DH101 QUIZ #3
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
All of the following are types of palpation when conducting an extraoral examination except:
bisagittal
The advantages of following a routine order for examination include all of the following, except:
inspiring the patient to have an examination on a daily basis.
A) A bilateral examination uses two hands at the same time to examine corresponding structures on opposite sides of the body. B) A bimanual examination uses fingers and thumb from each hand-applied simultaneously in coordination.
Both statements are true
A) A tumor is 1 cm or less in width. B) A nodule is greater than 5 mm but less than 2 cm in diameter.
Statement A is false and statement B is true
Which of the following is a depressed lesion?
ulcer
The definition of erythema is:
red area of variable size and shape.
The main objective of an extraoral and intraoral examination is to:
detect oral cancer at an early stage.
A) The most common sites for a neoplasm are the floor of the mouth, the lateral part of the tongue, the lower lip, and the soft palate complex. B) Self-examination of the patient's oral tissues at home is sufficient to detect cancer.
Statement A is true and statement B is false.
The ______________ lymph nodes are located directly in front of the ear.
pre auricular
A bulla is:
fluid filled
The pathologist has examined a cytology smear, and the dental office receives a report that states that the specimen is categorized as an HSIL ( High-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion- severe dysplasia). A white patch or plaque that cannot be scraped off is which of the following?
