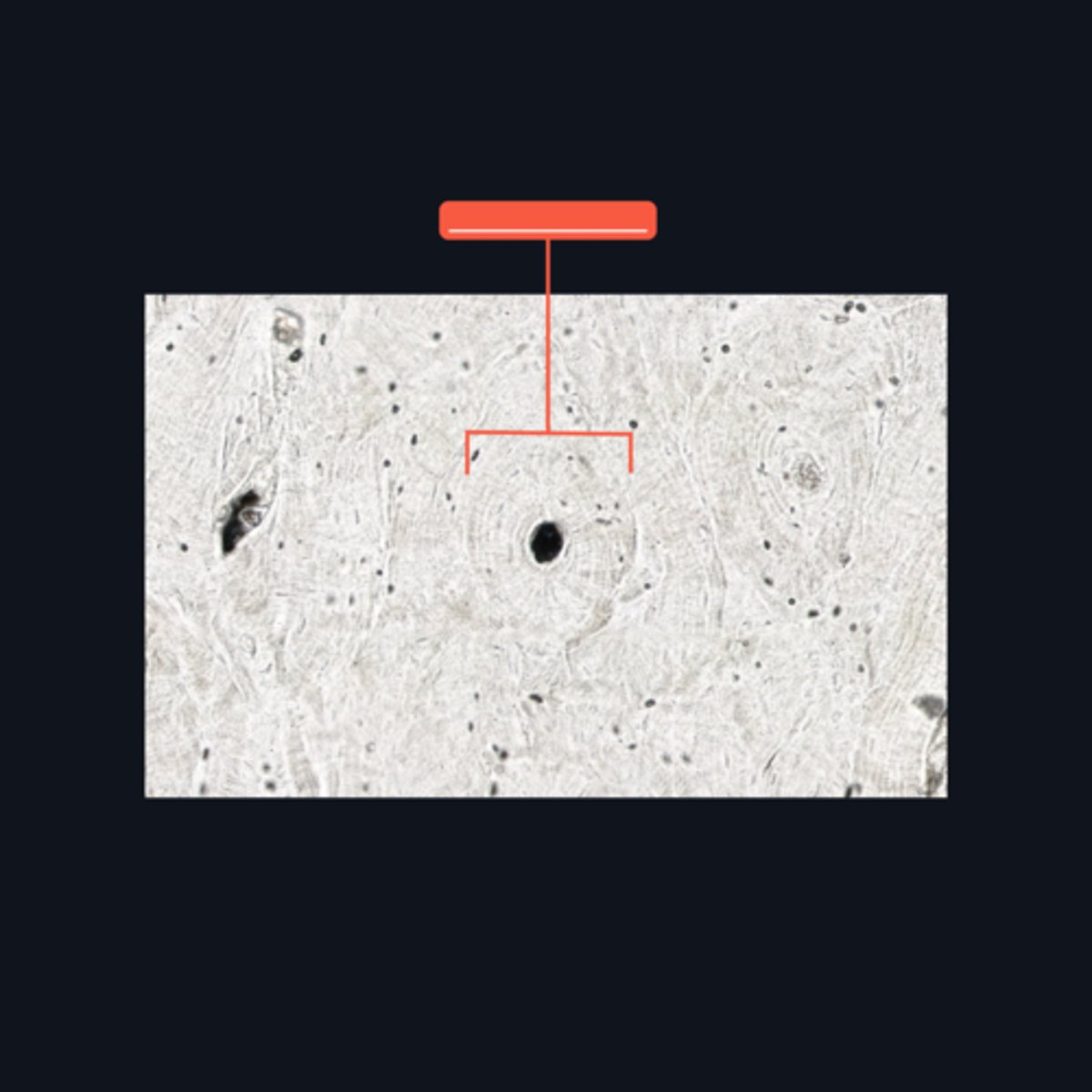
Bony lamellae and Lacunae
These are structures found at the ground bone which are concentrically arranged around the Haversian canal
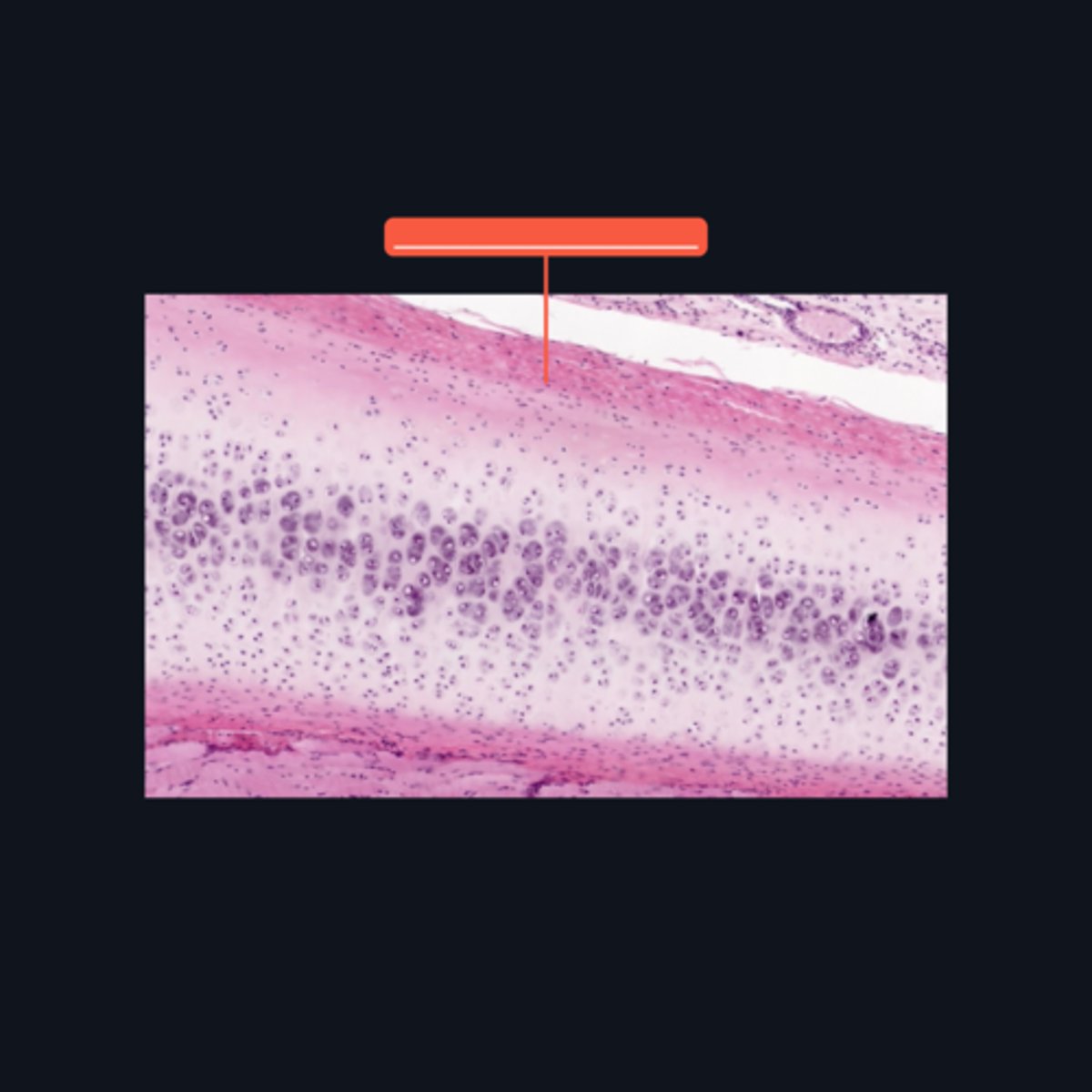
Hyaline cartilage
What structure is the presented? This is the most common type of cartilage in the body.
