GCSE (9-1) Biology - Assessment 1
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Cell Structure and Organization & Cell Division and Differentiation
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
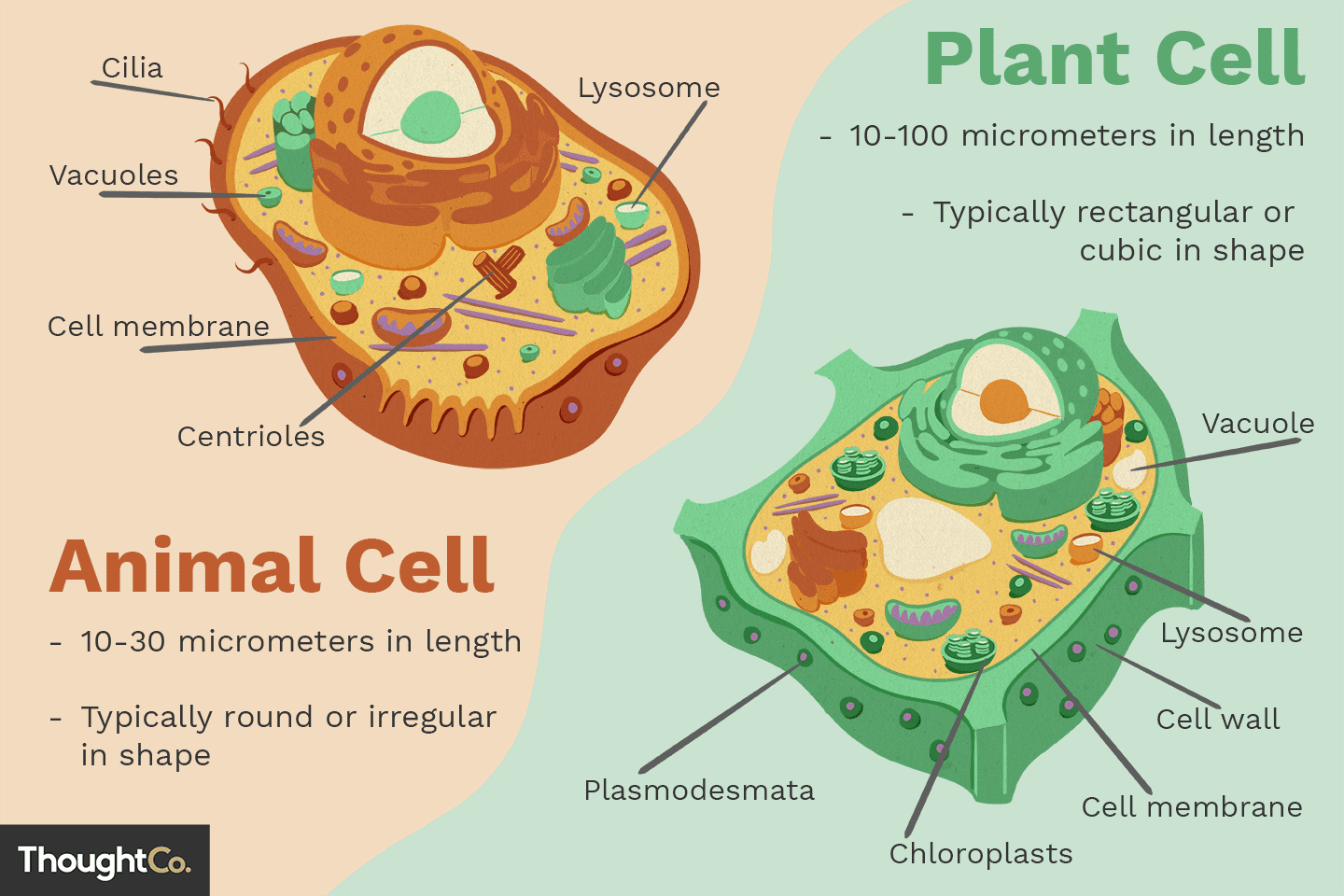
What is the function of the cell membrane in both plant and animal cells?
The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell. It’s selectively permeable, allowing essential nutrients in and waste out.
