Test 1-3 repeat
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Which non-covalent bond decreases the strength in water? Select TWO that apply.
A Ionic interaction
B. Hydrophobic interaction
C. Hydrogen bond
D. Van der Waals interaction
Hydrogen and ionic bonds are weakened in water due to its high polarity and ability to solvate ions and polar molecules.
Stereoisomers
are compounds that have the same molecular formula and sequence of bonded atoms but differ in the three-dimensional orientations of their atoms in space.
Which of the following statements is NOT CORRECT about "Hydrogen bond"?
A. Water molecules can participate in hydrogen bond formation with various macromolecules.
B. Hydrogen bond is the primary force to form an alpha-helix and a beta-strand secondarystructures.
C.Hydrogen bond is formed between two hydrogen atoms in water.
D. Hydrogen bond is crucial for complementary base pairing between nuclei acids.
C.Hydrogen bond is formed between two hydrogen atoms in water.
Which of the following processes is NOT involved in macromolecule (polymer) formation?
A.Anabolism
B.The generation of ATP
C.The generation of water molecules
D. Condensation reaction
B. The generation of ATP
The Gibbs free energy (G) describes the thermodynamic nature of a chemical reaction. Which of the following is CORRECT?
A. Enzymes change "G" to catalyze a chemical reaction.
B. Macromolecule formation is energetically favorable under physiological conditions.
C. A negative value of AG for a given chemical reaction indicates that the reaction will spontaneously occur.
D. The breakdown of ATP into ADP and Pi is energetically unfavorable under physiological conditions.
C. A negative value of AG for a given chemical reaction indicates that the reaction will spontaneously occur.
Which one of the following amino acids does not contain the basic side chains?
A. Argenine
B. Glycine
C. Lysine
D. Histidine
B. Glycine
7. Select one that INCORRECTLY describes the property of these amino acids.
A. The side chain of Tyrosine contains a hydroxyl group (-OH) that can be phosphorylated
B. The amino group (-NH2) in Lysine's side chain participates in ubiquitination reaction.
C. The carboxyl group (-C00H) from Proline is the reason why Proline tends to destabilize alpha helix.
D. The surface of an alpha-helix that is formed from consecutive Leucine residues displays hydrophobicity.
C. The carboxyl group (-C00H) from Proline is the reason why Proline tends to destabilize alpha helix.
Which of the following correctly describes "secondary structures" in protein folding?
A. It refers to the amino acid sequences in a protein.
B. The secondary structures are formed by the hydrogen bonds between peptide bonds.
C. The side chains of amino acid residues form the hydrophobic core in alpha helix.
D. The beta sheet structure is formed by ionic interaction between opposing strands.
B. The secondary structures are formed by the hydrogen bonds between peptide bonds.
Select one INCORRECT statement.
A. Ribosomes perform protein translation in the cytosol.
B. The genetic information in DNA is transcribed as RNA transcripts.
C. Nascent RNA undergoes RNA splicing to remove exons.
D. Multiple codons can encode the same amino acid by wobble base-pairing.
E. An mRNA contains a region that does not encode protein sequences, which is known as UTRs
C. Nascent RNA undergoes RNA splicing to remove exons
likely induces a conformational switch of an enzyme to destabilize substrate binding.
A. Poly-A tail
B. Allosteric activator
C. Ubiquitination
D. Allosteric inhibitor
E. Phosphorylation
D. Allosteric inhibitor
Which of these is FALSE about enzymes?
A Enzymes lower the activation energy barrier for a given chemical reaction
B. Enzymes lower the activation energy by providing binding siles for substrale, orienting them for chemical reaction.
C. Electron density in substrate molecules is often altered upon binding to enzyme
D. Enzymes catalyze energetically unfavorable reactions.
D. Enzymes catalyze energetically unfavorable reactions.
An oligomeric protein complex is composed of four identical subunits arranged in a symmetric way. It performs the conversion of Chemical-X to Chemical-Y. The protein complex has an allosteric binding site for Chemical-Z, which upon binding, destabilizes the binding of Chemical-X. Which of the following
trends best predicts the concentration of Chemical-Y over time?
B. Linear increase until addition of Chemical-Z then level off
True or False: Guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GET) is responsible for activating G proteins.
A. True
B. False
A. True
Which of the following is NOT an example of covalent protein modification?
A. Phosphorylation
B. Ubiquitination
C.Palmitoylation
D.Allosteric regulation
D.Allosteric regulation
15. For Src-type protein kinases to be activated..
A. A phosphorylation on a tyrosine residue must be removed.
B. SH2 domain must be poly-ubiquitinated.
C. A GTP must bind to the kinase domain.
D. All the steps are required.
A. A phosphorylation on a tyrosine residue must be removed.
Why is SDS used in SDS-PAGE?
