Module 7 (2025) Covalent Bonding and Intermolecular Forces
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Number of Valence electrons in a group 13 elements
3
Number of Valence electrons in a group 14 elements
4
Number of Valence electrons in a group 15 elements
5
Number of Valence electrons in a group 16 elements
6
Number of Valence electrons in a group 17 elements
7
Number of Valence electrons in a group 18 elements
2 for helium , 8 for the others
Why are group 18 electrons nonreactive?
They have full valence shells
Electronegativity
A measure of the ability of an atom to attract electrons
Elements with higher electronegativity
Form negative ions or covalent bonds
Nonmetals
elements with relatively high electronegativity
properties of ionic compounds
Form crystal lattices, conduct electricity in solution, and have high melting and boiling points.
properties of covalent compounds
low melting point, low boiling point, never conducts electricity
covalent bonding
sharing of electrons pairs between atoms
octet rule
States that atoms lose, gain or share electrons in order to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons
octet rule exceptions
hydrogen and helium have a full shell with only 2 electrons
Lewis Dot Model
lewis' method places dots around the elements symbol to represent the number of valence electrons
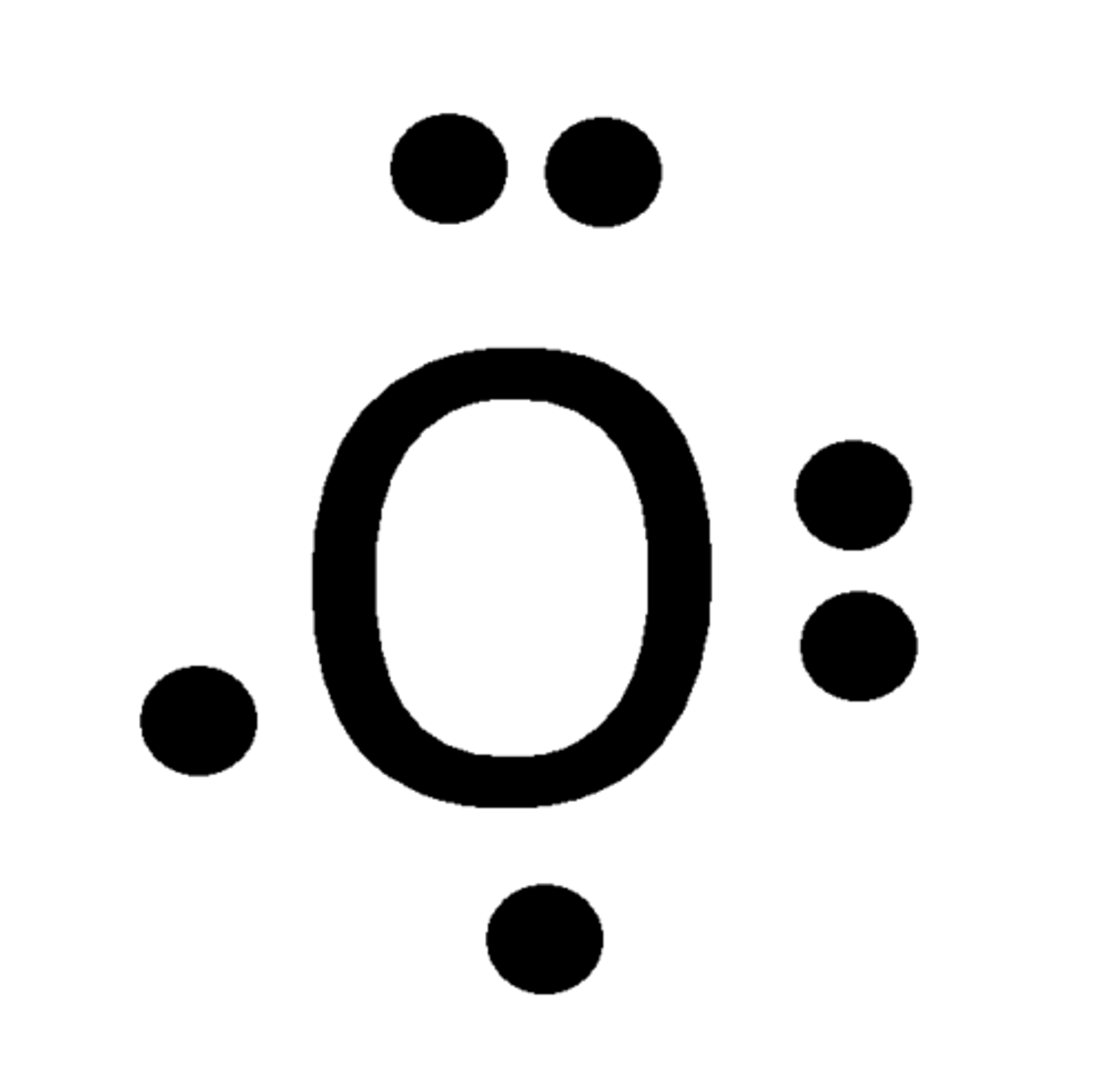
lewis dot model of a compound
shows how the atoms in the compound share electrons
each line is two electrons
lone pairs are dots
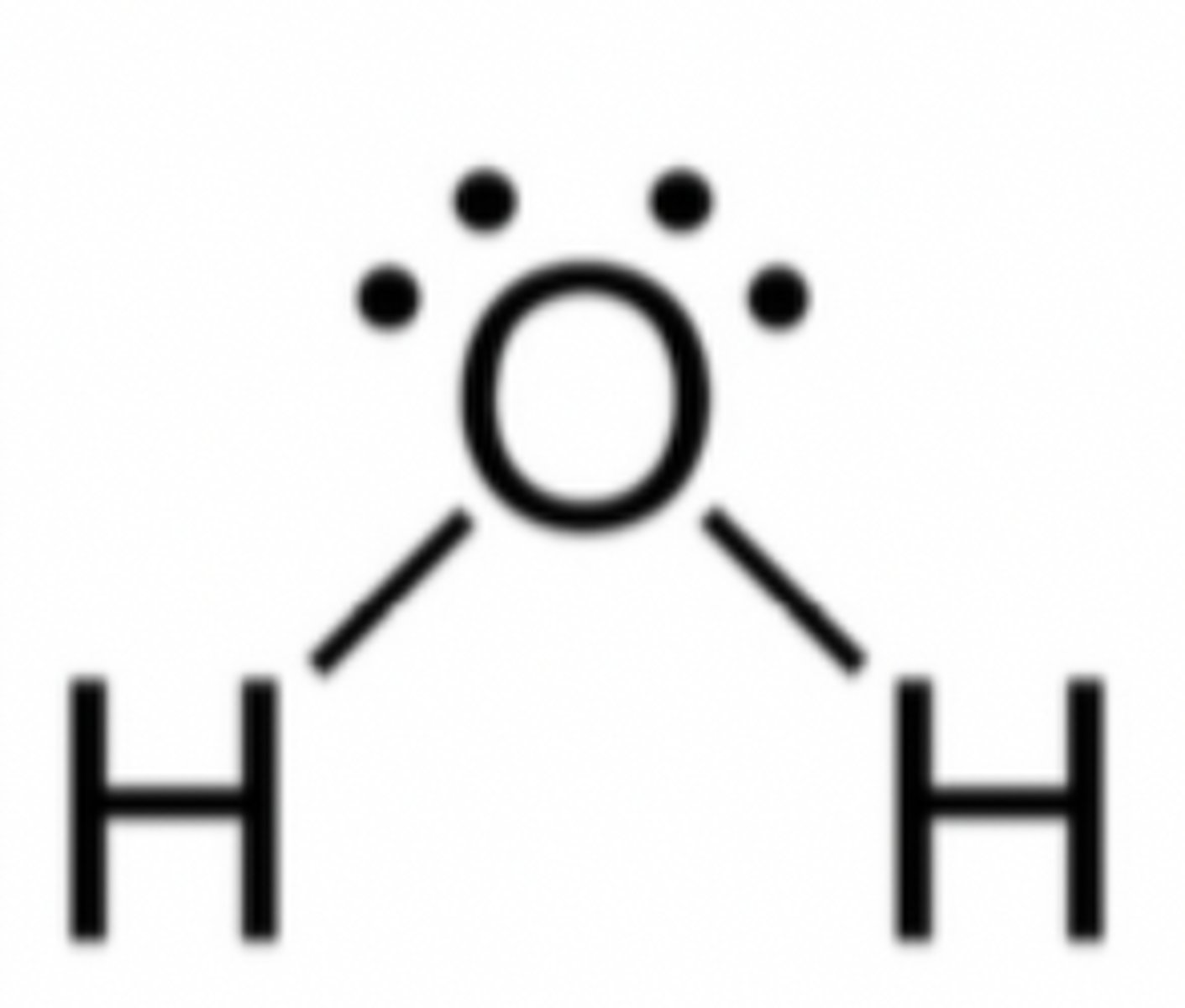
Lone pairs
pairs of valence electrons that are not involved in covalent bond formation
single bond
a covalent bond in which two atoms share one pair of electrons
double bond
A covalent bond formed when atoms share two pairs of electrons
triple bond
a covalent bond in which two atoms share three pairs of electrons
Predicting whether a bond is ionic or covalent
-big differences in electronegativity are ionic (example: metal and nonmetal)
-small differences in electronegativity are covalent (example: nonmetal and nonmetal)
shell
-location of the electrons that fill the principal energy level of an atom
- increasing number of shells generally increases the distance of the electrons in the shell from the nucleus
number of covalent bond made by a nonmetal
equals the number of spaces in the valence shell that can be filled.