Leukoplakia
verrucous
The texture of this lesion would BEST be described as:
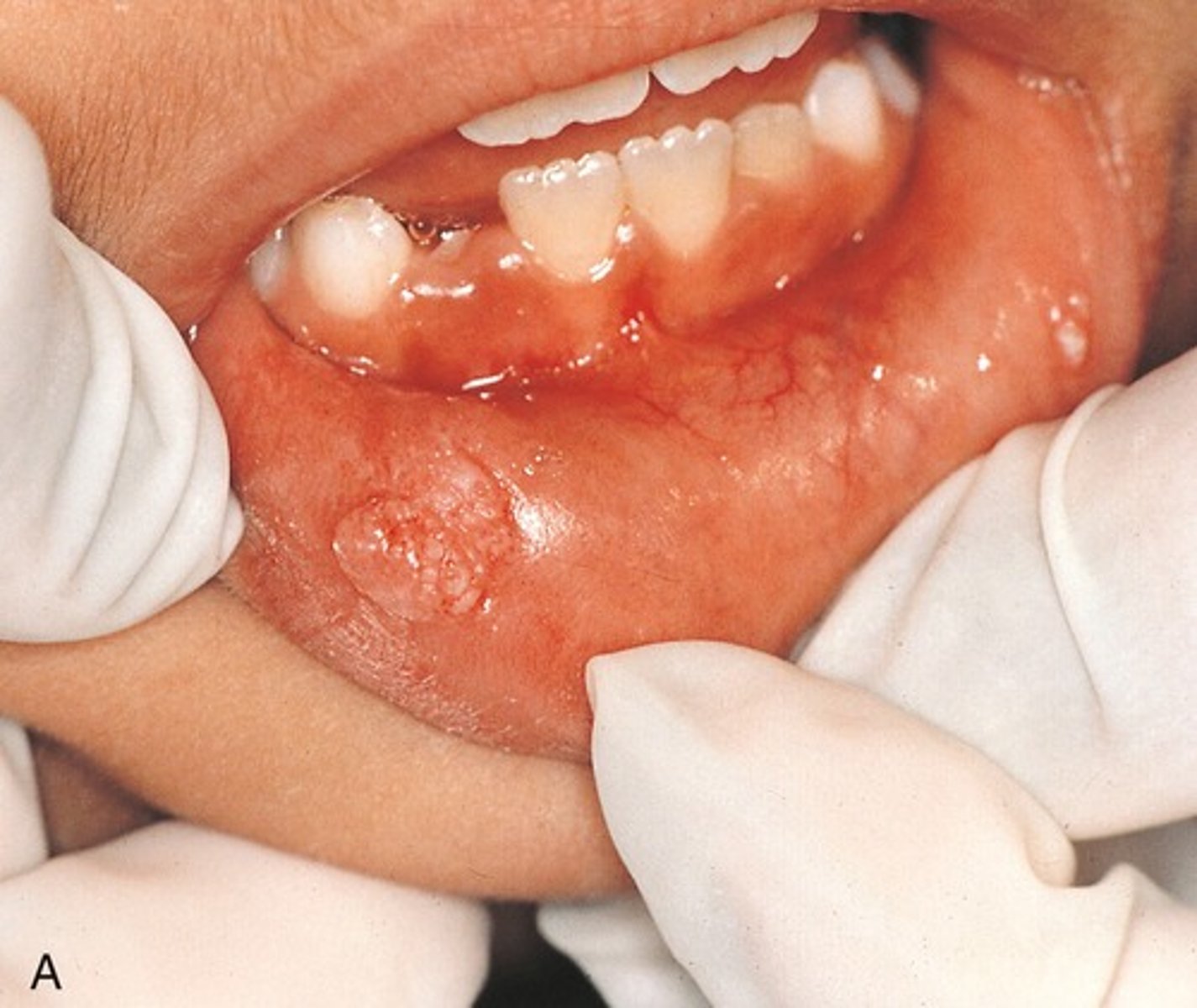
Pedunculated
The base of attachment for this lesion is:
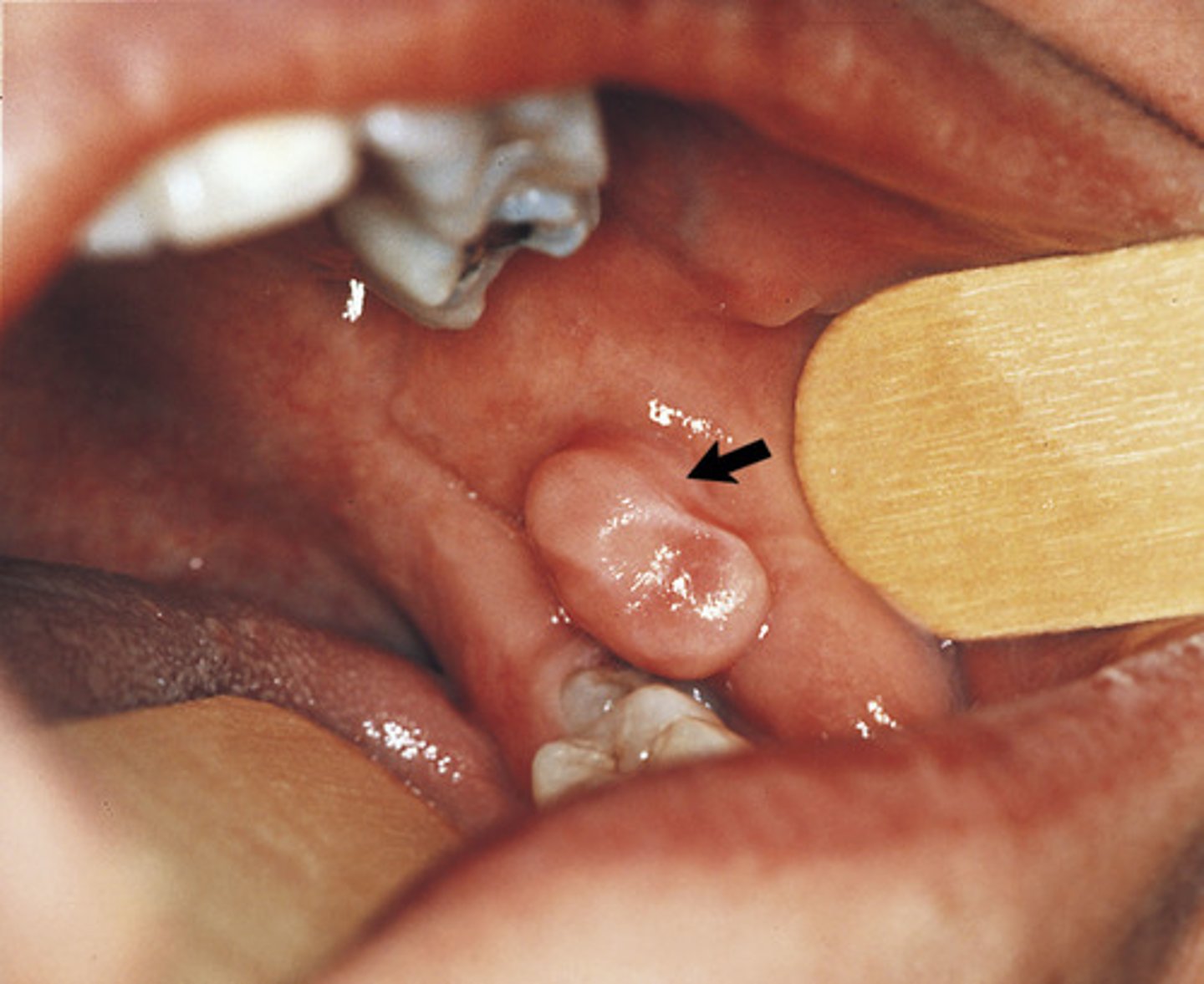
When primary teeth are being exfoliated and permanent teeth move in to take their places, which occurs between the ages of 6 and 12 years, this is considered:
mixed dentition
All of the following are requirements for the development of a carious lesion, except
biofilm
Which of the following is an example of a compound cavity?
Mesial-occlusal cavitiy
T/F Incipient lesions involve subsurface demineralization, which appears as a white area with no breakthrough to the enamel surface.
True
What are the two types of dental caries described by location?
Pit and fissure, and smooth surface
A soft, progressive lesion of cementum and dentin that involves bacterial infection and invasion is known as:
root caries
The wearing away of a tooth as a result of tooth-to-tooth contact is known as:
attrition
Distoclusion (Class II) occurs when:
The buccal groove of the mandibular first permanent molar is distal to the mesiobuccal cusp of the maxillary first permanent molar
The loss of tooth substance by a chemical process that does not involve known bacterial action is known as:
erosion
During an exam you notice that your patient's left mandibular second premolar (#20) is facial to the maxillary left second premolar (#13); this condition is called:
crossbite