A. To generate compact protein folding
B. To reduce disulfide bonds
C. To reinforce hydrophobic interactions
D. To cleave the protein into small fragments
E. To cover a polypeptide with negative charges
E. To cover a polypeptide with negative charges
_____ catalyze the addition of phosphate groups to molecules.
A. Proteases
B. Phosphatases
C. Nucleases
D. Kinases
E. Restriction enzymes
D. Kinases
Which of the following is NOT a common feature of a mature mRNA?
A. Intron
B. 5' untranslated region (UTR)
C. the coding region (ORF)
D. Poly-A tail
A. Intron
This genetic technique was originally discovered in bacteria and utilizes small RNA molecules to target specific sequences on DNA to induce double-strand DNA break.
A. SDS-PAGE
B. RNAi
C. GWAS
D. Restriction enzymes
E. CRISPR/CAS9
E. CRISPR/CAS9
Human B cells contain vast antibody diversity because of this process:
A. Cell fusion
B. tRNA wobble base-pairing
C Hybridoma cell proliferation
D. Somatic DNA recombination
E Alternative splicing
D. Somatic DNA recombination
26. Ras small G protein has two distinct protein conformations. Conformation-A forms GTP binding site while Conformation-B stabilizes GDP binding. You found a mutation in Ras that creates a very strong binding site for an abundant cellular protein-X. The binding site is formed when Ras is in Conformation- B. Select one that would predict the behavior of the mutant Ras protein.
A. The mutated Ras protein will enhance GTPase activity.
B. Protein-X forms a disulfide bond with mutated Ras.
C. The mutated Ras will promote cancer formation.
D. The mutated Ras will stay inactive.
E. The mutated Ras will have faster GTP - GDP exchange rate.
D. The mutated Ras will stay inactive
You performed a Western blot analysis on Protein-H. You made a cell lysate from gene-H knockout cells as well, which does not express Protein-H. You expected to see a band at 100 kDa because the calculated molecular weight of Protein-H is 100 Da. However, you didn't see a band at 100 kDa. You just realized that you forgot adding ß-mercaptoethanol during the SDS-PAGE. Which of the following conclusions is most likely?
A. Most of Protein-H undergoes ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation.
B. Protein-H binds DNA
C. Protein-H may form disulfide bonds with other protein(s).
D. Protein-H contains poly (A) tail.
E. Forget it. Nothing can be learned from a failed experiment. Do it again!
C. Protein-H may form disulfide bonds with other protein(s).
A tubular cellular compartment is labeled with a GFP-tagged protein. Assume that you are using a very high magnification lens (ie, 10,000,000,000x) for fluorescent microscope imaging. Which points in the figure will you be able to tell apart from the fluorescent images (can you tell those membranes are apart or making contact)? ** for GFP fluorescence, 480 nm wavelength light was
used.
c. 400 nm
Which of the following is NOT correct about Green fluorescent protein (GFP)
a) Is intrinsically fluorescent
b) It can be easily fused to a protein of interest through gene cloning.
c) Allows examining behavior of protein in living cells when tagged on the protein.
d) Requires additional fluorophores to be fluorescent.
Produces green light upon proper illumination.
d) Requires additional fluorophores to be fluorescent.
3. Exclusion of out-of-focus light in order to enhance optical resolution can be accomplished by the use of different techniques. Select one that is NOT correct.
a) Image deconvolution removes out-of-focus light by computation.
b) In Confocal microscopy, out-of-focus light is physically blocked out by pinholes.
c) Confocal microscopy achieves this via "optical sectioning".
d) In Multiphoton microscopy, out-of-focus light is cancelled out by simultaneous illumination of two lasers with different wavelengths.
d) In Multiphoton microscopy, out-of-focus light is cancelled out by simultaneous illumination of two lasers with different wavelengths.
You generated synthetic liposome A and B. You analyzed the phase transition of the liposomes using the differential scanning calorimetry as follows. Which of the following statements is most likely correct?
a) Liposome A is more fluidic than liposome B.
b) Liposome A will be more fluidic at 35°C than at 45°C.
c) Liposome B is more likely to have shorter fatty acid chains.
d) Liposome A contains more saturated fatty acid tails.
a) Liposome A is more fluidic than liposome B.
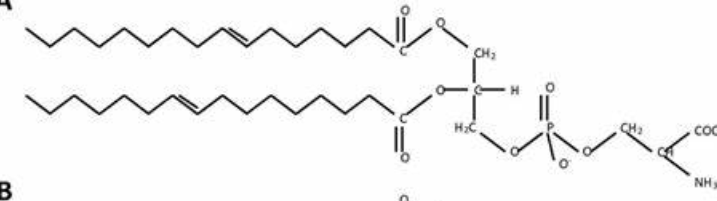
5. This phospholipid is almost exclusively located on the inner leaflet of the plasma membrane
D. Phosphatidylserine (PS) w NH3 and COOH
Which of the following is CORRECT about typical animal cell membrane?
a) Different cell organelle membranes have almost identical lipid composition for a given cell type.