Type II Collagen
What type of extracellular fibers are present in hyaline cartilage?

Hyaline cartilage; joints, ends of sternal ribs, ligaments, tendons and respiratory tract.
In an adult body, ______ is found in the following locations (5) ___________.
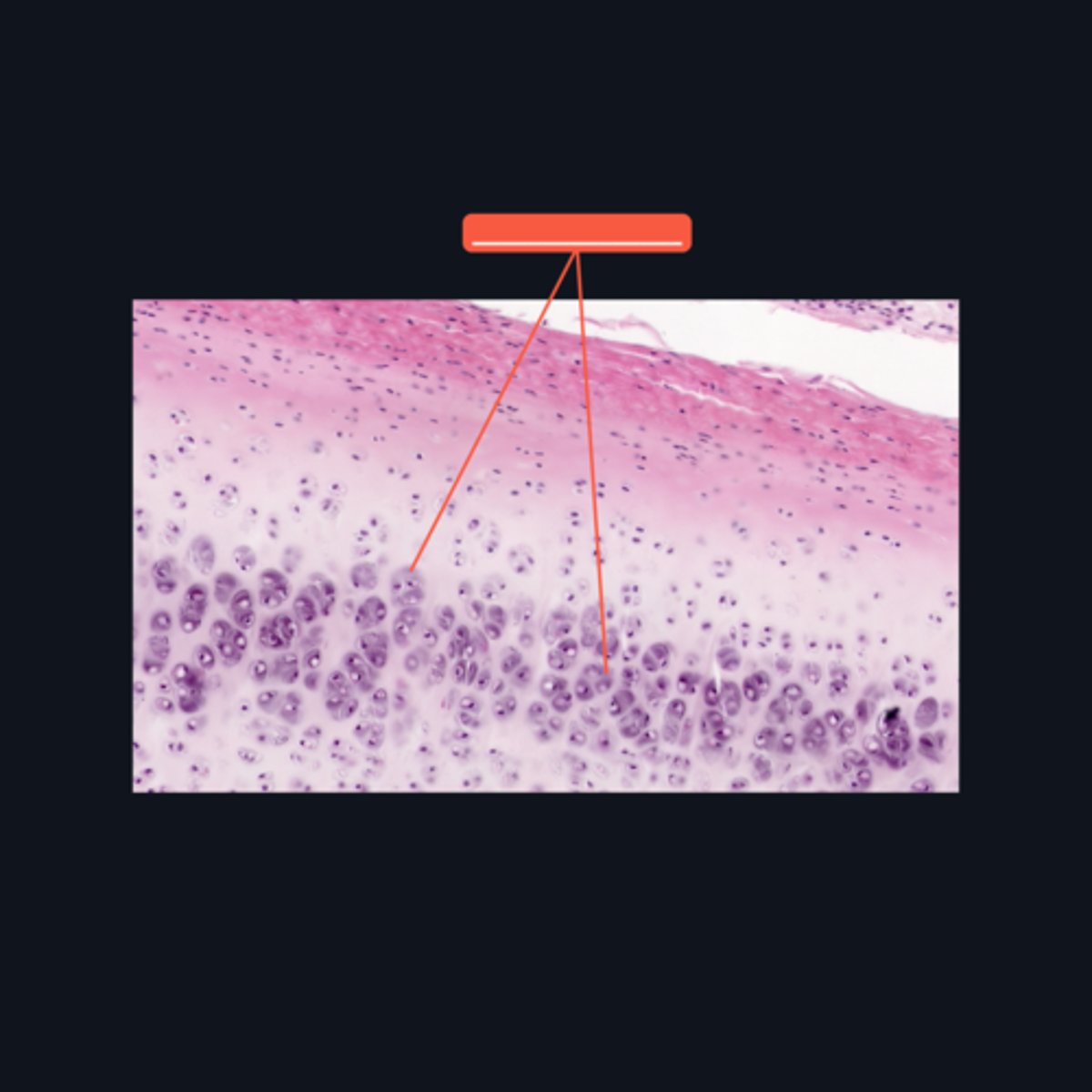
Lacunae
In what structure can we locate a chondrocyte?
