GCSE WJEC Physics- radiation
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
isotope definition
same element + protons diff neutrons
what is background radiation
low level of radiation
how radon enters house + prevention
cracks
artificial background radiation
medicine + nuclear
why are elements radioactive
due to an imbalance between no. of protons + neutrons in nucleus
ionization defintion
gaining or losing electrons
radon variation by area reason
rocks → diff amount in diff places
unit of radioactivity
becquerel (Bq)
1 Bq is equivalent to
1 radioactive decay per second
particles that make up nucleus
proton + neutron
half life definition
time taken for half the radioactive nucleii to decay OR drop to half the original radiation level
element decayed by beta emission what happens
mass stays same + atomic up by 1
how to reduce radioactive decay random effects
1) repeat experiment + calculate average
2) carry out experiment over longer period of time
element decayed by alpha emission what happens
mass down 4 + atomic down 2
alpha penetrating distance
low- absorbed by paper/ skin
beta penetrating distance
medium- absorbed by thin sheet of aluminium
gamma penetrating distance
high- reduced by thick lead
most dangerous radiation inside body
alpha
most dangerous radiation outside body
gamma
alpha particles charge
+
radiation biological effect
can cause cell mutation which can cause cancer
beta particles charge
-
gamma rays charge
0
gamma rays nature
electromagnetic wave
natural background radiation
-radon
-food
-cosmic rays
beta particles nature
high energy electron
alpha particles nature
helium nucleus (2 protons + 2 neutrons)


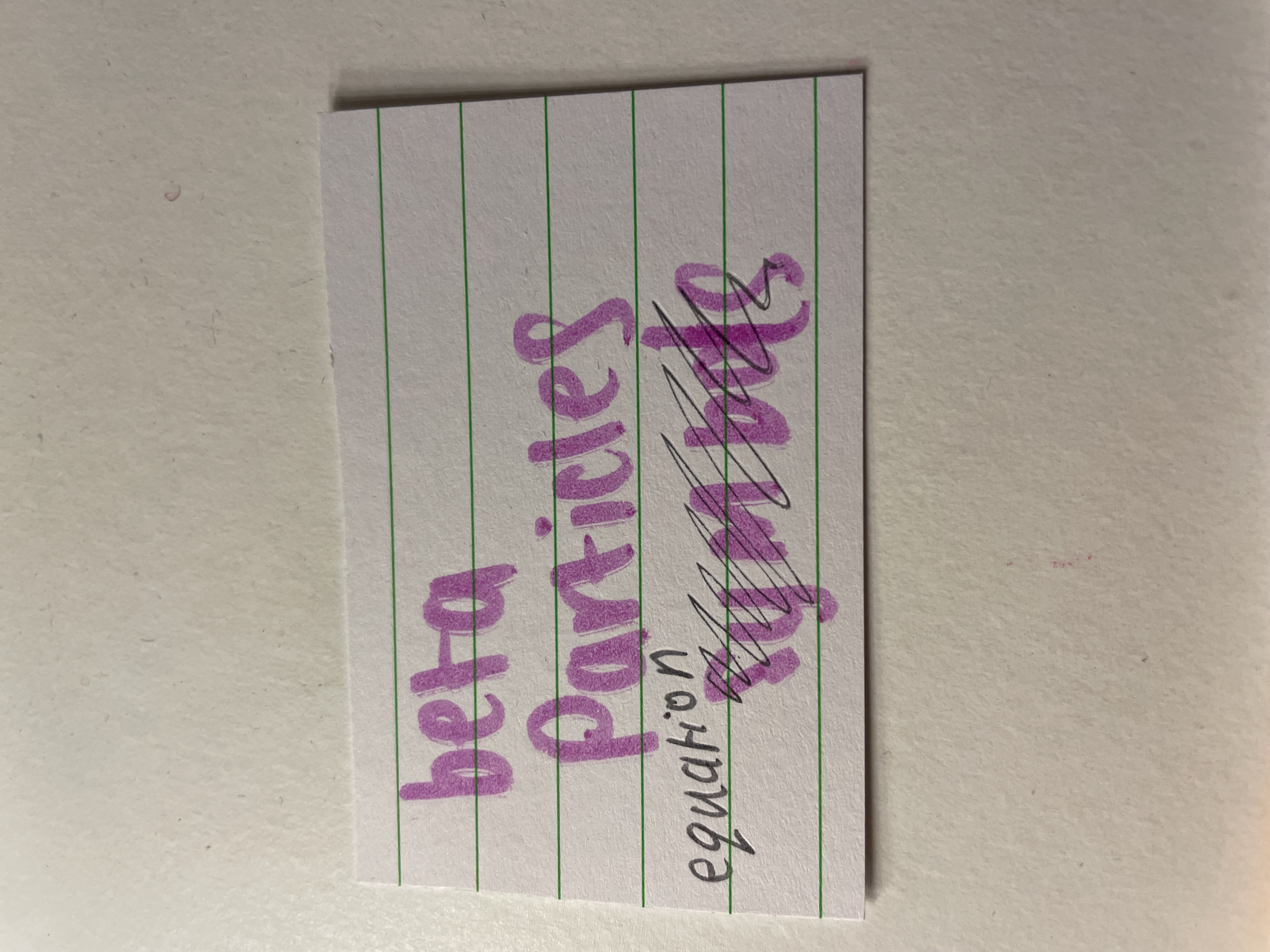

Radiation danger outside of body
alpha presents no danger + beta and gamma can get into body + beta is more ionising so more dangerous
A + D nuclear waste disposal storage underwater
A- well away from human activity + D- possible leakage in long term