(b) Cell membrane contains a large amount of membrane proteins.
c) Its hydrophobic core is mainly formed by free fatty acid molecules.
d) The cytoplasmic side of the plasma membrane contains glycosylated lipid and proteins
(b) Cell membrane contains a large amount of membrane proteins.
Which of the following is TRUE for Na*/K* pump?
a) It mediates facilitated diffusion.
b) It transports both Na+ and K+ into cytosol.
c) It requires ATP hydrolysis to perform ion transport.
d) It is responsible for generating electrochemical gradient on the inner mitochondrial
membrane.
c) It requires ATP hydrolysis to perform ion transport.
The concentration of Nat is greater on the [answer1) of typical animal cells, and the concentration of K+ is greater on the [answer1) of cells
a) outside, inside
b) outside, outside
c) inside, inside
d) inside, outside
a) outside, inside
The following is a Hydropathy analysis of a novel protein. Select one that is NOT correct.
a) Each of the peak regions above "O" likely form
alpha-helical structure
b) The darker gray regions likely form membrane
spanning segments.
c) The lighter gray areas below the Hydropathy index
"O" are composed of hydrophobic amino acids.
d)The protein likely spans seven times through the
membrane.
c) The lighter gray areas below the Hydropathy index
"O" are composed of hydrophobic amino acids.
You want to isolate a functional integral membrane protein to study its channel activity. What method would you use to isolate the integral membrane protein?
a) By adding SDS
b) By using highly concentrated KCI solution
c) By using a mild detergent
d) By adding beta-mercaptoethanol
c) By using a mild detergent
11. The graph shows the rate of solute transport across lipid bilayer as the concentration of solute is increased. Which of the following best describes the result? A- linear. B-levels off
a)A and B are both transporter-mediated.
b) A is simple diffusion while B is transporter-
mediated.
c) A is channel-mediated while B is simple
diffusion.
d) B is channel-mediated while A is simple diffusion.
b) A is simple diffusion while B is transporter-
mediated.
Which of the following statement is CORRECT about "Resting membrane potentia)"?
a) The membrane potential of a typical animal cell plasma membrane is positive.
b) The resting membrane potential is generated because the plasma membrane is more permeable to K+ than to Na+.
C) The generation of ATP in mitochondria and chloroplasts relies on the membrane potential that is generated by Na+ gradient.
d) A membrane potential arises when there is a difference in concentration gradient of glucose on the two sides of a membrane.
b) The resting membrane potential is generated because the plasma membrane is more permeable to K+ than to Na+.
Some K+ channels exhibit a high selectivity for K+ over Na+ although the size of Na+ ion is smaller than that of K+. Which of the following is a reason for such selectivity
a) k+ generates extensive hydrogen bonds with the peptide bonds to induce conformational change, hence the opening of K+ channel.
b) the smaller size of Na+ allows the K+ channel to flip- flop through the lipid bilayer in selective transport of K+ ions.
c) The electrochemical gradient through the selectivity pore allows the effective movement of K+, but not that of Na+.
d) The pore of K+ channel effectively dehydrates K+ ions by replacing water molecules with the carbonyl groups lining the passage.
d) The pore of K+ channel effectively dehydrates K+ ions by replacing water molecules with the carbonyl groups lining the passage.
You generated a synthetic liposome with phospholipid and cholesterol from a solution containing LiCI, glucose, and glycerol. You precipitated the liposomes and transferred them into a solution containing distilled water. Would this liposome ever generate a membrane potential? If so, which direction? Assume the internal lumen of the vesicle is equivalent to cytosol. Lower permeability for Cl than Li
a)Yes, +
b), Yes -
c) No
b), Yes -
You discovered a new channel-rhodopsin from a sea creature. The channel-rhodopsin is opened when red light is shined. You expressed the channel-rhodopsin in a neuron and found that the neurons hyperpolarize upon red light illumination. Which of the following is most likely true for this channel-rhodopsin?
a)The channel-rhodopsin is permeable to H+
b) The channel-rhodopsin is permeable to Na+
c) The channel-rhodopsin is permeable to Cl-
e) The channel-rhodopsin will generate action potential
c) The channel-rhodopsin is permeable to Cl-
Rotenone disrupts the electron transport chain in mitochondria. Which of the following would happen when you treat cells with Rotenone
a. A reduction in mitochondrial ATP production.
b. An increase in mitochondrial matrix pH.
c. Membrane potential will be lost on outer mitochondrial membrane
d) An increase in mitochondrial matrix protein import
a. A reduction in mitochondrial ATP production.