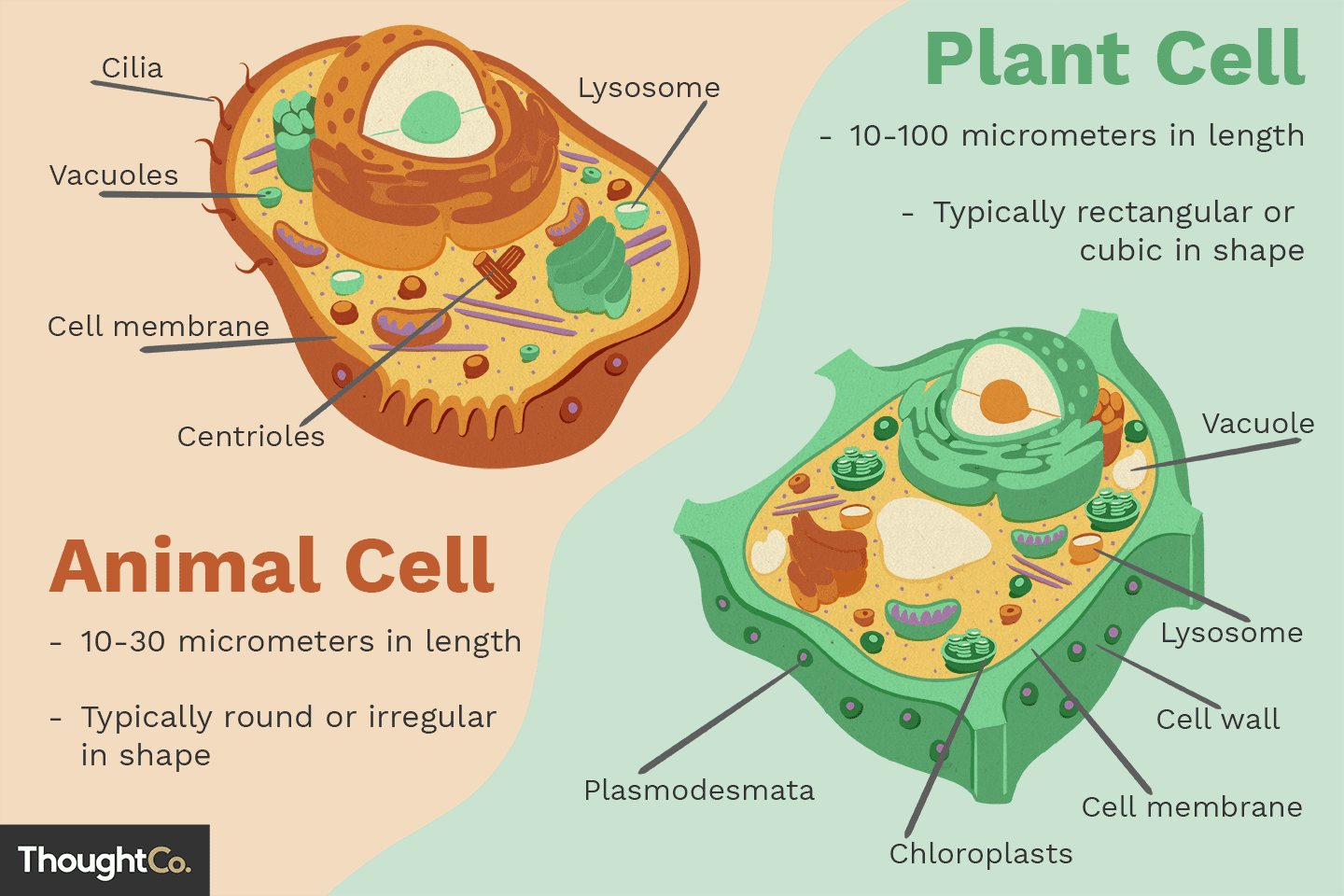
What does a plant cell's chloroplast do, and where can it be found?
Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll and perform photosynthesis by converting sunlight into energy. They are found in green parts of plants, especially in leaf cells.
How does the cell wall differ between plant and bacterial cells?
In plant cells, the cell wall is made of cellulose, providing structural support. In bacteria, the cell wall is made of peptidoglycan.
What are mitochondria, and what is their function in cells?
Mitochondria are known as the powerhouses of the cell. They convert glucose into ATP through cellular respiration, providing energy for the cell's activities.
How do specialized cells function differently? Provide an example.
Specialized cells have structures suited to their role. For example, nerve cells (neurons) are long and have dendrites to transmit electrical signals quickly across the body.
What is the nucleus's role in eukaryotic cells?
The nucleus stores genetic information (DNA) and controls cell activities by regulating gene expression.
Describe the function of ribosomes.
Ribosomes are responsible for synthesizing proteins by translating genetic information from mRNA.
What is the appearance of a vacuole, and what is its function in plant cells?
The vacuole is a large, fluid-filled sac that maintains cell turgor, stores nutrients, and waste products. It is essential for maintaining the plant cell's structure.
What are the stages of the cell cycle?
The cell cycle consists of interphase (G1, S, G2), mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase), and cytokinesis.
What is mitosis, and why is it important for growth?
Mitosis is a process where a single cell divides into two genetically identical daughter cells. It is crucial for growth, repair, and asexual reproduction.
What happens during the prophase stage of mitosis?
During prophase, chromosomes condense, becoming visible, and the nuclear envelope breaks down, allowing spindle fibers to form.
How do cells become specialized during differentiation?
Cells differentiate by activating specific genes and shutting off others, giving them unique structures and functions (e.g., muscle cells for contraction, red blood cells for oxygen transport).
What is the significance of stem cells in differentiation?
Stem cells can differentiate into various specialized cell types, offering potential in regenerative medicine for repairing damaged tissues.
What is the function and structure of a sperm cell?
Sperm cells are designed to fertilize the egg. They have a streamlined head with genetic material, a midsection packed with mitochondria for energy, and a flagellum for mobility.
How are nerve cells specialized for their function?
Nerve cells (neurons) have long extensions called axons to transmit electrical impulses across the body and dendrites to connect with other neurons. They carry signals from sensory organs to the brain and muscles.
How is a root hair cell specialized for its function?
Root hair cells have an elongated shape that increases surface area, allowing efficient absorption of water and minerals from the soil. Thin cell walls make this absorption faster.
What are epithelial cells and where are they found?
Epithelial cells line body surfaces and cavities, providing protection and controlling permeability. Types include squamous (thin, for diffusion) and columnar (tall, for absorption in intestines).
How does the structure of red blood cells enable their function?
Red blood cells have a biconcave shape for a large surface area, no nucleus to carry more hemoglobin, and flexibility to squeeze through capillaries, making them efficient oxygen transporters.
What are the key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic Cells: Simple structure, no nucleus, smaller size, lack membrane-bound organelles (e.g., bacteria).
Eukaryotic Cells: Complex structure, have a nucleus, larger size, and contain membrane-bound organelles (e.g., plants, animals, fungi).
What are the main functions of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell, provides structural support, and facilitates communication with other cells through receptors.