For example: oxygen has 6 valence electrons, so oxygen can make 2 bonds
Covalent Bonding Pattern of Oxygen
2 single bonds or 1 double bond
Covalent bonding pattern of fluorine
1 single bond
covalent bonding pattern of nitrogen
3 bonds total
- 3 single bonds or 1 single and 1 double or 1 triple bond
covalent bonding pattern of carbon
four bonds total
-4 single bonds, 2 single and 1 double, 2 double bonds, or 1 single and 1 triple bond.
covalent bonding pattern of hydrogen
one single bond
Principle Element
Element in the second period of the periodic table
-all elements in the group have the same chemistry because they have the same number of valence electrons
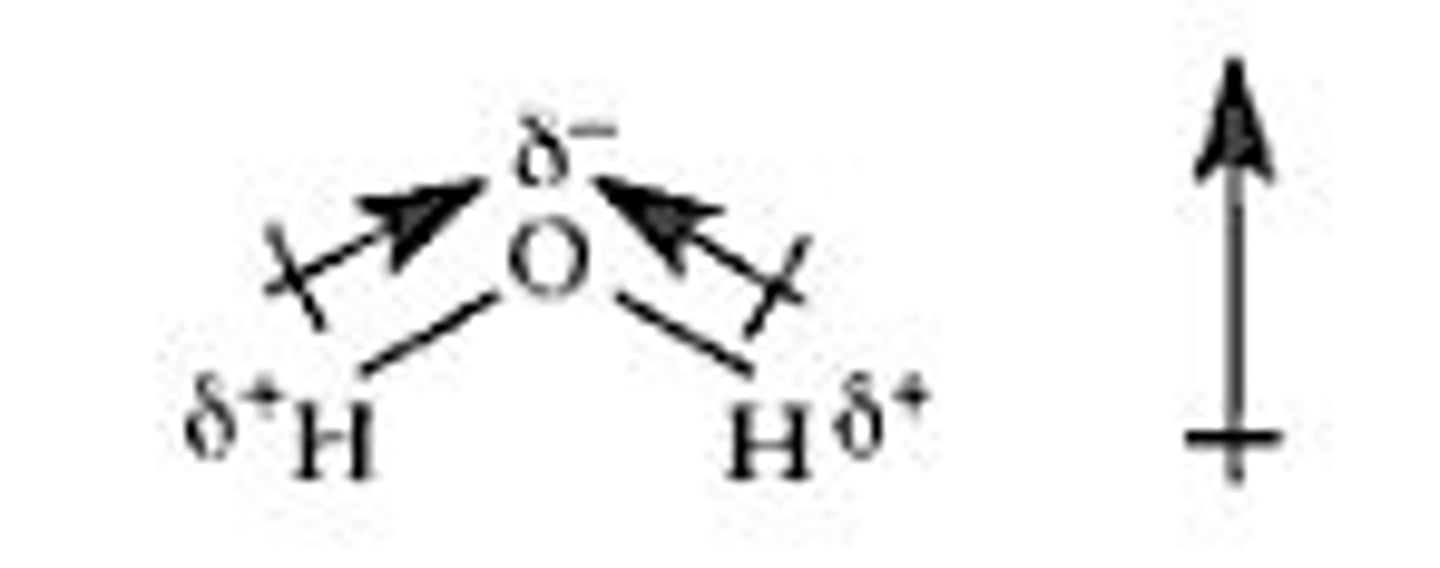
Dipole
created by equal but opposite charges that are separated by a short distance
hydrogen bond
Attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen atom and a slightly negative atom in another molecule. The other atom is usually oxygen or nitrogen.