Brown fat contains a large number of mitochondria. Unlike white fat, brown fat is not specialized in storing fat - but rather specialized in generating heat by using H+ electrochemical gradient across mitochondrial membrane. The Uncoupling Protein 1 or UCP1 is highly expressed on the inner mitochondrial membrane in brown fat tissue. What is the best guess of UCP1 function?
a) UCP1 forms H+ channel allowing free passage of H+ across mitochondrial membrane.
b) UCP1 is an essential component in the electron transport chain complexes.
c) UCP1 is an H+ pump for H+ electrochemical gradient across mitochondrial membrane.
d) UCP1 imports citric acid at the expense of H+ electrochemical gradient.
a) UCP1 forms H+ channel allowing free passage of H+ across mitochondrial membrane.
18, Protein-N is a large protein. Protein-N is imported into nucleus after its synthesis in cytosol. Which of the following best describes the consequence after the intrinsic GTPase activity of Ran is completely inhibited?
a) Protein-N will be translocated into ER for secretion.
b) Protein-N will be excluded from the nucleus and accumulate in cytosol.
c) Protein-N will slowly equilibrate between nucleus and cytosol.
Protein-N will be imported into nucleus as usual.
c) Protein-N will slowly equilibrate between nucleus and cytosol.
19. Which of the following is TRUE about protein transport into organelle lumen?
a) Rough ER is a site for membrane protein synthesis while ER luminal proteins are synthesized on the smooth ER.
b) All mitochondrial proteins are translated inside mitochondria.
c) SRP recognizes a signal from a growing polypeptide and guides the ribosome/mRNA complex onto the nuclear pore complexes.
d) Protein doesn't need to be unfolded to be transported into peroxisomes.
e) The cycle of Ran-GTP and Ran-GDP provides energy required for mitochondrial outer membrane protein import.
d) Protein doesn't need to be unfolded to be transported into peroxisomes.
Protein-N is present both in the nuclear envelope and ER. You used the FRAP (Fluorescence Recovery After Photobleaching) technique to monitor the mobility of protein-N as in the picture. Which of the following best describes Protein-N behavior?
Protein-N is very mobile in the nuclear envelope, but not in ER.
Which of the following does NOT describe the cellular response to the misfolded proteins in the ER?
a) Misfolded proteins are exported back to cytosol for proteosome-mediated degradation, which is called "ERAD".
b) Transcription regulator promotes increased transcription of genes encoding ER chaperones.
C) Misfolded proteins in ER activate IRE1, which leads to cytoplasmic RNA splicing.
d) Protein translation rate will be increased for membrane and secreted proteins.
d) Protein translation rate will be increased for membrane and secreted proteins.
Which of the following does NOT describe ER function?
a) Most membrane proteins are synthesized in Rough ER.
b) The complex glycosylation pattern on membrane proteins occurs in Smooth ER.
c) Most lipid bilayer biosynthesis takes place in Smooth ER.
d) Smooth ER performs drug detoxification using Cytochrome p450.
b) The complex glycosylation pattern on membrane proteins occurs in Smooth ER.
Which of the following is NOT true about vesicle budding?
a) Coat proteins such as clathrin create membrane curvature.
b) Same coat proteins are commonly used for both anterograde and retrograde traffic.
c) Adaptor proteins selectively package cargos into a vesicle.
d) Vesicle formation requires membrane pinching proteins because it is energetically highly unfavorable otherwise.
b) Same coat proteins are commonly used for both anterograde and retrograde traffic.
Sar1 is required for vesicle formation at the ER-exit site. Which of the following is FALSE about Sar1?
a) Sar1 is a small GTPase.
b) Activated Sar1 exposes amphiphilic helix, which anchors Sar1 at the R membrane.
c) Sar1 is specifically recruited to the ER-exit site by tethering proteins.
d) Activated Sar1 recruits coat proteins to initiate vesicle bud formation.
c) Sar1 is specifically recruited to the ER-exit site by tethering proteins.
Shown is an electron microscope image from the synaptic terminals when GTPase activity of Dynamin is inhibited. What is the most likely explanation of the event that is shown here?
a) This demonstrates that Dynamin GTPase activity is necessary for synaptic vesicle release.
b) Pinocytosis is normally suppressed by Dynamin GTPase.
c) Dynamin GTPase activity triggers coat protein assembly for generating vesicle bud curvature.
d) Dynamin GTPase activity is necessary for vesicle pinching-off.
d) Dynamin GTPase activity is necessary for vesicle pinching-off.