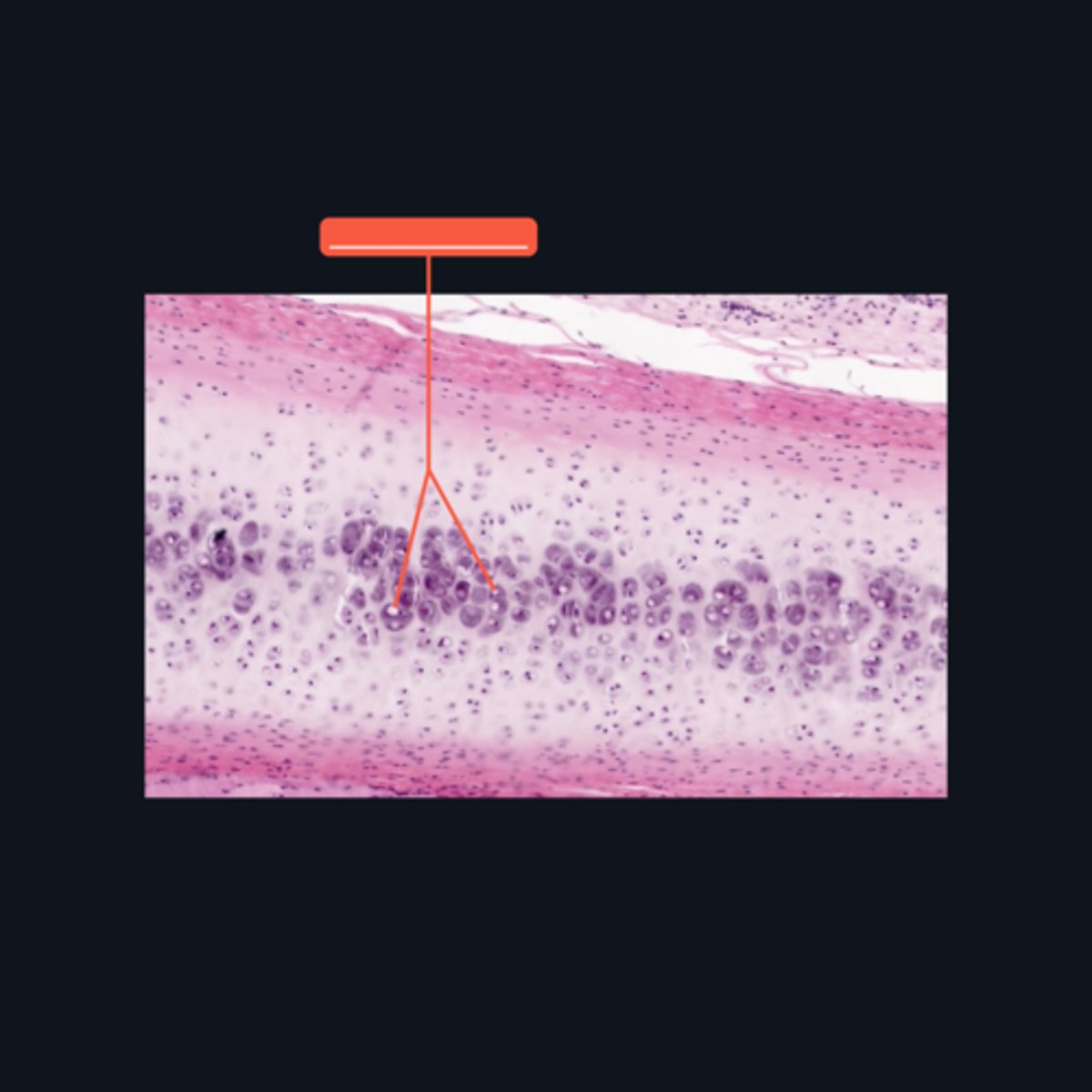
Cell nests
The chondrocytes in the central area of the cartilage form clusters, which are sometimes referred to as ________?
Chondronectin
In the ground substance of cartilage, what is the name of the fibronectin-like substance that promotes the adherence of collagen fibers to the cell surface of the chondrocyte?
Proteoglycans
Apart from water, the ground substance of hyaline cartilage is mostly made up of ____________.