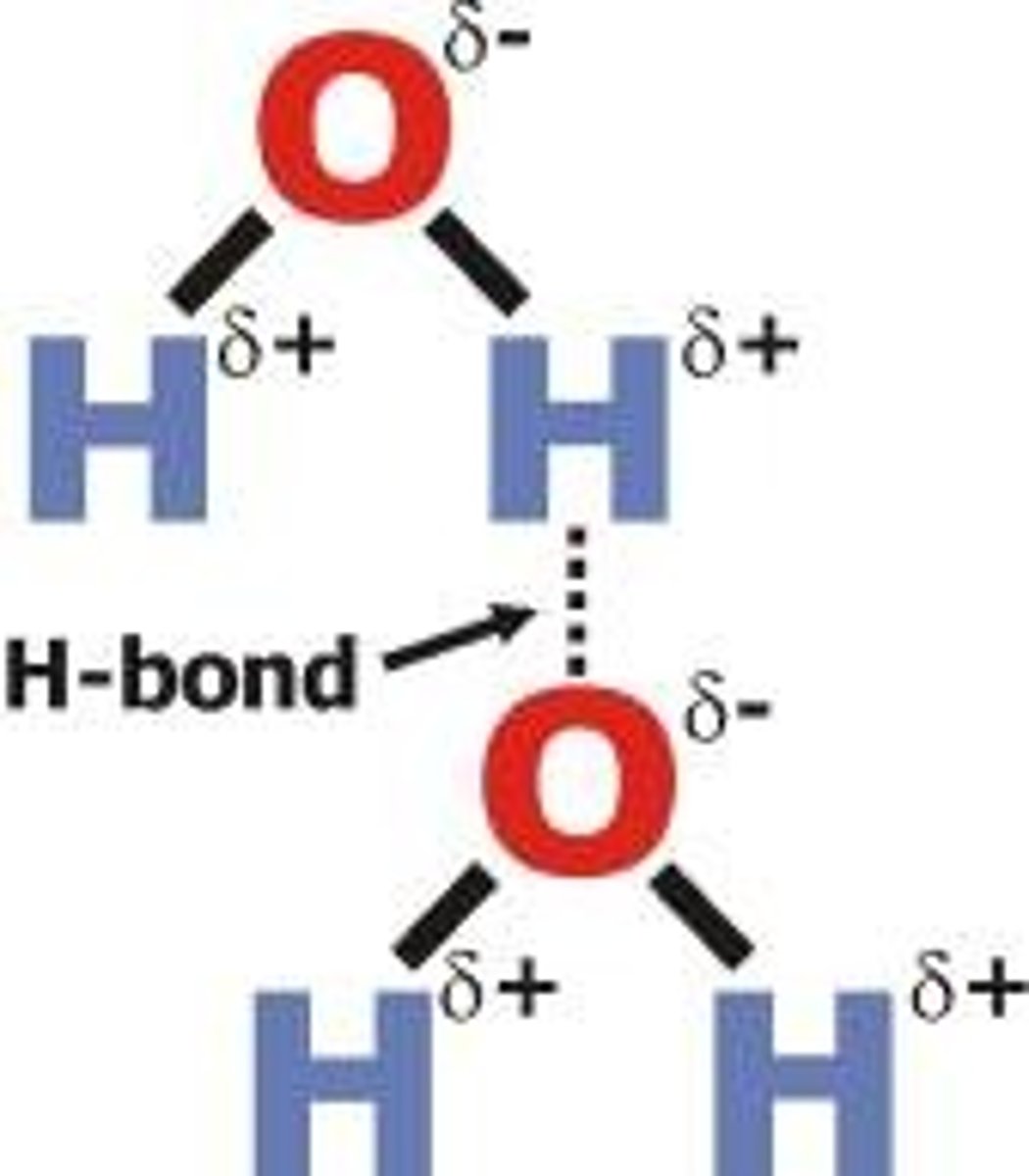
dipole-dipole forces
attractions between oppositely charged regions of polar molecules
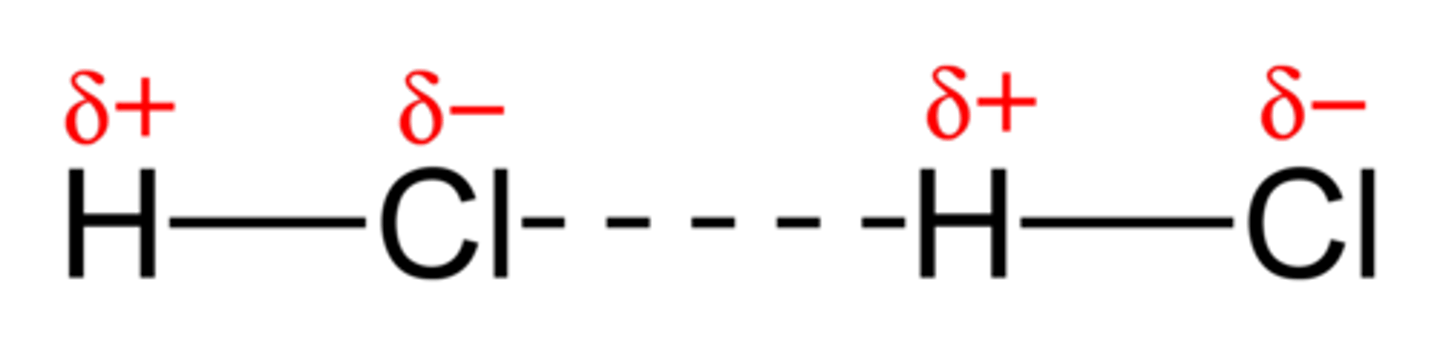
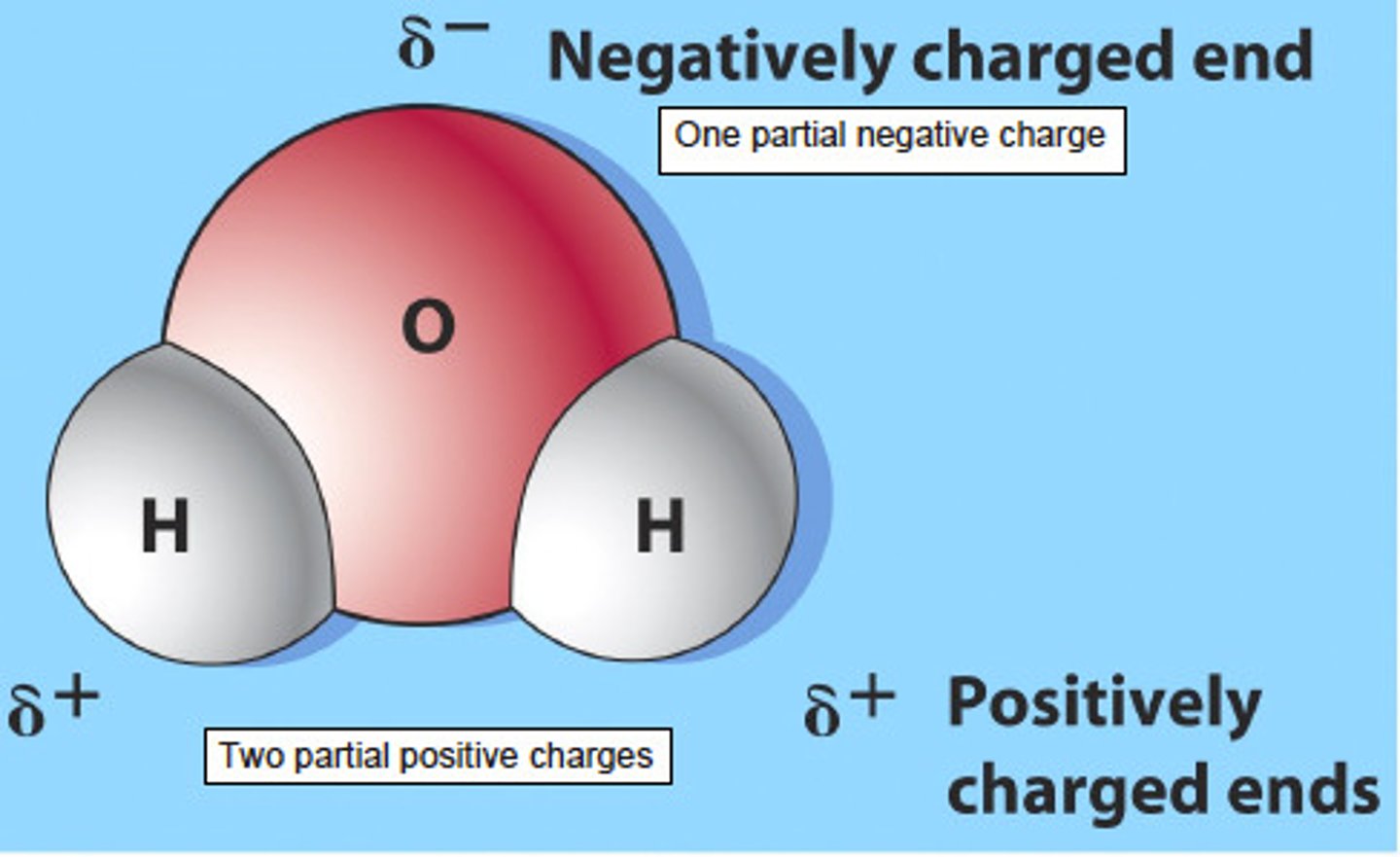
polar molecule
molecule with an unequal distribution of