Which endocytic process is best depicted in the following schematic diagram? Signal activation → Plasma membrane protrusion then closing of vacuole
a) Receptor-mediated endocvtosis
b) Phagocytosis
(c) Macropinocytosis
d) Pinocytosis
(c) Macropinocytosis
Which of the following is NOT true regarding Golgi?
a) Golgi targeted vesides from the ER enter through the cis-Golgi network
b) Golgi cisternae mediate processing of complex sugar groups on membrane proteins
C) Proteins containing mannose-6- phosphate in the trans-Golgi are targeted to lysosome via endosomes.
d) KDEL receptors dissociate from the KDEL proteins in Golgi because of lower pH, therefore retrieve the KDEL proteins.
d) KDEL receptors dissociate from the KDEL proteins in Golgi because of lower pH, therefore retrieve the KDEL proteins.
&. Organelles through the secretory pathway exhibit differential pH. What would NOT be the reason for this?
a) Lower endosomal pH aid recycling plasma membrane cargo receptors.
b) pH in Golgi is lower than that of ER, which helps retrieving ER resident proteins.
c) Acidic lysosome lumen triggers the activation of various hydrolases.
d) The differential pH in Golgi pulls it towards the nucleus so that Golgi location is always next to the nucleus.
d) The differential pH in Golgi pulls it towards the nucleus so that Golgi location is always next to the nucleus.
Select one that correctly describes Autophagy.
a) Autophagy degrades unwanted proteins and organelles.
b) Autophagy is also called cellular eating.
C) Autophagy recycles mitochondrial membrane proteins via endosomal sorting.
d) Autophagic vesicles are precursors to mitochondria.
a) Autophagy degrades unwanted proteins and organelles.
Which of the following is NOT true about regulated secretion??
a) Synaptic vesicle fusion is triggered by intracellular Ca2+ increase.
b) After the arrival of an action potential, synaptic vesicles fuse releasing neurotransmitter into the synapse.
c) Newly synthesized plasma membrane proteins are distributed along the cell membrane following fusion of vesicles.
d) Upon insulin signaling, GLUT4 receptors are translocated to the plasma membrane.
c) Newly synthesized plasma membrane proteins are distributed along the cell membrane following fusion of vesicles.
9. LDL is brought into the cell by Receptor-mediated endocytosis. What makes LDL-Receptor bind LDL at the plasma membrane, but dissociate from LDL inside the early endosome?
a) LOL is degraded in the early endosome by acidic hydrolases, which releases LDL-Receptor from. LDL for recycling.
b)LDL nas a lower affinity for LDL- Recepior in the acidic environment of early endosomes.
c) LDL is crosslinked to L.DL- Receptor at the plasma membrane by disulfide isomerase.
d) other ioroteins with higher affnity for L-DL-Recepior outcompele LDL inside the early endosome.
b)LDL nas a lower affinity for LDL- Recepior in the acidic environment of early endosomes.
Which type of signaling is a type of signaling over long distances by use of hormones as signaling molecules that are released into the bloodstream so that they can travel throughout the body?
a) Synaptic signaling
b) Contact-dependent signaling
c) Paracrine signaling
(d) Endocrine signaling
(d) Endocrine signaling
11. Which of the following correctly describes the All-or-none response?
a) Multi-valence allosteric activation
b) Gradual response to external signal intensity
c) Hyperbolic response curve
d) Negative feedback
a) Multi-valence allosteric activation
Which of the following enables cells to respond to ligand concentration changes rather than absolute concentration of extracellular signal molecules?
a) Down-regulation of receptor proteins from the plasma membrane into lysosomes.
b) Oscillation as a result of negative feedback loops.
c) Bistable cellular switches.
d) Kinases acting to promote their own phosphorylation and activation.
a) Down-regulation of receptor proteins from the plasma membrane into lysosomes.
13. Below is a diagram showing Circadian regulation in Drosophila. Which of the following steps is responsible for the downturn phase of Per protein concentration in cytosol (the phase in the dotted box area)?
a) Translation of Tim mRNA
b) Transcription of Tim and Per
c) The accumulation of Tim proteins in cytosol
d) Transcriptional suppression of Tim and Per by Per proteins
e) The heterodimerization of Tim and Per proteins in cytosol
d) Transcriptional suppression of Tim and Per by Per proteins
14. Which of the following is NOT true about G-protein coupled receptors (GPCR)?
a) GPCR has seven transmembrane segments.
b) GPCR directly activates small G-proteins such as Ras and Rho
c) The activation of G-proteins is mediated by GDP to GTP exchange
d) GPCR acts as a Guanine nucleotide exchange factor for G-proteins
b) GPCR directly activates small G-proteins such as Ras and Rho
15. Select one that is FALSE about Ca2+ signaling (*'CICR= Calcium-induced Calcium Release)
a) IP3 receptors are present on ER membrane.
b) Ca2+ together with diacylglycerol activates Protein kinase C.
c) The CICR refers to the positive feedback caused by auto-inhibition of Ca2+ channels.
d) Intracellular Ca2+ concentration is kept low by active Ca2+ pumping out of cytosol.
e) Calmodulin, once bound to Ca2+, activates target proteins.
c) The CICR refers to the positive feedback caused by auto-inhibition of Ca2+ channels.