Territorial Matrix; Glycosaminoglycans (GAG)
What do you call the intercellular substance that immediately surrounds the lacuna? This area is intensely basophilic because it is particularly rich in ___________.
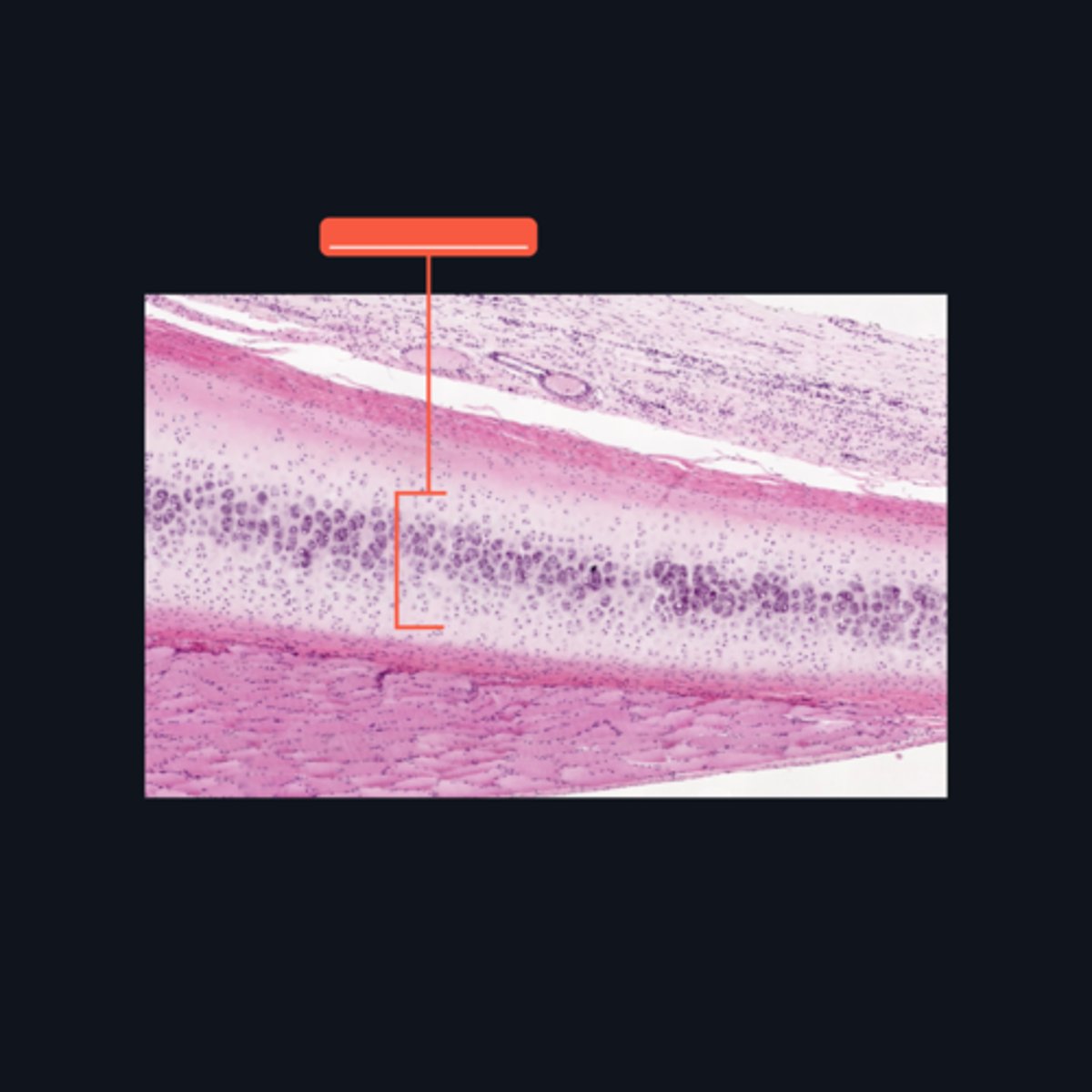
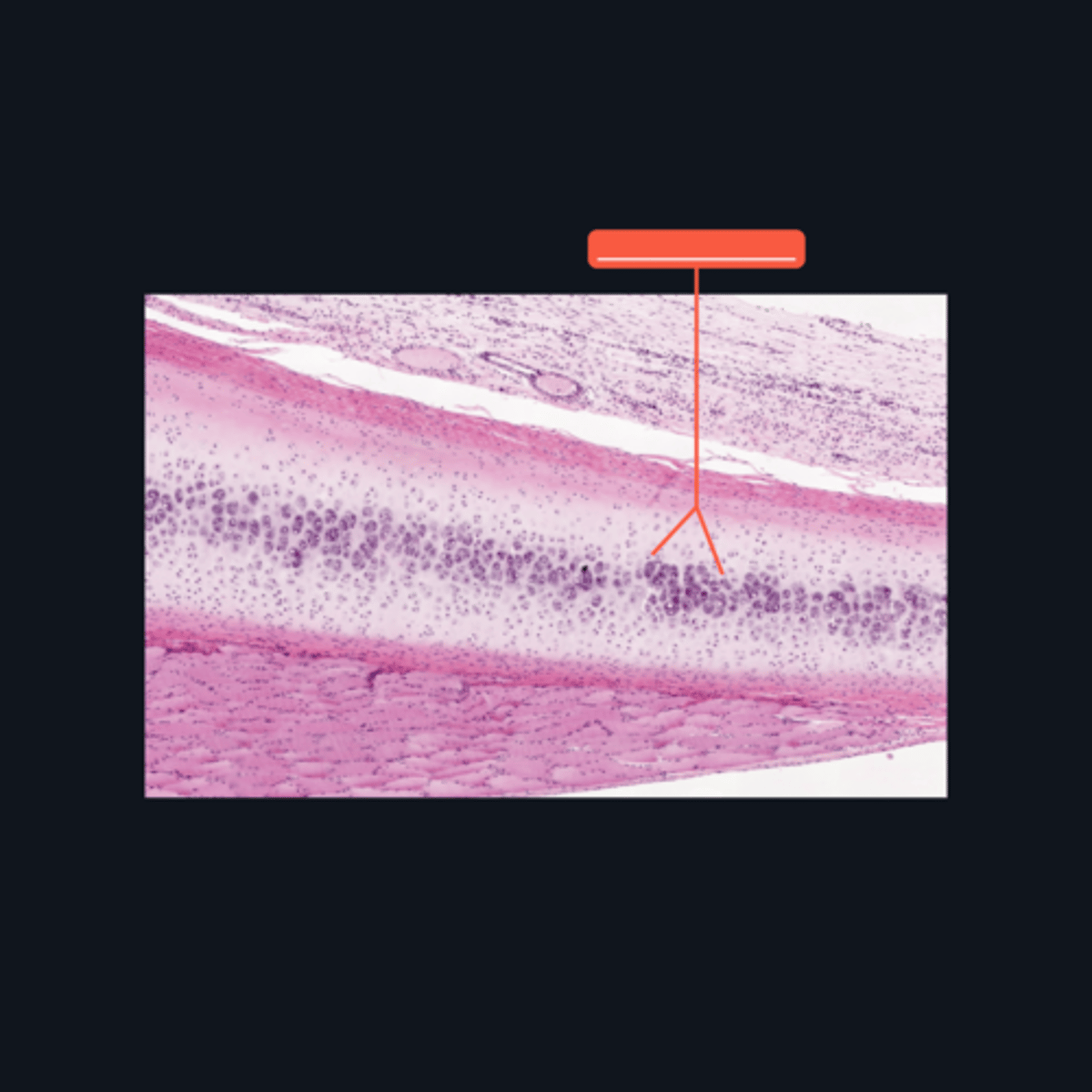
Elastic Cartilage
What type of cartilage is found in the auditory tube and epiglottis?