charge, resulting in the molecule having a positive end and a negative end
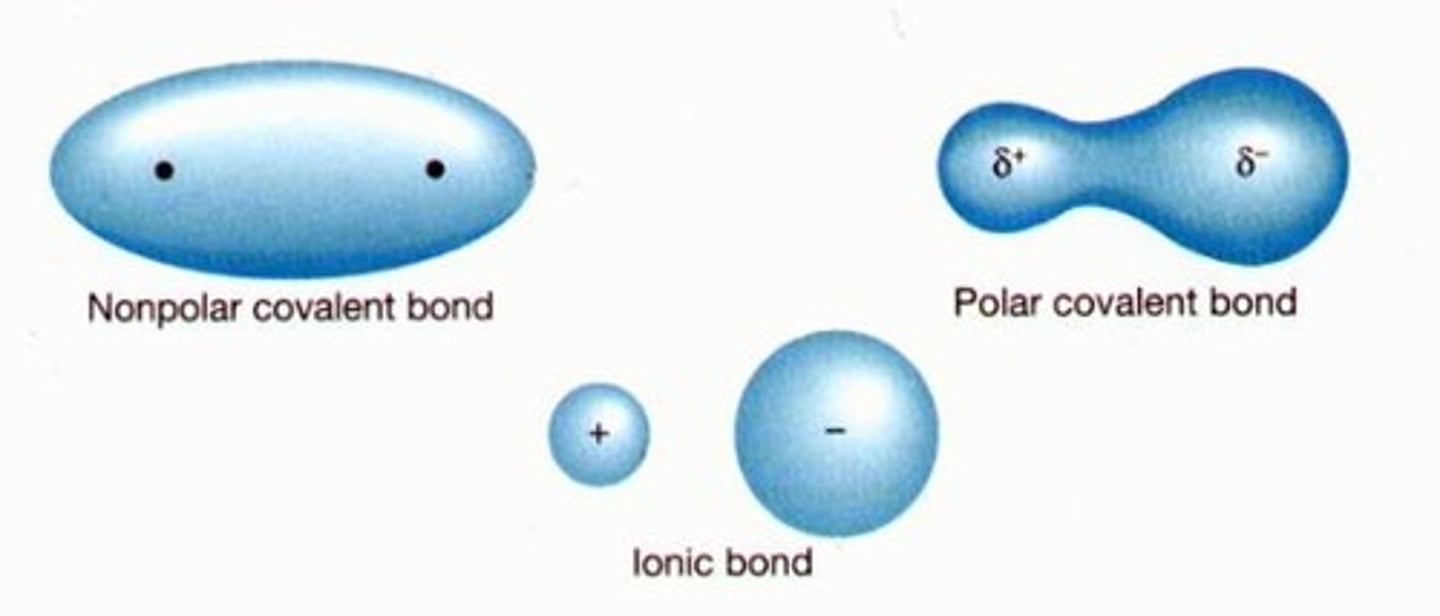
polar bond
a covalent bond in which electrons are shared unequally
intramolecular force
forces that hold atoms and ions together in molecules and compounds (covalent or ionic bonding)