Which is CORRECT about actin cytoskeleton?
a) Polymerization of actin filaments has a lag phase until oligomers of actin subunits, also referred to as "seed" form.
b) The rate of polymerization is higher at the minus end of F-actin.
c) Polymerization of actin filaments has a lag phase until the [G-actin] and [F-actin] reach a critical imbalance inside the cell.
d) GTP hydrolysis in actin monomers affects the dissociation rate of monomers from polymers.
a) Polymerization of actin filaments has a lag phase until oligomers of actin subunits, also referred to as "seed" form.
The graph shows the elongation rate at the
plus and minus ends of actin filaments as a
function of actin subunit concentration.
At what concentration (A to E), does the plus
end of filament stay at an equilibrium while the
minus end keeps shrinking?
B. Point where steeper line intersects 0 (usually before other line since + end is faster)
Arp2/3 complex ..
a) catalyzes cAMP production.
b) promotes the generation of long and uninterrupted F-actin filaments.
c) are enriched in the trailing edge of migrating cells.
d) resembles the preformed actin oligomers (seeds).
d) resembles the preformed actin oligomers (seeds).
Cofilin binds preferentially to ADP-actin rich filaments rather than to ATP-actin rich filaments. Consequently, this protein ...
a) stabilizes actin filaments.
b) Promotes stress fiber formation.
c) binds to the plus end of actin filaments.
(d) binds to older actin filaments
e) competes with profilin for actin binding.
(d) binds to older actin filaments
20. You expressed a PA-GFP (photo-activatable GFP) tagged-Actin in a cell. The incorporated PA-GFP-Actin in microfilaments was activated by illuminating the dotted box with UV light. You observed that the labeled Actin (in black lines) gradually moved toward the cell center over time. Which of the following is TRUE?
a. The microfilament endings at "a" has more association with cofilin than at "b".
b. The microfilament structures in the cell are contractile bundles.
c. The microfilaments are undergoing treadmilling process.
d. The microfilaments are undergoing rapid depolymerization.
c. The microfilaments are undergoing treadmilling process.
Skeletal muscle myosin is a plus end-directed motor protein. Where is(are) the plus end of microfilaments in the picture?
b. Z- disk in middle of light band
26. The activation of a stimulatory G protein activates adenylyl cyclase, and the activation of an inhibitory G protein suppresses adenylyl cyclase activation. Whereas the cholera toxin ADP-ribosylates the a subunit of stimulatory G protein (Gs), thereby blocking GTP hydrolysis, pertussis toxin ADP- ribosylates the a subunit of inhibitory G protein (G) and prevents interaction with a GPCR. What is then effect of these toxins on the concentration of intracellular cAMP?
a) Cholera toxin tends to increase cAMP concentration, whereas pertussis toxin tends to decrease CAMP concentration.
(b) Thev both tend to increase cAMP concentration
c) Cholera toxin tends to decrease cAMP concentration, whereas pertussis toxin tends to increase CAMP concentration.
d) They both tend to decrease cAMP concentration.
e) None of the toxins change cAMP concentration.
(b) Thev both tend to increase cAMP concentration
27. Intracellular Ca2+ oscillations, initiated by the activation of IP, receptors and orchestrated via intricate positive and negative feedback loops, can be subject to frequency modulation, an example of which is the increase in oscillation frequency with increasing stimulus strength. Caffeine is known to bind to and sensitize the ryanodine receptors, resulting in their opening in response to lower calcium ion concentrations. Which of the following is TRUE?
a) Caffeine will completely abolish Ca2+ increase.
b) Caffeine will abolish Ca2+ oscillation, instead will cause increased Ca2+ amplitude response upon ligand treatment.
c) caffeine will cause an increase in Ca2+ oscillation frequency.
d) Caffeine will cause a decrease in Ca2+ oscillation frequency.
e) Caffeine will cause a negative feedback with a shorter delay in Ca2+ oscillation.
c) caffeine will cause an increase in Ca2+ oscillation frequency.
Which of the following BEST describe the difference between treadmilling and dynamic instability?
A. [GTP-Actin] dictates which phase of dynamic instability microtubules will be in and [ATP-tubulin] dictates the rate of treadmilling.
B. Rapid disassembly during dynamic instability is restricted to the plus end of microtubules, but disassembly during treadmilling can occur at either the plus or minus end of actin filaments.