Type II Collagen
What type of extracellular fibers make up the elastic cartilage?
Black Streaks
When stained with orcein, elastic fibers characteristically appear like _____ in the matrix.
Diaphysis
In long bones, endochondral ossification start in the central region of the _________

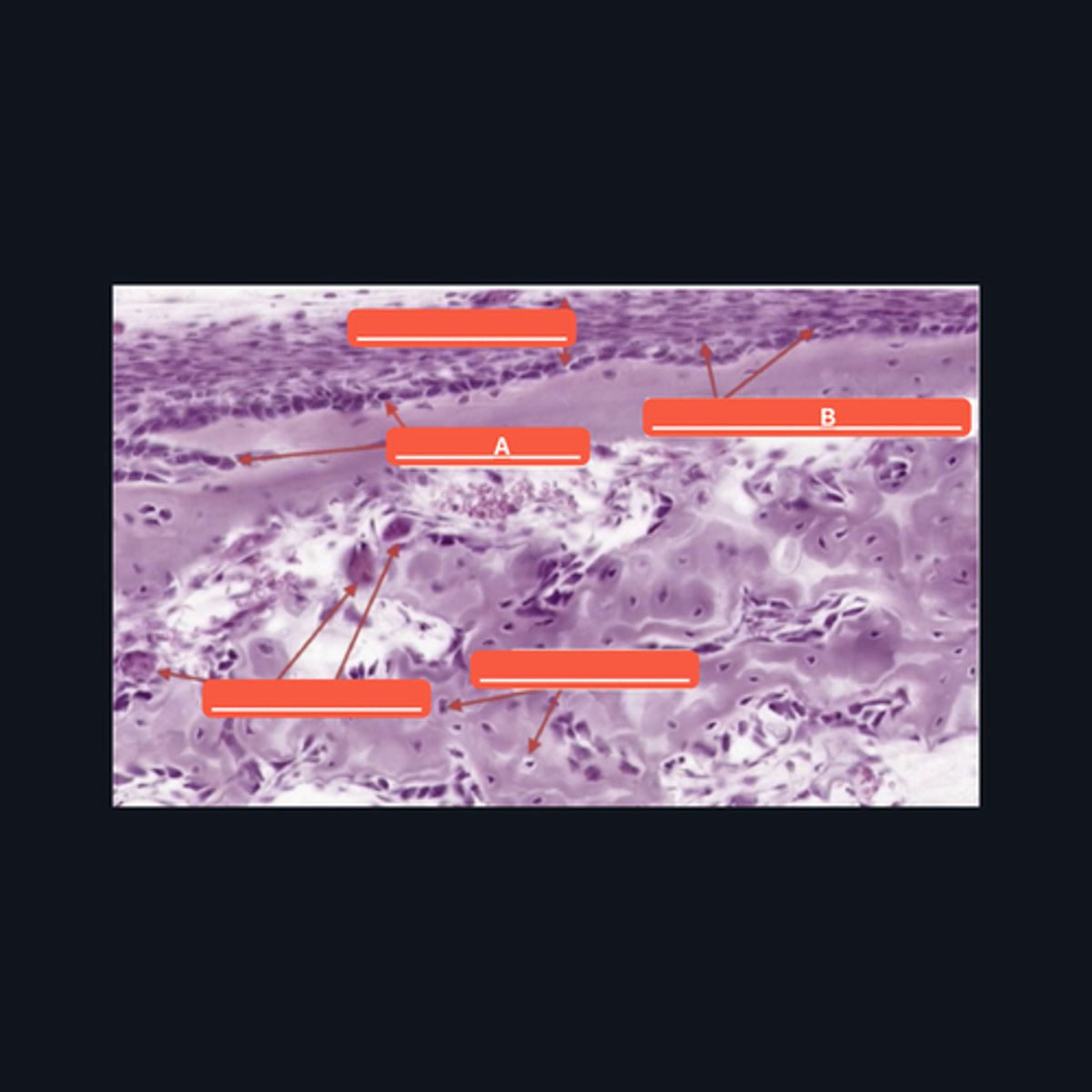
Osteoblast
Identify structure A
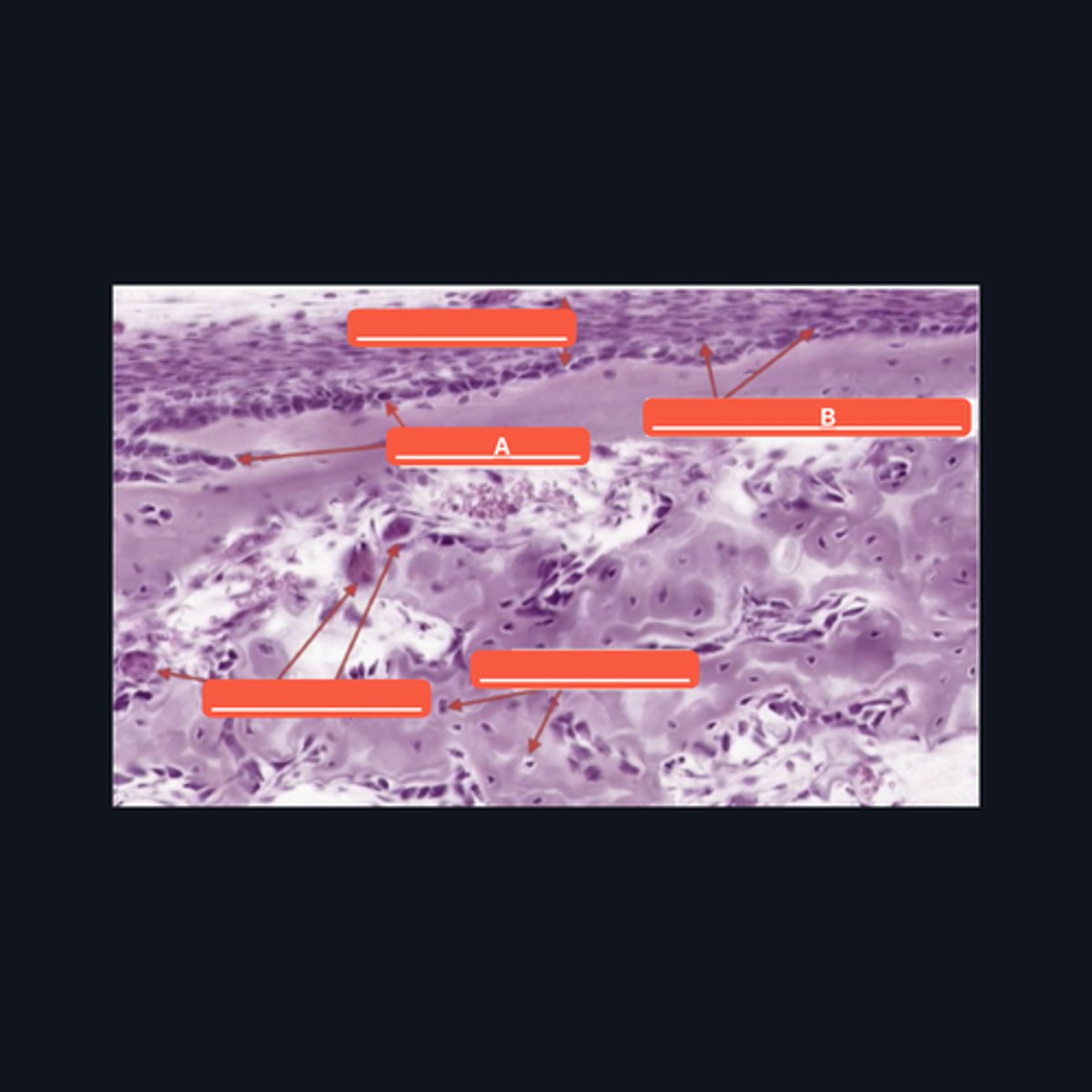
