Beam limitation and filtration pt 2 ( this is the limitation portion)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 12:05 AM on 11/1/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
1
New cards
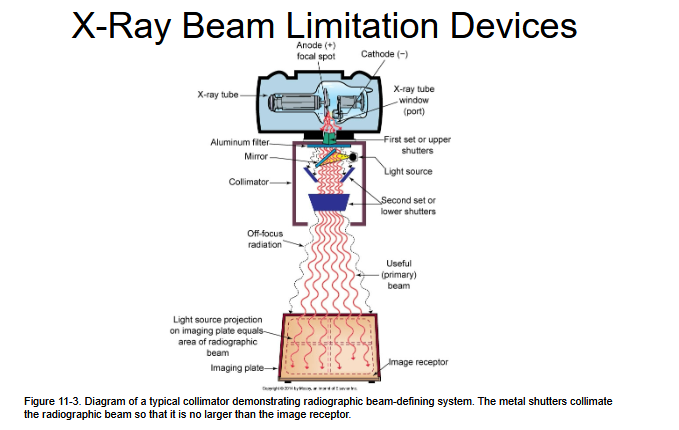
Understand with this image the first shutter is the green area and the blue area is the second shutter.
2
New cards
Off focus radiation or stem radiation
x-rays emitted from parts of the tube other
than the focal spot and at various angles from the x-ray tube
window.
3
New cards
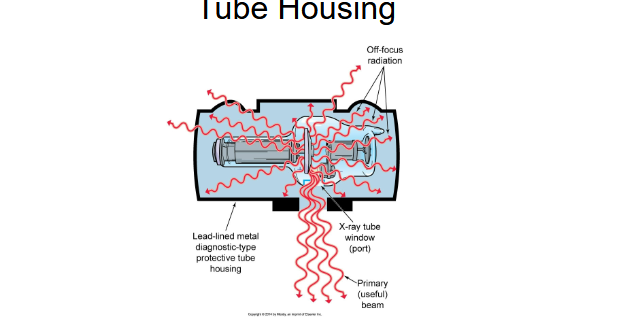
A lead-lined metal diagnostic-type protective tube housing protects patients and imaging
personnel from off-focus, or leakage, radiation by restricting x-ray emission to the area of the primary
(useful) beam
4
New cards
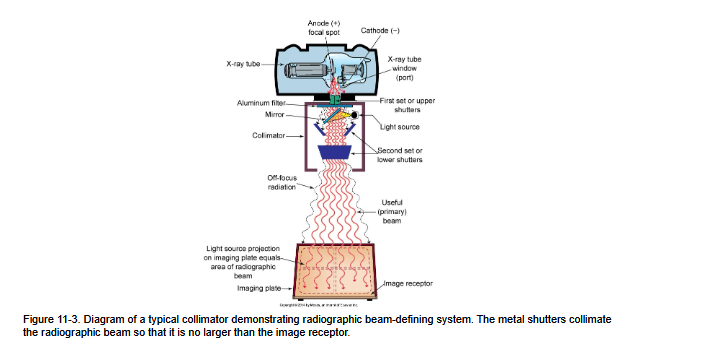
This is everything together
5
New cards
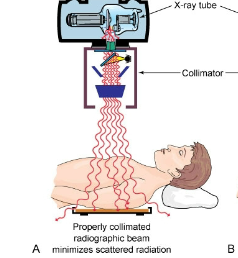
Is this image good collimation or bad
GOOD
6
New cards
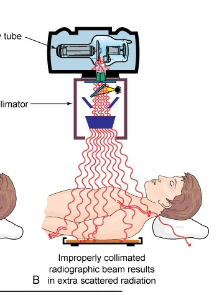
Is this image good collimation or bad
BAD
7
New cards
X-Ray Beam Limitation Devices
The primary x-ray beam must be collimated so that it is no larger than the size of the image receptor (IR) being used for the examination.
8
New cards
Light-localizing variable-aperture rectangular collimator
Used to manually or automatically adjust the size and shape of the x-ray beam; currently the predominant beam-limiting device.
9
New cards
Collimator assembly
The device used in modern radiology to change and customize the x-ray field size to fit the anatomy being imaged.
10
New cards
Importance of collimation
Reduces patient dose by limiting tissue exposure and decreases scatter radiation, improving image quality.
11
New cards
Collimation effects
Less scatter means lower dose to both the patient and technologist, especially important in thick anatomy like the lateral spine.
12
New cards
Benefits of collimation
Reduces patient dose, reduces scatter radiation, improves image contrast and overall image quality.
13
New cards
Collimator construction
Box-shaped device containing a series of adjustable components that control field size and beam shape.
14
New cards
Collimator components
Includes two sets of shutters (upper and lower), a light source to illuminate the field, and a mirror to reflect the light toward the patient.
15
New cards
First set of shutters
Located near the tube window; eliminates off-focus radiation that exits the tube at an angle.
16
New cards
Second set of shutters
Located below the light and mirror; reduces patient skin exposure by absorbing stray electrons produced by photon interactions.
17
New cards
Skin sparing
Minimizes skin exposure to electrons produced when photons interact with the lower collimator shutters.
18
New cards
Collimator safety standard
There must be at least 15 cm between the patient’s skin and the lowest set of collimator shutters to prevent electron exposure.
19
New cards
Field size
The x-ray field should never be larger than the image receptor, as that would unnecessarily expose more tissue.
20
New cards
Collimator light
The light must be bright enough to clearly outline the exposure field for accurate alignment.
21
New cards
Illuminated field standard
The illuminated light field must be within 2% of the actual x-ray field at the indicated SID.
22
New cards
Positive Beam Limitation (PBL)
Automatic collimation that restricts the beam to the size of the image receptor; no longer required since 1994 but still used in some systems.
23
New cards
PBL accuracy standard
PBL must be within 2% of the actual exposed field (2% of SID).
24
New cards
Cones
A fixed circular beam-limiting device that provides one field size; slides over the x-ray tube.
25
New cards
Use of cones
Commonly used for facial bones and sinus imaging.
26
New cards
Disadvantages of cones
Bulky and limited in flexibility; largely replaced by variable collimators.
27
New cards
Beam alignment
The radiographer must ensure the beam is properly aligned and collimated so it does not exceed the size of the IR.