C. Treadmilling only applies to the polymerization of actin filaments and only microtubules undergo dynamic instability.
D. During treadmilling, the polymer maintains a constant length while assembly at the plus and disassembly at the minus end occur at identical rates, whereas dynamic instability is an alteration between periods of slow growth and rapid disassembly.
D. During treadmilling, the polymer maintains a constant length while assembly at the plus and disassembly at the minus end occur at identical rates, whereas dynamic instability is an alteration between periods of slow growth and rapid disassembly.
What is the role of GTP in microtubule polymerization?
A. GTP-bound tubulin dimers stabilizes the tip of the microtubule, allowing more monomers to be added
B. GTP binds the alpha and beta tubulin subunits together to form the tubulin monomer
C. GTP is a second messenger that signals the need for polymerization/de-polymerization
D. GTP hydrolysis in beta tubulin provides the energy for the polymerization of the microtubule
A. GTP-bound tubulin dimers stabilizes the tip of the microtubule, allowing more monomers to be added
----- ["Kinesin", "Dynein"] ---- move cargo towards minus ends of microtubules, whereas ----- ["Dynein", "Kinesin"] ----- move cargo towards plus ends of microtubules.
Dynein
Kinesin
Why does the cell utilize a Microtubule-Organizing Center (MTOC) to organize microtubule polymerization?
A. MTOCs form critical cellular functions such as formation of mitotic spindles, cilium, and flagellum.
B. The concentrations of tubulin dimer that would be required for spontaneous seeding is too high.
C. A complex of γ-tubulin serves as a template for a microtubule consisting of 13 protofilaments.
D. All of the above are true
D. All of the above are true
Which components interact with microtubules
A. Tau
B. Dynein
C. Filamin
D. Myosin
E. A and B
E. A and B
Which components interact with Actin
A. Tau
B. Dynein
C. Filamin
D. Myosin
E. C and D
E. C and D
Select one FALSE statement regarding intermediate filaments.
A. Keratin family intermediate filaments are in skin, nail, and hair.
B. The plus end of intermediate filaments has lower Cc than that of minus end.
C. Nuclear lamina provide mechanical support for nuclear envelope
D. Intermediate filament assembly is through the lateral bundling of monomers.
E. Intermediate filaments primarily provide mechanical stability to cell structures.
B. The plus end of intermediate filaments has lower Cc than that of minus end.
Axonemal dyneins are
A. Responsible for axonal anterograde transport
B. Associated with organelle movement
C. Monomeric myosin-like proteins
D. Associated with cilia and flagella
D. Associated with cilia and flagella
Microtubules dynamic instability greatly increases during prometaphase and metaphase. What describes the reasoning behind this?
A. To survey the entire cytosol to find chromatids and attach to their kinetochores
B. To increase the microtubules half-life to promote chromatid/kinteochore attachment
C. To break down the nuclear envelope to allow access to genetic material
D. To promote cell movement for the remaining stages of the cell cycle
A. To survey the entire cytosol to find chromatids and attach to their kinetochores
All of the following are true of mitotic spindle attachment to chromatids during mitosis EXCEPT:
A. The dynamic instability of microtubules decreases, and this stable microtubule structure can attach to chromatids easier.
B. High [Ran-GTP] around mitotic chromosomes stabilizes microtubules and enhances attachment onto mitotic chromatids.
C. The half-life of microtubules shortens during prometaphase and metaphase.
D. Microtubules bind to kinetochores that are formed on the centromeres of mitotic chromatids.
A. The dynamic instability of microtubules decreases, and this stable microtubule structure can attach to chromatids easier.
Which force(s) enable the alignment of mitotic chromatids?
D. All of the above
C. Under high tension, distance between inner and outer kinetochore increases leading to reduction of phosphorylation of microtubule tethering proteins by Aurora-B kinase, allowing stronger microtubule-kinetochore attachment.
E. A & B only
A. Microtubule treadmilling requires kinetochore microtubules to constantly reattach to kinetochore proteins on mitotic chromatids, generating a pulling force towards the spindle pole.
B. Movement of chromatid bound kinesins along mitotic spindle generates a pushing force away from the spindle pole.
D. All of the above
Which of the following statements is TRUE about cytokinesis?
This is the process of creating two daughter cells through mitotic spindle contraction.
The cytoplasm is divided in two by a contractile ring of actin and myosin filaments
Cytoplasmic content and organelles double for cell division.