Osteoprogenitor cells
Identify structure B
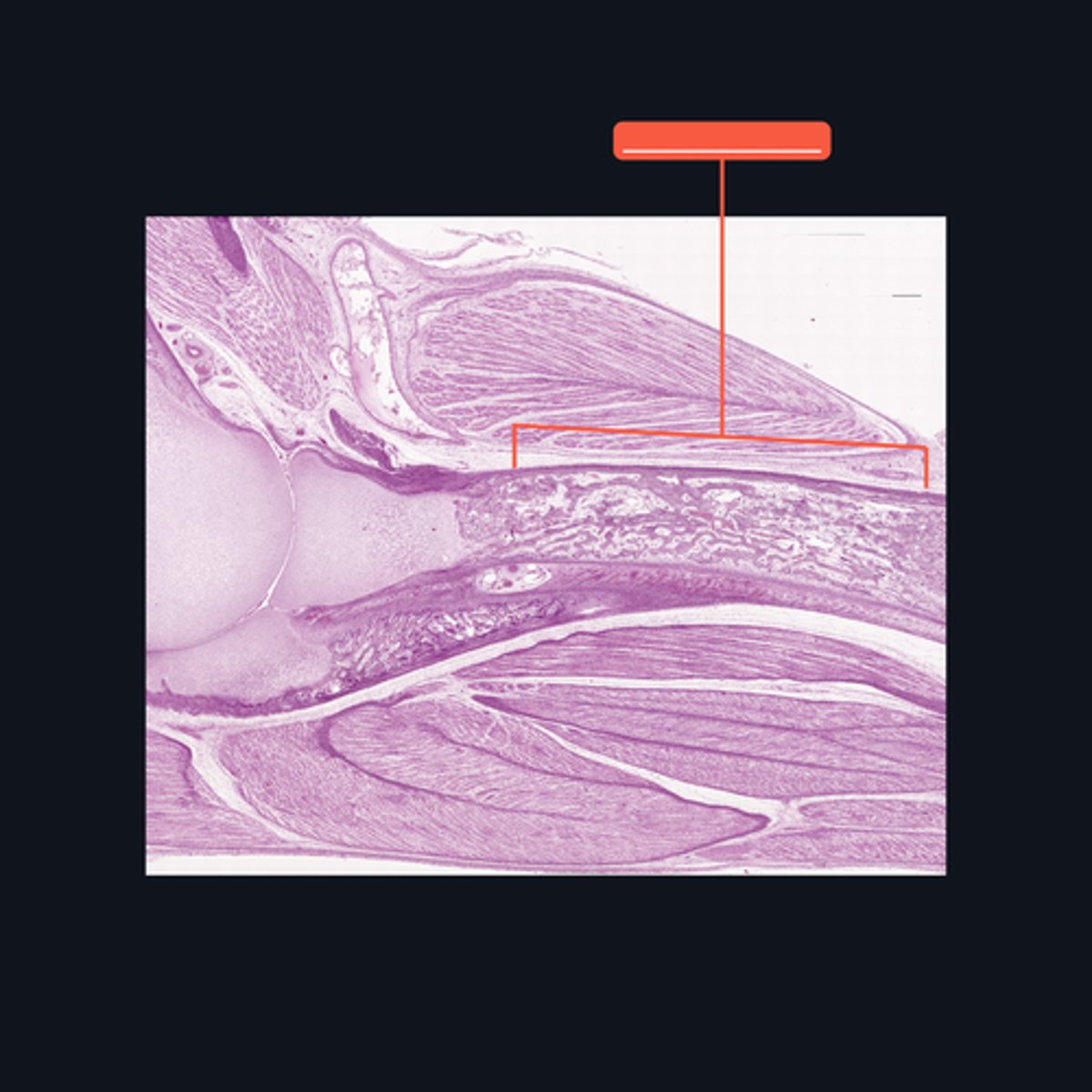
Diaphysis; shaft
Identify what part of a typical long bone is encompassed by the bracket symbol. It is also known as the _____ of a long bone.
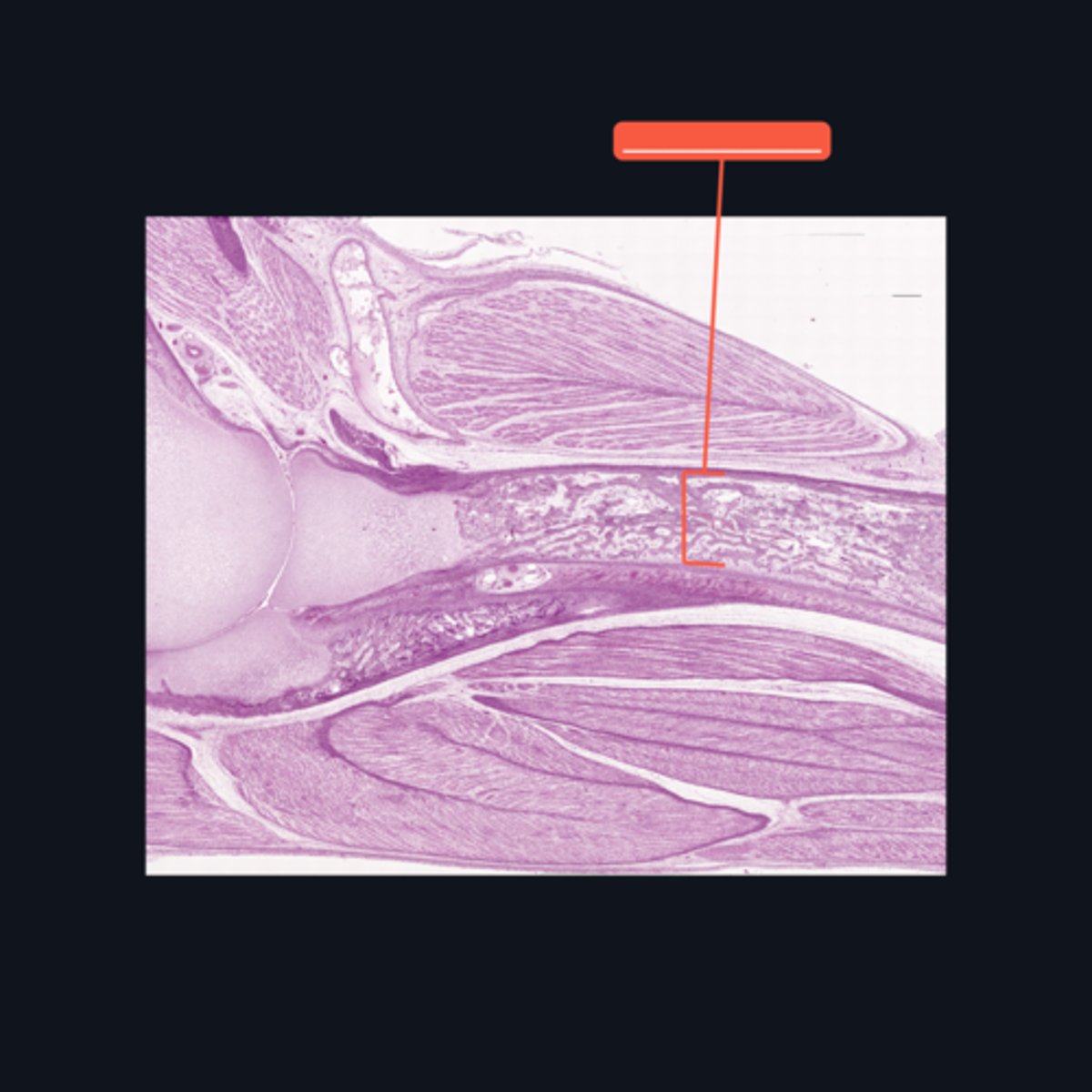
Medullary cavity
Identify the area encompassed by the bracket symbol, which is a hollow core that contains the developing blood cells and spongy bone spicules.