During your exam, you noticed that the incisal edges of #8 & #9 occlude with the cervical third of the facial surfaces of #24 & #25; this would be identified as:
deep overbite
Having a prominent maxilla and a mandible positioned posterior to its normal relationship would be classified as:
retrognathic
A patient who has a Class III occlusion would most likely have a profile that is:
prognathic
When molars and premolars occlude cusp to cusp as viewed mesiodistally, this is classified as :
end-to-end bite
When incisor surfaces of maxillary teeth occlude with incisor surfaces of mandibular teeth as viewed mesiodistally, this is classified as:
edge-to-edge bite
When there is a lack of occlusal or incisal contact between certain maxillary and mandibular teeth because either or both have failed to reach the line of occlusion, this is classified as:
open bite
The horizontal distance between the labioincisal surfaces of the mandibular incisors and the linguoincisal surfaces of the maxillary incisors is :
overjet
The vertical distance by which the maxillary incisors overlap the mandibular incisors is classified as:
overbite
The determination of the classification of occlusion is based on the principles of:
Edward Angle.
Occlusal contacts that are made outside of the normal range of function in occlusion of:
parafunctional contacts
The purpose of a proximal contact is:
All of the above (to prevent food impaction, to stabilize the position of the teeth in the dental arch, and to prevent drifting)
The shepherd's hook explorer is commonly used for examining:
pits and fissures and smooth surfaces.