Unit 1: Atomic Theory & Structure — Vocabulary Flashcards
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering major atomic theory concepts, models, and key experiments from Dalton to Heisenberg.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Dalton's Atomic Theory (Postulates)
The early idea that matter is composed of indivisible atoms; postulates include that atoms cannot be created or destroyed and that atoms of the same element are identical in size, mass, and properties, while atoms of different elements differ in size, mass, and properties (not all postulates are correct).
Atom
The basic unit of matter initially described by Dalton; in modern theory, a tiny unit composed of a nucleus of protons and neutrons with electrons surrounding it.
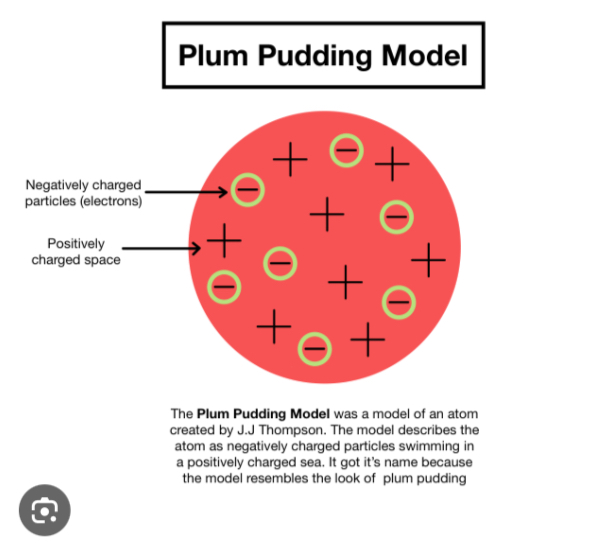
Plum Pudding Model
Thomson's model of the atom in which electrons are embedded in a positively charged 'pudding' or sphere.
Electron
A negatively charged subatomic particle discovered by Thomson; a fundamental component surrounding the nucleus.
Cathode Ray Tube
A vacuum tube used by Thomson to study cathode rays, leading to the discovery of electrons.
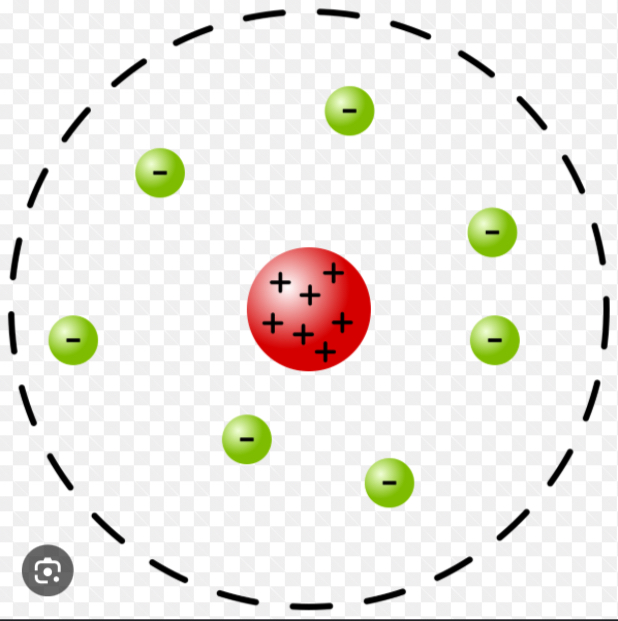
Rutherford's Nuclear Model
An atom model proposing a tiny, dense nucleus containing protons (and later neutrons) with most of the atom being empty space around it.
Gold Foil Experiment
Experiment where alpha particles mostly passed through a thin sheet with some deflections, indicating a small, dense nucleus.
Nucleus
The central, positively charged region of an atom containing protons and neutrons; the nucleus contains most of the atom's mass.
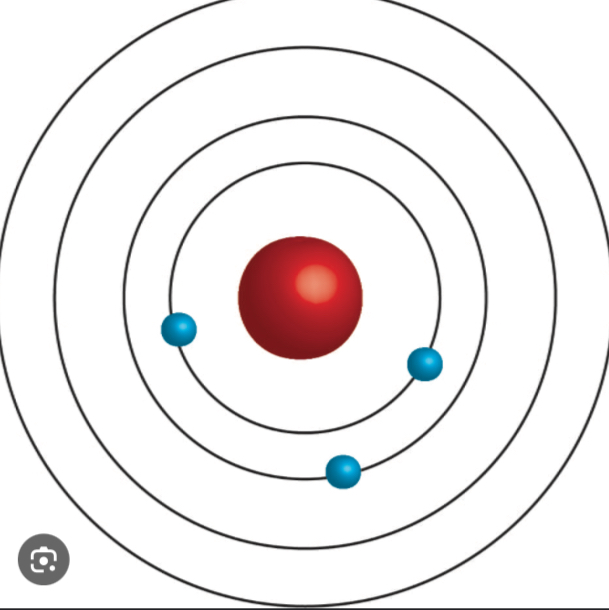
Bohr Model
A model in which electrons orbit the nucleus in fixed, quantized energy levels.
Energy Level
Discrete, allowed energies for electrons in Bohr's model, corresponding to specific orbits around the nucleus.
Quantum Mechanical Model
Modern atomic model describing electrons in terms of probability distributions (orbitals) rather than fixed paths.
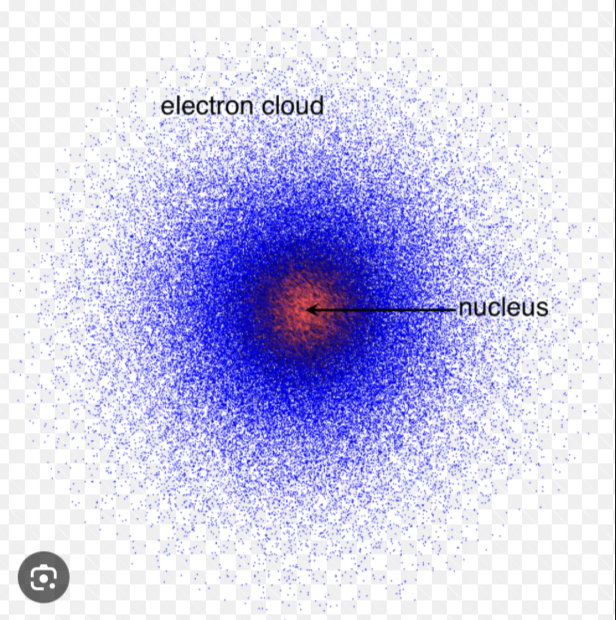
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
The principle that you cannot know both the exact position and exact momentum of an electron simultaneously.
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons, leading to different atomic masses; identity of the element remains the same.