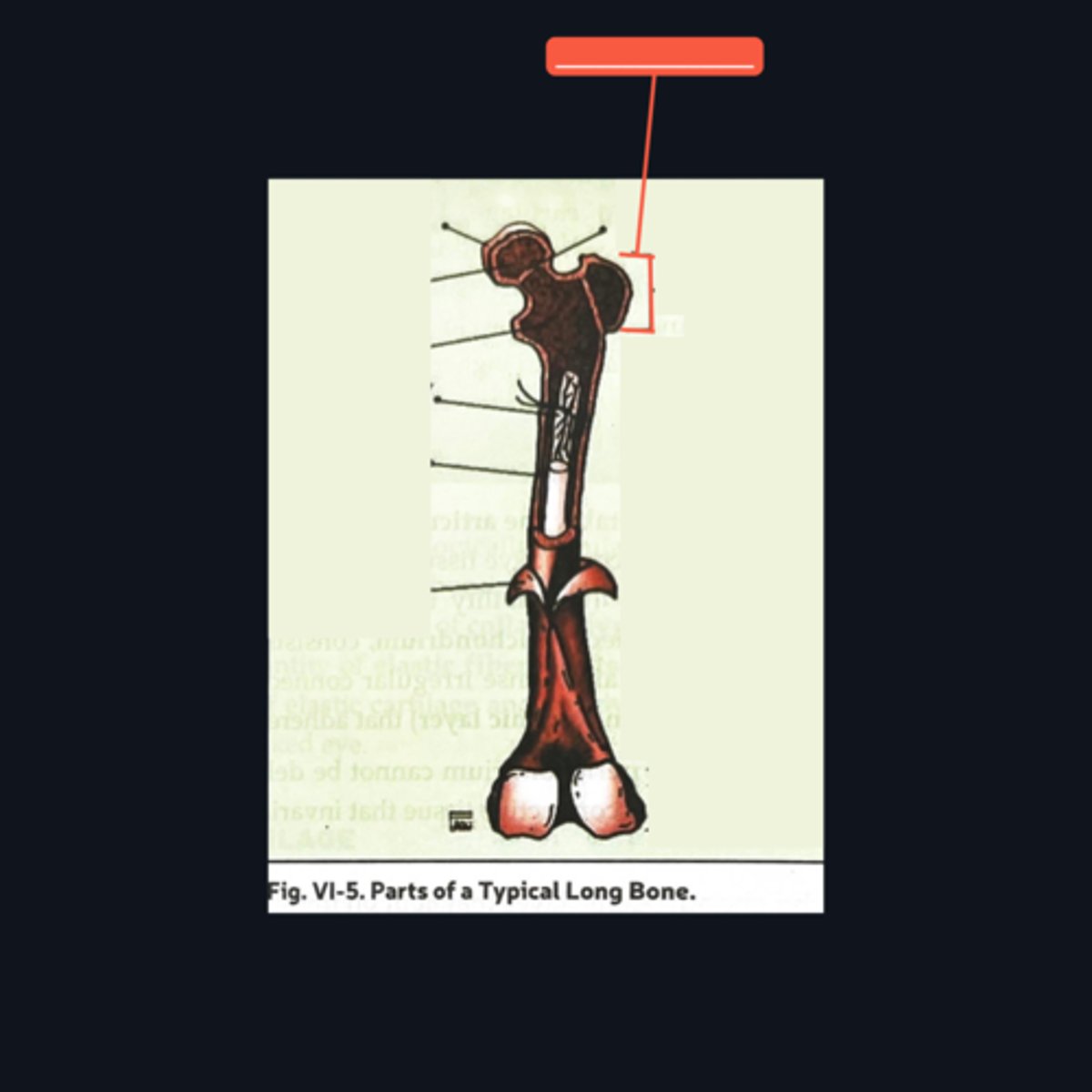
Proximal epiphysis; hyaline cartilage
Identify what part of a typical long bone is encompassed by the bracket symbol. What type of cartilage is it made up of?