The sister chromatids synchronously separate of form two daughter chromosomes
The cytoplasm is divided in two by a contractile ring of actin and myosin filaments
Cyclins…
A. Are necessary components for cdk activation.
B. p53 activates cyclins to promote DNA repair.
C. Are small GTPases that cycle between GDP and GTP bound state.
D. Their expression levels are highest during G0 phase.
A. Are necessary components for cdk activation.
PDGF (platelet-derived growth factor) activates PDGF receptors to promote G1/S progression. PDGF is an example of…
A. Cell death factor.
B. Anaphase promoting factor.
C. Mitogens.
D. DNA damage checkpoint factor.
C. Mitogens.
Which of the following is NOT a target for phosphorylation by mitotic cdks?
A. Microtubule-associated proteins: to promote spindle formation
B. Mitogen receptors: to induce MAP kinase activation
C. Condensin: to induce chromosome condensation
D. Nuclear lamins: to break down nuclear envelope
B. Mitogen receptors: to induce MAP kinase activation
True or False: Cell death by apoptosis results from tissue injury and is associated with inflammation and rupture of cells.
True
False
False
What is the role of p53 in the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis?
A. Active p53 inactivates Bcl-2, lifting the inhibition of cytochrome c release from mitochondria into the cytosol.
B. p53 multimerizes and forms protein channels on mitochondria.
C. Active p53 increases caspase synthesis.
D. p53 phosphorylation by ATM kinases target p53 for protein degradation
A. Active p53 inactivates Bcl-2, lifting the inhibition of cytochrome c release from mitochondria into the cytosol.
Which proteins are responsible for linking the extracellular matrix to the cytoskeleton?
A. Fibronectins
B. Cadherins
C. Connexins
D. Integrins
D. Integrins
Which of the following statements about cadherins is NOT true?
A. Cadherins are components in Adherens junction
B. Heterophilic cadherins interactions promote cell sorting during embryogenesis
C. Cells destined to form similar tissues are sorted according to which cadherin proteins they express during embryonic development
D. Cadherins include diverse transmembrane proteins
B. Heterophilic cadherins interactions promote cell sorting during embryogenesis
Desmosome
Connects cells by intermediate filaments
____underlines epithelial cells, separating them from connective tissues
A. Tight junction
B. Basal lamina
C. Adherens junction
D. GAP junction
B. Basal lamina
Extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins are often remodeled by the cells secreting them. Which of the following is an example of this remodeling?
A. GTP hydrolysis by Dynamin converts chemical energy to mechanical energy to assemble Fibronectin fibers.
B. Cadherin binding to Fibronectin provides mechanical stretching force via epical F-actin belt in an epithelial cell layer.
C. Integrins connect ECM to intracellular stress fibers.
D. Microtubule instability creates pulling force to transport collagen molecules to the spindle pole.
C. Integrins connect ECM to intracellular stress fibers.
Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) occurs during tissue/organ development. Which of the following is not correct about EMT?
A. Metalloproteinase expression is increased in cells undergoing EMT.
B. The transition of epithelial cells to fibroblasts is an example of EMT.
C. During EMT, epithelial cells start to lose epithelial cadherin proteins.
D. Cells undergoing EMT produces proteins for basal lamina formation.
D. Cells undergoing EMT produces proteins for basal lamina formation.
Which of the following describes integrin inside-out signaling
A. Phosphorylation by Focal Adhesion kinase
B. E-cadherin forms Adherens junction
C. Fibronectin binds integrin to activate AKT
D. GPCR activation leads to the opening of integrin configuration to induce platelet aggregation
D. GPCR activation leads to the opening of integrin configuration to induce platelet aggregation
How does an oncogene promote cancer?
A. by enhancing growth-signaling
B. by expressing caspase
C. by triggering spindle check point
D. by increasing Dynamic instability
A. by enhancing growth-signaling
What is an example of a Tumor Suppressor?
A. EGF Receptor
B. Src kinase
C. Rb (Retinoblastoma)
D. AKT
C. Rb (Retinoblastoma)
Which of following enzymes that catalyze breakdown of the basal lamina for cancer cell migration
A. Receptor tyrosine kinase
B. Adenylyl cyclase
C. metalloproteinases
D. Na+ K+ pump
C. metalloproteinases
Anchorage dep growth
Cells need to be connected to ECM to grow
Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transitions
Associated with control of cell-cell junction proteins
Integrins
Connect ECM to focal adhesions
____refers to an inability of cells to undergo further cell cycle progression
A. EMT
B. cell senescence
C. metastasis
D. Warburg effect
B. cell senescence
Angiogenesis…
A. is a process of converting tumor cells into endothelial tissue
B. is stimulated when a growing tumor tissue requires oxygen
C. Abundance of oxygen presence triggers the secretion of VEGF, which stimulates angiogenesis
D. is triggered by low HIF1a levels
B. is stimulated when a growing tumor tissue requires oxygen
Which of the following mutations best contribute to the Genetic instability of Cancer?
A. EGFR mutation
B. Src mutation
C. P53 mutation
D. Ras mutation
C. P53 mutation