intermolecular force
forces of attraction between molecules (hydrogen bonds, dipole-dipole interactions, dispersion forces)
dispersion forces
attractions between molecules caused by the electron motion on one molecule affecting the electron motion on the other through electrical forces; these are the weakest interactions between molecules
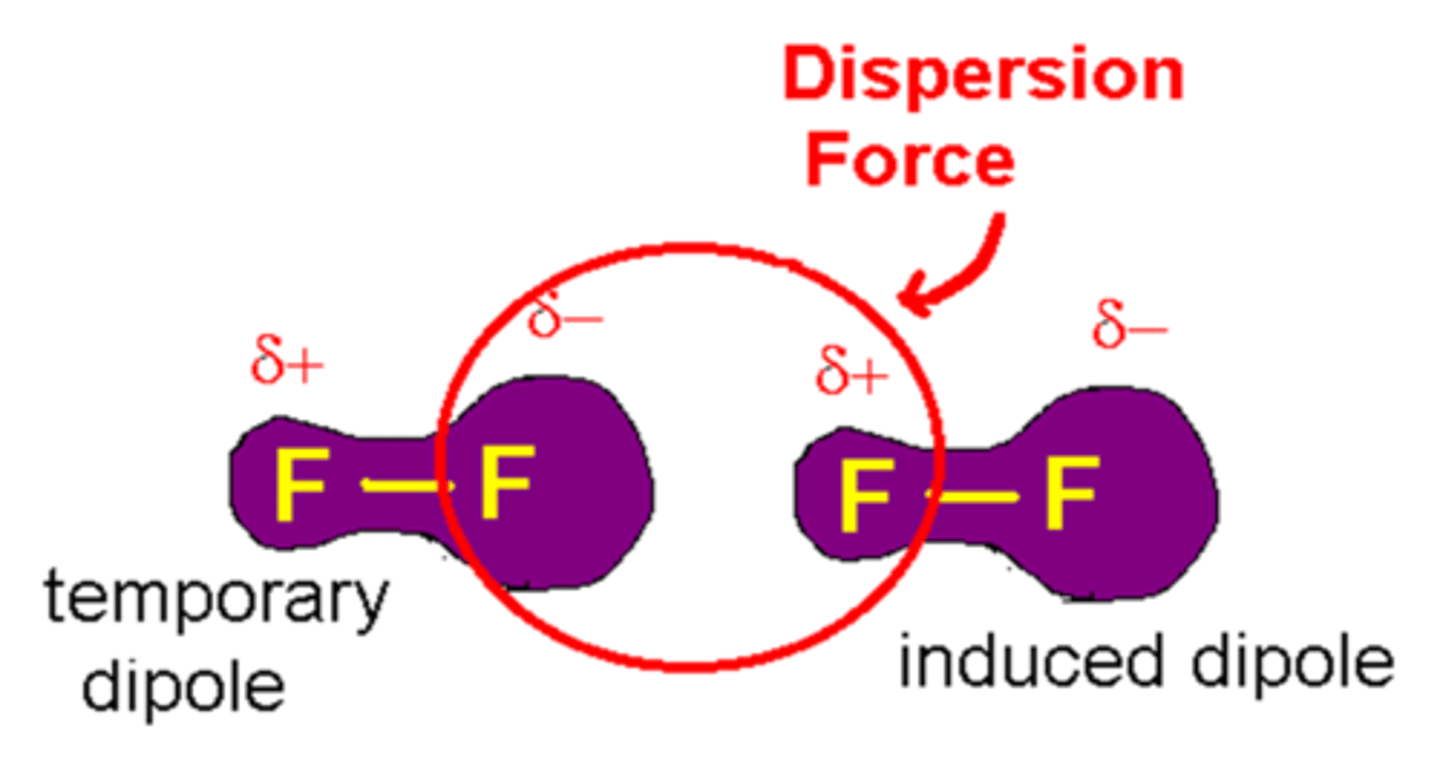
Van der Waal forces are
dispersion forces
Nonpolar molecule
molecule that shares electrons equally and does not have oppositely charged ends