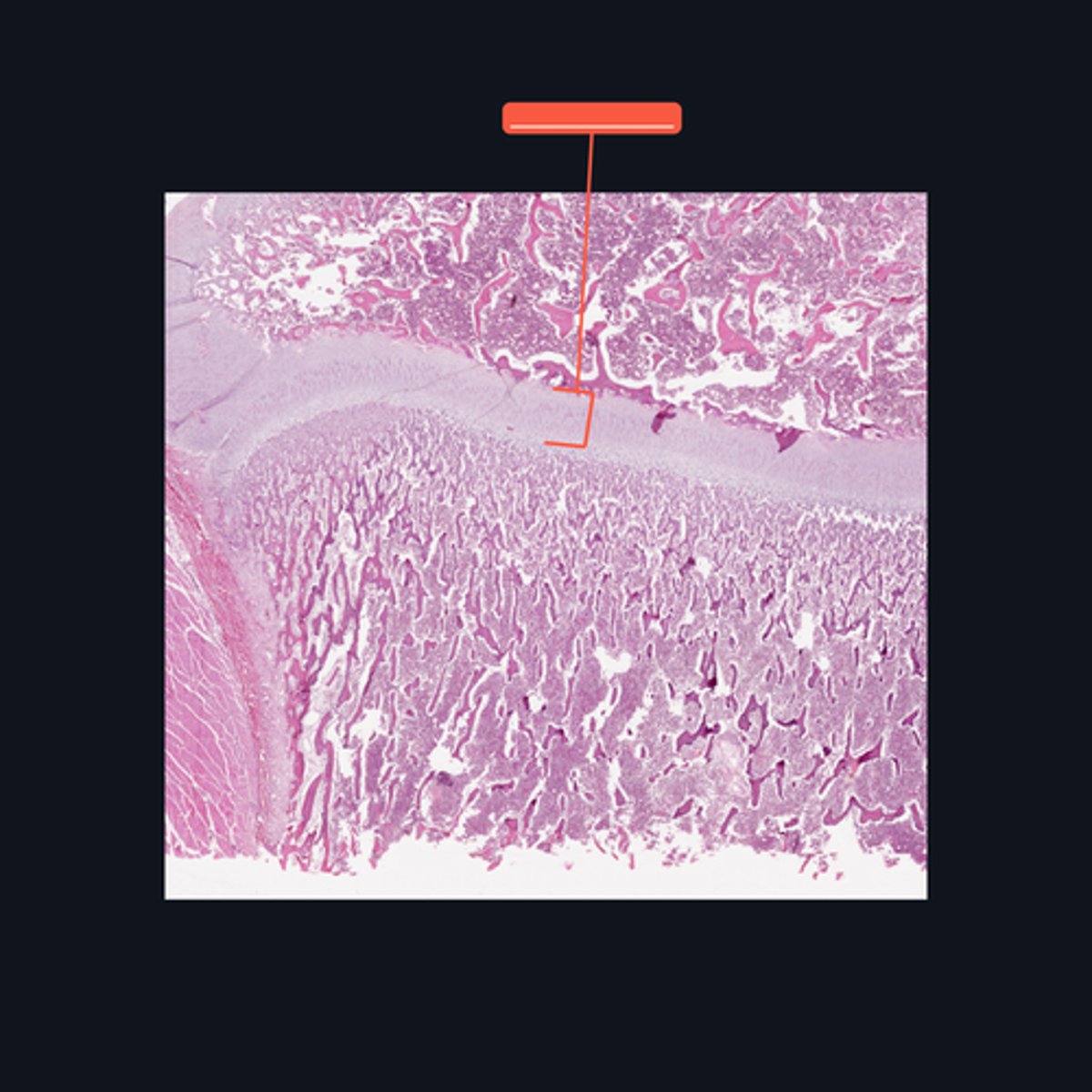
Epiphyseal Plate
Identify the pointed structure
End of the increase in length of bone
What signifies the closure of the pointed structure?
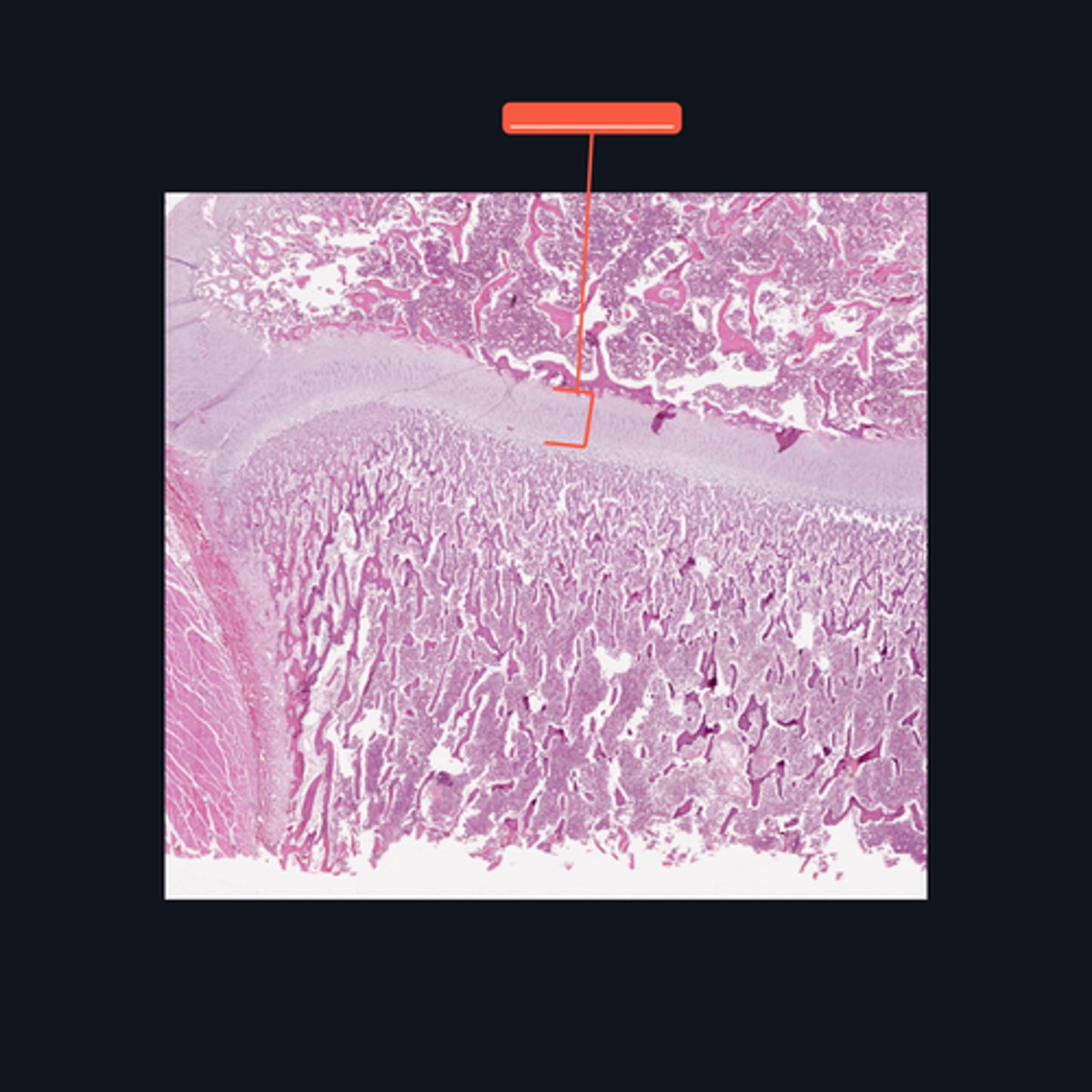
A - Zone of Resting Cartilage Cells
B - Zone of Proliferation
C - Zone of Maturation
D - Zone of Calcification
E - Zone of Ossification
Identify the pointed structures

B - Zone of Proliferation
Which pointed structure is the zone where instestitial growth occurs and what zone is it?

E - Zone of Ossification
Which pointed structure and what zone where many of the cavities left by cartilage cells merge to form marrow cavities?

C - Zone of Maturation
Which pointed structure and what zone do not divide anymore?

A - Zone of Resting Cartilage Cells
Which pointed structure and what zone anchors the epiphyseal plate to the epiphysis?

D - Zone of Calcification
Which pointed structure and what zone where the cartilage matrix is calcified
